Input variables for eos_designs¶
This document describes the supported input variables for the role arista.avd.eos_designs.
Since several data models have changed between AVD versions 3.x and 4.x, it is recommended to study the Porting Guide for AVD 4.x.x for existing deployments.
The input variables are documented below in tables and YAML.
Note
All input variables are validated by a schema. If additional custom keys are desired, a key starting with an underscore _, will be ignored.
Warning
Available features and variables may vary by platforms, refer to documentation on arista.com for specifics.
Warning
All the keys marked as PREVIEW or children of a key marked as PREVIEW are subject to change and are not supported.
Supported designs¶
eos_designs supports multiple options such as L3LS-EVPN with 3-stage or 5-stage, L2LS, MPLS, AutoVPN and CV Pathfinder. The sections below highlight some of these topologies, but you can extend eos_designs to support your own topology by using node_type_keys to create your own node type.
Design type¶
By setting the design.type variable, the default node-types described in Node Type Variables will be used.
Note
The node types for AutoVPN and CV Pathfinders are part of the l3ls-evpn design.
3-stage clos topology support (Leaf & Spine)¶
- The eos_designs role support various deployments with layer 3 leaf and spine (3-stage Clos) and optionally, with dedicated overlay controllers.
- 3 stage Clos fabric can be represented as spines, L3 leafs and L2 leafs, and also referred to as a “POD”.
See the following examples using the l3ls-evpn design:
5-stage clos topology support (Super Spine)¶
- The eos_designs role support lager deployments with super-spines (5-stage Clos) and optionally, with dedicated overlay controllers.
- 5 stage Clos fabric can be represented as multiple leaf-spine structures (called PODs - Point of Delivery) interconnected by super-spines.
- The logic to deploy every leaf-spine POD fabric remains unchanged.
- Super-spines can be deployed as a single plane (typically chassis switches) or multiple planes.
Layer 2 Leaf Spine¶
- The eos_designs role support various deployments with layer 2 leaf and spine. For example, routing may terminate at the spine level or an external L3 device.
- The Clos fabric can be represented as L3 spines, spines, and leafs.
See the following examples using the l2ls design:
MPLS¶
The eos_designs role with the mpls design type supports any arbitrary physical mesh topology by combining and interconnecting different node types with the core_interfaces settings.
The following underlay routing protocols are supported:
- ISIS-SR (default)
- ISIS + LDP
- ISIS-SR + LDP
- OSPF + LDP
The following overlay routing protocols are supported:
- IBGP (default)
Any node group of 2 or more rr-routers will form a Route Reflector cluster.
The MPLS design supports most fabric topology variables already supported by l3ls-evpn, barring the exceptions outlined below:
- Connectivity is defined with the
core_interfacessettings instead of Node type uplink settings. - No MLAG support.
- No VXLAN support.
- EVPN overlay settings are set with
mpls_overlay_roleandmpls_route_reflectorsinstead ofevpn_roleandevpn_route_servers. - No Inband Management support.
See the following example using the mpls design:
WAN - AutoVPN and CV Pathfinder¶
The eos_designs role with the l3ls-evpn design type supports the node types wan_rr and wan_router.
The default underlay routing protocol is set to none but eBGP is supported as well.
The following overlay routing protocols are supported:
- IBGP (default)
For more information please read the WAN how-to guide.
Fabric topology hierarchy¶
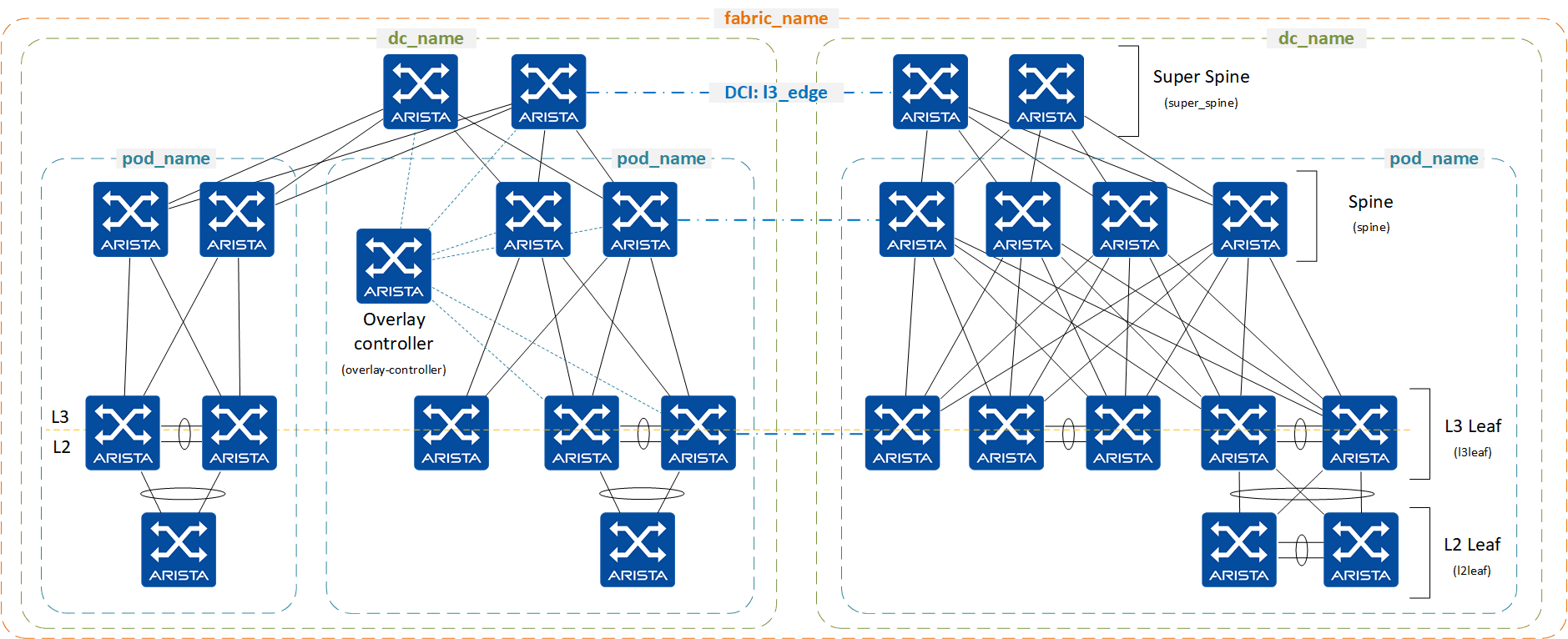
As per the diagram above, the topology hierarchy is the following:
- fabric_name
- dc_name
- pod_name
- dc_name
You must define the fabric_name variable and it must match the Ansible inventory group name covering all devices in scope of the fabric.
| Variable | Type | Required | Default | Value Restrictions | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| dc_name | String | POD Name is used in: - Fabric Documentation (Optional, falls back to fabric_name) - SNMP Location: snmp_settings.location (Optional)- HER Overlay DC scoped flood lists: overlay_her_flood_list_scope: dc (Required) |
|||
| fabric_name | String | Required | Fabric Name, required to match Ansible Group name covering all devices in the Fabric, must be an inventory group name. | ||
| pod_name | String | POD Name is used in: - Fabric Documentation (Optional, falls back to dc_name and then to fabric_name) - SNMP Location: snmp_settings.location (Optional)- VRF Loopbacks: vtep_diagnostic.loopback_ip_pools.pod (Required)Recommended to be common between Spines and Leafs within a POD (One l3ls topology). |
# POD Name is used in:
# - Fabric Documentation (Optional, falls back to fabric_name)
# - SNMP Location: `snmp_settings.location` (Optional)
# - HER Overlay DC scoped flood lists: `overlay_her_flood_list_scope: dc` (Required)
dc_name: <str>
# Fabric Name, required to match Ansible Group name covering all devices in the Fabric, **must** be an inventory group name.
fabric_name: <str; required>
# POD Name is used in:
# - Fabric Documentation (Optional, falls back to dc_name and then to fabric_name)
# - SNMP Location: `snmp_settings.location` (Optional)
# - VRF Loopbacks: `vtep_diagnostic.loopback_ip_pools.pod` (Required)
#
# Recommended to be common between Spines and Leafs within a POD (One l3ls topology).
pod_name: <str>
Fabric IP Addressing¶
| Variable | Type | Required | Default | Value Restrictions | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| fabric_ip_addressing | Dictionary | ||||
| mlag | Dictionary | ||||
| algorithm | String | first_id |
Valid Values: - first_id- odd_id- same_subnet |
This variable defines the Multi-chassis Link Aggregation (MLAG) algorithm used. Each MLAG link will have a /31* subnet with each subnet allocated from the relevant MLAG pool via a calculated offset. The offset is calculated using one of the following algorithms: - first_id: (mlag_primary_id - 1) * 2 where mlag_primary_id is the ID of the first node defined under the node_group.This allocation method will skip every other /31* subnet making it less space efficient than odd_id.- odd_id: (odd_id - 1) / 2. Requires the node_group to have a node with an odd ID and a node with an even ID.- same_subnet: the offset will always be zero. This allocation method will cause every MLAG link to be addressed with the same /31* subnet. * - The prefix length is configurable with a default of /31. |
|
| ipv4_prefix_length | Integer | 31 |
Min: 1 Max: 31 |
IPv4 prefix length used for MLAG peer-vlan and L3 point-to-point SVIs over the MLAG peer-link. | |
| p2p_uplinks | Dictionary | ||||
| ipv4_prefix_length | Integer | 31 |
Min: 1 Max: 31 |
IPv4 prefix length used for L3 point-to-point uplinks. |
fabric_ip_addressing:
mlag:
# This variable defines the Multi-chassis Link Aggregation (MLAG) algorithm used.
# Each MLAG link will have a /31* subnet with each subnet allocated from the relevant MLAG pool via a calculated offset.
# The offset is calculated using one of the following algorithms:
# - first_id: `(mlag_primary_id - 1) * 2` where `mlag_primary_id` is the ID of the first node defined under the node_group.
# This allocation method will skip every other /31* subnet making it less space efficient than `odd_id`.
# - odd_id: `(odd_id - 1) / 2`. Requires the node_group to have a node with an odd ID and a node with an even ID.
# - same_subnet: the offset will always be zero.
# This allocation method will cause every MLAG link to be addressed with the same /31* subnet.
# \* - The prefix length is configurable with a default of /31.
algorithm: <str; "first_id" | "odd_id" | "same_subnet"; default="first_id">
# IPv4 prefix length used for MLAG peer-vlan and L3 point-to-point SVIs over the MLAG peer-link.
ipv4_prefix_length: <int; 1-31; default=31>
p2p_uplinks:
# IPv4 prefix length used for L3 point-to-point uplinks.
ipv4_prefix_length: <int; 1-31; default=31>
Node Type Variables¶
The following tables provide information on the default node types that have been pre-defined in eos_designs for each design type.
To customize or create new node types, please refer to node type customization section.
L3LS EVPN¶
| Node Type Key | Underlay Router | Uplink Type | Default EVPN Role | L2 Network Services | L3 Network Services | VTEP | MLAG Support | Connected Endpoints | Default WAN Role | Default Underlay Routing Protocol | Default Overlay Routing Protocol |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| super_spine | ✅ | p2p | none | ✘ | ✘ | ✘ | ✘ | ✘ | ✘ | eBGP | eBGP |
| spine | ✅ | p2p | server | ✘ | ✘ | ✘ | ✘ | ✘ | ✘ | eBGP | eBGP |
| l3leaf | ✅ | p2p | client | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✘ | eBGP | eBGP |
| l2leaf | ✘ | port-channel | none | ✅ | ✘ | ✘ | ✅ | ✅ | ✘ | eBGP | eBGP |
| overlay_controller | ✅ | p2p | server | ✘ | ✘ | ✘ | ✘ | ✘ | ✘ | eBGP | eBGP |
| wan_rr | ✅ | p2p | server | ✘ | ✅ | ✅ | ✘ | ✘ | server | none | iBGP |
| wan_router | ✅ | p2p | client | ✘ | ✅ | ✅ | ✘ | ✘ | client | none | iBGP |
wan_router: Edge routers for AutoVPN or Edge and Transit routers for CV Pathfinder depending on thewan_modevalue.wan_rr: AutoVPN RR or Pathfinder depending on thewan_modevalue.
L2LS¶
| Node Type Key | Underlay Router | Uplink Type | Default EVPN Role | L2 Network Services | L3 Network Services | VTEP | MLAG Support | Connected Endpoints |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| l3spine | ✅ | p2p | none | ✅ | ✅ | ✘ | ✅ | ✅ |
| spine | ✘ | port-channel | none | ✅ | ✘ | ✘ | ✅ | ✅ |
| leaf | ✘ | port-channel | none | ✅ | ✘ | ✘ | ✅ | ✅ |
MPLS¶
| Node Type Key | Underlay Router | Uplink Type | Default Overlay Role | L2 Network Services | L3 Network Services | VTEP | MLAG Support | Connected Endpoints |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| p | ✅ | p2p | none | ✘ | ✘ | ✘ | ✘ | ✘ |
| rr | ✅ | p2p | server | ✘ | ✘ | ✘ | ✘ | ✘ |
| pe | ✅ | p2p | client | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✘ | ✅ |
Node type customization¶
AVD provides the capability to customize your node types, supporting a variety of designs.
Note
The default values will be overridden if defining this key, so it is recommended to copy the defaults and modify them.
Default value for design l3ls-evpn
node_type_keys:
- key: spine
type: spine
default_evpn_role: server
default_ptp_priority1: 20
- key: l3leaf
type: l3leaf
connected_endpoints: true
default_evpn_role: client
default_ptp_priority1: 30
mlag_support: true
network_services:
l2: true
l3: true
vtep: true
- key: l2leaf
type: l2leaf
connected_endpoints: true
mlag_support: true
network_services:
l2: true
underlay_router: false
uplink_type: port-channel
- key: super_spine
type: super-spine
- key: overlay_controller
type: overlay-controller
default_evpn_role: server
- key: wan_router
type: wan_router
default_evpn_role: client
default_wan_role: client
default_underlay_routing_protocol: none
default_overlay_routing_protocol: ibgp
network_services:
l3: true
vtep: true
- key: wan_rr
type: wan_rr
default_evpn_role: server
default_wan_role: server
default_underlay_routing_protocol: none
default_overlay_routing_protocol: ibgp
network_services:
l3: true
vtep: true
Default value for design l2ls
node_type_keys:
- key: l3spine
type: l3spine
connected_endpoints: true
default_overlay_routing_protocol: none
default_underlay_routing_protocol: none
mlag_support: true
network_services:
l2: true
l3: true
- key: spine
type: spine
connected_endpoints: true
mlag_support: true
network_services:
l2: true
underlay_router: false
uplink_type: port-channel
- key: leaf
type: leaf
connected_endpoints: true
mlag_support: true
network_services:
l2: true
underlay_router: false
uplink_type: port-channel
Default value for design mpls
node_type_keys:
- key: p
type: p
default_mpls_overlay_role: none
default_overlay_routing_protocol: ibgp
default_underlay_routing_protocol: isis-sr
mpls_lsr: true
- key: pe
type: pe
connected_endpoints: true
default_evpn_encapsulation: mpls
default_evpn_role: client
default_mpls_overlay_role: client
default_overlay_address_families:
- vpn-ipv4
default_overlay_routing_protocol: ibgp
default_underlay_routing_protocol: isis-sr
mpls_lsr: true
network_services:
l1: true
l2: true
l3: true
- key: rr
type: rr
default_evpn_encapsulation: mpls
default_evpn_role: server
default_mpls_overlay_role: server
default_overlay_address_families:
- vpn-ipv4
default_overlay_routing_protocol: ibgp
default_underlay_routing_protocol: isis-sr
mpls_lsr: true
| Variable | Type | Required | Default | Value Restrictions | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| node_type_keys | List, items: Dictionary | Define Node Type Keys, to specify the properties of each node type in the fabric. This allows for complete customization of the fabric layout and functionality. node_type_keys should be defined in top level group_var for the fabric.The default values will be overridden if defining this key, so it is recommended to copy the defaults and modify them. |
|||
| - key | String | Required, Unique | |||
| type | String | Type value matching this node_type_key. | |||
| connected_endpoints | Boolean | False |
Are endpoints connected to this node type. | ||
| default_evpn_role | String | none |
Valid Values: - none- client- server |
Default evpn_role. Can be overridden in topology vars. | |
| default_ptp_priority1 | Integer | 127 |
Min: 0 Max: 255 |
Default PTP priority 1 | |
| default_underlay_routing_protocol | String | ebgp |
Value is converted to lower case. Valid Values: - ebgp- ospf- ospf-ldp- isis- isis-sr- isis-ldp- isis-sr-ldp- none |
Set the default underlay routing_protocol. Can be overridden by setting “underlay_routing_protocol” host/group_vars. |
|
| default_overlay_routing_protocol | String | ebgp |
Value is converted to lower case. Valid Values: - ebgp- ibgp- her- cvx- none |
Set the default overlay routing_protocol. Can be overridden by setting “overlay_routing_protocol” host/group_vars. |
|
| default_mpls_overlay_role | String | Valid Values: - client- server- none |
Set the default mpls overlay role. Acting role in overlay control plane. |
||
| default_overlay_address_families | List, items: String | Set the default overlay address families. |
|||
| - <str> | String | Value is converted to lower case. Valid Values: - evpn- vpn-ipv4- vpn-ipv6 |
|||
| default_evpn_encapsulation | String | Value is converted to lower case. Valid Values: - mpls- vxlan |
Set the default evpn encapsulation. |
||
| default_wan_role | String | Valid Values: - client- server |
Set the default WAN role. This is used both for AutoVPN and Pathfinder designs. That means if wan_mode root key is set to autovpn or cv-pathfinder.server indicates that the router is a route-reflector.Only supported if overlay_routing_protocol is set to ibgp. |
||
| default_flow_tracker_type | String | sampled |
Valid Values: - sampled- hardware |
Set the default flow tracker type. | |
| mlag_support | Boolean | False |
Can this node type support mlag. | ||
| network_services | Dictionary | Will network services be deployed on this node type. | |||
| l1 | Boolean | False |
?? | ||
| l2 | Boolean | False |
Vlans | ||
| l3 | Boolean | False |
VRFs, SVIs (if l2 is true). Only supported with underlay_router. |
||
| underlay_router | Boolean | True |
Is this node type a L3 device. | ||
| uplink_type | String | p2p |
Valid Values: - p2p- port-channel- p2p-vrfs- lan |
uplink_type must be p2p, p2p-vrfs or lan if vtep or underlay_router is true.For p2p-vrfs, the uplinks are configured as L3 interfaces with a subinterface for each VRFin network_services present on both the uplink and the downlink switch.The subinterface ID is the vrf_id.‘underlay_router’ and ‘network_services.l3’ must be set to true. VRF default is always configured on the physical interface using the underlay routing protocol.All subinterfaces use the same IP address as the physical interface. Multicast is not supported. Only BGP is supported for subinterfaces. For lan, a single uplink interface is supported and will be configured as an L3 Interface withsubinterfaces for each SVI defined under the VRFs in network_services as long as the uplink switch alsohas the VLAN permitted by tag/tenant filtering. |
|
| vtep | Boolean | False |
Is this switch an EVPN VTEP. | ||
| mpls_lsr | Boolean | False |
Is this switch an MPLS LSR. | ||
| ip_addressing | Dictionary | Override ip_addressing templates. | |||
| python_module | String | Custom Python Module to import for IP addressing. | |||
| python_class_name | String | Name of Custom Python Class to import for IP addressing. | |||
| router_id | String | Path to Custom J2 template. | |||
| router_id_ipv6 | String | Path to Custom J2 template. | |||
| mlag_ip_primary | String | Path to Custom J2 template. | |||
| mlag_ip_secondary | String | Path to Custom J2 template. | |||
| mlag_l3_ip_primary | String | Path to Custom J2 template. | |||
| mlag_l3_ip_secondary | String | Path to Custom J2 template. | |||
| mlag_ibgp_peering_ip_primary | String | Path to Custom J2 template. | |||
| mlag_ibgp_peering_ip_secondary | String | Path to Custom J2 template. | |||
| p2p_uplinks_ip | String | Path to Custom J2 template. | |||
| p2p_uplinks_peer_ip | String | Path to Custom J2 template. | |||
| vtep_ip_mlag | String | Path to Custom J2 template. | |||
| vtep_ip | String | Path to Custom J2 template. | |||
| interface_descriptions | Dictionary | Override interface_descriptions templates. If description templates use Jinja2, they have to strip whitespaces using {%- -%} on any code blocks. |
|||
| python_module | String | Custom Python Module to import for interface descriptions. | |||
| python_class_name | String | Name of Custom Python Class to import for interface descriptions. | |||
| underlay_ethernet_interfaces | String | Path to Custom J2 template. | |||
| underlay_port_channel_interfaces | String | Path to Custom J2 template. | |||
| mlag_ethernet_interfaces | String | Path to Custom J2 template. | |||
| mlag_port_channel_interfaces | String | Path to Custom J2 template. | |||
| connected_endpoints_ethernet_interfaces | String | Path to Custom J2 template. | |||
| connected_endpoints_port_channel_interfaces | String | Path to Custom J2 template. | |||
| overlay_loopback_interface | String | Path to Custom J2 template. | |||
| vtep_loopback_interface | String | Path to Custom J2 template. |
# Define Node Type Keys, to specify the properties of each node type in the fabric.
# This allows for complete customization of the fabric layout and functionality.
# `node_type_keys` should be defined in top level group_var for the fabric.
# The default values will be overridden if defining this key, so it is recommended to copy the defaults and modify them.
node_type_keys:
- key: <str; required; unique>
# Type value matching this node_type_key.
type: <str>
# Are endpoints connected to this node type.
connected_endpoints: <bool; default=False>
# Default evpn_role. Can be overridden in topology vars.
default_evpn_role: <str; "none" | "client" | "server"; default="none">
# Default PTP priority 1
default_ptp_priority1: <int; 0-255; default=127>
# Set the default underlay routing_protocol.
# Can be overridden by setting "underlay_routing_protocol" host/group_vars.
default_underlay_routing_protocol: <str; "ebgp" | "ospf" | "ospf-ldp" | "isis" | "isis-sr" | "isis-ldp" | "isis-sr-ldp" | "none"; default="ebgp">
# Set the default overlay routing_protocol.
# Can be overridden by setting "overlay_routing_protocol" host/group_vars.
default_overlay_routing_protocol: <str; "ebgp" | "ibgp" | "her" | "cvx" | "none"; default="ebgp">
# Set the default mpls overlay role.
# Acting role in overlay control plane.
default_mpls_overlay_role: <str; "client" | "server" | "none">
# Set the default overlay address families.
default_overlay_address_families:
- <str; "evpn" | "vpn-ipv4" | "vpn-ipv6">
# Set the default evpn encapsulation.
default_evpn_encapsulation: <str; "mpls" | "vxlan">
# Set the default WAN role.
#
# This is used both for AutoVPN and Pathfinder designs.
# That means if `wan_mode` root key is set to `autovpn` or `cv-pathfinder`.
# `server` indicates that the router is a route-reflector.
#
# Only supported if `overlay_routing_protocol` is set to `ibgp`.
default_wan_role: <str; "client" | "server">
# Set the default flow tracker type.
default_flow_tracker_type: <str; "sampled" | "hardware"; default="sampled">
# Can this node type support mlag.
mlag_support: <bool; default=False>
# Will network services be deployed on this node type.
network_services:
# ??
l1: <bool; default=False>
# Vlans
l2: <bool; default=False>
# VRFs, SVIs (if l2 is true).
# Only supported with underlay_router.
l3: <bool; default=False>
# Is this node type a L3 device.
underlay_router: <bool; default=True>
# `uplink_type` must be `p2p`, `p2p-vrfs` or `lan` if `vtep` or `underlay_router` is true.
#
# For `p2p-vrfs`, the uplinks are configured as L3 interfaces with a subinterface for each VRF
# in `network_services` present on both the uplink and the downlink switch.
# The subinterface ID is the `vrf_id`.
# 'underlay_router' and 'network_services.l3' must be set to true.
# VRF `default` is always configured on the physical interface using the underlay routing protocol.
# All subinterfaces use the same IP address as the physical interface.
# Multicast is not supported.
# Only BGP is supported for subinterfaces.
#
# For `lan`, a single uplink interface is supported and will be configured as an L3 Interface with
# subinterfaces for each SVI defined under the VRFs in `network_services` as long as the uplink switch also
# has the VLAN permitted by tag/tenant filtering.
uplink_type: <str; "p2p" | "port-channel" | "p2p-vrfs" | "lan"; default="p2p">
# Is this switch an EVPN VTEP.
vtep: <bool; default=False>
# Is this switch an MPLS LSR.
mpls_lsr: <bool; default=False>
# Override ip_addressing templates.
ip_addressing:
# Custom Python Module to import for IP addressing.
python_module: <str>
# Name of Custom Python Class to import for IP addressing.
python_class_name: <str>
# Path to Custom J2 template.
router_id: <str>
# Path to Custom J2 template.
router_id_ipv6: <str>
# Path to Custom J2 template.
mlag_ip_primary: <str>
# Path to Custom J2 template.
mlag_ip_secondary: <str>
# Path to Custom J2 template.
mlag_l3_ip_primary: <str>
# Path to Custom J2 template.
mlag_l3_ip_secondary: <str>
# Path to Custom J2 template.
mlag_ibgp_peering_ip_primary: <str>
# Path to Custom J2 template.
mlag_ibgp_peering_ip_secondary: <str>
# Path to Custom J2 template.
p2p_uplinks_ip: <str>
# Path to Custom J2 template.
p2p_uplinks_peer_ip: <str>
# Path to Custom J2 template.
vtep_ip_mlag: <str>
# Path to Custom J2 template.
vtep_ip: <str>
# Override interface_descriptions templates.
# If description templates use Jinja2, they have to strip whitespaces using {%- -%} on any code blocks.
interface_descriptions:
# Custom Python Module to import for interface descriptions.
python_module: <str>
# Name of Custom Python Class to import for interface descriptions.
python_class_name: <str>
# Path to Custom J2 template.
underlay_ethernet_interfaces: <str>
# Path to Custom J2 template.
underlay_port_channel_interfaces: <str>
# Path to Custom J2 template.
mlag_ethernet_interfaces: <str>
# Path to Custom J2 template.
mlag_port_channel_interfaces: <str>
# Path to Custom J2 template.
connected_endpoints_ethernet_interfaces: <str>
# Path to Custom J2 template.
connected_endpoints_port_channel_interfaces: <str>
# Path to Custom J2 template.
overlay_loopback_interface: <str>
# Path to Custom J2 template.
vtep_loopback_interface: <str>
Context for ip_addressing templates¶
To help calculate the custom IP addressing, the following contextual variables are available to the custom templates:
router_id:
{{ switch_id }}{{ loopback_ipv4_pool }}{{ loopback_ipv4_offset }}- All group/hostvars
mlag_ip_primary & mlag_ip_secondary:
{{ mlag_primary_id }}{{ mlag_secondary_id }}{{ switch_data.combined.mlag_peer_ipv4_pool }}- All group/hostvars
mlag_l3_ip_primary & mlag_l3_ip_secondary:
{{ mlag_primary_id }}{{ mlag_secondary_id }}{{ switch_data.combined.mlag_peer_l3_ipv4_pool }}- All group/hostvars
p2p_uplinks_ip & p2p_uplinks_peer_ip:
{{ switch.uplink_ipv4_pool }}{{ switch.id }}{{ switch.max_uplink_switches }}{{ switch.max_parallel_uplinks }}{{ uplink_switch_index }}- All group/hostvars
vtep_ip_mlag:
{{ switch_vtep_loopback_ipv4_pool }}{{ mlag_primary_id }}{{ loopback_ipv4_offset }}- All group/hostvars
vtep_ip:
{{ switch_vtep_loopback_ipv4_pool }}{{ switch_id }}{{ loopback_ipv4_offset }}- All group/hostvars
While all templates can leverage the internal switch facts (switch.*) to customize the interface descriptions, the values are not part of the officially supported data models, and may change without notice.
Context for interface_descriptions templates¶
Caveat
In AVD 4.x, it is not possible to completely overwrite the description of the subinterfaces when uplink_type is set to p2p-vrfs. The string _vrf_<VRF> is always appended to the description.
To help format the custom interface descriptions, the following contextual variables are available to the custom templates:
underlay_ethernet_interfaces:
{{ link.peer }}{{ link.peer_interface }}{{ link.type }} (underlay_p2p or underlay_l2)- All group/hostvars
underlay_port_channel_interfaces:
{{ link.channel_description }}{{ link.channel_group_id }}{{ link.peer_channel_group_id }}- All group/hostvars
mlag_ethernet_interfaces:
{{ mlag_interface }}{{ mlag_peer }}- All group/hostvars
mlag_port_channel_interfaces:
{{ mlag_interfaces }}{{ mlag_peer }}- All group/hostvars
connected_endpoints_ethernet_interfaces:
{{ peer }}{{ peer_interface }}- All group/hostvars
connected_endpoints_port_channel_interfaces:
{{ peer }}{{ adapter_port_channel_description }}- All group/hostvars
While all templates can leverage the internal switch facts (switch.*) to customize the interface descriptions, the values are not part of the officially supported data models and may change without notice.
Type setting¶
- The
type:variable needs to be defined for each device in the fabric. - This is leveraged to load the appropriate settings to generate the configuration.
Tip
The node type setting can be automatically derived from a switch name by defining the patterns in the default_node_types data model.
Type setting example
# Defined in SPINE.yml file
# Can also be set directly in your inventory file under spine group
type: spine
# Defined in L3LEAFS.yml
# Can also be set directly in your inventory file under l3leaf group
type: l3leaf
# Defined in L2LEAFS.yml
# Can also be set directly in your inventory file under l2leaf group
type: l2leaf
# Defined in SUPER-SPINES.yml
# Can also be set directly in your inventory file under super-spine group
type: super-spine
# Defined in ROUTE-SERVERS.yml
# Can also be set directly in your inventory file under route-server group
type: overlay-controller
| Variable | Type | Required | Default | Value Restrictions | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| type | String | Valid Values: - |
The type: variable needs to be defined for each device in the fabric.This is leveraged to load the appropriate template to generate the configuration. |
Default node types settings¶
Node types can be defined statically on each node or in each group of nodes. By leveraging default_node_types, regular expressions can be used to determine the node type based
on the hostname.
Warning
Please note that using the default_node_types functionality will cause certain tests in the eos_validate_state role to not be executed.
This functionality will be restored as part of a later update to eos_validate_state and this note will then be removed.
| Variable | Type | Required | Default | Value Restrictions | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| default_node_types | List, items: Dictionary | Uses hostname matches against a regular expression to determine the node type. | |||
| - node_type | String | Required, Unique | Resulting node type when regex matches. | ||
| match_hostnames | List, items: String | Required | Regular expressions to match against hostnames. | ||
| - <str> | String | Required | Regex needs to match full hostname (i.e. is bounded by ^ and $ elements). |
# Uses hostname matches against a regular expression to determine the node type.
default_node_types:
# Resulting node type when regex matches.
- node_type: <str; required; unique>
# Regular expressions to match against hostnames.
match_hostnames: # required
# Regex needs to match full hostname (i.e. is bounded by ^ and $ elements).
- <str; required>
Node type settings¶
Node type settings are defined under the node_type_keys.key i.e spine:, l3leaf:, l2leaf: to configure management, underlay, overlay functionality.
Node type structure¶
All node types have the same structure based on defaults, node_group, node_group.node, node and all variables can be defined in any section and support inheritance like this:
Under node_type_keys.key:
Tip
Define common node settings under defaults. This reduces user input requirements, limiting errors.
| Variable | Type | Required | Default | Value Restrictions | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| <node_type_keys.key> | Dictionary | ||||
| defaults | Dictionary | Define variables for all nodes of this type. | |||
| flow_tracker_type | String | Valid Values: - sampled- hardware |
Set the flow tracker type. Override the default_flow_tracker_type`` set at thenode_type_keylevel.<br>default_flow_tracker_typedefault value issampled`. |
||
| node_groups | List, items: Dictionary | Define variables related to all nodes part of this group. | |||
| - group | String | Required, Unique | The Node Group Name is used for MLAG domain unless set with ‘mlag_domain_id’. The Node Group Name is also used for peer description on downstream switches’ uplinks. |
||
| nodes | List, items: Dictionary | Define variables per node. | |||
| - name | String | Required, Unique | The Node Name is used as “hostname”. | ||
| flow_tracker_type | String | Valid Values: - sampled- hardware |
Set the flow tracker type. Override the default_flow_tracker_type`` set at thenode_type_keylevel.<br>default_flow_tracker_typedefault value issampled`. |
||
| flow_tracker_type | String | Valid Values: - sampled- hardware |
Set the flow tracker type. Override the default_flow_tracker_type`` set at thenode_type_keylevel.<br>default_flow_tracker_typedefault value issampled`. |
||
| nodes | List, items: Dictionary | Define variables per node. | |||
| - name | String | Required, Unique | The Node Name is used as “hostname”. | ||
| flow_tracker_type | String | Valid Values: - sampled- hardware |
Set the flow tracker type. Override the default_flow_tracker_type`` set at thenode_type_keylevel.<br>default_flow_tracker_typedefault value issampled`. |
<node_type_keys.key>:
# Define variables for all nodes of this type.
defaults:
# Set the flow tracker type.
# Override the `default_flow_tracker_type`` set at the `node_type_key` level.
# `default_flow_tracker_type` default value is `sampled`.
flow_tracker_type: <str; "sampled" | "hardware">
# Define variables related to all nodes part of this group.
node_groups:
# The Node Group Name is used for MLAG domain unless set with 'mlag_domain_id'.
# The Node Group Name is also used for peer description on downstream switches' uplinks.
- group: <str; required; unique>
# Define variables per node.
nodes:
# The Node Name is used as "hostname".
- name: <str; required; unique>
# Set the flow tracker type.
# Override the `default_flow_tracker_type`` set at the `node_type_key` level.
# `default_flow_tracker_type` default value is `sampled`.
flow_tracker_type: <str; "sampled" | "hardware">
# Set the flow tracker type.
# Override the `default_flow_tracker_type`` set at the `node_type_key` level.
# `default_flow_tracker_type` default value is `sampled`.
flow_tracker_type: <str; "sampled" | "hardware">
# Define variables per node.
nodes:
# The Node Name is used as "hostname".
- name: <str; required; unique>
# Set the flow tracker type.
# Override the `default_flow_tracker_type`` set at the `node_type_key` level.
# `default_flow_tracker_type` default value is `sampled`.
flow_tracker_type: <str; "sampled" | "hardware">
Node type common configuration¶
Define your nodes, id, management and common configuration elements.
Tip
If a node is not deployed, leverage is_deployed: false to indicate the node as offline.
Info
A static unique identifier (id) is assigned to each device. This is leveraged to derive the IP address assignment from each summary defined in the Fabric Underlay and Overlay Topology Variables.
| Variable | Type | Required | Default | Value Restrictions | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| <node_type_keys.key> | Dictionary | ||||
| defaults | Dictionary | Define variables for all nodes of this type. | |||
| id | Integer | Unique identifier used for IP addressing and other algorithms. | |||
| platform | String | Arista platform family. | |||
| mac_address | String | Leverage to document management interface mac address. | |||
| system_mac_address | String | System MAC Address in this following format: “xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx”. Set to the same MAC address as available in “show version” on the device. “system_mac_address” can also be set directly as a hostvar. If both are set, the setting under node type settings takes precedence. |
|||
| serial_number | String | Set to the Serial Number of the device. Only used for documentation purpose in the fabric documentation and part of the structured_config. “serial_number” can also be set directly as a hostvar. If both are set, the setting under node type settings takes precedence. |
|||
| rack | String | Rack that the switch is located in (only used in snmp_settings location). | |||
| mgmt_ip | String | Format: cidr | Node management interface IPv4 address. | ||
| ipv6_mgmt_ip | String | Format: cidr | Node management interface IPv6 address. | ||
| mgmt_interface | String | Management Interface Name. Default -> platform_management_interface -> mgmt_interface -> “Management1”. |
|||
| lacp_port_id_range | Dictionary | This will generate the “lacp port-id range”, “begin” and “end” values based on node “id” and the number of nodes in the “node_group”. Unique LACP port-id ranges are recommended for EVPN Multihoming designs. |
|||
| enabled | Boolean | False |
|||
| size | Integer | 128 |
Recommended size > = number of ports in the switch. | ||
| offset | Integer | 0 |
Offset is used to avoid overlapping port-id ranges of different switches. Useful when a “connected-endpoint” is connected to switches in different “node_groups”. |
||
| always_configure_ip_routing | Boolean | False |
Force configuration of “ip routing” even on L2 devices. Use this to retain behavior of AVD versions below 4.0.0. |
||
| raw_eos_cli | String | EOS CLI rendered directly on the root level of the final EOS configuration. | |||
| structured_config | Dictionary | Custom structured config for eos_cli_config_gen. | |||
| node_groups | List, items: Dictionary | Define variables related to all nodes part of this group. | |||
| - group | String | Required, Unique | The Node Group Name is used for MLAG domain unless set with ‘mlag_domain_id’. The Node Group Name is also used for peer description on downstream switches’ uplinks. |
||
| nodes | List, items: Dictionary | Define variables per node. | |||
| - name | String | Required, Unique | The Node Name is used as “hostname”. | ||
| id | Integer | Unique identifier used for IP addressing and other algorithms. | |||
| platform | String | Arista platform family. | |||
| mac_address | String | Leverage to document management interface mac address. | |||
| system_mac_address | String | System MAC Address in this following format: “xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx”. Set to the same MAC address as available in “show version” on the device. “system_mac_address” can also be set directly as a hostvar. If both are set, the setting under node type settings takes precedence. |
|||
| serial_number | String | Set to the Serial Number of the device. Only used for documentation purpose in the fabric documentation and part of the structured_config. “serial_number” can also be set directly as a hostvar. If both are set, the setting under node type settings takes precedence. |
|||
| rack | String | Rack that the switch is located in (only used in snmp_settings location). | |||
| mgmt_ip | String | Format: cidr | Node management interface IPv4 address. | ||
| ipv6_mgmt_ip | String | Format: cidr | Node management interface IPv6 address. | ||
| mgmt_interface | String | Management Interface Name. Default -> platform_management_interface -> mgmt_interface -> “Management1”. |
|||
| lacp_port_id_range | Dictionary | This will generate the “lacp port-id range”, “begin” and “end” values based on node “id” and the number of nodes in the “node_group”. Unique LACP port-id ranges are recommended for EVPN Multihoming designs. |
|||
| enabled | Boolean | False |
|||
| size | Integer | 128 |
Recommended size > = number of ports in the switch. | ||
| offset | Integer | 0 |
Offset is used to avoid overlapping port-id ranges of different switches. Useful when a “connected-endpoint” is connected to switches in different “node_groups”. |
||
| always_configure_ip_routing | Boolean | False |
Force configuration of “ip routing” even on L2 devices. Use this to retain behavior of AVD versions below 4.0.0. |
||
| raw_eos_cli | String | EOS CLI rendered directly on the root level of the final EOS configuration. | |||
| structured_config | Dictionary | Custom structured config for eos_cli_config_gen. | |||
| id | Integer | Unique identifier used for IP addressing and other algorithms. | |||
| platform | String | Arista platform family. | |||
| mac_address | String | Leverage to document management interface mac address. | |||
| system_mac_address | String | System MAC Address in this following format: “xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx”. Set to the same MAC address as available in “show version” on the device. “system_mac_address” can also be set directly as a hostvar. If both are set, the setting under node type settings takes precedence. |
|||
| serial_number | String | Set to the Serial Number of the device. Only used for documentation purpose in the fabric documentation and part of the structured_config. “serial_number” can also be set directly as a hostvar. If both are set, the setting under node type settings takes precedence. |
|||
| rack | String | Rack that the switch is located in (only used in snmp_settings location). | |||
| mgmt_ip | String | Format: cidr | Node management interface IPv4 address. | ||
| ipv6_mgmt_ip | String | Format: cidr | Node management interface IPv6 address. | ||
| mgmt_interface | String | Management Interface Name. Default -> platform_management_interface -> mgmt_interface -> “Management1”. |
|||
| lacp_port_id_range | Dictionary | This will generate the “lacp port-id range”, “begin” and “end” values based on node “id” and the number of nodes in the “node_group”. Unique LACP port-id ranges are recommended for EVPN Multihoming designs. |
|||
| enabled | Boolean | False |
|||
| size | Integer | 128 |
Recommended size > = number of ports in the switch. | ||
| offset | Integer | 0 |
Offset is used to avoid overlapping port-id ranges of different switches. Useful when a “connected-endpoint” is connected to switches in different “node_groups”. |
||
| always_configure_ip_routing | Boolean | False |
Force configuration of “ip routing” even on L2 devices. Use this to retain behavior of AVD versions below 4.0.0. |
||
| raw_eos_cli | String | EOS CLI rendered directly on the root level of the final EOS configuration. | |||
| structured_config | Dictionary | Custom structured config for eos_cli_config_gen. | |||
| nodes | List, items: Dictionary | Define variables per node. | |||
| - name | String | Required, Unique | The Node Name is used as “hostname”. | ||
| id | Integer | Unique identifier used for IP addressing and other algorithms. | |||
| platform | String | Arista platform family. | |||
| mac_address | String | Leverage to document management interface mac address. | |||
| system_mac_address | String | System MAC Address in this following format: “xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx”. Set to the same MAC address as available in “show version” on the device. “system_mac_address” can also be set directly as a hostvar. If both are set, the setting under node type settings takes precedence. |
|||
| serial_number | String | Set to the Serial Number of the device. Only used for documentation purpose in the fabric documentation and part of the structured_config. “serial_number” can also be set directly as a hostvar. If both are set, the setting under node type settings takes precedence. |
|||
| rack | String | Rack that the switch is located in (only used in snmp_settings location). | |||
| mgmt_ip | String | Format: cidr | Node management interface IPv4 address. | ||
| ipv6_mgmt_ip | String | Format: cidr | Node management interface IPv6 address. | ||
| mgmt_interface | String | Management Interface Name. Default -> platform_management_interface -> mgmt_interface -> “Management1”. |
|||
| lacp_port_id_range | Dictionary | This will generate the “lacp port-id range”, “begin” and “end” values based on node “id” and the number of nodes in the “node_group”. Unique LACP port-id ranges are recommended for EVPN Multihoming designs. |
|||
| enabled | Boolean | False |
|||
| size | Integer | 128 |
Recommended size > = number of ports in the switch. | ||
| offset | Integer | 0 |
Offset is used to avoid overlapping port-id ranges of different switches. Useful when a “connected-endpoint” is connected to switches in different “node_groups”. |
||
| always_configure_ip_routing | Boolean | False |
Force configuration of “ip routing” even on L2 devices. Use this to retain behavior of AVD versions below 4.0.0. |
||
| raw_eos_cli | String | EOS CLI rendered directly on the root level of the final EOS configuration. | |||
| structured_config | Dictionary | Custom structured config for eos_cli_config_gen. |
<node_type_keys.key>:
# Define variables for all nodes of this type.
defaults:
# Unique identifier used for IP addressing and other algorithms.
id: <int>
# Arista platform family.
platform: <str>
# Leverage to document management interface mac address.
mac_address: <str>
# System MAC Address in this following format: "xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx".
# Set to the same MAC address as available in "show version" on the device.
# "system_mac_address" can also be set directly as a hostvar.
# If both are set, the setting under node type settings takes precedence.
system_mac_address: <str>
# Set to the Serial Number of the device.
# Only used for documentation purpose in the fabric documentation and part of the structured_config.
# "serial_number" can also be set directly as a hostvar.
# If both are set, the setting under node type settings takes precedence.
serial_number: <str>
# Rack that the switch is located in (only used in snmp_settings location).
rack: <str>
# Node management interface IPv4 address.
mgmt_ip: <str>
# Node management interface IPv6 address.
ipv6_mgmt_ip: <str>
# Management Interface Name.
# Default -> platform_management_interface -> mgmt_interface -> "Management1".
mgmt_interface: <str>
# This will generate the "lacp port-id range", "begin" and "end" values based on node "id" and the number of nodes in the "node_group".
# Unique LACP port-id ranges are recommended for EVPN Multihoming designs.
lacp_port_id_range:
enabled: <bool; default=False>
# Recommended size > = number of ports in the switch.
size: <int; default=128>
# Offset is used to avoid overlapping port-id ranges of different switches.
# Useful when a "connected-endpoint" is connected to switches in different "node_groups".
offset: <int; default=0>
# Force configuration of "ip routing" even on L2 devices.
# Use this to retain behavior of AVD versions below 4.0.0.
always_configure_ip_routing: <bool; default=False>
# EOS CLI rendered directly on the root level of the final EOS configuration.
raw_eos_cli: <str>
# Custom structured config for eos_cli_config_gen.
structured_config: <dict>
# Define variables related to all nodes part of this group.
node_groups:
# The Node Group Name is used for MLAG domain unless set with 'mlag_domain_id'.
# The Node Group Name is also used for peer description on downstream switches' uplinks.
- group: <str; required; unique>
# Define variables per node.
nodes:
# The Node Name is used as "hostname".
- name: <str; required; unique>
# Unique identifier used for IP addressing and other algorithms.
id: <int>
# Arista platform family.
platform: <str>
# Leverage to document management interface mac address.
mac_address: <str>
# System MAC Address in this following format: "xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx".
# Set to the same MAC address as available in "show version" on the device.
# "system_mac_address" can also be set directly as a hostvar.
# If both are set, the setting under node type settings takes precedence.
system_mac_address: <str>
# Set to the Serial Number of the device.
# Only used for documentation purpose in the fabric documentation and part of the structured_config.
# "serial_number" can also be set directly as a hostvar.
# If both are set, the setting under node type settings takes precedence.
serial_number: <str>
# Rack that the switch is located in (only used in snmp_settings location).
rack: <str>
# Node management interface IPv4 address.
mgmt_ip: <str>
# Node management interface IPv6 address.
ipv6_mgmt_ip: <str>
# Management Interface Name.
# Default -> platform_management_interface -> mgmt_interface -> "Management1".
mgmt_interface: <str>
# This will generate the "lacp port-id range", "begin" and "end" values based on node "id" and the number of nodes in the "node_group".
# Unique LACP port-id ranges are recommended for EVPN Multihoming designs.
lacp_port_id_range:
enabled: <bool; default=False>
# Recommended size > = number of ports in the switch.
size: <int; default=128>
# Offset is used to avoid overlapping port-id ranges of different switches.
# Useful when a "connected-endpoint" is connected to switches in different "node_groups".
offset: <int; default=0>
# Force configuration of "ip routing" even on L2 devices.
# Use this to retain behavior of AVD versions below 4.0.0.
always_configure_ip_routing: <bool; default=False>
# EOS CLI rendered directly on the root level of the final EOS configuration.
raw_eos_cli: <str>
# Custom structured config for eos_cli_config_gen.
structured_config: <dict>
# Unique identifier used for IP addressing and other algorithms.
id: <int>
# Arista platform family.
platform: <str>
# Leverage to document management interface mac address.
mac_address: <str>
# System MAC Address in this following format: "xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx".
# Set to the same MAC address as available in "show version" on the device.
# "system_mac_address" can also be set directly as a hostvar.
# If both are set, the setting under node type settings takes precedence.
system_mac_address: <str>
# Set to the Serial Number of the device.
# Only used for documentation purpose in the fabric documentation and part of the structured_config.
# "serial_number" can also be set directly as a hostvar.
# If both are set, the setting under node type settings takes precedence.
serial_number: <str>
# Rack that the switch is located in (only used in snmp_settings location).
rack: <str>
# Node management interface IPv4 address.
mgmt_ip: <str>
# Node management interface IPv6 address.
ipv6_mgmt_ip: <str>
# Management Interface Name.
# Default -> platform_management_interface -> mgmt_interface -> "Management1".
mgmt_interface: <str>
# This will generate the "lacp port-id range", "begin" and "end" values based on node "id" and the number of nodes in the "node_group".
# Unique LACP port-id ranges are recommended for EVPN Multihoming designs.
lacp_port_id_range:
enabled: <bool; default=False>
# Recommended size > = number of ports in the switch.
size: <int; default=128>
# Offset is used to avoid overlapping port-id ranges of different switches.
# Useful when a "connected-endpoint" is connected to switches in different "node_groups".
offset: <int; default=0>
# Force configuration of "ip routing" even on L2 devices.
# Use this to retain behavior of AVD versions below 4.0.0.
always_configure_ip_routing: <bool; default=False>
# EOS CLI rendered directly on the root level of the final EOS configuration.
raw_eos_cli: <str>
# Custom structured config for eos_cli_config_gen.
structured_config: <dict>
# Define variables per node.
nodes:
# The Node Name is used as "hostname".
- name: <str; required; unique>
# Unique identifier used for IP addressing and other algorithms.
id: <int>
# Arista platform family.
platform: <str>
# Leverage to document management interface mac address.
mac_address: <str>
# System MAC Address in this following format: "xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx".
# Set to the same MAC address as available in "show version" on the device.
# "system_mac_address" can also be set directly as a hostvar.
# If both are set, the setting under node type settings takes precedence.
system_mac_address: <str>
# Set to the Serial Number of the device.
# Only used for documentation purpose in the fabric documentation and part of the structured_config.
# "serial_number" can also be set directly as a hostvar.
# If both are set, the setting under node type settings takes precedence.
serial_number: <str>
# Rack that the switch is located in (only used in snmp_settings location).
rack: <str>
# Node management interface IPv4 address.
mgmt_ip: <str>
# Node management interface IPv6 address.
ipv6_mgmt_ip: <str>
# Management Interface Name.
# Default -> platform_management_interface -> mgmt_interface -> "Management1".
mgmt_interface: <str>
# This will generate the "lacp port-id range", "begin" and "end" values based on node "id" and the number of nodes in the "node_group".
# Unique LACP port-id ranges are recommended for EVPN Multihoming designs.
lacp_port_id_range:
enabled: <bool; default=False>
# Recommended size > = number of ports in the switch.
size: <int; default=128>
# Offset is used to avoid overlapping port-id ranges of different switches.
# Useful when a "connected-endpoint" is connected to switches in different "node_groups".
offset: <int; default=0>
# Force configuration of "ip routing" even on L2 devices.
# Use this to retain behavior of AVD versions below 4.0.0.
always_configure_ip_routing: <bool; default=False>
# EOS CLI rendered directly on the root level of the final EOS configuration.
raw_eos_cli: <str>
# Custom structured config for eos_cli_config_gen.
structured_config: <dict>
Node type inband management¶
| Variable | Type | Required | Default | Value Restrictions | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| <node_type_keys.key> | Dictionary | ||||
| defaults | Dictionary | Define variables for all nodes of this type. | |||
| inband_mgmt_interface | String | Pointer to interface used for inband management. All configuration must be done using other data models like network services or structured_config. ‘inband_mgmt_interface’ is only used to refer to this interface as source in various management protocol settings (future feature). On L2 switches, this defaults to Vlan |
|||
| inband_mgmt_vlan | Integer | 4092 |
VLAN number used for inband management on L2 switches (switches using port-channel trunks as uplinks). When using ‘inband_mgmt_subnet’ the VLAN and SVIs will be created automatically on this switch as well as all ‘uplink_switches’. When using ‘inband_mgmt_ip’ the VLAN and SVI will only be created on this device and added to uplink trunk. The VLAN and SVI on the parent switches must be created using network services data models. |
||
| inband_mgmt_subnet | String | Format: ipv4_cidr | Optional IP subnet assigned to inband management SVIs on L2 switches (switches using port-channels as uplinks). Parent l3leafs will have SVI with “ip virtual-router” and host-route injection based on ARP. This allows all l3leafs to reuse the same subnet across multiple racks without VXLAN extension. SVI IP address will be assigned as follows: virtual-router: l3leaf A : l3leaf B : l2leafs : GW on l2leafs : Assign range larger than total l2leafs + 5 Setting is ignored if ‘inband_mgmt_ip’ is set. This setting is applicable to L2 switches (switches using port-channel trunks as uplinks). |
||
| inband_mgmt_ip | String | Format: ipv4_cidr | IP address assigned to the inband management interface set with ‘inband_mgmt_vlan’. This overrides ‘inband_mgmt_subnet’, hence all behavior of ‘inband_mgmt_subnet’ is removed. If this is set the VLAN and SVI will only be created on the L2 switch and added to uplink trunk. The VLAN and SVI on the parent switches must be created using network services data models. This setting is applicable to L2 switches (switches using port-channel trunks as uplinks). |
||
| inband_mgmt_gateway | String | Format: ipv4 | Default gateway configured in the ‘inband_mgmt_vrf’ when using ‘inband_mgmt_ip’. Otherwise gateway is derived from ‘inband_mgmt_subnet’ if set. This setting is applicable to L2 switches (switches using port-channel trunks as uplinks). |
||
| inband_mgmt_ipv6_address | String | Format: ipv6 | IPv6 address assigned to the inband management interface set with ‘inband_mgmt_vlan’. This overrides ‘inband_mgmt_ipv6_subnet’, hence the configuration of ‘inband_mgmt_ipv6_subnet’ is ignored. If this is set the VLAN and SVI will only be created on the L2 switch and added to uplink trunk. The VLAN and SVI on the parent switches must be created using network services data models. This setting is applicable to L2 switches (switches using port-channel trunks as uplinks). |
||
| inband_mgmt_ipv6_subnet | String | Format: ipv6_cidr | Optional IPv6 prefix assigned to inband management SVIs on L2 switches (switches using port-channels as uplinks). Parent l3leafs will have SVI with “ipv6 virtual-router” and host-route injection based on ARP. This allows all l3leafs to reuse the same subnet across multiple racks without VXLAN extension. SVI IP address will be assigned as follows: virtual-router: l3leaf A : l3leaf B : l2leafs : GW on l2leafs : Assign range larger than total l2leafs + 5 Setting is ignored if ‘inband_mgmt_ipv6_address’ is set. This setting is applicable to L2 switches (switches using port-channel trunks as uplinks). |
||
| inband_mgmt_ipv6_gateway | String | Format: ipv6 | Default gateway configured in the ‘inband_mgmt_vrf’. Used when inband_mgmt_ipv6_address is set.Ignored when ‘inband_mgmt_ipv6_subnet’ is set (first IP in subnet used as gateway). This setting is applicable to L2 switches (switches using port-channel trunks as uplinks). |
||
| inband_mgmt_description | String | Inband Management |
Description configured on the Inband Management SVI. This setting is only applied on the devices where it is set, it does not automatically affect any parent/child devices configuration, so it must be set on each applicable node/node-group/node-type as needed. |
||
| inband_mgmt_vlan_name | String | Inband Management |
Name configured on the Inband Management VLAN. This setting is only applied on the devices where it is set, it does not automatically affect any parent/child devices configuration, so it must be set on each applicable node/node-group/node-type as needed. |
||
| inband_mgmt_vrf | String | default |
VRF configured on the Inband Management Interface. The VRF is created if not already created by other means. This setting is only applied on the devices where it is set, it does not automatically affect any parent/child devices configuration, so it must be set on each applicable node/node-group/node-type as needed. |
||
| inband_mgmt_mtu | Integer | 1500 |
MTU configured on the Inband Management Interface. This setting is only applied on the devices where it is set, it does not automatically affect any parent/child devices configuration, so it must be set on each applicable node/node-group/node-type as needed. |
||
| inband_ztp | Boolean | False |
Enable to configure upstream device with proper configuration to allow downstream devices to ZTP inband. This setting also requires that the inband_mgmt_vlan is set for the node. |
||
| inband_ztp_lacp_fallback_delay | Integer | 30 |
Min: 0 Max: 300 |
Set the LACP fallback timeout of the upstream device’s port-channel towards the downstream inband ZTP node. This setting also requires that inband_ztp is set for the node. |
|
| inband_management_subnet deprecated | String | Format: ipv4_cidr | Optional IP subnet assigned to inband management SVIs on L2 switches (switches using port-channels as uplinks). Parent l3leafs will have SVI with “ip virtual-router” and host-route injection based on ARP. This allows all l3leafs to reuse the same subnet across multiple racks without VXLAN extension. SVI IP address will be assigned as follows: virtual-router: l3leaf A : l3leaf B : l2leafs : GW on l2leafs : Assign range larger than total l2leafs + 5 Setting is ignored if ‘inband_mgmt_ip’ is set. This setting is applicable to L2 switches (switches using port-channel trunks as uplinks). This key is deprecated. Support will be removed in AVD version 5.0.0. Use inband_mgmt_subnet instead. |
||
| inband_management_vlan deprecated | Integer | 4092 |
VLAN number used for inband management on L2 switches (switches using port-channel trunks as uplinks). When using ‘inband_mgmt_subnet’ the VLAN and SVIs will be created automatically on this switch as well as all ‘uplink_switches’. When using ‘inband_mgmt_ip’ the VLAN and SVI will only be created on this device and added to uplink trunk. The VLAN and SVI on the parent switches must be created using network services data models.This key is deprecated. Support will be removed in AVD version 5.0.0. Use inband_mgmt_vlan instead. |
||
| node_groups | List, items: Dictionary | Define variables related to all nodes part of this group. | |||
| - group | String | Required, Unique | The Node Group Name is used for MLAG domain unless set with ‘mlag_domain_id’. The Node Group Name is also used for peer description on downstream switches’ uplinks. |
||
| nodes | List, items: Dictionary | Define variables per node. | |||
| - name | String | Required, Unique | The Node Name is used as “hostname”. | ||
| inband_mgmt_interface | String | Pointer to interface used for inband management. All configuration must be done using other data models like network services or structured_config. ‘inband_mgmt_interface’ is only used to refer to this interface as source in various management protocol settings (future feature). On L2 switches, this defaults to Vlan |
|||
| inband_mgmt_vlan | Integer | 4092 |
VLAN number used for inband management on L2 switches (switches using port-channel trunks as uplinks). When using ‘inband_mgmt_subnet’ the VLAN and SVIs will be created automatically on this switch as well as all ‘uplink_switches’. When using ‘inband_mgmt_ip’ the VLAN and SVI will only be created on this device and added to uplink trunk. The VLAN and SVI on the parent switches must be created using network services data models. |
||
| inband_mgmt_subnet | String | Format: ipv4_cidr | Optional IP subnet assigned to inband management SVIs on L2 switches (switches using port-channels as uplinks). Parent l3leafs will have SVI with “ip virtual-router” and host-route injection based on ARP. This allows all l3leafs to reuse the same subnet across multiple racks without VXLAN extension. SVI IP address will be assigned as follows: virtual-router: l3leaf A : l3leaf B : l2leafs : GW on l2leafs : Assign range larger than total l2leafs + 5 Setting is ignored if ‘inband_mgmt_ip’ is set. This setting is applicable to L2 switches (switches using port-channel trunks as uplinks). |
||
| inband_mgmt_ip | String | Format: ipv4_cidr | IP address assigned to the inband management interface set with ‘inband_mgmt_vlan’. This overrides ‘inband_mgmt_subnet’, hence all behavior of ‘inband_mgmt_subnet’ is removed. If this is set the VLAN and SVI will only be created on the L2 switch and added to uplink trunk. The VLAN and SVI on the parent switches must be created using network services data models. This setting is applicable to L2 switches (switches using port-channel trunks as uplinks). |
||
| inband_mgmt_gateway | String | Format: ipv4 | Default gateway configured in the ‘inband_mgmt_vrf’ when using ‘inband_mgmt_ip’. Otherwise gateway is derived from ‘inband_mgmt_subnet’ if set. This setting is applicable to L2 switches (switches using port-channel trunks as uplinks). |
||
| inband_mgmt_ipv6_address | String | Format: ipv6 | IPv6 address assigned to the inband management interface set with ‘inband_mgmt_vlan’. This overrides ‘inband_mgmt_ipv6_subnet’, hence the configuration of ‘inband_mgmt_ipv6_subnet’ is ignored. If this is set the VLAN and SVI will only be created on the L2 switch and added to uplink trunk. The VLAN and SVI on the parent switches must be created using network services data models. This setting is applicable to L2 switches (switches using port-channel trunks as uplinks). |
||
| inband_mgmt_ipv6_subnet | String | Format: ipv6_cidr | Optional IPv6 prefix assigned to inband management SVIs on L2 switches (switches using port-channels as uplinks). Parent l3leafs will have SVI with “ipv6 virtual-router” and host-route injection based on ARP. This allows all l3leafs to reuse the same subnet across multiple racks without VXLAN extension. SVI IP address will be assigned as follows: virtual-router: l3leaf A : l3leaf B : l2leafs : GW on l2leafs : Assign range larger than total l2leafs + 5 Setting is ignored if ‘inband_mgmt_ipv6_address’ is set. This setting is applicable to L2 switches (switches using port-channel trunks as uplinks). |
||
| inband_mgmt_ipv6_gateway | String | Format: ipv6 | Default gateway configured in the ‘inband_mgmt_vrf’. Used when inband_mgmt_ipv6_address is set.Ignored when ‘inband_mgmt_ipv6_subnet’ is set (first IP in subnet used as gateway). This setting is applicable to L2 switches (switches using port-channel trunks as uplinks). |
||
| inband_mgmt_description | String | Inband Management |
Description configured on the Inband Management SVI. This setting is only applied on the devices where it is set, it does not automatically affect any parent/child devices configuration, so it must be set on each applicable node/node-group/node-type as needed. |
||
| inband_mgmt_vlan_name | String | Inband Management |
Name configured on the Inband Management VLAN. This setting is only applied on the devices where it is set, it does not automatically affect any parent/child devices configuration, so it must be set on each applicable node/node-group/node-type as needed. |
||
| inband_mgmt_vrf | String | default |
VRF configured on the Inband Management Interface. The VRF is created if not already created by other means. This setting is only applied on the devices where it is set, it does not automatically affect any parent/child devices configuration, so it must be set on each applicable node/node-group/node-type as needed. |
||
| inband_mgmt_mtu | Integer | 1500 |
MTU configured on the Inband Management Interface. This setting is only applied on the devices where it is set, it does not automatically affect any parent/child devices configuration, so it must be set on each applicable node/node-group/node-type as needed. |
||
| inband_ztp | Boolean | False |
Enable to configure upstream device with proper configuration to allow downstream devices to ZTP inband. This setting also requires that the inband_mgmt_vlan is set for the node. |
||
| inband_ztp_lacp_fallback_delay | Integer | 30 |
Min: 0 Max: 300 |
Set the LACP fallback timeout of the upstream device’s port-channel towards the downstream inband ZTP node. This setting also requires that inband_ztp is set for the node. |
|
| inband_management_subnet deprecated | String | Format: ipv4_cidr | Optional IP subnet assigned to inband management SVIs on L2 switches (switches using port-channels as uplinks). Parent l3leafs will have SVI with “ip virtual-router” and host-route injection based on ARP. This allows all l3leafs to reuse the same subnet across multiple racks without VXLAN extension. SVI IP address will be assigned as follows: virtual-router: l3leaf A : l3leaf B : l2leafs : GW on l2leafs : Assign range larger than total l2leafs + 5 Setting is ignored if ‘inband_mgmt_ip’ is set. This setting is applicable to L2 switches (switches using port-channel trunks as uplinks). This key is deprecated. Support will be removed in AVD version 5.0.0. Use inband_mgmt_subnet instead. |
||
| inband_management_vlan deprecated | Integer | 4092 |
VLAN number used for inband management on L2 switches (switches using port-channel trunks as uplinks). When using ‘inband_mgmt_subnet’ the VLAN and SVIs will be created automatically on this switch as well as all ‘uplink_switches’. When using ‘inband_mgmt_ip’ the VLAN and SVI will only be created on this device and added to uplink trunk. The VLAN and SVI on the parent switches must be created using network services data models.This key is deprecated. Support will be removed in AVD version 5.0.0. Use inband_mgmt_vlan instead. |
||
| inband_mgmt_interface | String | Pointer to interface used for inband management. All configuration must be done using other data models like network services or structured_config. ‘inband_mgmt_interface’ is only used to refer to this interface as source in various management protocol settings (future feature). On L2 switches, this defaults to Vlan |
|||
| inband_mgmt_vlan | Integer | 4092 |
VLAN number used for inband management on L2 switches (switches using port-channel trunks as uplinks). When using ‘inband_mgmt_subnet’ the VLAN and SVIs will be created automatically on this switch as well as all ‘uplink_switches’. When using ‘inband_mgmt_ip’ the VLAN and SVI will only be created on this device and added to uplink trunk. The VLAN and SVI on the parent switches must be created using network services data models. |
||
| inband_mgmt_subnet | String | Format: ipv4_cidr | Optional IP subnet assigned to inband management SVIs on L2 switches (switches using port-channels as uplinks). Parent l3leafs will have SVI with “ip virtual-router” and host-route injection based on ARP. This allows all l3leafs to reuse the same subnet across multiple racks without VXLAN extension. SVI IP address will be assigned as follows: virtual-router: l3leaf A : l3leaf B : l2leafs : GW on l2leafs : Assign range larger than total l2leafs + 5 Setting is ignored if ‘inband_mgmt_ip’ is set. This setting is applicable to L2 switches (switches using port-channel trunks as uplinks). |
||
| inband_mgmt_ip | String | Format: ipv4_cidr | IP address assigned to the inband management interface set with ‘inband_mgmt_vlan’. This overrides ‘inband_mgmt_subnet’, hence all behavior of ‘inband_mgmt_subnet’ is removed. If this is set the VLAN and SVI will only be created on the L2 switch and added to uplink trunk. The VLAN and SVI on the parent switches must be created using network services data models. This setting is applicable to L2 switches (switches using port-channel trunks as uplinks). |
||
| inband_mgmt_gateway | String | Format: ipv4 | Default gateway configured in the ‘inband_mgmt_vrf’ when using ‘inband_mgmt_ip’. Otherwise gateway is derived from ‘inband_mgmt_subnet’ if set. This setting is applicable to L2 switches (switches using port-channel trunks as uplinks). |
||
| inband_mgmt_ipv6_address | String | Format: ipv6 | IPv6 address assigned to the inband management interface set with ‘inband_mgmt_vlan’. This overrides ‘inband_mgmt_ipv6_subnet’, hence the configuration of ‘inband_mgmt_ipv6_subnet’ is ignored. If this is set the VLAN and SVI will only be created on the L2 switch and added to uplink trunk. The VLAN and SVI on the parent switches must be created using network services data models. This setting is applicable to L2 switches (switches using port-channel trunks as uplinks). |
||
| inband_mgmt_ipv6_subnet | String | Format: ipv6_cidr | Optional IPv6 prefix assigned to inband management SVIs on L2 switches (switches using port-channels as uplinks). Parent l3leafs will have SVI with “ipv6 virtual-router” and host-route injection based on ARP. This allows all l3leafs to reuse the same subnet across multiple racks without VXLAN extension. SVI IP address will be assigned as follows: virtual-router: l3leaf A : l3leaf B : l2leafs : GW on l2leafs : Assign range larger than total l2leafs + 5 Setting is ignored if ‘inband_mgmt_ipv6_address’ is set. This setting is applicable to L2 switches (switches using port-channel trunks as uplinks). |
||
| inband_mgmt_ipv6_gateway | String | Format: ipv6 | Default gateway configured in the ‘inband_mgmt_vrf’. Used when inband_mgmt_ipv6_address is set.Ignored when ‘inband_mgmt_ipv6_subnet’ is set (first IP in subnet used as gateway). This setting is applicable to L2 switches (switches using port-channel trunks as uplinks). |
||
| inband_mgmt_description | String | Inband Management |
Description configured on the Inband Management SVI. This setting is only applied on the devices where it is set, it does not automatically affect any parent/child devices configuration, so it must be set on each applicable node/node-group/node-type as needed. |
||
| inband_mgmt_vlan_name | String | Inband Management |
Name configured on the Inband Management VLAN. This setting is only applied on the devices where it is set, it does not automatically affect any parent/child devices configuration, so it must be set on each applicable node/node-group/node-type as needed. |
||
| inband_mgmt_vrf | String | default |
VRF configured on the Inband Management Interface. The VRF is created if not already created by other means. This setting is only applied on the devices where it is set, it does not automatically affect any parent/child devices configuration, so it must be set on each applicable node/node-group/node-type as needed. |
||
| inband_mgmt_mtu | Integer | 1500 |
MTU configured on the Inband Management Interface. This setting is only applied on the devices where it is set, it does not automatically affect any parent/child devices configuration, so it must be set on each applicable node/node-group/node-type as needed. |
||
| inband_ztp | Boolean | False |
Enable to configure upstream device with proper configuration to allow downstream devices to ZTP inband. This setting also requires that the inband_mgmt_vlan is set for the node. |
||
| inband_ztp_lacp_fallback_delay | Integer | 30 |
Min: 0 Max: 300 |
Set the LACP fallback timeout of the upstream device’s port-channel towards the downstream inband ZTP node. This setting also requires that inband_ztp is set for the node. |
|
| inband_management_subnet deprecated | String | Format: ipv4_cidr | Optional IP subnet assigned to inband management SVIs on L2 switches (switches using port-channels as uplinks). Parent l3leafs will have SVI with “ip virtual-router” and host-route injection based on ARP. This allows all l3leafs to reuse the same subnet across multiple racks without VXLAN extension. SVI IP address will be assigned as follows: virtual-router: l3leaf A : l3leaf B : l2leafs : GW on l2leafs : Assign range larger than total l2leafs + 5 Setting is ignored if ‘inband_mgmt_ip’ is set. This setting is applicable to L2 switches (switches using port-channel trunks as uplinks). This key is deprecated. Support will be removed in AVD version 5.0.0. Use inband_mgmt_subnet instead. |
||
| inband_management_vlan deprecated | Integer | 4092 |
VLAN number used for inband management on L2 switches (switches using port-channel trunks as uplinks). When using ‘inband_mgmt_subnet’ the VLAN and SVIs will be created automatically on this switch as well as all ‘uplink_switches’. When using ‘inband_mgmt_ip’ the VLAN and SVI will only be created on this device and added to uplink trunk. The VLAN and SVI on the parent switches must be created using network services data models.This key is deprecated. Support will be removed in AVD version 5.0.0. Use inband_mgmt_vlan instead. |
||
| nodes | List, items: Dictionary | Define variables per node. | |||
| - name | String | Required, Unique | The Node Name is used as “hostname”. | ||
| inband_mgmt_interface | String | Pointer to interface used for inband management. All configuration must be done using other data models like network services or structured_config. ‘inband_mgmt_interface’ is only used to refer to this interface as source in various management protocol settings (future feature). On L2 switches, this defaults to Vlan |
|||
| inband_mgmt_vlan | Integer | 4092 |
VLAN number used for inband management on L2 switches (switches using port-channel trunks as uplinks). When using ‘inband_mgmt_subnet’ the VLAN and SVIs will be created automatically on this switch as well as all ‘uplink_switches’. When using ‘inband_mgmt_ip’ the VLAN and SVI will only be created on this device and added to uplink trunk. The VLAN and SVI on the parent switches must be created using network services data models. |
||
| inband_mgmt_subnet | String | Format: ipv4_cidr | Optional IP subnet assigned to inband management SVIs on L2 switches (switches using port-channels as uplinks). Parent l3leafs will have SVI with “ip virtual-router” and host-route injection based on ARP. This allows all l3leafs to reuse the same subnet across multiple racks without VXLAN extension. SVI IP address will be assigned as follows: virtual-router: l3leaf A : l3leaf B : l2leafs : GW on l2leafs : Assign range larger than total l2leafs + 5 Setting is ignored if ‘inband_mgmt_ip’ is set. This setting is applicable to L2 switches (switches using port-channel trunks as uplinks). |
||
| inband_mgmt_ip | String | Format: ipv4_cidr | IP address assigned to the inband management interface set with ‘inband_mgmt_vlan’. This overrides ‘inband_mgmt_subnet’, hence all behavior of ‘inband_mgmt_subnet’ is removed. If this is set the VLAN and SVI will only be created on the L2 switch and added to uplink trunk. The VLAN and SVI on the parent switches must be created using network services data models. This setting is applicable to L2 switches (switches using port-channel trunks as uplinks). |
||
| inband_mgmt_gateway | String | Format: ipv4 | Default gateway configured in the ‘inband_mgmt_vrf’ when using ‘inband_mgmt_ip’. Otherwise gateway is derived from ‘inband_mgmt_subnet’ if set. This setting is applicable to L2 switches (switches using port-channel trunks as uplinks). |
||
| inband_mgmt_ipv6_address | String | Format: ipv6 | IPv6 address assigned to the inband management interface set with ‘inband_mgmt_vlan’. This overrides ‘inband_mgmt_ipv6_subnet’, hence the configuration of ‘inband_mgmt_ipv6_subnet’ is ignored. If this is set the VLAN and SVI will only be created on the L2 switch and added to uplink trunk. The VLAN and SVI on the parent switches must be created using network services data models. This setting is applicable to L2 switches (switches using port-channel trunks as uplinks). |
||
| inband_mgmt_ipv6_subnet | String | Format: ipv6_cidr | Optional IPv6 prefix assigned to inband management SVIs on L2 switches (switches using port-channels as uplinks). Parent l3leafs will have SVI with “ipv6 virtual-router” and host-route injection based on ARP. This allows all l3leafs to reuse the same subnet across multiple racks without VXLAN extension. SVI IP address will be assigned as follows: virtual-router: l3leaf A : l3leaf B : l2leafs : GW on l2leafs : Assign range larger than total l2leafs + 5 Setting is ignored if ‘inband_mgmt_ipv6_address’ is set. This setting is applicable to L2 switches (switches using port-channel trunks as uplinks). |
||
| inband_mgmt_ipv6_gateway | String | Format: ipv6 | Default gateway configured in the ‘inband_mgmt_vrf’. Used when inband_mgmt_ipv6_address is set.Ignored when ‘inband_mgmt_ipv6_subnet’ is set (first IP in subnet used as gateway). This setting is applicable to L2 switches (switches using port-channel trunks as uplinks). |
||
| inband_mgmt_description | String | Inband Management |
Description configured on the Inband Management SVI. This setting is only applied on the devices where it is set, it does not automatically affect any parent/child devices configuration, so it must be set on each applicable node/node-group/node-type as needed. |
||
| inband_mgmt_vlan_name | String | Inband Management |
Name configured on the Inband Management VLAN. This setting is only applied on the devices where it is set, it does not automatically affect any parent/child devices configuration, so it must be set on each applicable node/node-group/node-type as needed. |
||
| inband_mgmt_vrf | String | default |
VRF configured on the Inband Management Interface. The VRF is created if not already created by other means. This setting is only applied on the devices where it is set, it does not automatically affect any parent/child devices configuration, so it must be set on each applicable node/node-group/node-type as needed. |
||
| inband_mgmt_mtu | Integer | 1500 |
MTU configured on the Inband Management Interface. This setting is only applied on the devices where it is set, it does not automatically affect any parent/child devices configuration, so it must be set on each applicable node/node-group/node-type as needed. |
||
| inband_ztp | Boolean | False |
Enable to configure upstream device with proper configuration to allow downstream devices to ZTP inband. This setting also requires that the inband_mgmt_vlan is set for the node. |
||
| inband_ztp_lacp_fallback_delay | Integer | 30 |
Min: 0 Max: 300 |
Set the LACP fallback timeout of the upstream device’s port-channel towards the downstream inband ZTP node. This setting also requires that inband_ztp is set for the node. |
|
| inband_management_subnet deprecated | String | Format: ipv4_cidr | Optional IP subnet assigned to inband management SVIs on L2 switches (switches using port-channels as uplinks). Parent l3leafs will have SVI with “ip virtual-router” and host-route injection based on ARP. This allows all l3leafs to reuse the same subnet across multiple racks without VXLAN extension. SVI IP address will be assigned as follows: virtual-router: l3leaf A : l3leaf B : l2leafs : GW on l2leafs : Assign range larger than total l2leafs + 5 Setting is ignored if ‘inband_mgmt_ip’ is set. This setting is applicable to L2 switches (switches using port-channel trunks as uplinks). This key is deprecated. Support will be removed in AVD version 5.0.0. Use inband_mgmt_subnet instead. |
||
| inband_management_vlan deprecated | Integer | 4092 |
VLAN number used for inband management on L2 switches (switches using port-channel trunks as uplinks). When using ‘inband_mgmt_subnet’ the VLAN and SVIs will be created automatically on this switch as well as all ‘uplink_switches’. When using ‘inband_mgmt_ip’ the VLAN and SVI will only be created on this device and added to uplink trunk. The VLAN and SVI on the parent switches must be created using network services data models.This key is deprecated. Support will be removed in AVD version 5.0.0. Use inband_mgmt_vlan instead. |
<node_type_keys.key>:
# Define variables for all nodes of this type.
defaults:
# Pointer to interface used for inband management.
# All configuration must be done using other data models like network services or structured_config.
# 'inband_mgmt_interface' is only used to refer to this interface as source in various management protocol settings (future feature).
#
# On L2 switches, this defaults to Vlan<inband_mgmt_vlan> if either 'inband_mgmt_subnet' or 'inband_mgmt_ip' is set.
inband_mgmt_interface: <str>
# VLAN number used for inband management on L2 switches (switches using port-channel trunks as uplinks).
# When using 'inband_mgmt_subnet' the VLAN and SVIs will be created automatically on this switch as well as all 'uplink_switches'.
# When using 'inband_mgmt_ip' the VLAN and SVI will only be created on this device and added to uplink trunk. The VLAN and SVI on the parent switches must be created using network services data models.
inband_mgmt_vlan: <int; default=4092>
# Optional IP subnet assigned to inband management SVIs on L2 switches (switches using port-channels as uplinks).
# Parent l3leafs will have SVI with "ip virtual-router" and host-route injection based on ARP.
# This allows all l3leafs to reuse the same subnet across multiple racks without VXLAN extension.
# SVI IP address will be assigned as follows:
# virtual-router: <subnet> + 1
# l3leaf A : <subnet> + 2 (same IP on all l3leaf A)
# l3leaf B : <subnet> + 3 (same IP on all l3leaf B)
# l2leafs : <subnet> + 3 + <l2leaf id>
# GW on l2leafs : <subnet> + 1
# Assign range larger than total l2leafs + 5
#
# Setting is ignored if 'inband_mgmt_ip' is set.
#
# This setting is applicable to L2 switches (switches using port-channel trunks as uplinks).
inband_mgmt_subnet: <str>
# IP address assigned to the inband management interface set with 'inband_mgmt_vlan'.
# This overrides 'inband_mgmt_subnet', hence all behavior of 'inband_mgmt_subnet' is removed.
#
# If this is set the VLAN and SVI will only be created on the L2 switch and added to uplink trunk.
# The VLAN and SVI on the parent switches must be created using network services data models.
#
# This setting is applicable to L2 switches (switches using port-channel trunks as uplinks).
inband_mgmt_ip: <str>
# Default gateway configured in the 'inband_mgmt_vrf' when using 'inband_mgmt_ip'. Otherwise gateway is derived from 'inband_mgmt_subnet' if set.
#
# This setting is applicable to L2 switches (switches using port-channel trunks as uplinks).
inband_mgmt_gateway: <str>
# IPv6 address assigned to the inband management interface set with 'inband_mgmt_vlan'.
# This overrides 'inband_mgmt_ipv6_subnet', hence the configuration of 'inband_mgmt_ipv6_subnet' is ignored.
#
# If this is set the VLAN and SVI will only be created on the L2 switch and added to uplink trunk.
# The VLAN and SVI on the parent switches must be created using network services data models.
#
# This setting is applicable to L2 switches (switches using port-channel trunks as uplinks).
inband_mgmt_ipv6_address: <str>
# Optional IPv6 prefix assigned to inband management SVIs on L2 switches (switches using port-channels as uplinks).
# Parent l3leafs will have SVI with "ipv6 virtual-router" and host-route injection based on ARP.
# This allows all l3leafs to reuse the same subnet across multiple racks without VXLAN extension.
# SVI IP address will be assigned as follows:
# virtual-router: <subnet> + 1
# l3leaf A : <subnet> + 2 (same IP on all l3leaf A)
# l3leaf B : <subnet> + 3 (same IP on all l3leaf B)
# l2leafs : <subnet> + 3 + <l2leaf id>
# GW on l2leafs : <subnet> + 1
# Assign range larger than total l2leafs + 5
#
# Setting is ignored if 'inband_mgmt_ipv6_address' is set.
#
# This setting is applicable to L2 switches (switches using port-channel trunks as uplinks).
inband_mgmt_ipv6_subnet: <str>
# Default gateway configured in the 'inband_mgmt_vrf'.
# Used when `inband_mgmt_ipv6_address` is set.
# Ignored when 'inband_mgmt_ipv6_subnet' is set (first IP in subnet used as gateway).
#
# This setting is applicable to L2 switches (switches using port-channel trunks as uplinks).
inband_mgmt_ipv6_gateway: <str>
# Description configured on the Inband Management SVI.
#
# This setting is only applied on the devices where it is set, it does not automatically affect any parent/child devices configuration, so it must be set on each applicable node/node-group/node-type as needed.
inband_mgmt_description: <str; default="Inband Management">
# Name configured on the Inband Management VLAN.
# This setting is only applied on the devices where it is set, it does not automatically affect any parent/child devices configuration, so it must be set on each applicable node/node-group/node-type as needed.
inband_mgmt_vlan_name: <str; default="Inband Management">
# VRF configured on the Inband Management Interface.
# The VRF is created if not already created by other means.
# This setting is only applied on the devices where it is set, it does not automatically affect any parent/child devices configuration, so it must be set on each applicable node/node-group/node-type as needed.
inband_mgmt_vrf: <str; default="default">
# MTU configured on the Inband Management Interface.
# This setting is only applied on the devices where it is set, it does not automatically affect any parent/child devices configuration, so it must be set on each applicable node/node-group/node-type as needed.
inband_mgmt_mtu: <int; default=1500>
# Enable to configure upstream device with proper configuration to allow downstream devices to ZTP inband.
# This setting also requires that the `inband_mgmt_vlan` is set for the node.
inband_ztp: <bool; default=False>
# Set the LACP fallback timeout of the upstream device's port-channel towards the downstream inband ZTP node.
# This setting also requires that `inband_ztp` is set for the node.
inband_ztp_lacp_fallback_delay: <int; 0-300; default=30>
# Optional IP subnet assigned to inband management SVIs on L2 switches (switches using port-channels as uplinks).
# Parent l3leafs will have SVI with "ip virtual-router" and host-route injection based on ARP.
# This allows all l3leafs to reuse the same subnet across multiple racks without VXLAN extension.
# SVI IP address will be assigned as follows:
# virtual-router: <subnet> + 1
# l3leaf A : <subnet> + 2 (same IP on all l3leaf A)
# l3leaf B : <subnet> + 3 (same IP on all l3leaf B)
# l2leafs : <subnet> + 3 + <l2leaf id>
# GW on l2leafs : <subnet> + 1
# Assign range larger than total l2leafs + 5
#
# Setting is ignored if 'inband_mgmt_ip' is set.
#
# This setting is applicable to L2 switches (switches using port-channel trunks as uplinks).
# This key is deprecated.
# Support will be removed in AVD version 5.0.0.
# Use <samp>inband_mgmt_subnet</samp> instead.
inband_management_subnet: <str>
# VLAN number used for inband management on L2 switches (switches using port-channel trunks as uplinks).
# When using 'inband_mgmt_subnet' the VLAN and SVIs will be created automatically on this switch as well as all 'uplink_switches'.
# When using 'inband_mgmt_ip' the VLAN and SVI will only be created on this device and added to uplink trunk. The VLAN and SVI on the parent switches must be created using network services data models.
# This key is deprecated.
# Support will be removed in AVD version 5.0.0.
# Use <samp>inband_mgmt_vlan</samp> instead.
inband_management_vlan: <int; default=4092>
# Define variables related to all nodes part of this group.
node_groups:
# The Node Group Name is used for MLAG domain unless set with 'mlag_domain_id'.
# The Node Group Name is also used for peer description on downstream switches' uplinks.
- group: <str; required; unique>
# Define variables per node.
nodes:
# The Node Name is used as "hostname".
- name: <str; required; unique>
# Pointer to interface used for inband management.
# All configuration must be done using other data models like network services or structured_config.
# 'inband_mgmt_interface' is only used to refer to this interface as source in various management protocol settings (future feature).
#
# On L2 switches, this defaults to Vlan<inband_mgmt_vlan> if either 'inband_mgmt_subnet' or 'inband_mgmt_ip' is set.
inband_mgmt_interface: <str>
# VLAN number used for inband management on L2 switches (switches using port-channel trunks as uplinks).
# When using 'inband_mgmt_subnet' the VLAN and SVIs will be created automatically on this switch as well as all 'uplink_switches'.
# When using 'inband_mgmt_ip' the VLAN and SVI will only be created on this device and added to uplink trunk. The VLAN and SVI on the parent switches must be created using network services data models.
inband_mgmt_vlan: <int; default=4092>
# Optional IP subnet assigned to inband management SVIs on L2 switches (switches using port-channels as uplinks).
# Parent l3leafs will have SVI with "ip virtual-router" and host-route injection based on ARP.
# This allows all l3leafs to reuse the same subnet across multiple racks without VXLAN extension.
# SVI IP address will be assigned as follows:
# virtual-router: <subnet> + 1
# l3leaf A : <subnet> + 2 (same IP on all l3leaf A)
# l3leaf B : <subnet> + 3 (same IP on all l3leaf B)
# l2leafs : <subnet> + 3 + <l2leaf id>
# GW on l2leafs : <subnet> + 1
# Assign range larger than total l2leafs + 5
#
# Setting is ignored if 'inband_mgmt_ip' is set.
#
# This setting is applicable to L2 switches (switches using port-channel trunks as uplinks).
inband_mgmt_subnet: <str>
# IP address assigned to the inband management interface set with 'inband_mgmt_vlan'.
# This overrides 'inband_mgmt_subnet', hence all behavior of 'inband_mgmt_subnet' is removed.
#
# If this is set the VLAN and SVI will only be created on the L2 switch and added to uplink trunk.
# The VLAN and SVI on the parent switches must be created using network services data models.
#
# This setting is applicable to L2 switches (switches using port-channel trunks as uplinks).
inband_mgmt_ip: <str>
# Default gateway configured in the 'inband_mgmt_vrf' when using 'inband_mgmt_ip'. Otherwise gateway is derived from 'inband_mgmt_subnet' if set.
#
# This setting is applicable to L2 switches (switches using port-channel trunks as uplinks).
inband_mgmt_gateway: <str>
# IPv6 address assigned to the inband management interface set with 'inband_mgmt_vlan'.
# This overrides 'inband_mgmt_ipv6_subnet', hence the configuration of 'inband_mgmt_ipv6_subnet' is ignored.
#
# If this is set the VLAN and SVI will only be created on the L2 switch and added to uplink trunk.
# The VLAN and SVI on the parent switches must be created using network services data models.
#
# This setting is applicable to L2 switches (switches using port-channel trunks as uplinks).
inband_mgmt_ipv6_address: <str>
# Optional IPv6 prefix assigned to inband management SVIs on L2 switches (switches using port-channels as uplinks).
# Parent l3leafs will have SVI with "ipv6 virtual-router" and host-route injection based on ARP.
# This allows all l3leafs to reuse the same subnet across multiple racks without VXLAN extension.
# SVI IP address will be assigned as follows:
# virtual-router: <subnet> + 1
# l3leaf A : <subnet> + 2 (same IP on all l3leaf A)
# l3leaf B : <subnet> + 3 (same IP on all l3leaf B)
# l2leafs : <subnet> + 3 + <l2leaf id>
# GW on l2leafs : <subnet> + 1
# Assign range larger than total l2leafs + 5
#
# Setting is ignored if 'inband_mgmt_ipv6_address' is set.
#
# This setting is applicable to L2 switches (switches using port-channel trunks as uplinks).
inband_mgmt_ipv6_subnet: <str>
# Default gateway configured in the 'inband_mgmt_vrf'.
# Used when `inband_mgmt_ipv6_address` is set.
# Ignored when 'inband_mgmt_ipv6_subnet' is set (first IP in subnet used as gateway).
#
# This setting is applicable to L2 switches (switches using port-channel trunks as uplinks).
inband_mgmt_ipv6_gateway: <str>
# Description configured on the Inband Management SVI.
#
# This setting is only applied on the devices where it is set, it does not automatically affect any parent/child devices configuration, so it must be set on each applicable node/node-group/node-type as needed.
inband_mgmt_description: <str; default="Inband Management">
# Name configured on the Inband Management VLAN.
# This setting is only applied on the devices where it is set, it does not automatically affect any parent/child devices configuration, so it must be set on each applicable node/node-group/node-type as needed.
inband_mgmt_vlan_name: <str; default="Inband Management">
# VRF configured on the Inband Management Interface.
# The VRF is created if not already created by other means.
# This setting is only applied on the devices where it is set, it does not automatically affect any parent/child devices configuration, so it must be set on each applicable node/node-group/node-type as needed.
inband_mgmt_vrf: <str; default="default">
# MTU configured on the Inband Management Interface.
# This setting is only applied on the devices where it is set, it does not automatically affect any parent/child devices configuration, so it must be set on each applicable node/node-group/node-type as needed.
inband_mgmt_mtu: <int; default=1500>
# Enable to configure upstream device with proper configuration to allow downstream devices to ZTP inband.
# This setting also requires that the `inband_mgmt_vlan` is set for the node.
inband_ztp: <bool; default=False>
# Set the LACP fallback timeout of the upstream device's port-channel towards the downstream inband ZTP node.
# This setting also requires that `inband_ztp` is set for the node.
inband_ztp_lacp_fallback_delay: <int; 0-300; default=30>
# Optional IP subnet assigned to inband management SVIs on L2 switches (switches using port-channels as uplinks).
# Parent l3leafs will have SVI with "ip virtual-router" and host-route injection based on ARP.
# This allows all l3leafs to reuse the same subnet across multiple racks without VXLAN extension.
# SVI IP address will be assigned as follows:
# virtual-router: <subnet> + 1
# l3leaf A : <subnet> + 2 (same IP on all l3leaf A)
# l3leaf B : <subnet> + 3 (same IP on all l3leaf B)
# l2leafs : <subnet> + 3 + <l2leaf id>
# GW on l2leafs : <subnet> + 1
# Assign range larger than total l2leafs + 5
#
# Setting is ignored if 'inband_mgmt_ip' is set.
#
# This setting is applicable to L2 switches (switches using port-channel trunks as uplinks).
# This key is deprecated.
# Support will be removed in AVD version 5.0.0.
# Use <samp>inband_mgmt_subnet</samp> instead.
inband_management_subnet: <str>
# VLAN number used for inband management on L2 switches (switches using port-channel trunks as uplinks).
# When using 'inband_mgmt_subnet' the VLAN and SVIs will be created automatically on this switch as well as all 'uplink_switches'.
# When using 'inband_mgmt_ip' the VLAN and SVI will only be created on this device and added to uplink trunk. The VLAN and SVI on the parent switches must be created using network services data models.
# This key is deprecated.
# Support will be removed in AVD version 5.0.0.
# Use <samp>inband_mgmt_vlan</samp> instead.
inband_management_vlan: <int; default=4092>
# Pointer to interface used for inband management.
# All configuration must be done using other data models like network services or structured_config.
# 'inband_mgmt_interface' is only used to refer to this interface as source in various management protocol settings (future feature).
#
# On L2 switches, this defaults to Vlan<inband_mgmt_vlan> if either 'inband_mgmt_subnet' or 'inband_mgmt_ip' is set.
inband_mgmt_interface: <str>
# VLAN number used for inband management on L2 switches (switches using port-channel trunks as uplinks).
# When using 'inband_mgmt_subnet' the VLAN and SVIs will be created automatically on this switch as well as all 'uplink_switches'.
# When using 'inband_mgmt_ip' the VLAN and SVI will only be created on this device and added to uplink trunk. The VLAN and SVI on the parent switches must be created using network services data models.
inband_mgmt_vlan: <int; default=4092>
# Optional IP subnet assigned to inband management SVIs on L2 switches (switches using port-channels as uplinks).
# Parent l3leafs will have SVI with "ip virtual-router" and host-route injection based on ARP.
# This allows all l3leafs to reuse the same subnet across multiple racks without VXLAN extension.
# SVI IP address will be assigned as follows:
# virtual-router: <subnet> + 1
# l3leaf A : <subnet> + 2 (same IP on all l3leaf A)
# l3leaf B : <subnet> + 3 (same IP on all l3leaf B)
# l2leafs : <subnet> + 3 + <l2leaf id>
# GW on l2leafs : <subnet> + 1
# Assign range larger than total l2leafs + 5
#
# Setting is ignored if 'inband_mgmt_ip' is set.
#
# This setting is applicable to L2 switches (switches using port-channel trunks as uplinks).
inband_mgmt_subnet: <str>
# IP address assigned to the inband management interface set with 'inband_mgmt_vlan'.
# This overrides 'inband_mgmt_subnet', hence all behavior of 'inband_mgmt_subnet' is removed.
#
# If this is set the VLAN and SVI will only be created on the L2 switch and added to uplink trunk.
# The VLAN and SVI on the parent switches must be created using network services data models.
#
# This setting is applicable to L2 switches (switches using port-channel trunks as uplinks).
inband_mgmt_ip: <str>
# Default gateway configured in the 'inband_mgmt_vrf' when using 'inband_mgmt_ip'. Otherwise gateway is derived from 'inband_mgmt_subnet' if set.
#
# This setting is applicable to L2 switches (switches using port-channel trunks as uplinks).
inband_mgmt_gateway: <str>
# IPv6 address assigned to the inband management interface set with 'inband_mgmt_vlan'.
# This overrides 'inband_mgmt_ipv6_subnet', hence the configuration of 'inband_mgmt_ipv6_subnet' is ignored.
#
# If this is set the VLAN and SVI will only be created on the L2 switch and added to uplink trunk.
# The VLAN and SVI on the parent switches must be created using network services data models.
#
# This setting is applicable to L2 switches (switches using port-channel trunks as uplinks).
inband_mgmt_ipv6_address: <str>
# Optional IPv6 prefix assigned to inband management SVIs on L2 switches (switches using port-channels as uplinks).
# Parent l3leafs will have SVI with "ipv6 virtual-router" and host-route injection based on ARP.
# This allows all l3leafs to reuse the same subnet across multiple racks without VXLAN extension.
# SVI IP address will be assigned as follows:
# virtual-router: <subnet> + 1
# l3leaf A : <subnet> + 2 (same IP on all l3leaf A)
# l3leaf B : <subnet> + 3 (same IP on all l3leaf B)
# l2leafs : <subnet> + 3 + <l2leaf id>
# GW on l2leafs : <subnet> + 1
# Assign range larger than total l2leafs + 5
#
# Setting is ignored if 'inband_mgmt_ipv6_address' is set.
#
# This setting is applicable to L2 switches (switches using port-channel trunks as uplinks).
inband_mgmt_ipv6_subnet: <str>
# Default gateway configured in the 'inband_mgmt_vrf'.
# Used when `inband_mgmt_ipv6_address` is set.
# Ignored when 'inband_mgmt_ipv6_subnet' is set (first IP in subnet used as gateway).
#
# This setting is applicable to L2 switches (switches using port-channel trunks as uplinks).
inband_mgmt_ipv6_gateway: <str>
# Description configured on the Inband Management SVI.
#
# This setting is only applied on the devices where it is set, it does not automatically affect any parent/child devices configuration, so it must be set on each applicable node/node-group/node-type as needed.
inband_mgmt_description: <str; default="Inband Management">
# Name configured on the Inband Management VLAN.
# This setting is only applied on the devices where it is set, it does not automatically affect any parent/child devices configuration, so it must be set on each applicable node/node-group/node-type as needed.
inband_mgmt_vlan_name: <str; default="Inband Management">
# VRF configured on the Inband Management Interface.
# The VRF is created if not already created by other means.
# This setting is only applied on the devices where it is set, it does not automatically affect any parent/child devices configuration, so it must be set on each applicable node/node-group/node-type as needed.
inband_mgmt_vrf: <str; default="default">
# MTU configured on the Inband Management Interface.
# This setting is only applied on the devices where it is set, it does not automatically affect any parent/child devices configuration, so it must be set on each applicable node/node-group/node-type as needed.
inband_mgmt_mtu: <int; default=1500>
# Enable to configure upstream device with proper configuration to allow downstream devices to ZTP inband.
# This setting also requires that the `inband_mgmt_vlan` is set for the node.
inband_ztp: <bool; default=False>
# Set the LACP fallback timeout of the upstream device's port-channel towards the downstream inband ZTP node.
# This setting also requires that `inband_ztp` is set for the node.
inband_ztp_lacp_fallback_delay: <int; 0-300; default=30>
# Optional IP subnet assigned to inband management SVIs on L2 switches (switches using port-channels as uplinks).
# Parent l3leafs will have SVI with "ip virtual-router" and host-route injection based on ARP.
# This allows all l3leafs to reuse the same subnet across multiple racks without VXLAN extension.
# SVI IP address will be assigned as follows:
# virtual-router: <subnet> + 1
# l3leaf A : <subnet> + 2 (same IP on all l3leaf A)
# l3leaf B : <subnet> + 3 (same IP on all l3leaf B)
# l2leafs : <subnet> + 3 + <l2leaf id>
# GW on l2leafs : <subnet> + 1
# Assign range larger than total l2leafs + 5
#
# Setting is ignored if 'inband_mgmt_ip' is set.
#
# This setting is applicable to L2 switches (switches using port-channel trunks as uplinks).
# This key is deprecated.
# Support will be removed in AVD version 5.0.0.
# Use <samp>inband_mgmt_subnet</samp> instead.
inband_management_subnet: <str>
# VLAN number used for inband management on L2 switches (switches using port-channel trunks as uplinks).
# When using 'inband_mgmt_subnet' the VLAN and SVIs will be created automatically on this switch as well as all 'uplink_switches'.
# When using 'inband_mgmt_ip' the VLAN and SVI will only be created on this device and added to uplink trunk. The VLAN and SVI on the parent switches must be created using network services data models.
# This key is deprecated.
# Support will be removed in AVD version 5.0.0.
# Use <samp>inband_mgmt_vlan</samp> instead.
inband_management_vlan: <int; default=4092>
# Define variables per node.
nodes:
# The Node Name is used as "hostname".
- name: <str; required; unique>
# Pointer to interface used for inband management.
# All configuration must be done using other data models like network services or structured_config.
# 'inband_mgmt_interface' is only used to refer to this interface as source in various management protocol settings (future feature).
#
# On L2 switches, this defaults to Vlan<inband_mgmt_vlan> if either 'inband_mgmt_subnet' or 'inband_mgmt_ip' is set.
inband_mgmt_interface: <str>
# VLAN number used for inband management on L2 switches (switches using port-channel trunks as uplinks).
# When using 'inband_mgmt_subnet' the VLAN and SVIs will be created automatically on this switch as well as all 'uplink_switches'.
# When using 'inband_mgmt_ip' the VLAN and SVI will only be created on this device and added to uplink trunk. The VLAN and SVI on the parent switches must be created using network services data models.
inband_mgmt_vlan: <int; default=4092>
# Optional IP subnet assigned to inband management SVIs on L2 switches (switches using port-channels as uplinks).
# Parent l3leafs will have SVI with "ip virtual-router" and host-route injection based on ARP.
# This allows all l3leafs to reuse the same subnet across multiple racks without VXLAN extension.
# SVI IP address will be assigned as follows:
# virtual-router: <subnet> + 1
# l3leaf A : <subnet> + 2 (same IP on all l3leaf A)
# l3leaf B : <subnet> + 3 (same IP on all l3leaf B)
# l2leafs : <subnet> + 3 + <l2leaf id>
# GW on l2leafs : <subnet> + 1
# Assign range larger than total l2leafs + 5
#
# Setting is ignored if 'inband_mgmt_ip' is set.
#
# This setting is applicable to L2 switches (switches using port-channel trunks as uplinks).
inband_mgmt_subnet: <str>
# IP address assigned to the inband management interface set with 'inband_mgmt_vlan'.
# This overrides 'inband_mgmt_subnet', hence all behavior of 'inband_mgmt_subnet' is removed.
#
# If this is set the VLAN and SVI will only be created on the L2 switch and added to uplink trunk.
# The VLAN and SVI on the parent switches must be created using network services data models.
#
# This setting is applicable to L2 switches (switches using port-channel trunks as uplinks).
inband_mgmt_ip: <str>
# Default gateway configured in the 'inband_mgmt_vrf' when using 'inband_mgmt_ip'. Otherwise gateway is derived from 'inband_mgmt_subnet' if set.
#
# This setting is applicable to L2 switches (switches using port-channel trunks as uplinks).
inband_mgmt_gateway: <str>
# IPv6 address assigned to the inband management interface set with 'inband_mgmt_vlan'.
# This overrides 'inband_mgmt_ipv6_subnet', hence the configuration of 'inband_mgmt_ipv6_subnet' is ignored.
#
# If this is set the VLAN and SVI will only be created on the L2 switch and added to uplink trunk.
# The VLAN and SVI on the parent switches must be created using network services data models.
#
# This setting is applicable to L2 switches (switches using port-channel trunks as uplinks).
inband_mgmt_ipv6_address: <str>
# Optional IPv6 prefix assigned to inband management SVIs on L2 switches (switches using port-channels as uplinks).
# Parent l3leafs will have SVI with "ipv6 virtual-router" and host-route injection based on ARP.
# This allows all l3leafs to reuse the same subnet across multiple racks without VXLAN extension.
# SVI IP address will be assigned as follows:
# virtual-router: <subnet> + 1
# l3leaf A : <subnet> + 2 (same IP on all l3leaf A)
# l3leaf B : <subnet> + 3 (same IP on all l3leaf B)
# l2leafs : <subnet> + 3 + <l2leaf id>
# GW on l2leafs : <subnet> + 1
# Assign range larger than total l2leafs + 5
#
# Setting is ignored if 'inband_mgmt_ipv6_address' is set.
#
# This setting is applicable to L2 switches (switches using port-channel trunks as uplinks).
inband_mgmt_ipv6_subnet: <str>
# Default gateway configured in the 'inband_mgmt_vrf'.
# Used when `inband_mgmt_ipv6_address` is set.
# Ignored when 'inband_mgmt_ipv6_subnet' is set (first IP in subnet used as gateway).
#
# This setting is applicable to L2 switches (switches using port-channel trunks as uplinks).
inband_mgmt_ipv6_gateway: <str>
# Description configured on the Inband Management SVI.
#
# This setting is only applied on the devices where it is set, it does not automatically affect any parent/child devices configuration, so it must be set on each applicable node/node-group/node-type as needed.
inband_mgmt_description: <str; default="Inband Management">
# Name configured on the Inband Management VLAN.
# This setting is only applied on the devices where it is set, it does not automatically affect any parent/child devices configuration, so it must be set on each applicable node/node-group/node-type as needed.
inband_mgmt_vlan_name: <str; default="Inband Management">
# VRF configured on the Inband Management Interface.
# The VRF is created if not already created by other means.
# This setting is only applied on the devices where it is set, it does not automatically affect any parent/child devices configuration, so it must be set on each applicable node/node-group/node-type as needed.
inband_mgmt_vrf: <str; default="default">
# MTU configured on the Inband Management Interface.
# This setting is only applied on the devices where it is set, it does not automatically affect any parent/child devices configuration, so it must be set on each applicable node/node-group/node-type as needed.
inband_mgmt_mtu: <int; default=1500>
# Enable to configure upstream device with proper configuration to allow downstream devices to ZTP inband.
# This setting also requires that the `inband_mgmt_vlan` is set for the node.
inband_ztp: <bool; default=False>
# Set the LACP fallback timeout of the upstream device's port-channel towards the downstream inband ZTP node.
# This setting also requires that `inband_ztp` is set for the node.
inband_ztp_lacp_fallback_delay: <int; 0-300; default=30>
# Optional IP subnet assigned to inband management SVIs on L2 switches (switches using port-channels as uplinks).
# Parent l3leafs will have SVI with "ip virtual-router" and host-route injection based on ARP.
# This allows all l3leafs to reuse the same subnet across multiple racks without VXLAN extension.
# SVI IP address will be assigned as follows:
# virtual-router: <subnet> + 1
# l3leaf A : <subnet> + 2 (same IP on all l3leaf A)
# l3leaf B : <subnet> + 3 (same IP on all l3leaf B)
# l2leafs : <subnet> + 3 + <l2leaf id>
# GW on l2leafs : <subnet> + 1
# Assign range larger than total l2leafs + 5
#
# Setting is ignored if 'inband_mgmt_ip' is set.
#
# This setting is applicable to L2 switches (switches using port-channel trunks as uplinks).
# This key is deprecated.
# Support will be removed in AVD version 5.0.0.
# Use <samp>inband_mgmt_subnet</samp> instead.
inband_management_subnet: <str>
# VLAN number used for inband management on L2 switches (switches using port-channel trunks as uplinks).
# When using 'inband_mgmt_subnet' the VLAN and SVIs will be created automatically on this switch as well as all 'uplink_switches'.
# When using 'inband_mgmt_ip' the VLAN and SVI will only be created on this device and added to uplink trunk. The VLAN and SVI on the parent switches must be created using network services data models.
# This key is deprecated.
# Support will be removed in AVD version 5.0.0.
# Use <samp>inband_mgmt_vlan</samp> instead.
inband_management_vlan: <int; default=4092>
Node type uplink management¶
Connectivity is defined from the child’s device perspective. Source uplink interfaces and parent interfaces are defined on the child.
Tip
Leverage default_interfaces data model to auto define uplink and downlink interfaces based on the node id.
| Variable | Type | Required | Default | Value Restrictions | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| <node_type_keys.key> | Dictionary | ||||
| defaults | Dictionary | Define variables for all nodes of this type. | |||
| link_tracking | Dictionary | This configures the Link Tracking Group on a switch as well as adds the p2p-uplinks of the switch as the upstream interfaces. Useful in EVPN multhoming designs. |
|||
| enabled | Boolean | False |
|||
| groups | List, items: Dictionary | [{'name': 'LT_GROUP1'}] |
Link Tracking Groups. By default a single group named “LT_GROUP1” is defined with default values. Any groups defined under “groups” will replace the default. |
||
| - name | String | Tracking group name. | |||
| recovery_delay | Integer | Min: 0 Max: 3600 |
default -> platform_settings_mlag_reload_delay -> 300. | ||
| links_minimum | Integer | Min: 1 Max: 100000 |
|||
| uplink_type | String | p2p |
Valid Values: - p2p- port-channel- p2p-vrfs- lan |
Override the default uplink_type set at the node_type_key level.uplink_type must be “p2p” if vtep or underlay_router is true for the node_type_key definition. |
|
| uplink_ipv4_pool | String | Format: ipv4_cidr | IPv4 subnet to use to connect to uplink switches. | ||
| uplink_interfaces | List, items: String | Local uplink interfaces. Each list item supports range syntax that can be expanded into a list of interfaces. If uplink_interfaces is not defined, platform-specific defaults (defined under default_interfaces) will be used instead. Please note that default_interfaces are not defined by default, you should define these yourself. |
|||
| - <str> | String | Pattern: Ethernet[\d/]+ | |||
| uplink_switch_interfaces | List, items: String | Interfaces located on uplink switches. | |||
| - <str> | String | Pattern: Ethernet[\d/]+ | |||
| uplink_switches | List, items: String | ||||
| - <str> | String | Required | Hostname of uplink switch. If parallel uplinks are in use, update max_parallel_uplinks below and specify each uplink switch multiple times. e.g. uplink_switches: [ ‘DC1-SPINE1’, ‘DC1-SPINE1’, ‘DC1-SPINE2’, ‘DC1-SPINE2’ ]. |
||
| uplink_interface_speed | String | Set point-to-Point interface speed and will apply to uplink interfaces on both ends. (Uplink switch interface speed can be overridden with uplink_switch_interface_speed).Speed should be set in the format <interface_speed> or forced <interface_speed> or auto <interface_speed>. |
|||
| uplink_switch_interface_speed | String | Set point-to-Point interface speed for the uplink switch interface only. Speed should be set in the format <interface_speed> or forced <interface_speed> or auto <interface_speed>. |
|||
| max_uplink_switches | Integer | Maximum number of uplink switches. Changing this value may change IP Addressing on uplinks. Can be used to reserve IP space for future expansions. |
|||
| max_parallel_uplinks | Integer | Number of parallel links towards uplink switches. Changing this value may change interface naming on uplinks (and corresponding downlinks). Can be used to reserve interfaces for future parallel uplinks. |
|||
| uplink_bfd | Boolean | False |
Enable bfd on uplink interfaces. | ||
| uplink_native_vlan | Integer | Min: 1 Max: 4094 |
Only applicable to switches with layer-2 port-channel uplinks. A suspended (disabled) vlan will be created in both ends of the link unless the vlan is defined under network services. By default the uplink will not have a native_vlan configured, so EOS defaults to vlan 1. |
||
| uplink_ptp | Dictionary | Enable PTP on all infrastructure links. | |||
| enable | Boolean | False |
|||
| uplink_macsec | Dictionary | Enable MacSec on all uplinks. | |||
| profile | String | ||||
| uplink_port_channel_id | Integer | Min: 1 Max: 999999 |
Only applicable for L2 switches with uplink_type: port-channel.By default the uplink Port-channel ID will be set to the number of the lowest member interface defined under uplink_interfaces.For example: member ports [ Eth22, Eth23 ] -> ID 22 member ports [ Eth11/1, Eth22/1 ] -> ID 111 For MLAG port-channels ID will be based on the lowest member interface on the first MLAG switch. This option overrides the default behavior and statically sets the local Port-channel ID. Note! Make sure the ID is unique and does not overlap with autogenerated Port-channel IDs in the Network Services. Note! For MLAG pairs the ID must be between 1 and 2000 and both MLAG switches must have the same value. |
||
| uplink_switch_port_channel_id | Integer | Min: 1 Max: 999999 |
Only applicable for L2 switches with uplink_type: port-channel.By default the uplink switch Port-channel ID will be set to the number of the first interface defined under uplink_switch_interfaces.For example: member ports [ Eth22, Eth23 ] -> ID 22 member ports [ Eth11/1, Eth22/1 ] -> ID 111 For MLAG port-channels ID will be based on the lowest member interface on the first MLAG switch. This option overrides the default behavior and statically sets the Port-channel ID on the uplink switch. Note! Make sure the ID is unique and does not overlap with autogenerated Port-channel IDs in the Network Services. Note! For MLAG pairs the ID must be between 1 and 2000 and both MLAG switches must have the same value. |
||
| uplink_structured_config | Dictionary | Custom structured config applied to “uplink_interfaces”, and “uplink_switch_interfaces”. When uplink_type == “p2p”, custom structured config added under ethernet_interfaces.[name= When uplink_type == “port-channel”, custom structured config added under port_channel_interfaces.[name= “uplink_structured_config” is applied after “structured_config”, so it can override “structured_config” defined on node-level. Note! The content of this dictionary is not validated by the schema, since it can be either ethernet_interfaces or port_channel_interfaces. |
|||
| short_esi | String | short_esi only valid for l2leaf devices using port-channel uplink. Setting short_esi to “auto” generates the short_esi automatically using a hash of configuration elements. < 0000:0000:0000 |
|||
| node_groups | List, items: Dictionary | Define variables related to all nodes part of this group. | |||
| - group | String | Required, Unique | The Node Group Name is used for MLAG domain unless set with ‘mlag_domain_id’. The Node Group Name is also used for peer description on downstream switches’ uplinks. |
||
| nodes | List, items: Dictionary | Define variables per node. | |||
| - name | String | Required, Unique | The Node Name is used as “hostname”. | ||
| downlink_pools | List, items: Dictionary | IPv4 pools used for links to downlink switches. Set this on the parent switch. Cannot be combined with uplink_ipv4_pool set on the downlink switch. |
|||
| - ipv4_pool | String | Format: ipv4_cidr | IPv4 pool from which subnets will be allocated for links to downlink switches. | ||
| downlink_interfaces | List, items: String | List of downlink interfaces or ranges of interfaces to use this pool. The index of the interface in this list will determine which subnet will be taken from the pool. | |||
| - <str> | String | ||||
| link_tracking | Dictionary | This configures the Link Tracking Group on a switch as well as adds the p2p-uplinks of the switch as the upstream interfaces. Useful in EVPN multhoming designs. |
|||
| enabled | Boolean | False |
|||
| groups | List, items: Dictionary | [{'name': 'LT_GROUP1'}] |
Link Tracking Groups. By default a single group named “LT_GROUP1” is defined with default values. Any groups defined under “groups” will replace the default. |
||
| - name | String | Tracking group name. | |||
| recovery_delay | Integer | Min: 0 Max: 3600 |
default -> platform_settings_mlag_reload_delay -> 300. | ||
| links_minimum | Integer | Min: 1 Max: 100000 |
|||
| uplink_type | String | p2p |
Valid Values: - p2p- port-channel- p2p-vrfs- lan |
Override the default uplink_type set at the node_type_key level.uplink_type must be “p2p” if vtep or underlay_router is true for the node_type_key definition. |
|
| uplink_ipv4_pool | String | Format: ipv4_cidr | IPv4 subnet to use to connect to uplink switches. | ||
| uplink_interfaces | List, items: String | Local uplink interfaces. Each list item supports range syntax that can be expanded into a list of interfaces. If uplink_interfaces is not defined, platform-specific defaults (defined under default_interfaces) will be used instead. Please note that default_interfaces are not defined by default, you should define these yourself. |
|||
| - <str> | String | Pattern: Ethernet[\d/]+ | |||
| uplink_switch_interfaces | List, items: String | Interfaces located on uplink switches. | |||
| - <str> | String | Pattern: Ethernet[\d/]+ | |||
| uplink_switches | List, items: String | ||||
| - <str> | String | Required | Hostname of uplink switch. If parallel uplinks are in use, update max_parallel_uplinks below and specify each uplink switch multiple times. e.g. uplink_switches: [ ‘DC1-SPINE1’, ‘DC1-SPINE1’, ‘DC1-SPINE2’, ‘DC1-SPINE2’ ]. |
||
| uplink_interface_speed | String | Set point-to-Point interface speed and will apply to uplink interfaces on both ends. (Uplink switch interface speed can be overridden with uplink_switch_interface_speed).Speed should be set in the format <interface_speed> or forced <interface_speed> or auto <interface_speed>. |
|||
| uplink_switch_interface_speed | String | Set point-to-Point interface speed for the uplink switch interface only. Speed should be set in the format <interface_speed> or forced <interface_speed> or auto <interface_speed>. |
|||
| max_uplink_switches | Integer | Maximum number of uplink switches. Changing this value may change IP Addressing on uplinks. Can be used to reserve IP space for future expansions. |
|||
| max_parallel_uplinks | Integer | Number of parallel links towards uplink switches. Changing this value may change interface naming on uplinks (and corresponding downlinks). Can be used to reserve interfaces for future parallel uplinks. |
|||
| uplink_bfd | Boolean | False |
Enable bfd on uplink interfaces. | ||
| uplink_native_vlan | Integer | Min: 1 Max: 4094 |
Only applicable to switches with layer-2 port-channel uplinks. A suspended (disabled) vlan will be created in both ends of the link unless the vlan is defined under network services. By default the uplink will not have a native_vlan configured, so EOS defaults to vlan 1. |
||
| uplink_ptp | Dictionary | Enable PTP on all infrastructure links. | |||
| enable | Boolean | False |
|||
| uplink_macsec | Dictionary | Enable MacSec on all uplinks. | |||
| profile | String | ||||
| uplink_port_channel_id | Integer | Min: 1 Max: 999999 |
Only applicable for L2 switches with uplink_type: port-channel.By default the uplink Port-channel ID will be set to the number of the lowest member interface defined under uplink_interfaces.For example: member ports [ Eth22, Eth23 ] -> ID 22 member ports [ Eth11/1, Eth22/1 ] -> ID 111 For MLAG port-channels ID will be based on the lowest member interface on the first MLAG switch. This option overrides the default behavior and statically sets the local Port-channel ID. Note! Make sure the ID is unique and does not overlap with autogenerated Port-channel IDs in the Network Services. Note! For MLAG pairs the ID must be between 1 and 2000 and both MLAG switches must have the same value. |
||
| uplink_switch_port_channel_id | Integer | Min: 1 Max: 999999 |
Only applicable for L2 switches with uplink_type: port-channel.By default the uplink switch Port-channel ID will be set to the number of the first interface defined under uplink_switch_interfaces.For example: member ports [ Eth22, Eth23 ] -> ID 22 member ports [ Eth11/1, Eth22/1 ] -> ID 111 For MLAG port-channels ID will be based on the lowest member interface on the first MLAG switch. This option overrides the default behavior and statically sets the Port-channel ID on the uplink switch. Note! Make sure the ID is unique and does not overlap with autogenerated Port-channel IDs in the Network Services. Note! For MLAG pairs the ID must be between 1 and 2000 and both MLAG switches must have the same value. |
||
| uplink_structured_config | Dictionary | Custom structured config applied to “uplink_interfaces”, and “uplink_switch_interfaces”. When uplink_type == “p2p”, custom structured config added under ethernet_interfaces.[name= When uplink_type == “port-channel”, custom structured config added under port_channel_interfaces.[name= “uplink_structured_config” is applied after “structured_config”, so it can override “structured_config” defined on node-level. Note! The content of this dictionary is not validated by the schema, since it can be either ethernet_interfaces or port_channel_interfaces. |
|||
| short_esi | String | short_esi only valid for l2leaf devices using port-channel uplink. Setting short_esi to “auto” generates the short_esi automatically using a hash of configuration elements. < 0000:0000:0000 |
|||
| link_tracking | Dictionary | This configures the Link Tracking Group on a switch as well as adds the p2p-uplinks of the switch as the upstream interfaces. Useful in EVPN multhoming designs. |
|||
| enabled | Boolean | False |
|||
| groups | List, items: Dictionary | [{'name': 'LT_GROUP1'}] |
Link Tracking Groups. By default a single group named “LT_GROUP1” is defined with default values. Any groups defined under “groups” will replace the default. |
||
| - name | String | Tracking group name. | |||
| recovery_delay | Integer | Min: 0 Max: 3600 |
default -> platform_settings_mlag_reload_delay -> 300. | ||
| links_minimum | Integer | Min: 1 Max: 100000 |
|||
| uplink_type | String | p2p |
Valid Values: - p2p- port-channel- p2p-vrfs- lan |
Override the default uplink_type set at the node_type_key level.uplink_type must be “p2p” if vtep or underlay_router is true for the node_type_key definition. |
|
| uplink_ipv4_pool | String | Format: ipv4_cidr | IPv4 subnet to use to connect to uplink switches. | ||
| uplink_interfaces | List, items: String | Local uplink interfaces. Each list item supports range syntax that can be expanded into a list of interfaces. If uplink_interfaces is not defined, platform-specific defaults (defined under default_interfaces) will be used instead. Please note that default_interfaces are not defined by default, you should define these yourself. |
|||
| - <str> | String | Pattern: Ethernet[\d/]+ | |||
| uplink_switch_interfaces | List, items: String | Interfaces located on uplink switches. | |||
| - <str> | String | Pattern: Ethernet[\d/]+ | |||
| uplink_switches | List, items: String | ||||
| - <str> | String | Required | Hostname of uplink switch. If parallel uplinks are in use, update max_parallel_uplinks below and specify each uplink switch multiple times. e.g. uplink_switches: [ ‘DC1-SPINE1’, ‘DC1-SPINE1’, ‘DC1-SPINE2’, ‘DC1-SPINE2’ ]. |
||
| uplink_interface_speed | String | Set point-to-Point interface speed and will apply to uplink interfaces on both ends. (Uplink switch interface speed can be overridden with uplink_switch_interface_speed).Speed should be set in the format <interface_speed> or forced <interface_speed> or auto <interface_speed>. |
|||
| uplink_switch_interface_speed | String | Set point-to-Point interface speed for the uplink switch interface only. Speed should be set in the format <interface_speed> or forced <interface_speed> or auto <interface_speed>. |
|||
| max_uplink_switches | Integer | Maximum number of uplink switches. Changing this value may change IP Addressing on uplinks. Can be used to reserve IP space for future expansions. |
|||
| max_parallel_uplinks | Integer | Number of parallel links towards uplink switches. Changing this value may change interface naming on uplinks (and corresponding downlinks). Can be used to reserve interfaces for future parallel uplinks. |
|||
| uplink_bfd | Boolean | False |
Enable bfd on uplink interfaces. | ||
| uplink_native_vlan | Integer | Min: 1 Max: 4094 |
Only applicable to switches with layer-2 port-channel uplinks. A suspended (disabled) vlan will be created in both ends of the link unless the vlan is defined under network services. By default the uplink will not have a native_vlan configured, so EOS defaults to vlan 1. |
||
| uplink_ptp | Dictionary | Enable PTP on all infrastructure links. | |||
| enable | Boolean | False |
|||
| uplink_macsec | Dictionary | Enable MacSec on all uplinks. | |||
| profile | String | ||||
| uplink_port_channel_id | Integer | Min: 1 Max: 999999 |
Only applicable for L2 switches with uplink_type: port-channel.By default the uplink Port-channel ID will be set to the number of the lowest member interface defined under uplink_interfaces.For example: member ports [ Eth22, Eth23 ] -> ID 22 member ports [ Eth11/1, Eth22/1 ] -> ID 111 For MLAG port-channels ID will be based on the lowest member interface on the first MLAG switch. This option overrides the default behavior and statically sets the local Port-channel ID. Note! Make sure the ID is unique and does not overlap with autogenerated Port-channel IDs in the Network Services. Note! For MLAG pairs the ID must be between 1 and 2000 and both MLAG switches must have the same value. |
||
| uplink_switch_port_channel_id | Integer | Min: 1 Max: 999999 |
Only applicable for L2 switches with uplink_type: port-channel.By default the uplink switch Port-channel ID will be set to the number of the first interface defined under uplink_switch_interfaces.For example: member ports [ Eth22, Eth23 ] -> ID 22 member ports [ Eth11/1, Eth22/1 ] -> ID 111 For MLAG port-channels ID will be based on the lowest member interface on the first MLAG switch. This option overrides the default behavior and statically sets the Port-channel ID on the uplink switch. Note! Make sure the ID is unique and does not overlap with autogenerated Port-channel IDs in the Network Services. Note! For MLAG pairs the ID must be between 1 and 2000 and both MLAG switches must have the same value. |
||
| uplink_structured_config | Dictionary | Custom structured config applied to “uplink_interfaces”, and “uplink_switch_interfaces”. When uplink_type == “p2p”, custom structured config added under ethernet_interfaces.[name= When uplink_type == “port-channel”, custom structured config added under port_channel_interfaces.[name= “uplink_structured_config” is applied after “structured_config”, so it can override “structured_config” defined on node-level. Note! The content of this dictionary is not validated by the schema, since it can be either ethernet_interfaces or port_channel_interfaces. |
|||
| short_esi | String | short_esi only valid for l2leaf devices using port-channel uplink. Setting short_esi to “auto” generates the short_esi automatically using a hash of configuration elements. < 0000:0000:0000 |
|||
| nodes | List, items: Dictionary | Define variables per node. | |||
| - name | String | Required, Unique | The Node Name is used as “hostname”. | ||
| downlink_pools | List, items: Dictionary | IPv4 pools used for links to downlink switches. Set this on the parent switch. Cannot be combined with uplink_ipv4_pool set on the downlink switch. |
|||
| - ipv4_pool | String | Format: ipv4_cidr | IPv4 pool from which subnets will be allocated for links to downlink switches. | ||
| downlink_interfaces | List, items: String | List of downlink interfaces or ranges of interfaces to use this pool. The index of the interface in this list will determine which subnet will be taken from the pool. | |||
| - <str> | String | ||||
| link_tracking | Dictionary | This configures the Link Tracking Group on a switch as well as adds the p2p-uplinks of the switch as the upstream interfaces. Useful in EVPN multhoming designs. |
|||
| enabled | Boolean | False |
|||
| groups | List, items: Dictionary | [{'name': 'LT_GROUP1'}] |
Link Tracking Groups. By default a single group named “LT_GROUP1” is defined with default values. Any groups defined under “groups” will replace the default. |
||
| - name | String | Tracking group name. | |||
| recovery_delay | Integer | Min: 0 Max: 3600 |
default -> platform_settings_mlag_reload_delay -> 300. | ||
| links_minimum | Integer | Min: 1 Max: 100000 |
|||
| uplink_type | String | p2p |
Valid Values: - p2p- port-channel- p2p-vrfs- lan |
Override the default uplink_type set at the node_type_key level.uplink_type must be “p2p” if vtep or underlay_router is true for the node_type_key definition. |
|
| uplink_ipv4_pool | String | Format: ipv4_cidr | IPv4 subnet to use to connect to uplink switches. | ||
| uplink_interfaces | List, items: String | Local uplink interfaces. Each list item supports range syntax that can be expanded into a list of interfaces. If uplink_interfaces is not defined, platform-specific defaults (defined under default_interfaces) will be used instead. Please note that default_interfaces are not defined by default, you should define these yourself. |
|||
| - <str> | String | Pattern: Ethernet[\d/]+ | |||
| uplink_switch_interfaces | List, items: String | Interfaces located on uplink switches. | |||
| - <str> | String | Pattern: Ethernet[\d/]+ | |||
| uplink_switches | List, items: String | ||||
| - <str> | String | Required | Hostname of uplink switch. If parallel uplinks are in use, update max_parallel_uplinks below and specify each uplink switch multiple times. e.g. uplink_switches: [ ‘DC1-SPINE1’, ‘DC1-SPINE1’, ‘DC1-SPINE2’, ‘DC1-SPINE2’ ]. |
||
| uplink_interface_speed | String | Set point-to-Point interface speed and will apply to uplink interfaces on both ends. (Uplink switch interface speed can be overridden with uplink_switch_interface_speed).Speed should be set in the format <interface_speed> or forced <interface_speed> or auto <interface_speed>. |
|||
| uplink_switch_interface_speed | String | Set point-to-Point interface speed for the uplink switch interface only. Speed should be set in the format <interface_speed> or forced <interface_speed> or auto <interface_speed>. |
|||
| max_uplink_switches | Integer | Maximum number of uplink switches. Changing this value may change IP Addressing on uplinks. Can be used to reserve IP space for future expansions. |
|||
| max_parallel_uplinks | Integer | Number of parallel links towards uplink switches. Changing this value may change interface naming on uplinks (and corresponding downlinks). Can be used to reserve interfaces for future parallel uplinks. |
|||
| uplink_bfd | Boolean | False |
Enable bfd on uplink interfaces. | ||
| uplink_native_vlan | Integer | Min: 1 Max: 4094 |
Only applicable to switches with layer-2 port-channel uplinks. A suspended (disabled) vlan will be created in both ends of the link unless the vlan is defined under network services. By default the uplink will not have a native_vlan configured, so EOS defaults to vlan 1. |
||
| uplink_ptp | Dictionary | Enable PTP on all infrastructure links. | |||
| enable | Boolean | False |
|||
| uplink_macsec | Dictionary | Enable MacSec on all uplinks. | |||
| profile | String | ||||
| uplink_port_channel_id | Integer | Min: 1 Max: 999999 |
Only applicable for L2 switches with uplink_type: port-channel.By default the uplink Port-channel ID will be set to the number of the lowest member interface defined under uplink_interfaces.For example: member ports [ Eth22, Eth23 ] -> ID 22 member ports [ Eth11/1, Eth22/1 ] -> ID 111 For MLAG port-channels ID will be based on the lowest member interface on the first MLAG switch. This option overrides the default behavior and statically sets the local Port-channel ID. Note! Make sure the ID is unique and does not overlap with autogenerated Port-channel IDs in the Network Services. Note! For MLAG pairs the ID must be between 1 and 2000 and both MLAG switches must have the same value. |
||
| uplink_switch_port_channel_id | Integer | Min: 1 Max: 999999 |
Only applicable for L2 switches with uplink_type: port-channel.By default the uplink switch Port-channel ID will be set to the number of the first interface defined under uplink_switch_interfaces.For example: member ports [ Eth22, Eth23 ] -> ID 22 member ports [ Eth11/1, Eth22/1 ] -> ID 111 For MLAG port-channels ID will be based on the lowest member interface on the first MLAG switch. This option overrides the default behavior and statically sets the Port-channel ID on the uplink switch. Note! Make sure the ID is unique and does not overlap with autogenerated Port-channel IDs in the Network Services. Note! For MLAG pairs the ID must be between 1 and 2000 and both MLAG switches must have the same value. |
||
| uplink_structured_config | Dictionary | Custom structured config applied to “uplink_interfaces”, and “uplink_switch_interfaces”. When uplink_type == “p2p”, custom structured config added under ethernet_interfaces.[name= When uplink_type == “port-channel”, custom structured config added under port_channel_interfaces.[name= “uplink_structured_config” is applied after “structured_config”, so it can override “structured_config” defined on node-level. Note! The content of this dictionary is not validated by the schema, since it can be either ethernet_interfaces or port_channel_interfaces. |
|||
| short_esi | String | short_esi only valid for l2leaf devices using port-channel uplink. Setting short_esi to “auto” generates the short_esi automatically using a hash of configuration elements. < 0000:0000:0000 |
<node_type_keys.key>:
# Define variables for all nodes of this type.
defaults:
# This configures the Link Tracking Group on a switch as well as adds the p2p-uplinks of the switch as the upstream interfaces.
# Useful in EVPN multhoming designs.
link_tracking:
enabled: <bool; default=False>
# Link Tracking Groups.
# By default a single group named "LT_GROUP1" is defined with default values.
# Any groups defined under "groups" will replace the default.
groups: # default=[{'name': 'LT_GROUP1'}]
# Tracking group name.
- name: <str>
# default -> platform_settings_mlag_reload_delay -> 300.
recovery_delay: <int; 0-3600>
links_minimum: <int; 1-100000>
# Override the default `uplink_type` set at the `node_type_key` level.
# `uplink_type` must be "p2p" if `vtep` or `underlay_router` is true for the `node_type_key` definition.
uplink_type: <str; "p2p" | "port-channel" | "p2p-vrfs" | "lan"; default="p2p">
# IPv4 subnet to use to connect to uplink switches.
uplink_ipv4_pool: <str>
# Local uplink interfaces.
# Each list item supports range syntax that can be expanded into a list of interfaces.
# If uplink_interfaces is not defined, platform-specific defaults (defined under default_interfaces) will be used instead.
# Please note that default_interfaces are not defined by default, you should define these yourself.
uplink_interfaces:
- <str>
# Interfaces located on uplink switches.
uplink_switch_interfaces:
- <str>
uplink_switches:
# Hostname of uplink switch.
# If parallel uplinks are in use, update max_parallel_uplinks below and specify each uplink switch multiple times.
# e.g. uplink_switches: [ 'DC1-SPINE1', 'DC1-SPINE1', 'DC1-SPINE2', 'DC1-SPINE2' ].
- <str; required>
# Set point-to-Point interface speed and will apply to uplink interfaces on both ends.
# (Uplink switch interface speed can be overridden with `uplink_switch_interface_speed`).
# Speed should be set in the format `<interface_speed>` or `forced <interface_speed>` or `auto <interface_speed>`.
uplink_interface_speed: <str>
# Set point-to-Point interface speed for the uplink switch interface only.
# Speed should be set in the format `<interface_speed>` or `forced <interface_speed>` or `auto <interface_speed>`.
uplink_switch_interface_speed: <str>
# Maximum number of uplink switches.
# Changing this value may change IP Addressing on uplinks.
# Can be used to reserve IP space for future expansions.
max_uplink_switches: <int>
# Number of parallel links towards uplink switches.
# Changing this value may change interface naming on uplinks (and corresponding downlinks).
# Can be used to reserve interfaces for future parallel uplinks.
max_parallel_uplinks: <int>
# Enable bfd on uplink interfaces.
uplink_bfd: <bool; default=False>
# Only applicable to switches with layer-2 port-channel uplinks.
# A suspended (disabled) vlan will be created in both ends of the link unless the vlan is defined under network services.
# By default the uplink will not have a native_vlan configured, so EOS defaults to vlan 1.
uplink_native_vlan: <int; 1-4094>
# Enable PTP on all infrastructure links.
uplink_ptp:
enable: <bool; default=False>
# Enable MacSec on all uplinks.
uplink_macsec:
profile: <str>
# Only applicable for L2 switches with `uplink_type: port-channel`.
# By default the uplink Port-channel ID will be set to the number of the lowest member interface defined under `uplink_interfaces`.
# For example:
# member ports [ Eth22, Eth23 ] -> ID 22
# member ports [ Eth11/1, Eth22/1 ] -> ID 111
# For MLAG port-channels ID will be based on the lowest member interface on the first MLAG switch.
# This option overrides the default behavior and statically sets the local Port-channel ID.
# Note! Make sure the ID is unique and does not overlap with autogenerated Port-channel IDs in the Network Services.
# Note! For MLAG pairs the ID must be between 1 and 2000 and both MLAG switches must have the same value.
uplink_port_channel_id: <int; 1-999999>
# Only applicable for L2 switches with `uplink_type: port-channel`.
# By default the uplink switch Port-channel ID will be set to the number of the first interface defined under `uplink_switch_interfaces`.
# For example:
# member ports [ Eth22, Eth23 ] -> ID 22
# member ports [ Eth11/1, Eth22/1 ] -> ID 111
# For MLAG port-channels ID will be based on the lowest member interface on the first MLAG switch.
# This option overrides the default behavior and statically sets the Port-channel ID on the uplink switch.
# Note! Make sure the ID is unique and does not overlap with autogenerated Port-channel IDs in the Network Services.
# Note! For MLAG pairs the ID must be between 1 and 2000 and both MLAG switches must have the same value.
uplink_switch_port_channel_id: <int; 1-999999>
# Custom structured config applied to "uplink_interfaces", and "uplink_switch_interfaces".
# When uplink_type == "p2p", custom structured config added under ethernet_interfaces.[name=<interface>] for eos_cli_config_gen overrides the settings on the ethernet interface level.
# When uplink_type == "port-channel", custom structured config added under port_channel_interfaces.[name=<interface>] for eos_cli_config_gen overrides the settings on the port-channel interface level.
# "uplink_structured_config" is applied after "structured_config", so it can override "structured_config" defined on node-level.
# Note! The content of this dictionary is _not_ validated by the schema, since it can be either ethernet_interfaces or port_channel_interfaces.
uplink_structured_config: <dict>
# short_esi only valid for l2leaf devices using port-channel uplink.
# Setting short_esi to "auto" generates the short_esi automatically using a hash of configuration elements.
# < 0000:0000:0000 | auto >.
short_esi: <str>
# Define variables related to all nodes part of this group.
node_groups:
# The Node Group Name is used for MLAG domain unless set with 'mlag_domain_id'.
# The Node Group Name is also used for peer description on downstream switches' uplinks.
- group: <str; required; unique>
# Define variables per node.
nodes:
# The Node Name is used as "hostname".
- name: <str; required; unique>
# IPv4 pools used for links to downlink switches. Set this on the parent switch. Cannot be combined with `uplink_ipv4_pool` set on the downlink switch.
downlink_pools:
# IPv4 pool from which subnets will be allocated for links to downlink switches.
- ipv4_pool: <str>
# List of downlink interfaces or ranges of interfaces to use this pool. The index of the interface in this list will determine which subnet will be taken from the pool.
downlink_interfaces:
- <str>
# This configures the Link Tracking Group on a switch as well as adds the p2p-uplinks of the switch as the upstream interfaces.
# Useful in EVPN multhoming designs.
link_tracking:
enabled: <bool; default=False>
# Link Tracking Groups.
# By default a single group named "LT_GROUP1" is defined with default values.
# Any groups defined under "groups" will replace the default.
groups: # default=[{'name': 'LT_GROUP1'}]
# Tracking group name.
- name: <str>
# default -> platform_settings_mlag_reload_delay -> 300.
recovery_delay: <int; 0-3600>
links_minimum: <int; 1-100000>
# Override the default `uplink_type` set at the `node_type_key` level.
# `uplink_type` must be "p2p" if `vtep` or `underlay_router` is true for the `node_type_key` definition.
uplink_type: <str; "p2p" | "port-channel" | "p2p-vrfs" | "lan"; default="p2p">
# IPv4 subnet to use to connect to uplink switches.
uplink_ipv4_pool: <str>
# Local uplink interfaces.
# Each list item supports range syntax that can be expanded into a list of interfaces.
# If uplink_interfaces is not defined, platform-specific defaults (defined under default_interfaces) will be used instead.
# Please note that default_interfaces are not defined by default, you should define these yourself.
uplink_interfaces:
- <str>
# Interfaces located on uplink switches.
uplink_switch_interfaces:
- <str>
uplink_switches:
# Hostname of uplink switch.
# If parallel uplinks are in use, update max_parallel_uplinks below and specify each uplink switch multiple times.
# e.g. uplink_switches: [ 'DC1-SPINE1', 'DC1-SPINE1', 'DC1-SPINE2', 'DC1-SPINE2' ].
- <str; required>
# Set point-to-Point interface speed and will apply to uplink interfaces on both ends.
# (Uplink switch interface speed can be overridden with `uplink_switch_interface_speed`).
# Speed should be set in the format `<interface_speed>` or `forced <interface_speed>` or `auto <interface_speed>`.
uplink_interface_speed: <str>
# Set point-to-Point interface speed for the uplink switch interface only.
# Speed should be set in the format `<interface_speed>` or `forced <interface_speed>` or `auto <interface_speed>`.
uplink_switch_interface_speed: <str>
# Maximum number of uplink switches.
# Changing this value may change IP Addressing on uplinks.
# Can be used to reserve IP space for future expansions.
max_uplink_switches: <int>
# Number of parallel links towards uplink switches.
# Changing this value may change interface naming on uplinks (and corresponding downlinks).
# Can be used to reserve interfaces for future parallel uplinks.
max_parallel_uplinks: <int>
# Enable bfd on uplink interfaces.
uplink_bfd: <bool; default=False>
# Only applicable to switches with layer-2 port-channel uplinks.
# A suspended (disabled) vlan will be created in both ends of the link unless the vlan is defined under network services.
# By default the uplink will not have a native_vlan configured, so EOS defaults to vlan 1.
uplink_native_vlan: <int; 1-4094>
# Enable PTP on all infrastructure links.
uplink_ptp:
enable: <bool; default=False>
# Enable MacSec on all uplinks.
uplink_macsec:
profile: <str>
# Only applicable for L2 switches with `uplink_type: port-channel`.
# By default the uplink Port-channel ID will be set to the number of the lowest member interface defined under `uplink_interfaces`.
# For example:
# member ports [ Eth22, Eth23 ] -> ID 22
# member ports [ Eth11/1, Eth22/1 ] -> ID 111
# For MLAG port-channels ID will be based on the lowest member interface on the first MLAG switch.
# This option overrides the default behavior and statically sets the local Port-channel ID.
# Note! Make sure the ID is unique and does not overlap with autogenerated Port-channel IDs in the Network Services.
# Note! For MLAG pairs the ID must be between 1 and 2000 and both MLAG switches must have the same value.
uplink_port_channel_id: <int; 1-999999>
# Only applicable for L2 switches with `uplink_type: port-channel`.
# By default the uplink switch Port-channel ID will be set to the number of the first interface defined under `uplink_switch_interfaces`.
# For example:
# member ports [ Eth22, Eth23 ] -> ID 22
# member ports [ Eth11/1, Eth22/1 ] -> ID 111
# For MLAG port-channels ID will be based on the lowest member interface on the first MLAG switch.
# This option overrides the default behavior and statically sets the Port-channel ID on the uplink switch.
# Note! Make sure the ID is unique and does not overlap with autogenerated Port-channel IDs in the Network Services.
# Note! For MLAG pairs the ID must be between 1 and 2000 and both MLAG switches must have the same value.
uplink_switch_port_channel_id: <int; 1-999999>
# Custom structured config applied to "uplink_interfaces", and "uplink_switch_interfaces".
# When uplink_type == "p2p", custom structured config added under ethernet_interfaces.[name=<interface>] for eos_cli_config_gen overrides the settings on the ethernet interface level.
# When uplink_type == "port-channel", custom structured config added under port_channel_interfaces.[name=<interface>] for eos_cli_config_gen overrides the settings on the port-channel interface level.
# "uplink_structured_config" is applied after "structured_config", so it can override "structured_config" defined on node-level.
# Note! The content of this dictionary is _not_ validated by the schema, since it can be either ethernet_interfaces or port_channel_interfaces.
uplink_structured_config: <dict>
# short_esi only valid for l2leaf devices using port-channel uplink.
# Setting short_esi to "auto" generates the short_esi automatically using a hash of configuration elements.
# < 0000:0000:0000 | auto >.
short_esi: <str>
# This configures the Link Tracking Group on a switch as well as adds the p2p-uplinks of the switch as the upstream interfaces.
# Useful in EVPN multhoming designs.
link_tracking:
enabled: <bool; default=False>
# Link Tracking Groups.
# By default a single group named "LT_GROUP1" is defined with default values.
# Any groups defined under "groups" will replace the default.
groups: # default=[{'name': 'LT_GROUP1'}]
# Tracking group name.
- name: <str>
# default -> platform_settings_mlag_reload_delay -> 300.
recovery_delay: <int; 0-3600>
links_minimum: <int; 1-100000>
# Override the default `uplink_type` set at the `node_type_key` level.
# `uplink_type` must be "p2p" if `vtep` or `underlay_router` is true for the `node_type_key` definition.
uplink_type: <str; "p2p" | "port-channel" | "p2p-vrfs" | "lan"; default="p2p">
# IPv4 subnet to use to connect to uplink switches.
uplink_ipv4_pool: <str>
# Local uplink interfaces.
# Each list item supports range syntax that can be expanded into a list of interfaces.
# If uplink_interfaces is not defined, platform-specific defaults (defined under default_interfaces) will be used instead.
# Please note that default_interfaces are not defined by default, you should define these yourself.
uplink_interfaces:
- <str>
# Interfaces located on uplink switches.
uplink_switch_interfaces:
- <str>
uplink_switches:
# Hostname of uplink switch.
# If parallel uplinks are in use, update max_parallel_uplinks below and specify each uplink switch multiple times.
# e.g. uplink_switches: [ 'DC1-SPINE1', 'DC1-SPINE1', 'DC1-SPINE2', 'DC1-SPINE2' ].
- <str; required>
# Set point-to-Point interface speed and will apply to uplink interfaces on both ends.
# (Uplink switch interface speed can be overridden with `uplink_switch_interface_speed`).
# Speed should be set in the format `<interface_speed>` or `forced <interface_speed>` or `auto <interface_speed>`.
uplink_interface_speed: <str>
# Set point-to-Point interface speed for the uplink switch interface only.
# Speed should be set in the format `<interface_speed>` or `forced <interface_speed>` or `auto <interface_speed>`.
uplink_switch_interface_speed: <str>
# Maximum number of uplink switches.
# Changing this value may change IP Addressing on uplinks.
# Can be used to reserve IP space for future expansions.
max_uplink_switches: <int>
# Number of parallel links towards uplink switches.
# Changing this value may change interface naming on uplinks (and corresponding downlinks).
# Can be used to reserve interfaces for future parallel uplinks.
max_parallel_uplinks: <int>
# Enable bfd on uplink interfaces.
uplink_bfd: <bool; default=False>
# Only applicable to switches with layer-2 port-channel uplinks.
# A suspended (disabled) vlan will be created in both ends of the link unless the vlan is defined under network services.
# By default the uplink will not have a native_vlan configured, so EOS defaults to vlan 1.
uplink_native_vlan: <int; 1-4094>
# Enable PTP on all infrastructure links.
uplink_ptp:
enable: <bool; default=False>
# Enable MacSec on all uplinks.
uplink_macsec:
profile: <str>
# Only applicable for L2 switches with `uplink_type: port-channel`.
# By default the uplink Port-channel ID will be set to the number of the lowest member interface defined under `uplink_interfaces`.
# For example:
# member ports [ Eth22, Eth23 ] -> ID 22
# member ports [ Eth11/1, Eth22/1 ] -> ID 111
# For MLAG port-channels ID will be based on the lowest member interface on the first MLAG switch.
# This option overrides the default behavior and statically sets the local Port-channel ID.
# Note! Make sure the ID is unique and does not overlap with autogenerated Port-channel IDs in the Network Services.
# Note! For MLAG pairs the ID must be between 1 and 2000 and both MLAG switches must have the same value.
uplink_port_channel_id: <int; 1-999999>
# Only applicable for L2 switches with `uplink_type: port-channel`.
# By default the uplink switch Port-channel ID will be set to the number of the first interface defined under `uplink_switch_interfaces`.
# For example:
# member ports [ Eth22, Eth23 ] -> ID 22
# member ports [ Eth11/1, Eth22/1 ] -> ID 111
# For MLAG port-channels ID will be based on the lowest member interface on the first MLAG switch.
# This option overrides the default behavior and statically sets the Port-channel ID on the uplink switch.
# Note! Make sure the ID is unique and does not overlap with autogenerated Port-channel IDs in the Network Services.
# Note! For MLAG pairs the ID must be between 1 and 2000 and both MLAG switches must have the same value.
uplink_switch_port_channel_id: <int; 1-999999>
# Custom structured config applied to "uplink_interfaces", and "uplink_switch_interfaces".
# When uplink_type == "p2p", custom structured config added under ethernet_interfaces.[name=<interface>] for eos_cli_config_gen overrides the settings on the ethernet interface level.
# When uplink_type == "port-channel", custom structured config added under port_channel_interfaces.[name=<interface>] for eos_cli_config_gen overrides the settings on the port-channel interface level.
# "uplink_structured_config" is applied after "structured_config", so it can override "structured_config" defined on node-level.
# Note! The content of this dictionary is _not_ validated by the schema, since it can be either ethernet_interfaces or port_channel_interfaces.
uplink_structured_config: <dict>
# short_esi only valid for l2leaf devices using port-channel uplink.
# Setting short_esi to "auto" generates the short_esi automatically using a hash of configuration elements.
# < 0000:0000:0000 | auto >.
short_esi: <str>
# Define variables per node.
nodes:
# The Node Name is used as "hostname".
- name: <str; required; unique>
# IPv4 pools used for links to downlink switches. Set this on the parent switch. Cannot be combined with `uplink_ipv4_pool` set on the downlink switch.
downlink_pools:
# IPv4 pool from which subnets will be allocated for links to downlink switches.
- ipv4_pool: <str>
# List of downlink interfaces or ranges of interfaces to use this pool. The index of the interface in this list will determine which subnet will be taken from the pool.
downlink_interfaces:
- <str>
# This configures the Link Tracking Group on a switch as well as adds the p2p-uplinks of the switch as the upstream interfaces.
# Useful in EVPN multhoming designs.
link_tracking:
enabled: <bool; default=False>
# Link Tracking Groups.
# By default a single group named "LT_GROUP1" is defined with default values.
# Any groups defined under "groups" will replace the default.
groups: # default=[{'name': 'LT_GROUP1'}]
# Tracking group name.
- name: <str>
# default -> platform_settings_mlag_reload_delay -> 300.
recovery_delay: <int; 0-3600>
links_minimum: <int; 1-100000>
# Override the default `uplink_type` set at the `node_type_key` level.
# `uplink_type` must be "p2p" if `vtep` or `underlay_router` is true for the `node_type_key` definition.
uplink_type: <str; "p2p" | "port-channel" | "p2p-vrfs" | "lan"; default="p2p">
# IPv4 subnet to use to connect to uplink switches.
uplink_ipv4_pool: <str>
# Local uplink interfaces.
# Each list item supports range syntax that can be expanded into a list of interfaces.
# If uplink_interfaces is not defined, platform-specific defaults (defined under default_interfaces) will be used instead.
# Please note that default_interfaces are not defined by default, you should define these yourself.
uplink_interfaces:
- <str>
# Interfaces located on uplink switches.
uplink_switch_interfaces:
- <str>
uplink_switches:
# Hostname of uplink switch.
# If parallel uplinks are in use, update max_parallel_uplinks below and specify each uplink switch multiple times.
# e.g. uplink_switches: [ 'DC1-SPINE1', 'DC1-SPINE1', 'DC1-SPINE2', 'DC1-SPINE2' ].
- <str; required>
# Set point-to-Point interface speed and will apply to uplink interfaces on both ends.
# (Uplink switch interface speed can be overridden with `uplink_switch_interface_speed`).
# Speed should be set in the format `<interface_speed>` or `forced <interface_speed>` or `auto <interface_speed>`.
uplink_interface_speed: <str>
# Set point-to-Point interface speed for the uplink switch interface only.
# Speed should be set in the format `<interface_speed>` or `forced <interface_speed>` or `auto <interface_speed>`.
uplink_switch_interface_speed: <str>
# Maximum number of uplink switches.
# Changing this value may change IP Addressing on uplinks.
# Can be used to reserve IP space for future expansions.
max_uplink_switches: <int>
# Number of parallel links towards uplink switches.
# Changing this value may change interface naming on uplinks (and corresponding downlinks).
# Can be used to reserve interfaces for future parallel uplinks.
max_parallel_uplinks: <int>
# Enable bfd on uplink interfaces.
uplink_bfd: <bool; default=False>
# Only applicable to switches with layer-2 port-channel uplinks.
# A suspended (disabled) vlan will be created in both ends of the link unless the vlan is defined under network services.
# By default the uplink will not have a native_vlan configured, so EOS defaults to vlan 1.
uplink_native_vlan: <int; 1-4094>
# Enable PTP on all infrastructure links.
uplink_ptp:
enable: <bool; default=False>
# Enable MacSec on all uplinks.
uplink_macsec:
profile: <str>
# Only applicable for L2 switches with `uplink_type: port-channel`.
# By default the uplink Port-channel ID will be set to the number of the lowest member interface defined under `uplink_interfaces`.
# For example:
# member ports [ Eth22, Eth23 ] -> ID 22
# member ports [ Eth11/1, Eth22/1 ] -> ID 111
# For MLAG port-channels ID will be based on the lowest member interface on the first MLAG switch.
# This option overrides the default behavior and statically sets the local Port-channel ID.
# Note! Make sure the ID is unique and does not overlap with autogenerated Port-channel IDs in the Network Services.
# Note! For MLAG pairs the ID must be between 1 and 2000 and both MLAG switches must have the same value.
uplink_port_channel_id: <int; 1-999999>
# Only applicable for L2 switches with `uplink_type: port-channel`.
# By default the uplink switch Port-channel ID will be set to the number of the first interface defined under `uplink_switch_interfaces`.
# For example:
# member ports [ Eth22, Eth23 ] -> ID 22
# member ports [ Eth11/1, Eth22/1 ] -> ID 111
# For MLAG port-channels ID will be based on the lowest member interface on the first MLAG switch.
# This option overrides the default behavior and statically sets the Port-channel ID on the uplink switch.
# Note! Make sure the ID is unique and does not overlap with autogenerated Port-channel IDs in the Network Services.
# Note! For MLAG pairs the ID must be between 1 and 2000 and both MLAG switches must have the same value.
uplink_switch_port_channel_id: <int; 1-999999>
# Custom structured config applied to "uplink_interfaces", and "uplink_switch_interfaces".
# When uplink_type == "p2p", custom structured config added under ethernet_interfaces.[name=<interface>] for eos_cli_config_gen overrides the settings on the ethernet interface level.
# When uplink_type == "port-channel", custom structured config added under port_channel_interfaces.[name=<interface>] for eos_cli_config_gen overrides the settings on the port-channel interface level.
# "uplink_structured_config" is applied after "structured_config", so it can override "structured_config" defined on node-level.
# Note! The content of this dictionary is _not_ validated by the schema, since it can be either ethernet_interfaces or port_channel_interfaces.
uplink_structured_config: <dict>
# short_esi only valid for l2leaf devices using port-channel uplink.
# Setting short_esi to "auto" generates the short_esi automatically using a hash of configuration elements.
# < 0000:0000:0000 | auto >.
short_esi: <str>
Node type L2 and MLAG configuration¶
Tip
Alternate addressing schemes are available at fabric_ip_addressing.
| Variable | Type | Required | Default | Value Restrictions | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| <node_type_keys.key> | Dictionary | ||||
| defaults | Dictionary | Define variables for all nodes of this type. | |||
| mlag_port_channel_structured_config | Dictionary | Custom structured config applied to MLAG peer link port-channel id. Added under port_channel_interfaces.[name= Overrides the settings on the port-channel interface level. “mlag_port_channel_structured_config” is applied after “structured_config”, so it can override “structured_config” defined on node-level. |
|||
| mlag_peer_vlan_structured_config | Dictionary | Custom structured config applied to MLAG Peer Link (control link) SVI interface id. Added under vlan_interfaces.[name= Overrides the settings on the vlan interface level. “mlag_peer_vlan_structured_config” is applied after “structured_config”, so it can override “structured_config” defined on node-level. |
|||
| mlag_peer_l3_vlan_structured_config | Dictionary | Custom structured config applied to MLAG underlay L3 peering SVI interface id. Added under vlan_interfaces.[name= Overrides the settings on the vlan interface level. “mlag_peer_l3_vlan_structured_config” is applied after “structured_config”, so it can override “structured_config” defined on node-level. |
|||
| mlag | Boolean | True |
Enable / Disable auto MLAG, when two nodes are defined in node group. | ||
| mlag_dual_primary_detection | Boolean | False |
Enable / Disable MLAG dual primary detection. | ||
| mlag_ibgp_origin_incomplete | Boolean | True |
Set origin of routes received from MLAG iBGP peer to incomplete. The purpose is to optimize routing for leaf loopbacks from spine perspective and avoid suboptimal routing via peerlink for control plane traffic. |
||
| mlag_interfaces | List, items: String | Each list item supports range syntax that can be expanded into a list of interfaces. Required when MLAG leafs are present in the topology. |
|||
| - <str> | String | ||||
| mlag_interfaces_speed | String | Set MLAG interface speed. Speed should be set in the format <interface_speed> or forced <interface_speed> or auto <interface_speed>. |
|||
| mlag_peer_l3_vlan | Integer | 4093 |
Min: 0 Max: 4094 |
Underlay L3 peering SVI interface id. If set to 0 or the same vlan as mlag_peer_vlan, the mlag_peer_vlan will be used for L3 peering. |
|
| mlag_peer_l3_ipv4_pool | String | Format: ipv4_cidr | IP address pool used for MLAG underlay L3 peering. IP is derived from the node id. Required when MLAG leafs present in topology and they are using a separate L3 peering VLAN. |
||
| mlag_peer_vlan | Integer | 4094 |
Min: 1 Max: 4094 |
MLAG Peer Link (control link) SVI interface id. | |
| mlag_peer_link_allowed_vlans | String | ||||
| mlag_peer_ipv4_pool | String | Format: ipv4_cidr | IP address pool used for MLAG Peer Link (control link). IP is derived from the node id. Required when MLAG leafs present in topology. |
||
| mlag_port_channel_id | Integer | If not set, the mlag port-channel id is generated based on the digits of the first interface present in ‘mlag_interfaces’. Valid port-channel id numbers are < 1-2000 > for EOS < 4.25.0F and < 1 - 999999 > for EOS >= 4.25.0F. |
|||
| mlag_domain_id | String | MLAG Domain ID. If not set the node group name (Set with “group” key) will be used. | |||
| spanning_tree_mode | String | Valid Values: - mstp- rstp- rapid-pvst- none |
|||
| spanning_tree_priority | Integer | 32768 |
Spanning-tree priority configured for the selected mode. For rapid-pvst the priority can also be set per VLAN under network services. |
||
| spanning_tree_root_super | Boolean | False |
|||
| virtual_router_mac_address | String | Format: mac | Virtual router mac address for anycast gateway. | ||
| node_groups | List, items: Dictionary | Define variables related to all nodes part of this group. | |||
| - group | String | Required, Unique | The Node Group Name is used for MLAG domain unless set with ‘mlag_domain_id’. The Node Group Name is also used for peer description on downstream switches’ uplinks. |
||
| nodes | List, items: Dictionary | Define variables per node. | |||
| - name | String | Required, Unique | The Node Name is used as “hostname”. | ||
| mlag_port_channel_structured_config | Dictionary | Custom structured config applied to MLAG peer link port-channel id. Added under port_channel_interfaces.[name= Overrides the settings on the port-channel interface level. “mlag_port_channel_structured_config” is applied after “structured_config”, so it can override “structured_config” defined on node-level. |
|||
| mlag_peer_vlan_structured_config | Dictionary | Custom structured config applied to MLAG Peer Link (control link) SVI interface id. Added under vlan_interfaces.[name= Overrides the settings on the vlan interface level. “mlag_peer_vlan_structured_config” is applied after “structured_config”, so it can override “structured_config” defined on node-level. |
|||
| mlag_peer_l3_vlan_structured_config | Dictionary | Custom structured config applied to MLAG underlay L3 peering SVI interface id. Added under vlan_interfaces.[name= Overrides the settings on the vlan interface level. “mlag_peer_l3_vlan_structured_config” is applied after “structured_config”, so it can override “structured_config” defined on node-level. |
|||
| mlag | Boolean | True |
Enable / Disable auto MLAG, when two nodes are defined in node group. | ||
| mlag_dual_primary_detection | Boolean | False |
Enable / Disable MLAG dual primary detection. | ||
| mlag_ibgp_origin_incomplete | Boolean | True |
Set origin of routes received from MLAG iBGP peer to incomplete. The purpose is to optimize routing for leaf loopbacks from spine perspective and avoid suboptimal routing via peerlink for control plane traffic. |
||
| mlag_interfaces | List, items: String | Each list item supports range syntax that can be expanded into a list of interfaces. Required when MLAG leafs are present in the topology. |
|||
| - <str> | String | ||||
| mlag_interfaces_speed | String | Set MLAG interface speed. Speed should be set in the format <interface_speed> or forced <interface_speed> or auto <interface_speed>. |
|||
| mlag_peer_l3_vlan | Integer | 4093 |
Min: 0 Max: 4094 |
Underlay L3 peering SVI interface id. If set to 0 or the same vlan as mlag_peer_vlan, the mlag_peer_vlan will be used for L3 peering. |
|
| mlag_peer_l3_ipv4_pool | String | Format: ipv4_cidr | IP address pool used for MLAG underlay L3 peering. IP is derived from the node id. Required when MLAG leafs present in topology and they are using a separate L3 peering VLAN. |
||
| mlag_peer_vlan | Integer | 4094 |
Min: 1 Max: 4094 |
MLAG Peer Link (control link) SVI interface id. | |
| mlag_peer_link_allowed_vlans | String | ||||
| mlag_peer_ipv4_pool | String | Format: ipv4_cidr | IP address pool used for MLAG Peer Link (control link). IP is derived from the node id. Required when MLAG leafs present in topology. |
||
| mlag_port_channel_id | Integer | If not set, the mlag port-channel id is generated based on the digits of the first interface present in ‘mlag_interfaces’. Valid port-channel id numbers are < 1-2000 > for EOS < 4.25.0F and < 1 - 999999 > for EOS >= 4.25.0F. |
|||
| mlag_domain_id | String | MLAG Domain ID. If not set the node group name (Set with “group” key) will be used. | |||
| spanning_tree_mode | String | Valid Values: - mstp- rstp- rapid-pvst- none |
|||
| spanning_tree_priority | Integer | 32768 |
Spanning-tree priority configured for the selected mode. For rapid-pvst the priority can also be set per VLAN under network services. |
||
| spanning_tree_root_super | Boolean | False |
|||
| virtual_router_mac_address | String | Format: mac | Virtual router mac address for anycast gateway. | ||
| mlag_port_channel_structured_config | Dictionary | Custom structured config applied to MLAG peer link port-channel id. Added under port_channel_interfaces.[name= Overrides the settings on the port-channel interface level. “mlag_port_channel_structured_config” is applied after “structured_config”, so it can override “structured_config” defined on node-level. |
|||
| mlag_peer_vlan_structured_config | Dictionary | Custom structured config applied to MLAG Peer Link (control link) SVI interface id. Added under vlan_interfaces.[name= Overrides the settings on the vlan interface level. “mlag_peer_vlan_structured_config” is applied after “structured_config”, so it can override “structured_config” defined on node-level. |
|||
| mlag_peer_l3_vlan_structured_config | Dictionary | Custom structured config applied to MLAG underlay L3 peering SVI interface id. Added under vlan_interfaces.[name= Overrides the settings on the vlan interface level. “mlag_peer_l3_vlan_structured_config” is applied after “structured_config”, so it can override “structured_config” defined on node-level. |
|||
| mlag | Boolean | True |
Enable / Disable auto MLAG, when two nodes are defined in node group. | ||
| mlag_dual_primary_detection | Boolean | False |
Enable / Disable MLAG dual primary detection. | ||
| mlag_ibgp_origin_incomplete | Boolean | True |
Set origin of routes received from MLAG iBGP peer to incomplete. The purpose is to optimize routing for leaf loopbacks from spine perspective and avoid suboptimal routing via peerlink for control plane traffic. |
||
| mlag_interfaces | List, items: String | Each list item supports range syntax that can be expanded into a list of interfaces. Required when MLAG leafs are present in the topology. |
|||
| - <str> | String | ||||
| mlag_interfaces_speed | String | Set MLAG interface speed. Speed should be set in the format <interface_speed> or forced <interface_speed> or auto <interface_speed>. |
|||
| mlag_peer_l3_vlan | Integer | 4093 |
Min: 0 Max: 4094 |
Underlay L3 peering SVI interface id. If set to 0 or the same vlan as mlag_peer_vlan, the mlag_peer_vlan will be used for L3 peering. |
|
| mlag_peer_l3_ipv4_pool | String | Format: ipv4_cidr | IP address pool used for MLAG underlay L3 peering. IP is derived from the node id. Required when MLAG leafs present in topology and they are using a separate L3 peering VLAN. |
||
| mlag_peer_vlan | Integer | 4094 |
Min: 1 Max: 4094 |
MLAG Peer Link (control link) SVI interface id. | |
| mlag_peer_link_allowed_vlans | String | ||||
| mlag_peer_ipv4_pool | String | Format: ipv4_cidr | IP address pool used for MLAG Peer Link (control link). IP is derived from the node id. Required when MLAG leafs present in topology. |
||
| mlag_port_channel_id | Integer | If not set, the mlag port-channel id is generated based on the digits of the first interface present in ‘mlag_interfaces’. Valid port-channel id numbers are < 1-2000 > for EOS < 4.25.0F and < 1 - 999999 > for EOS >= 4.25.0F. |
|||
| mlag_domain_id | String | MLAG Domain ID. If not set the node group name (Set with “group” key) will be used. | |||
| spanning_tree_mode | String | Valid Values: - mstp- rstp- rapid-pvst- none |
|||
| spanning_tree_priority | Integer | 32768 |
Spanning-tree priority configured for the selected mode. For rapid-pvst the priority can also be set per VLAN under network services. |
||
| spanning_tree_root_super | Boolean | False |
|||
| virtual_router_mac_address | String | Format: mac | Virtual router mac address for anycast gateway. | ||
| nodes | List, items: Dictionary | Define variables per node. | |||
| - name | String | Required, Unique | The Node Name is used as “hostname”. | ||
| mlag_port_channel_structured_config | Dictionary | Custom structured config applied to MLAG peer link port-channel id. Added under port_channel_interfaces.[name= Overrides the settings on the port-channel interface level. “mlag_port_channel_structured_config” is applied after “structured_config”, so it can override “structured_config” defined on node-level. |
|||
| mlag_peer_vlan_structured_config | Dictionary | Custom structured config applied to MLAG Peer Link (control link) SVI interface id. Added under vlan_interfaces.[name= Overrides the settings on the vlan interface level. “mlag_peer_vlan_structured_config” is applied after “structured_config”, so it can override “structured_config” defined on node-level. |
|||
| mlag_peer_l3_vlan_structured_config | Dictionary | Custom structured config applied to MLAG underlay L3 peering SVI interface id. Added under vlan_interfaces.[name= Overrides the settings on the vlan interface level. “mlag_peer_l3_vlan_structured_config” is applied after “structured_config”, so it can override “structured_config” defined on node-level. |
|||
| mlag | Boolean | True |
Enable / Disable auto MLAG, when two nodes are defined in node group. | ||
| mlag_dual_primary_detection | Boolean | False |
Enable / Disable MLAG dual primary detection. | ||
| mlag_ibgp_origin_incomplete | Boolean | True |
Set origin of routes received from MLAG iBGP peer to incomplete. The purpose is to optimize routing for leaf loopbacks from spine perspective and avoid suboptimal routing via peerlink for control plane traffic. |
||
| mlag_interfaces | List, items: String | Each list item supports range syntax that can be expanded into a list of interfaces. Required when MLAG leafs are present in the topology. |
|||
| - <str> | String | ||||
| mlag_interfaces_speed | String | Set MLAG interface speed. Speed should be set in the format <interface_speed> or forced <interface_speed> or auto <interface_speed>. |
|||
| mlag_peer_l3_vlan | Integer | 4093 |
Min: 0 Max: 4094 |
Underlay L3 peering SVI interface id. If set to 0 or the same vlan as mlag_peer_vlan, the mlag_peer_vlan will be used for L3 peering. |
|
| mlag_peer_l3_ipv4_pool | String | Format: ipv4_cidr | IP address pool used for MLAG underlay L3 peering. IP is derived from the node id. Required when MLAG leafs present in topology and they are using a separate L3 peering VLAN. |
||
| mlag_peer_vlan | Integer | 4094 |
Min: 1 Max: 4094 |
MLAG Peer Link (control link) SVI interface id. | |
| mlag_peer_link_allowed_vlans | String | ||||
| mlag_peer_ipv4_pool | String | Format: ipv4_cidr | IP address pool used for MLAG Peer Link (control link). IP is derived from the node id. Required when MLAG leafs present in topology. |
||
| mlag_port_channel_id | Integer | If not set, the mlag port-channel id is generated based on the digits of the first interface present in ‘mlag_interfaces’. Valid port-channel id numbers are < 1-2000 > for EOS < 4.25.0F and < 1 - 999999 > for EOS >= 4.25.0F. |
|||
| mlag_domain_id | String | MLAG Domain ID. If not set the node group name (Set with “group” key) will be used. | |||
| spanning_tree_mode | String | Valid Values: - mstp- rstp- rapid-pvst- none |
|||
| spanning_tree_priority | Integer | 32768 |
Spanning-tree priority configured for the selected mode. For rapid-pvst the priority can also be set per VLAN under network services. |
||
| spanning_tree_root_super | Boolean | False |
|||
| virtual_router_mac_address | String | Format: mac | Virtual router mac address for anycast gateway. |
<node_type_keys.key>:
# Define variables for all nodes of this type.
defaults:
# Custom structured config applied to MLAG peer link port-channel id.
# Added under port_channel_interfaces.[name=<interface>] for eos_cli_config_gen.
# Overrides the settings on the port-channel interface level.
# "mlag_port_channel_structured_config" is applied after "structured_config", so it can override "structured_config" defined on node-level.
mlag_port_channel_structured_config: <dict>
# Custom structured config applied to MLAG Peer Link (control link) SVI interface id.
# Added under vlan_interfaces.[name=<interface>] for eos_cli_config_gen.
# Overrides the settings on the vlan interface level.
# "mlag_peer_vlan_structured_config" is applied after "structured_config", so it can override "structured_config" defined on node-level.
mlag_peer_vlan_structured_config: <dict>
# Custom structured config applied to MLAG underlay L3 peering SVI interface id.
# Added under vlan_interfaces.[name=<interface>] for eos_cli_config_gen.
# Overrides the settings on the vlan interface level.
# "mlag_peer_l3_vlan_structured_config" is applied after "structured_config", so it can override "structured_config" defined on node-level.
mlag_peer_l3_vlan_structured_config: <dict>
# Enable / Disable auto MLAG, when two nodes are defined in node group.
mlag: <bool; default=True>
# Enable / Disable MLAG dual primary detection.
mlag_dual_primary_detection: <bool; default=False>
# Set origin of routes received from MLAG iBGP peer to incomplete.
# The purpose is to optimize routing for leaf loopbacks from spine perspective and
# avoid suboptimal routing via peerlink for control plane traffic.
mlag_ibgp_origin_incomplete: <bool; default=True>
# Each list item supports range syntax that can be expanded into a list of interfaces.
# Required when MLAG leafs are present in the topology.
mlag_interfaces:
- <str>
# Set MLAG interface speed.
# Speed should be set in the format `<interface_speed>` or `forced <interface_speed>` or `auto <interface_speed>`.
mlag_interfaces_speed: <str>
# Underlay L3 peering SVI interface id.
# If set to 0 or the same vlan as mlag_peer_vlan, the mlag_peer_vlan will be used for L3 peering.
mlag_peer_l3_vlan: <int; 0-4094; default=4093>
# IP address pool used for MLAG underlay L3 peering. IP is derived from the node id.
# Required when MLAG leafs present in topology and they are using a separate L3 peering VLAN.
mlag_peer_l3_ipv4_pool: <str>
# MLAG Peer Link (control link) SVI interface id.
mlag_peer_vlan: <int; 1-4094; default=4094>
mlag_peer_link_allowed_vlans: <str>
# IP address pool used for MLAG Peer Link (control link). IP is derived from the node id.
# Required when MLAG leafs present in topology.
mlag_peer_ipv4_pool: <str>
# If not set, the mlag port-channel id is generated based on the digits of the first interface present in 'mlag_interfaces'.
# Valid port-channel id numbers are < 1-2000 > for EOS < 4.25.0F and < 1 - 999999 > for EOS >= 4.25.0F.
mlag_port_channel_id: <int>
# MLAG Domain ID. If not set the node group name (Set with "group" key) will be used.
mlag_domain_id: <str>
spanning_tree_mode: <str; "mstp" | "rstp" | "rapid-pvst" | "none">
# Spanning-tree priority configured for the selected mode.
# For `rapid-pvst` the priority can also be set per VLAN under network services.
spanning_tree_priority: <int; default=32768>
spanning_tree_root_super: <bool; default=False>
# Virtual router mac address for anycast gateway.
virtual_router_mac_address: <str>
# Define variables related to all nodes part of this group.
node_groups:
# The Node Group Name is used for MLAG domain unless set with 'mlag_domain_id'.
# The Node Group Name is also used for peer description on downstream switches' uplinks.
- group: <str; required; unique>
# Define variables per node.
nodes:
# The Node Name is used as "hostname".
- name: <str; required; unique>
# Custom structured config applied to MLAG peer link port-channel id.
# Added under port_channel_interfaces.[name=<interface>] for eos_cli_config_gen.
# Overrides the settings on the port-channel interface level.
# "mlag_port_channel_structured_config" is applied after "structured_config", so it can override "structured_config" defined on node-level.
mlag_port_channel_structured_config: <dict>
# Custom structured config applied to MLAG Peer Link (control link) SVI interface id.
# Added under vlan_interfaces.[name=<interface>] for eos_cli_config_gen.
# Overrides the settings on the vlan interface level.
# "mlag_peer_vlan_structured_config" is applied after "structured_config", so it can override "structured_config" defined on node-level.
mlag_peer_vlan_structured_config: <dict>
# Custom structured config applied to MLAG underlay L3 peering SVI interface id.
# Added under vlan_interfaces.[name=<interface>] for eos_cli_config_gen.
# Overrides the settings on the vlan interface level.
# "mlag_peer_l3_vlan_structured_config" is applied after "structured_config", so it can override "structured_config" defined on node-level.
mlag_peer_l3_vlan_structured_config: <dict>
# Enable / Disable auto MLAG, when two nodes are defined in node group.
mlag: <bool; default=True>
# Enable / Disable MLAG dual primary detection.
mlag_dual_primary_detection: <bool; default=False>
# Set origin of routes received from MLAG iBGP peer to incomplete.
# The purpose is to optimize routing for leaf loopbacks from spine perspective and
# avoid suboptimal routing via peerlink for control plane traffic.
mlag_ibgp_origin_incomplete: <bool; default=True>
# Each list item supports range syntax that can be expanded into a list of interfaces.
# Required when MLAG leafs are present in the topology.
mlag_interfaces:
- <str>
# Set MLAG interface speed.
# Speed should be set in the format `<interface_speed>` or `forced <interface_speed>` or `auto <interface_speed>`.
mlag_interfaces_speed: <str>
# Underlay L3 peering SVI interface id.
# If set to 0 or the same vlan as mlag_peer_vlan, the mlag_peer_vlan will be used for L3 peering.
mlag_peer_l3_vlan: <int; 0-4094; default=4093>
# IP address pool used for MLAG underlay L3 peering. IP is derived from the node id.
# Required when MLAG leafs present in topology and they are using a separate L3 peering VLAN.
mlag_peer_l3_ipv4_pool: <str>
# MLAG Peer Link (control link) SVI interface id.
mlag_peer_vlan: <int; 1-4094; default=4094>
mlag_peer_link_allowed_vlans: <str>
# IP address pool used for MLAG Peer Link (control link). IP is derived from the node id.
# Required when MLAG leafs present in topology.
mlag_peer_ipv4_pool: <str>
# If not set, the mlag port-channel id is generated based on the digits of the first interface present in 'mlag_interfaces'.
# Valid port-channel id numbers are < 1-2000 > for EOS < 4.25.0F and < 1 - 999999 > for EOS >= 4.25.0F.
mlag_port_channel_id: <int>
# MLAG Domain ID. If not set the node group name (Set with "group" key) will be used.
mlag_domain_id: <str>
spanning_tree_mode: <str; "mstp" | "rstp" | "rapid-pvst" | "none">
# Spanning-tree priority configured for the selected mode.
# For `rapid-pvst` the priority can also be set per VLAN under network services.
spanning_tree_priority: <int; default=32768>
spanning_tree_root_super: <bool; default=False>
# Virtual router mac address for anycast gateway.
virtual_router_mac_address: <str>
# Custom structured config applied to MLAG peer link port-channel id.
# Added under port_channel_interfaces.[name=<interface>] for eos_cli_config_gen.
# Overrides the settings on the port-channel interface level.
# "mlag_port_channel_structured_config" is applied after "structured_config", so it can override "structured_config" defined on node-level.
mlag_port_channel_structured_config: <dict>
# Custom structured config applied to MLAG Peer Link (control link) SVI interface id.
# Added under vlan_interfaces.[name=<interface>] for eos_cli_config_gen.
# Overrides the settings on the vlan interface level.
# "mlag_peer_vlan_structured_config" is applied after "structured_config", so it can override "structured_config" defined on node-level.
mlag_peer_vlan_structured_config: <dict>
# Custom structured config applied to MLAG underlay L3 peering SVI interface id.
# Added under vlan_interfaces.[name=<interface>] for eos_cli_config_gen.
# Overrides the settings on the vlan interface level.
# "mlag_peer_l3_vlan_structured_config" is applied after "structured_config", so it can override "structured_config" defined on node-level.
mlag_peer_l3_vlan_structured_config: <dict>
# Enable / Disable auto MLAG, when two nodes are defined in node group.
mlag: <bool; default=True>
# Enable / Disable MLAG dual primary detection.
mlag_dual_primary_detection: <bool; default=False>
# Set origin of routes received from MLAG iBGP peer to incomplete.
# The purpose is to optimize routing for leaf loopbacks from spine perspective and
# avoid suboptimal routing via peerlink for control plane traffic.
mlag_ibgp_origin_incomplete: <bool; default=True>
# Each list item supports range syntax that can be expanded into a list of interfaces.
# Required when MLAG leafs are present in the topology.
mlag_interfaces:
- <str>
# Set MLAG interface speed.
# Speed should be set in the format `<interface_speed>` or `forced <interface_speed>` or `auto <interface_speed>`.
mlag_interfaces_speed: <str>
# Underlay L3 peering SVI interface id.
# If set to 0 or the same vlan as mlag_peer_vlan, the mlag_peer_vlan will be used for L3 peering.
mlag_peer_l3_vlan: <int; 0-4094; default=4093>
# IP address pool used for MLAG underlay L3 peering. IP is derived from the node id.
# Required when MLAG leafs present in topology and they are using a separate L3 peering VLAN.
mlag_peer_l3_ipv4_pool: <str>
# MLAG Peer Link (control link) SVI interface id.
mlag_peer_vlan: <int; 1-4094; default=4094>
mlag_peer_link_allowed_vlans: <str>
# IP address pool used for MLAG Peer Link (control link). IP is derived from the node id.
# Required when MLAG leafs present in topology.
mlag_peer_ipv4_pool: <str>
# If not set, the mlag port-channel id is generated based on the digits of the first interface present in 'mlag_interfaces'.
# Valid port-channel id numbers are < 1-2000 > for EOS < 4.25.0F and < 1 - 999999 > for EOS >= 4.25.0F.
mlag_port_channel_id: <int>
# MLAG Domain ID. If not set the node group name (Set with "group" key) will be used.
mlag_domain_id: <str>
spanning_tree_mode: <str; "mstp" | "rstp" | "rapid-pvst" | "none">
# Spanning-tree priority configured for the selected mode.
# For `rapid-pvst` the priority can also be set per VLAN under network services.
spanning_tree_priority: <int; default=32768>
spanning_tree_root_super: <bool; default=False>
# Virtual router mac address for anycast gateway.
virtual_router_mac_address: <str>
# Define variables per node.
nodes:
# The Node Name is used as "hostname".
- name: <str; required; unique>
# Custom structured config applied to MLAG peer link port-channel id.
# Added under port_channel_interfaces.[name=<interface>] for eos_cli_config_gen.
# Overrides the settings on the port-channel interface level.
# "mlag_port_channel_structured_config" is applied after "structured_config", so it can override "structured_config" defined on node-level.
mlag_port_channel_structured_config: <dict>
# Custom structured config applied to MLAG Peer Link (control link) SVI interface id.
# Added under vlan_interfaces.[name=<interface>] for eos_cli_config_gen.
# Overrides the settings on the vlan interface level.
# "mlag_peer_vlan_structured_config" is applied after "structured_config", so it can override "structured_config" defined on node-level.
mlag_peer_vlan_structured_config: <dict>
# Custom structured config applied to MLAG underlay L3 peering SVI interface id.
# Added under vlan_interfaces.[name=<interface>] for eos_cli_config_gen.
# Overrides the settings on the vlan interface level.
# "mlag_peer_l3_vlan_structured_config" is applied after "structured_config", so it can override "structured_config" defined on node-level.
mlag_peer_l3_vlan_structured_config: <dict>
# Enable / Disable auto MLAG, when two nodes are defined in node group.
mlag: <bool; default=True>
# Enable / Disable MLAG dual primary detection.
mlag_dual_primary_detection: <bool; default=False>
# Set origin of routes received from MLAG iBGP peer to incomplete.
# The purpose is to optimize routing for leaf loopbacks from spine perspective and
# avoid suboptimal routing via peerlink for control plane traffic.
mlag_ibgp_origin_incomplete: <bool; default=True>
# Each list item supports range syntax that can be expanded into a list of interfaces.
# Required when MLAG leafs are present in the topology.
mlag_interfaces:
- <str>
# Set MLAG interface speed.
# Speed should be set in the format `<interface_speed>` or `forced <interface_speed>` or `auto <interface_speed>`.
mlag_interfaces_speed: <str>
# Underlay L3 peering SVI interface id.
# If set to 0 or the same vlan as mlag_peer_vlan, the mlag_peer_vlan will be used for L3 peering.
mlag_peer_l3_vlan: <int; 0-4094; default=4093>
# IP address pool used for MLAG underlay L3 peering. IP is derived from the node id.
# Required when MLAG leafs present in topology and they are using a separate L3 peering VLAN.
mlag_peer_l3_ipv4_pool: <str>
# MLAG Peer Link (control link) SVI interface id.
mlag_peer_vlan: <int; 1-4094; default=4094>
mlag_peer_link_allowed_vlans: <str>
# IP address pool used for MLAG Peer Link (control link). IP is derived from the node id.
# Required when MLAG leafs present in topology.
mlag_peer_ipv4_pool: <str>
# If not set, the mlag port-channel id is generated based on the digits of the first interface present in 'mlag_interfaces'.
# Valid port-channel id numbers are < 1-2000 > for EOS < 4.25.0F and < 1 - 999999 > for EOS >= 4.25.0F.
mlag_port_channel_id: <int>
# MLAG Domain ID. If not set the node group name (Set with "group" key) will be used.
mlag_domain_id: <str>
spanning_tree_mode: <str; "mstp" | "rstp" | "rapid-pvst" | "none">
# Spanning-tree priority configured for the selected mode.
# For `rapid-pvst` the priority can also be set per VLAN under network services.
spanning_tree_priority: <int; default=32768>
spanning_tree_root_super: <bool; default=False>
# Virtual router mac address for anycast gateway.
virtual_router_mac_address: <str>
Node type Loopback and VTEP configuration¶
| Variable | Type | Required | Default | Value Restrictions | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| <node_type_keys.key> | Dictionary | ||||
| defaults | Dictionary | Define variables for all nodes of this type. | |||
| loopback_ipv4_pool | String | Format: ipv4_cidr | IPv4 subnet for Loopback0 allocation. | ||
| vtep_loopback_ipv4_pool | String | Format: ipv4_cidr | IPv4 subnet for VTEP-Loopback allocation. | ||
| loopback_ipv4_offset | Integer | 0 |
Offset all assigned loopback IP addresses. Required when the < loopback_ipv4_pool > is same for 2 different node_types (like spine and l3leaf) to avoid over-lapping IPs. For example, set the minimum offset l3leaf.defaults.loopback_ipv4_offset: < total # spine switches > or vice versa. |
||
| loopback_ipv6_pool | String | Format: ipv6_cidr | IPv6 subnet for Loopback0 allocation. | ||
| loopback_ipv6_offset | Integer | 0 |
Offset all assigned loopback IPv6 addresses. Required when the < loopback_ipv6_pool > is same for 2 different node_types (like spine and l3leaf) to avoid overlapping IPs. For example, set the minimum offset l3leaf.defaults.loopback_ipv6_offset: < total # spine switches > or vice versa. |
||
| vtep | Boolean | Node is configured as a VTEP when applicable based on ‘overlay_routing_protocol’. Overrides VTEP setting inherited from node_type_keys. |
|||
| vtep_loopback | String | Pattern: Loopback[\d/]+ | Set VXLAN source interface. | ||
| node_groups | List, items: Dictionary | Define variables related to all nodes part of this group. | |||
| - group | String | Required, Unique | The Node Group Name is used for MLAG domain unless set with ‘mlag_domain_id’. The Node Group Name is also used for peer description on downstream switches’ uplinks. |
||
| nodes | List, items: Dictionary | Define variables per node. | |||
| - name | String | Required, Unique | The Node Name is used as “hostname”. | ||
| loopback_ipv4_pool | String | Format: ipv4_cidr | IPv4 subnet for Loopback0 allocation. | ||
| vtep_loopback_ipv4_pool | String | Format: ipv4_cidr | IPv4 subnet for VTEP-Loopback allocation. | ||
| loopback_ipv4_offset | Integer | 0 |
Offset all assigned loopback IP addresses. Required when the < loopback_ipv4_pool > is same for 2 different node_types (like spine and l3leaf) to avoid over-lapping IPs. For example, set the minimum offset l3leaf.defaults.loopback_ipv4_offset: < total # spine switches > or vice versa. |
||
| loopback_ipv6_pool | String | Format: ipv6_cidr | IPv6 subnet for Loopback0 allocation. | ||
| loopback_ipv6_offset | Integer | 0 |
Offset all assigned loopback IPv6 addresses. Required when the < loopback_ipv6_pool > is same for 2 different node_types (like spine and l3leaf) to avoid overlapping IPs. For example, set the minimum offset l3leaf.defaults.loopback_ipv6_offset: < total # spine switches > or vice versa. |
||
| vtep | Boolean | Node is configured as a VTEP when applicable based on ‘overlay_routing_protocol’. Overrides VTEP setting inherited from node_type_keys. |
|||
| vtep_loopback | String | Pattern: Loopback[\d/]+ | Set VXLAN source interface. | ||
| loopback_ipv4_pool | String | Format: ipv4_cidr | IPv4 subnet for Loopback0 allocation. | ||
| vtep_loopback_ipv4_pool | String | Format: ipv4_cidr | IPv4 subnet for VTEP-Loopback allocation. | ||
| loopback_ipv4_offset | Integer | 0 |
Offset all assigned loopback IP addresses. Required when the < loopback_ipv4_pool > is same for 2 different node_types (like spine and l3leaf) to avoid over-lapping IPs. For example, set the minimum offset l3leaf.defaults.loopback_ipv4_offset: < total # spine switches > or vice versa. |
||
| loopback_ipv6_pool | String | Format: ipv6_cidr | IPv6 subnet for Loopback0 allocation. | ||
| loopback_ipv6_offset | Integer | 0 |
Offset all assigned loopback IPv6 addresses. Required when the < loopback_ipv6_pool > is same for 2 different node_types (like spine and l3leaf) to avoid overlapping IPs. For example, set the minimum offset l3leaf.defaults.loopback_ipv6_offset: < total # spine switches > or vice versa. |
||
| vtep | Boolean | Node is configured as a VTEP when applicable based on ‘overlay_routing_protocol’. Overrides VTEP setting inherited from node_type_keys. |
|||
| vtep_loopback | String | Pattern: Loopback[\d/]+ | Set VXLAN source interface. | ||
| nodes | List, items: Dictionary | Define variables per node. | |||
| - name | String | Required, Unique | The Node Name is used as “hostname”. | ||
| loopback_ipv4_pool | String | Format: ipv4_cidr | IPv4 subnet for Loopback0 allocation. | ||
| vtep_loopback_ipv4_pool | String | Format: ipv4_cidr | IPv4 subnet for VTEP-Loopback allocation. | ||
| loopback_ipv4_offset | Integer | 0 |
Offset all assigned loopback IP addresses. Required when the < loopback_ipv4_pool > is same for 2 different node_types (like spine and l3leaf) to avoid over-lapping IPs. For example, set the minimum offset l3leaf.defaults.loopback_ipv4_offset: < total # spine switches > or vice versa. |
||
| loopback_ipv6_pool | String | Format: ipv6_cidr | IPv6 subnet for Loopback0 allocation. | ||
| loopback_ipv6_offset | Integer | 0 |
Offset all assigned loopback IPv6 addresses. Required when the < loopback_ipv6_pool > is same for 2 different node_types (like spine and l3leaf) to avoid overlapping IPs. For example, set the minimum offset l3leaf.defaults.loopback_ipv6_offset: < total # spine switches > or vice versa. |
||
| vtep | Boolean | Node is configured as a VTEP when applicable based on ‘overlay_routing_protocol’. Overrides VTEP setting inherited from node_type_keys. |
|||
| vtep_loopback | String | Pattern: Loopback[\d/]+ | Set VXLAN source interface. |
<node_type_keys.key>:
# Define variables for all nodes of this type.
defaults:
# IPv4 subnet for Loopback0 allocation.
loopback_ipv4_pool: <str>
# IPv4 subnet for VTEP-Loopback allocation.
vtep_loopback_ipv4_pool: <str>
# Offset all assigned loopback IP addresses.
# Required when the < loopback_ipv4_pool > is same for 2 different node_types (like spine and l3leaf) to avoid over-lapping IPs.
# For example, set the minimum offset l3leaf.defaults.loopback_ipv4_offset: < total # spine switches > or vice versa.
loopback_ipv4_offset: <int; default=0>
# IPv6 subnet for Loopback0 allocation.
loopback_ipv6_pool: <str>
# Offset all assigned loopback IPv6 addresses.
# Required when the < loopback_ipv6_pool > is same for 2 different node_types (like spine and l3leaf) to avoid overlapping IPs.
# For example, set the minimum offset l3leaf.defaults.loopback_ipv6_offset: < total # spine switches > or vice versa.
loopback_ipv6_offset: <int; default=0>
# Node is configured as a VTEP when applicable based on 'overlay_routing_protocol'.
# Overrides VTEP setting inherited from node_type_keys.
vtep: <bool>
# Set VXLAN source interface.
vtep_loopback: <str>
# Define variables related to all nodes part of this group.
node_groups:
# The Node Group Name is used for MLAG domain unless set with 'mlag_domain_id'.
# The Node Group Name is also used for peer description on downstream switches' uplinks.
- group: <str; required; unique>
# Define variables per node.
nodes:
# The Node Name is used as "hostname".
- name: <str; required; unique>
# IPv4 subnet for Loopback0 allocation.
loopback_ipv4_pool: <str>
# IPv4 subnet for VTEP-Loopback allocation.
vtep_loopback_ipv4_pool: <str>
# Offset all assigned loopback IP addresses.
# Required when the < loopback_ipv4_pool > is same for 2 different node_types (like spine and l3leaf) to avoid over-lapping IPs.
# For example, set the minimum offset l3leaf.defaults.loopback_ipv4_offset: < total # spine switches > or vice versa.
loopback_ipv4_offset: <int; default=0>
# IPv6 subnet for Loopback0 allocation.
loopback_ipv6_pool: <str>
# Offset all assigned loopback IPv6 addresses.
# Required when the < loopback_ipv6_pool > is same for 2 different node_types (like spine and l3leaf) to avoid overlapping IPs.
# For example, set the minimum offset l3leaf.defaults.loopback_ipv6_offset: < total # spine switches > or vice versa.
loopback_ipv6_offset: <int; default=0>
# Node is configured as a VTEP when applicable based on 'overlay_routing_protocol'.
# Overrides VTEP setting inherited from node_type_keys.
vtep: <bool>
# Set VXLAN source interface.
vtep_loopback: <str>
# IPv4 subnet for Loopback0 allocation.
loopback_ipv4_pool: <str>
# IPv4 subnet for VTEP-Loopback allocation.
vtep_loopback_ipv4_pool: <str>
# Offset all assigned loopback IP addresses.
# Required when the < loopback_ipv4_pool > is same for 2 different node_types (like spine and l3leaf) to avoid over-lapping IPs.
# For example, set the minimum offset l3leaf.defaults.loopback_ipv4_offset: < total # spine switches > or vice versa.
loopback_ipv4_offset: <int; default=0>
# IPv6 subnet for Loopback0 allocation.
loopback_ipv6_pool: <str>
# Offset all assigned loopback IPv6 addresses.
# Required when the < loopback_ipv6_pool > is same for 2 different node_types (like spine and l3leaf) to avoid overlapping IPs.
# For example, set the minimum offset l3leaf.defaults.loopback_ipv6_offset: < total # spine switches > or vice versa.
loopback_ipv6_offset: <int; default=0>
# Node is configured as a VTEP when applicable based on 'overlay_routing_protocol'.
# Overrides VTEP setting inherited from node_type_keys.
vtep: <bool>
# Set VXLAN source interface.
vtep_loopback: <str>
# Define variables per node.
nodes:
# The Node Name is used as "hostname".
- name: <str; required; unique>
# IPv4 subnet for Loopback0 allocation.
loopback_ipv4_pool: <str>
# IPv4 subnet for VTEP-Loopback allocation.
vtep_loopback_ipv4_pool: <str>
# Offset all assigned loopback IP addresses.
# Required when the < loopback_ipv4_pool > is same for 2 different node_types (like spine and l3leaf) to avoid over-lapping IPs.
# For example, set the minimum offset l3leaf.defaults.loopback_ipv4_offset: < total # spine switches > or vice versa.
loopback_ipv4_offset: <int; default=0>
# IPv6 subnet for Loopback0 allocation.
loopback_ipv6_pool: <str>
# Offset all assigned loopback IPv6 addresses.
# Required when the < loopback_ipv6_pool > is same for 2 different node_types (like spine and l3leaf) to avoid overlapping IPs.
# For example, set the minimum offset l3leaf.defaults.loopback_ipv6_offset: < total # spine switches > or vice versa.
loopback_ipv6_offset: <int; default=0>
# Node is configured as a VTEP when applicable based on 'overlay_routing_protocol'.
# Overrides VTEP setting inherited from node_type_keys.
vtep: <bool>
# Set VXLAN source interface.
vtep_loopback: <str>
Node type L3 interfaces configuration¶
| Variable | Type | Required | Default | Value Restrictions | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| <node_type_keys.key> | Dictionary | ||||
| defaults | Dictionary | Define variables for all nodes of this type. | |||
| l3_interfaces | List, items: Dictionary | L3 Interfaces to configure on the node. Used to define the node for WAN interfaces when wan_carrier is set. |
|||
| - profile | String | L3 interface profile name. Profile defined under l3_interface_profiles. |
|||
| name | String | Required, Unique | Pattern: Ethernet[\d/]+(.[\d]+)? | Ethernet interface name like ‘Ethernet2’ or subinterface name like ‘Ethernet2.42’. For a subinterface, the parent physical interface is automatically created. |
|
| description | String | Interface description. If not set a default description will be configured with ‘[ |
|||
| ip_address | String | Node IPv4 address/Mask or ‘dhcp’. | |||
| dhcp_ip | String | When the ip_address is dhcp, this optional field allows to indicate the expectedIPv4 address (without mask) to be allocated on the interface if known. This is not rendered in the configuration but can be used for substitution of ‘interface_ip’ in the Access-list set under ipv4_acl_in and ipv4_acl_out. |
|||
| public_ip | String | Node IPv4 address (no mask). This is used to get the public IP (if known) when the device is behind NAT. This is only used for wan_rr routers (AutoVPN RRs and Pathfinders) to determine the Public IPwith the following preference: wan_route_servers.path_groups.interfaces.ip_address-> l3_interfaces.public_ip-> l3_interfaces.ip_addressThe determined Public IP is used by WAN routers when peering with this interface. |
|||
| encapsulation_dot1q_vlan | Integer | Min: 1 Max: 4094 |
For subinterfaces the dot1q vlan is derived from the interface name by default, but can also be specified. | ||
| dhcp_accept_default_route | Boolean | True |
Accept a default route from DHCP if ip_address is set to dhcp. |
||
| enabled | Boolean | True |
Enable or Shutdown the interface. | ||
| speed | String | Speed should be set in the format <interface_speed> or forced <interface_speed> or auto <interface_speed>. |
|||
| peer | String | The peer device name. Used for description and documentation. | |||
| peer_interface | String | The peer device interface. Used for description and documentation. | |||
| peer_ip | String | The peer device IPv4 address (no mask). Used as default route gateway if set_default_route is true and ip is an IP address. |
|||
| ipv4_acl_in | String | Name of the IPv4 access-list to be assigned in the ingress direction. The access-list must be defined under ipv4_acls.Required for all WAN interfaces ( wan_carrier is set) unless the carrier is marked as ‘trusted’ under wan_carriers. |
|||
| ipv4_acl_out | String | Name of the IPv4 Access-list to be assigned in the egress direction. The access-list must be defined under ipv4_acls. |
|||
| static_routes | List, items: Dictionary | Min Length: 1 | Configure IPv4 static routes pointing to peer_ip. |
||
| - prefix | String | Required | IPv4_network/Mask. | ||
| qos_profile | String | QOS service profile. | |||
| wan_carrier | String | The WAN carrier this interface is connected to. This is used to infer the path-groups in which this interface should be configured. Unless the carrier is marked as ‘trusted’ under wan_carriers, ipv4_acl_in is also required on all WAN interfaces. |
|||
| wan_circuit_id | String | The WAN circuit ID for this interface. This is not rendered in the configuration but used for WAN designs. |
|||
| connected_to_pathfinder | Boolean | True |
For a WAN interface (wan_carrier is set), allow to disable the static tunnel towards Pathfinders. |
||
| cv_pathfinder_internet_exit | Dictionary | PREVIEW: This key is in preview mode | |||
| policies | List, items: Dictionary | List of Internet-exit policies using this interface as exit. | |||
| - name | String | Required, Unique | Internet-exit policy name. | ||
| tunnel_interface_numbers | String | Required | Number range to use for Tunnel interfaces to an internet-exit service provider using this local interface. Examples: ‘1-3’ or ‘100,200,300’ |
||
| raw_eos_cli | String | EOS CLI rendered directly on the interface in the final EOS configuration. | |||
| flow_tracking | Dictionary | Configures flow-tracking on the interface. Overrides fabric_flow_tracking.l3_interfaces setting. |
|||
| enabled | Boolean | ||||
| name | String | Flow tracker name as defined in flow_tracking_settings. | |||
| structured_config | Dictionary | Custom structured config for the Ethernet interface. | |||
| node_groups | List, items: Dictionary | Define variables related to all nodes part of this group. | |||
| - group | String | Required, Unique | The Node Group Name is used for MLAG domain unless set with ‘mlag_domain_id’. The Node Group Name is also used for peer description on downstream switches’ uplinks. |
||
| nodes | List, items: Dictionary | Define variables per node. | |||
| - name | String | Required, Unique | The Node Name is used as “hostname”. | ||
| l3_interfaces | List, items: Dictionary | L3 Interfaces to configure on the node. Used to define the node for WAN interfaces when wan_carrier is set. |
|||
| - profile | String | L3 interface profile name. Profile defined under l3_interface_profiles. |
|||
| name | String | Required, Unique | Pattern: Ethernet[\d/]+(.[\d]+)? | Ethernet interface name like ‘Ethernet2’ or subinterface name like ‘Ethernet2.42’. For a subinterface, the parent physical interface is automatically created. |
|
| description | String | Interface description. If not set a default description will be configured with ‘[ |
|||
| ip_address | String | Node IPv4 address/Mask or ‘dhcp’. | |||
| dhcp_ip | String | When the ip_address is dhcp, this optional field allows to indicate the expectedIPv4 address (without mask) to be allocated on the interface if known. This is not rendered in the configuration but can be used for substitution of ‘interface_ip’ in the Access-list set under ipv4_acl_in and ipv4_acl_out. |
|||
| public_ip | String | Node IPv4 address (no mask). This is used to get the public IP (if known) when the device is behind NAT. This is only used for wan_rr routers (AutoVPN RRs and Pathfinders) to determine the Public IPwith the following preference: wan_route_servers.path_groups.interfaces.ip_address-> l3_interfaces.public_ip-> l3_interfaces.ip_addressThe determined Public IP is used by WAN routers when peering with this interface. |
|||
| encapsulation_dot1q_vlan | Integer | Min: 1 Max: 4094 |
For subinterfaces the dot1q vlan is derived from the interface name by default, but can also be specified. | ||
| dhcp_accept_default_route | Boolean | True |
Accept a default route from DHCP if ip_address is set to dhcp. |
||
| enabled | Boolean | True |
Enable or Shutdown the interface. | ||
| speed | String | Speed should be set in the format <interface_speed> or forced <interface_speed> or auto <interface_speed>. |
|||
| peer | String | The peer device name. Used for description and documentation. | |||
| peer_interface | String | The peer device interface. Used for description and documentation. | |||
| peer_ip | String | The peer device IPv4 address (no mask). Used as default route gateway if set_default_route is true and ip is an IP address. |
|||
| ipv4_acl_in | String | Name of the IPv4 access-list to be assigned in the ingress direction. The access-list must be defined under ipv4_acls.Required for all WAN interfaces ( wan_carrier is set) unless the carrier is marked as ‘trusted’ under wan_carriers. |
|||
| ipv4_acl_out | String | Name of the IPv4 Access-list to be assigned in the egress direction. The access-list must be defined under ipv4_acls. |
|||
| static_routes | List, items: Dictionary | Min Length: 1 | Configure IPv4 static routes pointing to peer_ip. |
||
| - prefix | String | Required | IPv4_network/Mask. | ||
| qos_profile | String | QOS service profile. | |||
| wan_carrier | String | The WAN carrier this interface is connected to. This is used to infer the path-groups in which this interface should be configured. Unless the carrier is marked as ‘trusted’ under wan_carriers, ipv4_acl_in is also required on all WAN interfaces. |
|||
| wan_circuit_id | String | The WAN circuit ID for this interface. This is not rendered in the configuration but used for WAN designs. |
|||
| connected_to_pathfinder | Boolean | True |
For a WAN interface (wan_carrier is set), allow to disable the static tunnel towards Pathfinders. |
||
| cv_pathfinder_internet_exit | Dictionary | PREVIEW: This key is in preview mode | |||
| policies | List, items: Dictionary | List of Internet-exit policies using this interface as exit. | |||
| - name | String | Required, Unique | Internet-exit policy name. | ||
| tunnel_interface_numbers | String | Required | Number range to use for Tunnel interfaces to an internet-exit service provider using this local interface. Examples: ‘1-3’ or ‘100,200,300’ |
||
| raw_eos_cli | String | EOS CLI rendered directly on the interface in the final EOS configuration. | |||
| flow_tracking | Dictionary | Configures flow-tracking on the interface. Overrides fabric_flow_tracking.l3_interfaces setting. |
|||
| enabled | Boolean | ||||
| name | String | Flow tracker name as defined in flow_tracking_settings. | |||
| structured_config | Dictionary | Custom structured config for the Ethernet interface. | |||
| l3_interfaces | List, items: Dictionary | L3 Interfaces to configure on the node. Used to define the node for WAN interfaces when wan_carrier is set. |
|||
| - profile | String | L3 interface profile name. Profile defined under l3_interface_profiles. |
|||
| name | String | Required, Unique | Pattern: Ethernet[\d/]+(.[\d]+)? | Ethernet interface name like ‘Ethernet2’ or subinterface name like ‘Ethernet2.42’. For a subinterface, the parent physical interface is automatically created. |
|
| description | String | Interface description. If not set a default description will be configured with ‘[ |
|||
| ip_address | String | Node IPv4 address/Mask or ‘dhcp’. | |||
| dhcp_ip | String | When the ip_address is dhcp, this optional field allows to indicate the expectedIPv4 address (without mask) to be allocated on the interface if known. This is not rendered in the configuration but can be used for substitution of ‘interface_ip’ in the Access-list set under ipv4_acl_in and ipv4_acl_out. |
|||
| public_ip | String | Node IPv4 address (no mask). This is used to get the public IP (if known) when the device is behind NAT. This is only used for wan_rr routers (AutoVPN RRs and Pathfinders) to determine the Public IPwith the following preference: wan_route_servers.path_groups.interfaces.ip_address-> l3_interfaces.public_ip-> l3_interfaces.ip_addressThe determined Public IP is used by WAN routers when peering with this interface. |
|||
| encapsulation_dot1q_vlan | Integer | Min: 1 Max: 4094 |
For subinterfaces the dot1q vlan is derived from the interface name by default, but can also be specified. | ||
| dhcp_accept_default_route | Boolean | True |
Accept a default route from DHCP if ip_address is set to dhcp. |
||
| enabled | Boolean | True |
Enable or Shutdown the interface. | ||
| speed | String | Speed should be set in the format <interface_speed> or forced <interface_speed> or auto <interface_speed>. |
|||
| peer | String | The peer device name. Used for description and documentation. | |||
| peer_interface | String | The peer device interface. Used for description and documentation. | |||
| peer_ip | String | The peer device IPv4 address (no mask). Used as default route gateway if set_default_route is true and ip is an IP address. |
|||
| ipv4_acl_in | String | Name of the IPv4 access-list to be assigned in the ingress direction. The access-list must be defined under ipv4_acls.Required for all WAN interfaces ( wan_carrier is set) unless the carrier is marked as ‘trusted’ under wan_carriers. |
|||
| ipv4_acl_out | String | Name of the IPv4 Access-list to be assigned in the egress direction. The access-list must be defined under ipv4_acls. |
|||
| static_routes | List, items: Dictionary | Min Length: 1 | Configure IPv4 static routes pointing to peer_ip. |
||
| - prefix | String | Required | IPv4_network/Mask. | ||
| qos_profile | String | QOS service profile. | |||
| wan_carrier | String | The WAN carrier this interface is connected to. This is used to infer the path-groups in which this interface should be configured. Unless the carrier is marked as ‘trusted’ under wan_carriers, ipv4_acl_in is also required on all WAN interfaces. |
|||
| wan_circuit_id | String | The WAN circuit ID for this interface. This is not rendered in the configuration but used for WAN designs. |
|||
| connected_to_pathfinder | Boolean | True |
For a WAN interface (wan_carrier is set), allow to disable the static tunnel towards Pathfinders. |
||
| cv_pathfinder_internet_exit | Dictionary | PREVIEW: This key is in preview mode | |||
| policies | List, items: Dictionary | List of Internet-exit policies using this interface as exit. | |||
| - name | String | Required, Unique | Internet-exit policy name. | ||
| tunnel_interface_numbers | String | Required | Number range to use for Tunnel interfaces to an internet-exit service provider using this local interface. Examples: ‘1-3’ or ‘100,200,300’ |
||
| raw_eos_cli | String | EOS CLI rendered directly on the interface in the final EOS configuration. | |||
| flow_tracking | Dictionary | Configures flow-tracking on the interface. Overrides fabric_flow_tracking.l3_interfaces setting. |
|||
| enabled | Boolean | ||||
| name | String | Flow tracker name as defined in flow_tracking_settings. | |||
| structured_config | Dictionary | Custom structured config for the Ethernet interface. | |||
| nodes | List, items: Dictionary | Define variables per node. | |||
| - name | String | Required, Unique | The Node Name is used as “hostname”. | ||
| l3_interfaces | List, items: Dictionary | L3 Interfaces to configure on the node. Used to define the node for WAN interfaces when wan_carrier is set. |
|||
| - profile | String | L3 interface profile name. Profile defined under l3_interface_profiles. |
|||
| name | String | Required, Unique | Pattern: Ethernet[\d/]+(.[\d]+)? | Ethernet interface name like ‘Ethernet2’ or subinterface name like ‘Ethernet2.42’. For a subinterface, the parent physical interface is automatically created. |
|
| description | String | Interface description. If not set a default description will be configured with ‘[ |
|||
| ip_address | String | Node IPv4 address/Mask or ‘dhcp’. | |||
| dhcp_ip | String | When the ip_address is dhcp, this optional field allows to indicate the expectedIPv4 address (without mask) to be allocated on the interface if known. This is not rendered in the configuration but can be used for substitution of ‘interface_ip’ in the Access-list set under ipv4_acl_in and ipv4_acl_out. |
|||
| public_ip | String | Node IPv4 address (no mask). This is used to get the public IP (if known) when the device is behind NAT. This is only used for wan_rr routers (AutoVPN RRs and Pathfinders) to determine the Public IPwith the following preference: wan_route_servers.path_groups.interfaces.ip_address-> l3_interfaces.public_ip-> l3_interfaces.ip_addressThe determined Public IP is used by WAN routers when peering with this interface. |
|||
| encapsulation_dot1q_vlan | Integer | Min: 1 Max: 4094 |
For subinterfaces the dot1q vlan is derived from the interface name by default, but can also be specified. | ||
| dhcp_accept_default_route | Boolean | True |
Accept a default route from DHCP if ip_address is set to dhcp. |
||
| enabled | Boolean | True |
Enable or Shutdown the interface. | ||
| speed | String | Speed should be set in the format <interface_speed> or forced <interface_speed> or auto <interface_speed>. |
|||
| peer | String | The peer device name. Used for description and documentation. | |||
| peer_interface | String | The peer device interface. Used for description and documentation. | |||
| peer_ip | String | The peer device IPv4 address (no mask). Used as default route gateway if set_default_route is true and ip is an IP address. |
|||
| ipv4_acl_in | String | Name of the IPv4 access-list to be assigned in the ingress direction. The access-list must be defined under ipv4_acls.Required for all WAN interfaces ( wan_carrier is set) unless the carrier is marked as ‘trusted’ under wan_carriers. |
|||
| ipv4_acl_out | String | Name of the IPv4 Access-list to be assigned in the egress direction. The access-list must be defined under ipv4_acls. |
|||
| static_routes | List, items: Dictionary | Min Length: 1 | Configure IPv4 static routes pointing to peer_ip. |
||
| - prefix | String | Required | IPv4_network/Mask. | ||
| qos_profile | String | QOS service profile. | |||
| wan_carrier | String | The WAN carrier this interface is connected to. This is used to infer the path-groups in which this interface should be configured. Unless the carrier is marked as ‘trusted’ under wan_carriers, ipv4_acl_in is also required on all WAN interfaces. |
|||
| wan_circuit_id | String | The WAN circuit ID for this interface. This is not rendered in the configuration but used for WAN designs. |
|||
| connected_to_pathfinder | Boolean | True |
For a WAN interface (wan_carrier is set), allow to disable the static tunnel towards Pathfinders. |
||
| cv_pathfinder_internet_exit | Dictionary | PREVIEW: This key is in preview mode | |||
| policies | List, items: Dictionary | List of Internet-exit policies using this interface as exit. | |||
| - name | String | Required, Unique | Internet-exit policy name. | ||
| tunnel_interface_numbers | String | Required | Number range to use for Tunnel interfaces to an internet-exit service provider using this local interface. Examples: ‘1-3’ or ‘100,200,300’ |
||
| raw_eos_cli | String | EOS CLI rendered directly on the interface in the final EOS configuration. | |||
| flow_tracking | Dictionary | Configures flow-tracking on the interface. Overrides fabric_flow_tracking.l3_interfaces setting. |
|||
| enabled | Boolean | ||||
| name | String | Flow tracker name as defined in flow_tracking_settings. | |||
| structured_config | Dictionary | Custom structured config for the Ethernet interface. | |||
| l3_interface_profiles | List, items: Dictionary | Profiles to inherit common settings for l3_interfaces defined under the node type key. These profiles will not work for l3_interfaces defined under vrfs. |
|||
| - profile | String | Required, Unique | L3 interface profile name. Any variable supported under l3_interfaces can be inherited from a profile. |
||
| name | String | Pattern: Ethernet[\d/]+(.[\d]+)? | Ethernet interface name like ‘Ethernet2’ or subinterface name like ‘Ethernet2.42’. For a subinterface, the parent physical interface is automatically created. |
||
| description | String | Interface description. If not set a default description will be configured with ‘[ |
|||
| ip_address | String | Node IPv4 address/Mask or ‘dhcp’. | |||
| dhcp_ip | String | When the ip_address is dhcp, this optional field allows to indicate the expectedIPv4 address (without mask) to be allocated on the interface if known. This is not rendered in the configuration but can be used for substitution of ‘interface_ip’ in the Access-list set under ipv4_acl_in and ipv4_acl_out. |
|||
| public_ip | String | Node IPv4 address (no mask). This is used to get the public IP (if known) when the device is behind NAT. This is only used for wan_rr routers (AutoVPN RRs and Pathfinders) to determine the Public IPwith the following preference: wan_route_servers.path_groups.interfaces.ip_address-> l3_interfaces.public_ip-> l3_interfaces.ip_addressThe determined Public IP is used by WAN routers when peering with this interface. |
|||
| encapsulation_dot1q_vlan | Integer | Min: 1 Max: 4094 |
For subinterfaces the dot1q vlan is derived from the interface name by default, but can also be specified. | ||
| dhcp_accept_default_route | Boolean | True |
Accept a default route from DHCP if ip_address is set to dhcp. |
||
| enabled | Boolean | True |
Enable or Shutdown the interface. | ||
| speed | String | Speed should be set in the format <interface_speed> or forced <interface_speed> or auto <interface_speed>. |
|||
| peer | String | The peer device name. Used for description and documentation. | |||
| peer_interface | String | The peer device interface. Used for description and documentation. | |||
| peer_ip | String | The peer device IPv4 address (no mask). Used as default route gateway if set_default_route is true and ip is an IP address. |
|||
| ipv4_acl_in | String | Name of the IPv4 access-list to be assigned in the ingress direction. The access-list must be defined under ipv4_acls.Required for all WAN interfaces ( wan_carrier is set) unless the carrier is marked as ‘trusted’ under wan_carriers. |
|||
| ipv4_acl_out | String | Name of the IPv4 Access-list to be assigned in the egress direction. The access-list must be defined under ipv4_acls. |
|||
| static_routes | List, items: Dictionary | Min Length: 1 | Configure IPv4 static routes pointing to peer_ip. |
||
| - prefix | String | Required | IPv4_network/Mask. | ||
| qos_profile | String | QOS service profile. | |||
| wan_carrier | String | The WAN carrier this interface is connected to. This is used to infer the path-groups in which this interface should be configured. Unless the carrier is marked as ‘trusted’ under wan_carriers, ipv4_acl_in is also required on all WAN interfaces. |
|||
| wan_circuit_id | String | The WAN circuit ID for this interface. This is not rendered in the configuration but used for WAN designs. |
|||
| connected_to_pathfinder | Boolean | True |
For a WAN interface (wan_carrier is set), allow to disable the static tunnel towards Pathfinders. |
||
| cv_pathfinder_internet_exit | Dictionary | PREVIEW: This key is in preview mode | |||
| policies | List, items: Dictionary | List of Internet-exit policies using this interface as exit. | |||
| - name | String | Required, Unique | Internet-exit policy name. | ||
| tunnel_interface_numbers | String | Required | Number range to use for Tunnel interfaces to an internet-exit service provider using this local interface. Examples: ‘1-3’ or ‘100,200,300’ |
||
| raw_eos_cli | String | EOS CLI rendered directly on the interface in the final EOS configuration. | |||
| flow_tracking | Dictionary | Configures flow-tracking on the interface. Overrides fabric_flow_tracking.l3_interfaces setting. |
|||
| enabled | Boolean | ||||
| name | String | Flow tracker name as defined in flow_tracking_settings. | |||
| structured_config | Dictionary | Custom structured config for the Ethernet interface. |
<node_type_keys.key>:
# Define variables for all nodes of this type.
defaults:
# L3 Interfaces to configure on the node.
# Used to define the node for WAN interfaces when `wan_carrier` is set.
l3_interfaces:
# L3 interface profile name. Profile defined under `l3_interface_profiles`.
- profile: <str>
# Ethernet interface name like 'Ethernet2' or subinterface name like 'Ethernet2.42'.
# For a subinterface, the parent physical interface is automatically created.
name: <str; required; unique>
# Interface description.
# If not set a default description will be configured with '[<peer>[ <peer_interface>]]'.
description: <str>
# Node IPv4 address/Mask or 'dhcp'.
ip_address: <str>
# When the `ip_address` is `dhcp`, this optional field allows to indicate the expected
# IPv4 address (without mask) to be allocated on the interface if known.
# This is not rendered in the configuration but can be used for substitution of 'interface_ip' in the Access-list
# set under `ipv4_acl_in` and `ipv4_acl_out`.
dhcp_ip: <str>
# Node IPv4 address (no mask).
#
# This is used to get the public IP (if known) when the device is behind NAT.
# This is only used for `wan_rr` routers (AutoVPN RRs and Pathfinders) to determine the Public IP
# with the following preference:
# `wan_route_servers.path_groups.interfaces.ip_address`
# -> `l3_interfaces.public_ip`
# -> `l3_interfaces.ip_address`
#
# The determined Public IP is used by WAN routers when peering with this interface.
public_ip: <str>
# For subinterfaces the dot1q vlan is derived from the interface name by default, but can also be specified.
encapsulation_dot1q_vlan: <int; 1-4094>
# Accept a default route from DHCP if `ip_address` is set to `dhcp`.
dhcp_accept_default_route: <bool; default=True>
# Enable or Shutdown the interface.
enabled: <bool; default=True>
# Speed should be set in the format `<interface_speed>` or `forced <interface_speed>` or `auto <interface_speed>`.
speed: <str>
# The peer device name. Used for description and documentation.
peer: <str>
# The peer device interface. Used for description and documentation.
peer_interface: <str>
# The peer device IPv4 address (no mask). Used as default route gateway if `set_default_route` is true and `ip` is an IP address.
peer_ip: <str>
# Name of the IPv4 access-list to be assigned in the ingress direction.
# The access-list must be defined under `ipv4_acls`.
# Required for all WAN interfaces (`wan_carrier` is set) unless the carrier is marked as 'trusted' under `wan_carriers`.
ipv4_acl_in: <str>
# Name of the IPv4 Access-list to be assigned in the egress direction.
# The access-list must be defined under `ipv4_acls`.
ipv4_acl_out: <str>
# Configure IPv4 static routes pointing to `peer_ip`.
static_routes: # >=1 items
# IPv4_network/Mask.
- prefix: <str; required>
# QOS service profile.
qos_profile: <str>
# The WAN carrier this interface is connected to.
# This is used to infer the path-groups in which this interface should be configured.
# Unless the carrier is marked as 'trusted' under `wan_carriers`, `ipv4_acl_in` is also required on all WAN interfaces.
wan_carrier: <str>
# The WAN circuit ID for this interface.
# This is not rendered in the configuration but used for WAN designs.
wan_circuit_id: <str>
# For a WAN interface (`wan_carrier` is set), allow to disable the static tunnel towards Pathfinders.
connected_to_pathfinder: <bool; default=True>
# PREVIEW: This key is in preview mode
cv_pathfinder_internet_exit:
# List of Internet-exit policies using this interface as exit.
policies:
# Internet-exit policy name.
- name: <str; required; unique>
# Number range to use for Tunnel interfaces to an internet-exit service provider using this local interface.
# Examples: '1-3' or '100,200,300'
tunnel_interface_numbers: <str; required>
# EOS CLI rendered directly on the interface in the final EOS configuration.
raw_eos_cli: <str>
# Configures flow-tracking on the interface. Overrides `fabric_flow_tracking.l3_interfaces` setting.
flow_tracking:
enabled: <bool>
# Flow tracker name as defined in flow_tracking_settings.
name: <str>
# Custom structured config for the Ethernet interface.
structured_config: <dict>
# Define variables related to all nodes part of this group.
node_groups:
# The Node Group Name is used for MLAG domain unless set with 'mlag_domain_id'.
# The Node Group Name is also used for peer description on downstream switches' uplinks.
- group: <str; required; unique>
# Define variables per node.
nodes:
# The Node Name is used as "hostname".
- name: <str; required; unique>
# L3 Interfaces to configure on the node.
# Used to define the node for WAN interfaces when `wan_carrier` is set.
l3_interfaces:
# L3 interface profile name. Profile defined under `l3_interface_profiles`.
- profile: <str>
# Ethernet interface name like 'Ethernet2' or subinterface name like 'Ethernet2.42'.
# For a subinterface, the parent physical interface is automatically created.
name: <str; required; unique>
# Interface description.
# If not set a default description will be configured with '[<peer>[ <peer_interface>]]'.
description: <str>
# Node IPv4 address/Mask or 'dhcp'.
ip_address: <str>
# When the `ip_address` is `dhcp`, this optional field allows to indicate the expected
# IPv4 address (without mask) to be allocated on the interface if known.
# This is not rendered in the configuration but can be used for substitution of 'interface_ip' in the Access-list
# set under `ipv4_acl_in` and `ipv4_acl_out`.
dhcp_ip: <str>
# Node IPv4 address (no mask).
#
# This is used to get the public IP (if known) when the device is behind NAT.
# This is only used for `wan_rr` routers (AutoVPN RRs and Pathfinders) to determine the Public IP
# with the following preference:
# `wan_route_servers.path_groups.interfaces.ip_address`
# -> `l3_interfaces.public_ip`
# -> `l3_interfaces.ip_address`
#
# The determined Public IP is used by WAN routers when peering with this interface.
public_ip: <str>
# For subinterfaces the dot1q vlan is derived from the interface name by default, but can also be specified.
encapsulation_dot1q_vlan: <int; 1-4094>
# Accept a default route from DHCP if `ip_address` is set to `dhcp`.
dhcp_accept_default_route: <bool; default=True>
# Enable or Shutdown the interface.
enabled: <bool; default=True>
# Speed should be set in the format `<interface_speed>` or `forced <interface_speed>` or `auto <interface_speed>`.
speed: <str>
# The peer device name. Used for description and documentation.
peer: <str>
# The peer device interface. Used for description and documentation.
peer_interface: <str>
# The peer device IPv4 address (no mask). Used as default route gateway if `set_default_route` is true and `ip` is an IP address.
peer_ip: <str>
# Name of the IPv4 access-list to be assigned in the ingress direction.
# The access-list must be defined under `ipv4_acls`.
# Required for all WAN interfaces (`wan_carrier` is set) unless the carrier is marked as 'trusted' under `wan_carriers`.
ipv4_acl_in: <str>
# Name of the IPv4 Access-list to be assigned in the egress direction.
# The access-list must be defined under `ipv4_acls`.
ipv4_acl_out: <str>
# Configure IPv4 static routes pointing to `peer_ip`.
static_routes: # >=1 items
# IPv4_network/Mask.
- prefix: <str; required>
# QOS service profile.
qos_profile: <str>
# The WAN carrier this interface is connected to.
# This is used to infer the path-groups in which this interface should be configured.
# Unless the carrier is marked as 'trusted' under `wan_carriers`, `ipv4_acl_in` is also required on all WAN interfaces.
wan_carrier: <str>
# The WAN circuit ID for this interface.
# This is not rendered in the configuration but used for WAN designs.
wan_circuit_id: <str>
# For a WAN interface (`wan_carrier` is set), allow to disable the static tunnel towards Pathfinders.
connected_to_pathfinder: <bool; default=True>
# PREVIEW: This key is in preview mode
cv_pathfinder_internet_exit:
# List of Internet-exit policies using this interface as exit.
policies:
# Internet-exit policy name.
- name: <str; required; unique>
# Number range to use for Tunnel interfaces to an internet-exit service provider using this local interface.
# Examples: '1-3' or '100,200,300'
tunnel_interface_numbers: <str; required>
# EOS CLI rendered directly on the interface in the final EOS configuration.
raw_eos_cli: <str>
# Configures flow-tracking on the interface. Overrides `fabric_flow_tracking.l3_interfaces` setting.
flow_tracking:
enabled: <bool>
# Flow tracker name as defined in flow_tracking_settings.
name: <str>
# Custom structured config for the Ethernet interface.
structured_config: <dict>
# L3 Interfaces to configure on the node.
# Used to define the node for WAN interfaces when `wan_carrier` is set.
l3_interfaces:
# L3 interface profile name. Profile defined under `l3_interface_profiles`.
- profile: <str>
# Ethernet interface name like 'Ethernet2' or subinterface name like 'Ethernet2.42'.
# For a subinterface, the parent physical interface is automatically created.
name: <str; required; unique>
# Interface description.
# If not set a default description will be configured with '[<peer>[ <peer_interface>]]'.
description: <str>
# Node IPv4 address/Mask or 'dhcp'.
ip_address: <str>
# When the `ip_address` is `dhcp`, this optional field allows to indicate the expected
# IPv4 address (without mask) to be allocated on the interface if known.
# This is not rendered in the configuration but can be used for substitution of 'interface_ip' in the Access-list
# set under `ipv4_acl_in` and `ipv4_acl_out`.
dhcp_ip: <str>
# Node IPv4 address (no mask).
#
# This is used to get the public IP (if known) when the device is behind NAT.
# This is only used for `wan_rr` routers (AutoVPN RRs and Pathfinders) to determine the Public IP
# with the following preference:
# `wan_route_servers.path_groups.interfaces.ip_address`
# -> `l3_interfaces.public_ip`
# -> `l3_interfaces.ip_address`
#
# The determined Public IP is used by WAN routers when peering with this interface.
public_ip: <str>
# For subinterfaces the dot1q vlan is derived from the interface name by default, but can also be specified.
encapsulation_dot1q_vlan: <int; 1-4094>
# Accept a default route from DHCP if `ip_address` is set to `dhcp`.
dhcp_accept_default_route: <bool; default=True>
# Enable or Shutdown the interface.
enabled: <bool; default=True>
# Speed should be set in the format `<interface_speed>` or `forced <interface_speed>` or `auto <interface_speed>`.
speed: <str>
# The peer device name. Used for description and documentation.
peer: <str>
# The peer device interface. Used for description and documentation.
peer_interface: <str>
# The peer device IPv4 address (no mask). Used as default route gateway if `set_default_route` is true and `ip` is an IP address.
peer_ip: <str>
# Name of the IPv4 access-list to be assigned in the ingress direction.
# The access-list must be defined under `ipv4_acls`.
# Required for all WAN interfaces (`wan_carrier` is set) unless the carrier is marked as 'trusted' under `wan_carriers`.
ipv4_acl_in: <str>
# Name of the IPv4 Access-list to be assigned in the egress direction.
# The access-list must be defined under `ipv4_acls`.
ipv4_acl_out: <str>
# Configure IPv4 static routes pointing to `peer_ip`.
static_routes: # >=1 items
# IPv4_network/Mask.
- prefix: <str; required>
# QOS service profile.
qos_profile: <str>
# The WAN carrier this interface is connected to.
# This is used to infer the path-groups in which this interface should be configured.
# Unless the carrier is marked as 'trusted' under `wan_carriers`, `ipv4_acl_in` is also required on all WAN interfaces.
wan_carrier: <str>
# The WAN circuit ID for this interface.
# This is not rendered in the configuration but used for WAN designs.
wan_circuit_id: <str>
# For a WAN interface (`wan_carrier` is set), allow to disable the static tunnel towards Pathfinders.
connected_to_pathfinder: <bool; default=True>
# PREVIEW: This key is in preview mode
cv_pathfinder_internet_exit:
# List of Internet-exit policies using this interface as exit.
policies:
# Internet-exit policy name.
- name: <str; required; unique>
# Number range to use for Tunnel interfaces to an internet-exit service provider using this local interface.
# Examples: '1-3' or '100,200,300'
tunnel_interface_numbers: <str; required>
# EOS CLI rendered directly on the interface in the final EOS configuration.
raw_eos_cli: <str>
# Configures flow-tracking on the interface. Overrides `fabric_flow_tracking.l3_interfaces` setting.
flow_tracking:
enabled: <bool>
# Flow tracker name as defined in flow_tracking_settings.
name: <str>
# Custom structured config for the Ethernet interface.
structured_config: <dict>
# Define variables per node.
nodes:
# The Node Name is used as "hostname".
- name: <str; required; unique>
# L3 Interfaces to configure on the node.
# Used to define the node for WAN interfaces when `wan_carrier` is set.
l3_interfaces:
# L3 interface profile name. Profile defined under `l3_interface_profiles`.
- profile: <str>
# Ethernet interface name like 'Ethernet2' or subinterface name like 'Ethernet2.42'.
# For a subinterface, the parent physical interface is automatically created.
name: <str; required; unique>
# Interface description.
# If not set a default description will be configured with '[<peer>[ <peer_interface>]]'.
description: <str>
# Node IPv4 address/Mask or 'dhcp'.
ip_address: <str>
# When the `ip_address` is `dhcp`, this optional field allows to indicate the expected
# IPv4 address (without mask) to be allocated on the interface if known.
# This is not rendered in the configuration but can be used for substitution of 'interface_ip' in the Access-list
# set under `ipv4_acl_in` and `ipv4_acl_out`.
dhcp_ip: <str>
# Node IPv4 address (no mask).
#
# This is used to get the public IP (if known) when the device is behind NAT.
# This is only used for `wan_rr` routers (AutoVPN RRs and Pathfinders) to determine the Public IP
# with the following preference:
# `wan_route_servers.path_groups.interfaces.ip_address`
# -> `l3_interfaces.public_ip`
# -> `l3_interfaces.ip_address`
#
# The determined Public IP is used by WAN routers when peering with this interface.
public_ip: <str>
# For subinterfaces the dot1q vlan is derived from the interface name by default, but can also be specified.
encapsulation_dot1q_vlan: <int; 1-4094>
# Accept a default route from DHCP if `ip_address` is set to `dhcp`.
dhcp_accept_default_route: <bool; default=True>
# Enable or Shutdown the interface.
enabled: <bool; default=True>
# Speed should be set in the format `<interface_speed>` or `forced <interface_speed>` or `auto <interface_speed>`.
speed: <str>
# The peer device name. Used for description and documentation.
peer: <str>
# The peer device interface. Used for description and documentation.
peer_interface: <str>
# The peer device IPv4 address (no mask). Used as default route gateway if `set_default_route` is true and `ip` is an IP address.
peer_ip: <str>
# Name of the IPv4 access-list to be assigned in the ingress direction.
# The access-list must be defined under `ipv4_acls`.
# Required for all WAN interfaces (`wan_carrier` is set) unless the carrier is marked as 'trusted' under `wan_carriers`.
ipv4_acl_in: <str>
# Name of the IPv4 Access-list to be assigned in the egress direction.
# The access-list must be defined under `ipv4_acls`.
ipv4_acl_out: <str>
# Configure IPv4 static routes pointing to `peer_ip`.
static_routes: # >=1 items
# IPv4_network/Mask.
- prefix: <str; required>
# QOS service profile.
qos_profile: <str>
# The WAN carrier this interface is connected to.
# This is used to infer the path-groups in which this interface should be configured.
# Unless the carrier is marked as 'trusted' under `wan_carriers`, `ipv4_acl_in` is also required on all WAN interfaces.
wan_carrier: <str>
# The WAN circuit ID for this interface.
# This is not rendered in the configuration but used for WAN designs.
wan_circuit_id: <str>
# For a WAN interface (`wan_carrier` is set), allow to disable the static tunnel towards Pathfinders.
connected_to_pathfinder: <bool; default=True>
# PREVIEW: This key is in preview mode
cv_pathfinder_internet_exit:
# List of Internet-exit policies using this interface as exit.
policies:
# Internet-exit policy name.
- name: <str; required; unique>
# Number range to use for Tunnel interfaces to an internet-exit service provider using this local interface.
# Examples: '1-3' or '100,200,300'
tunnel_interface_numbers: <str; required>
# EOS CLI rendered directly on the interface in the final EOS configuration.
raw_eos_cli: <str>
# Configures flow-tracking on the interface. Overrides `fabric_flow_tracking.l3_interfaces` setting.
flow_tracking:
enabled: <bool>
# Flow tracker name as defined in flow_tracking_settings.
name: <str>
# Custom structured config for the Ethernet interface.
structured_config: <dict>
# Profiles to inherit common settings for l3_interfaces defined under the node type key.
# These profiles will *not* work for `l3_interfaces` defined under `vrfs`.
l3_interface_profiles:
# L3 interface profile name. Any variable supported under `l3_interfaces` can be inherited from a profile.
- profile: <str; required; unique>
# Ethernet interface name like 'Ethernet2' or subinterface name like 'Ethernet2.42'.
# For a subinterface, the parent physical interface is automatically created.
name: <str>
# Interface description.
# If not set a default description will be configured with '[<peer>[ <peer_interface>]]'.
description: <str>
# Node IPv4 address/Mask or 'dhcp'.
ip_address: <str>
# When the `ip_address` is `dhcp`, this optional field allows to indicate the expected
# IPv4 address (without mask) to be allocated on the interface if known.
# This is not rendered in the configuration but can be used for substitution of 'interface_ip' in the Access-list
# set under `ipv4_acl_in` and `ipv4_acl_out`.
dhcp_ip: <str>
# Node IPv4 address (no mask).
#
# This is used to get the public IP (if known) when the device is behind NAT.
# This is only used for `wan_rr` routers (AutoVPN RRs and Pathfinders) to determine the Public IP
# with the following preference:
# `wan_route_servers.path_groups.interfaces.ip_address`
# -> `l3_interfaces.public_ip`
# -> `l3_interfaces.ip_address`
#
# The determined Public IP is used by WAN routers when peering with this interface.
public_ip: <str>
# For subinterfaces the dot1q vlan is derived from the interface name by default, but can also be specified.
encapsulation_dot1q_vlan: <int; 1-4094>
# Accept a default route from DHCP if `ip_address` is set to `dhcp`.
dhcp_accept_default_route: <bool; default=True>
# Enable or Shutdown the interface.
enabled: <bool; default=True>
# Speed should be set in the format `<interface_speed>` or `forced <interface_speed>` or `auto <interface_speed>`.
speed: <str>
# The peer device name. Used for description and documentation.
peer: <str>
# The peer device interface. Used for description and documentation.
peer_interface: <str>
# The peer device IPv4 address (no mask). Used as default route gateway if `set_default_route` is true and `ip` is an IP address.
peer_ip: <str>
# Name of the IPv4 access-list to be assigned in the ingress direction.
# The access-list must be defined under `ipv4_acls`.
# Required for all WAN interfaces (`wan_carrier` is set) unless the carrier is marked as 'trusted' under `wan_carriers`.
ipv4_acl_in: <str>
# Name of the IPv4 Access-list to be assigned in the egress direction.
# The access-list must be defined under `ipv4_acls`.
ipv4_acl_out: <str>
# Configure IPv4 static routes pointing to `peer_ip`.
static_routes: # >=1 items
# IPv4_network/Mask.
- prefix: <str; required>
# QOS service profile.
qos_profile: <str>
# The WAN carrier this interface is connected to.
# This is used to infer the path-groups in which this interface should be configured.
# Unless the carrier is marked as 'trusted' under `wan_carriers`, `ipv4_acl_in` is also required on all WAN interfaces.
wan_carrier: <str>
# The WAN circuit ID for this interface.
# This is not rendered in the configuration but used for WAN designs.
wan_circuit_id: <str>
# For a WAN interface (`wan_carrier` is set), allow to disable the static tunnel towards Pathfinders.
connected_to_pathfinder: <bool; default=True>
# PREVIEW: This key is in preview mode
cv_pathfinder_internet_exit:
# List of Internet-exit policies using this interface as exit.
policies:
# Internet-exit policy name.
- name: <str; required; unique>
# Number range to use for Tunnel interfaces to an internet-exit service provider using this local interface.
# Examples: '1-3' or '100,200,300'
tunnel_interface_numbers: <str; required>
# EOS CLI rendered directly on the interface in the final EOS configuration.
raw_eos_cli: <str>
# Configures flow-tracking on the interface. Overrides `fabric_flow_tracking.l3_interfaces` setting.
flow_tracking:
enabled: <bool>
# Flow tracker name as defined in flow_tracking_settings.
name: <str>
# Custom structured config for the Ethernet interface.
structured_config: <dict>
Node type BGP configuration¶
| Variable | Type | Required | Default | Value Restrictions | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| <node_type_keys.key> | Dictionary | ||||
| defaults | Dictionary | Define variables for all nodes of this type. | |||
| bgp_as | String | BGP AS <1-4294967295> or AS number in asdot notation “<1-65535>.<0-65535>”. For asdot notation in YAML inputs, the value must be put in quotes, to prevent it from being interpreted as a float number. Required with eBGP. |
|||
| bgp_defaults | List, items: String | List of EOS commands to apply to BGP daemon. | |||
| - <str> | String | ||||
| evpn_role | String | Valid Values: - client- server- none |
Acting role in EVPN control plane. Default is set in node_type definition from node_type_keys. |
||
| evpn_route_servers | List, items: String | List of nodes acting as EVPN Route-Servers / Route-Reflectors. | |||
| - <str> | String | ||||
| node_groups | List, items: Dictionary | Define variables related to all nodes part of this group. | |||
| - group | String | Required, Unique | The Node Group Name is used for MLAG domain unless set with ‘mlag_domain_id’. The Node Group Name is also used for peer description on downstream switches’ uplinks. |
||
| nodes | List, items: Dictionary | Define variables per node. | |||
| - name | String | Required, Unique | The Node Name is used as “hostname”. | ||
| bgp_as | String | BGP AS <1-4294967295> or AS number in asdot notation “<1-65535>.<0-65535>”. For asdot notation in YAML inputs, the value must be put in quotes, to prevent it from being interpreted as a float number. Required with eBGP. |
|||
| bgp_defaults | List, items: String | List of EOS commands to apply to BGP daemon. | |||
| - <str> | String | ||||
| evpn_role | String | Valid Values: - client- server- none |
Acting role in EVPN control plane. Default is set in node_type definition from node_type_keys. |
||
| evpn_route_servers | List, items: String | List of nodes acting as EVPN Route-Servers / Route-Reflectors. | |||
| - <str> | String | ||||
| bgp_as | String | BGP AS <1-4294967295> or AS number in asdot notation “<1-65535>.<0-65535>”. For asdot notation in YAML inputs, the value must be put in quotes, to prevent it from being interpreted as a float number. Required with eBGP. |
|||
| bgp_defaults | List, items: String | List of EOS commands to apply to BGP daemon. | |||
| - <str> | String | ||||
| evpn_role | String | Valid Values: - client- server- none |
Acting role in EVPN control plane. Default is set in node_type definition from node_type_keys. |
||
| evpn_route_servers | List, items: String | List of nodes acting as EVPN Route-Servers / Route-Reflectors. | |||
| - <str> | String | ||||
| nodes | List, items: Dictionary | Define variables per node. | |||
| - name | String | Required, Unique | The Node Name is used as “hostname”. | ||
| bgp_as | String | BGP AS <1-4294967295> or AS number in asdot notation “<1-65535>.<0-65535>”. For asdot notation in YAML inputs, the value must be put in quotes, to prevent it from being interpreted as a float number. Required with eBGP. |
|||
| bgp_defaults | List, items: String | List of EOS commands to apply to BGP daemon. | |||
| - <str> | String | ||||
| evpn_role | String | Valid Values: - client- server- none |
Acting role in EVPN control plane. Default is set in node_type definition from node_type_keys. |
||
| evpn_route_servers | List, items: String | List of nodes acting as EVPN Route-Servers / Route-Reflectors. | |||
| - <str> | String |
<node_type_keys.key>:
# Define variables for all nodes of this type.
defaults:
# BGP AS <1-4294967295> or AS number in asdot notation "<1-65535>.<0-65535>".
# For asdot notation in YAML inputs, the value must be put in quotes, to prevent it from being interpreted as a float number.
# Required with eBGP.
bgp_as: <str>
# List of EOS commands to apply to BGP daemon.
bgp_defaults:
- <str>
# Acting role in EVPN control plane.
# Default is set in node_type definition from node_type_keys.
evpn_role: <str; "client" | "server" | "none">
# List of nodes acting as EVPN Route-Servers / Route-Reflectors.
evpn_route_servers:
- <str>
# Define variables related to all nodes part of this group.
node_groups:
# The Node Group Name is used for MLAG domain unless set with 'mlag_domain_id'.
# The Node Group Name is also used for peer description on downstream switches' uplinks.
- group: <str; required; unique>
# Define variables per node.
nodes:
# The Node Name is used as "hostname".
- name: <str; required; unique>
# BGP AS <1-4294967295> or AS number in asdot notation "<1-65535>.<0-65535>".
# For asdot notation in YAML inputs, the value must be put in quotes, to prevent it from being interpreted as a float number.
# Required with eBGP.
bgp_as: <str>
# List of EOS commands to apply to BGP daemon.
bgp_defaults:
- <str>
# Acting role in EVPN control plane.
# Default is set in node_type definition from node_type_keys.
evpn_role: <str; "client" | "server" | "none">
# List of nodes acting as EVPN Route-Servers / Route-Reflectors.
evpn_route_servers:
- <str>
# BGP AS <1-4294967295> or AS number in asdot notation "<1-65535>.<0-65535>".
# For asdot notation in YAML inputs, the value must be put in quotes, to prevent it from being interpreted as a float number.
# Required with eBGP.
bgp_as: <str>
# List of EOS commands to apply to BGP daemon.
bgp_defaults:
- <str>
# Acting role in EVPN control plane.
# Default is set in node_type definition from node_type_keys.
evpn_role: <str; "client" | "server" | "none">
# List of nodes acting as EVPN Route-Servers / Route-Reflectors.
evpn_route_servers:
- <str>
# Define variables per node.
nodes:
# The Node Name is used as "hostname".
- name: <str; required; unique>
# BGP AS <1-4294967295> or AS number in asdot notation "<1-65535>.<0-65535>".
# For asdot notation in YAML inputs, the value must be put in quotes, to prevent it from being interpreted as a float number.
# Required with eBGP.
bgp_as: <str>
# List of EOS commands to apply to BGP daemon.
bgp_defaults:
- <str>
# Acting role in EVPN control plane.
# Default is set in node_type definition from node_type_keys.
evpn_role: <str; "client" | "server" | "none">
# List of nodes acting as EVPN Route-Servers / Route-Reflectors.
evpn_route_servers:
- <str>
Node type network services configuration¶
| Variable | Type | Required | Default | Value Restrictions | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| <node_type_keys.key> | Dictionary | ||||
| defaults | Dictionary | Define variables for all nodes of this type. | |||
| evpn_services_l2_only | Boolean | False |
Possibility to prevent configuration of Tenant VRFs and SVIs. Override node definition “network_services_l3” from node_type_keys. This allows support for centralized routing. |
||
| filter | Dictionary | Filter L3 and L2 network services based on tenant and tags (and operation filter). If filter is not defined it will default to all. |
|||
| tenants | List, items: String | ['all'] |
Limit configured Network Services to those defined under these Tenants. Set to [‘all’] for all Tenants (default). This list also limits Tenants included by always_include_vrfs_in_tenants. |
||
| - <str> | String | ||||
| tags | List, items: String | ['all'] |
Limit configured VLANs to those matching the given tags. Set to [‘all’] for all VLANs (default). | ||
| - <str> | String | ||||
| allow_vrfs | List, items: String | ['all'] |
Limit configured Network Services to those defined under these VRFs. Set to [‘all’] for all VRFs (default). This list also limits VRFs included by always_include_vrfs_in_tenants. |
||
| - <str> | String | ||||
| deny_vrfs | List, items: String | ['all'] |
Prevent configuration of Network Services defined under these VRFs. This list prevents the given VRFs to be included by any other filtering mechanism. |
||
| - <str> | String | ||||
| always_include_vrfs_in_tenants | List, items: String | List of tenants where VRFs will be configured even if VLANs are not included in tags. Useful for L3 “border” leaf. |
|||
| - <str> | String | ||||
| only_vlans_in_use | Boolean | False |
Only configure VLANs, SVIs, VRFs in use by connected endpoints or downstream L2 switches. Note! This feature only considers configuration managed by eos_designs. This excludes structured_config, custom_structured_configuration_, raw_eos_cli, eos_cli, custom templates, configlets etc. |
||
| igmp_snooping_enabled | Boolean | True |
Activate or deactivate IGMP snooping on device level. | ||
| node_groups | List, items: Dictionary | Define variables related to all nodes part of this group. | |||
| - group | String | Required, Unique | The Node Group Name is used for MLAG domain unless set with ‘mlag_domain_id’. The Node Group Name is also used for peer description on downstream switches’ uplinks. |
||
| nodes | List, items: Dictionary | Define variables per node. | |||
| - name | String | Required, Unique | The Node Name is used as “hostname”. | ||
| evpn_services_l2_only | Boolean | False |
Possibility to prevent configuration of Tenant VRFs and SVIs. Override node definition “network_services_l3” from node_type_keys. This allows support for centralized routing. |
||
| filter | Dictionary | Filter L3 and L2 network services based on tenant and tags (and operation filter). If filter is not defined it will default to all. |
|||
| tenants | List, items: String | ['all'] |
Limit configured Network Services to those defined under these Tenants. Set to [‘all’] for all Tenants (default). This list also limits Tenants included by always_include_vrfs_in_tenants. |
||
| - <str> | String | ||||
| tags | List, items: String | ['all'] |
Limit configured VLANs to those matching the given tags. Set to [‘all’] for all VLANs (default). | ||
| - <str> | String | ||||
| allow_vrfs | List, items: String | ['all'] |
Limit configured Network Services to those defined under these VRFs. Set to [‘all’] for all VRFs (default). This list also limits VRFs included by always_include_vrfs_in_tenants. |
||
| - <str> | String | ||||
| deny_vrfs | List, items: String | ['all'] |
Prevent configuration of Network Services defined under these VRFs. This list prevents the given VRFs to be included by any other filtering mechanism. |
||
| - <str> | String | ||||
| always_include_vrfs_in_tenants | List, items: String | List of tenants where VRFs will be configured even if VLANs are not included in tags. Useful for L3 “border” leaf. |
|||
| - <str> | String | ||||
| only_vlans_in_use | Boolean | False |
Only configure VLANs, SVIs, VRFs in use by connected endpoints or downstream L2 switches. Note! This feature only considers configuration managed by eos_designs. This excludes structured_config, custom_structured_configuration_, raw_eos_cli, eos_cli, custom templates, configlets etc. |
||
| igmp_snooping_enabled | Boolean | True |
Activate or deactivate IGMP snooping on device level. | ||
| evpn_services_l2_only | Boolean | False |
Possibility to prevent configuration of Tenant VRFs and SVIs. Override node definition “network_services_l3” from node_type_keys. This allows support for centralized routing. |
||
| filter | Dictionary | Filter L3 and L2 network services based on tenant and tags (and operation filter). If filter is not defined it will default to all. |
|||
| tenants | List, items: String | ['all'] |
Limit configured Network Services to those defined under these Tenants. Set to [‘all’] for all Tenants (default). This list also limits Tenants included by always_include_vrfs_in_tenants. |
||
| - <str> | String | ||||
| tags | List, items: String | ['all'] |
Limit configured VLANs to those matching the given tags. Set to [‘all’] for all VLANs (default). | ||
| - <str> | String | ||||
| allow_vrfs | List, items: String | ['all'] |
Limit configured Network Services to those defined under these VRFs. Set to [‘all’] for all VRFs (default). This list also limits VRFs included by always_include_vrfs_in_tenants. |
||
| - <str> | String | ||||
| deny_vrfs | List, items: String | ['all'] |
Prevent configuration of Network Services defined under these VRFs. This list prevents the given VRFs to be included by any other filtering mechanism. |
||
| - <str> | String | ||||
| always_include_vrfs_in_tenants | List, items: String | List of tenants where VRFs will be configured even if VLANs are not included in tags. Useful for L3 “border” leaf. |
|||
| - <str> | String | ||||
| only_vlans_in_use | Boolean | False |
Only configure VLANs, SVIs, VRFs in use by connected endpoints or downstream L2 switches. Note! This feature only considers configuration managed by eos_designs. This excludes structured_config, custom_structured_configuration_, raw_eos_cli, eos_cli, custom templates, configlets etc. |
||
| igmp_snooping_enabled | Boolean | True |
Activate or deactivate IGMP snooping on device level. | ||
| nodes | List, items: Dictionary | Define variables per node. | |||
| - name | String | Required, Unique | The Node Name is used as “hostname”. | ||
| evpn_services_l2_only | Boolean | False |
Possibility to prevent configuration of Tenant VRFs and SVIs. Override node definition “network_services_l3” from node_type_keys. This allows support for centralized routing. |
||
| filter | Dictionary | Filter L3 and L2 network services based on tenant and tags (and operation filter). If filter is not defined it will default to all. |
|||
| tenants | List, items: String | ['all'] |
Limit configured Network Services to those defined under these Tenants. Set to [‘all’] for all Tenants (default). This list also limits Tenants included by always_include_vrfs_in_tenants. |
||
| - <str> | String | ||||
| tags | List, items: String | ['all'] |
Limit configured VLANs to those matching the given tags. Set to [‘all’] for all VLANs (default). | ||
| - <str> | String | ||||
| allow_vrfs | List, items: String | ['all'] |
Limit configured Network Services to those defined under these VRFs. Set to [‘all’] for all VRFs (default). This list also limits VRFs included by always_include_vrfs_in_tenants. |
||
| - <str> | String | ||||
| deny_vrfs | List, items: String | ['all'] |
Prevent configuration of Network Services defined under these VRFs. This list prevents the given VRFs to be included by any other filtering mechanism. |
||
| - <str> | String | ||||
| always_include_vrfs_in_tenants | List, items: String | List of tenants where VRFs will be configured even if VLANs are not included in tags. Useful for L3 “border” leaf. |
|||
| - <str> | String | ||||
| only_vlans_in_use | Boolean | False |
Only configure VLANs, SVIs, VRFs in use by connected endpoints or downstream L2 switches. Note! This feature only considers configuration managed by eos_designs. This excludes structured_config, custom_structured_configuration_, raw_eos_cli, eos_cli, custom templates, configlets etc. |
||
| igmp_snooping_enabled | Boolean | True |
Activate or deactivate IGMP snooping on device level. |
<node_type_keys.key>:
# Define variables for all nodes of this type.
defaults:
# Possibility to prevent configuration of Tenant VRFs and SVIs.
# Override node definition "network_services_l3" from node_type_keys.
# This allows support for centralized routing.
evpn_services_l2_only: <bool; default=False>
# Filter L3 and L2 network services based on tenant and tags (and operation filter).
# If filter is not defined it will default to all.
filter:
# Limit configured Network Services to those defined under these Tenants. Set to ['all'] for all Tenants (default).
# This list also limits Tenants included by `always_include_vrfs_in_tenants`.
tenants: # default=['all']
- <str>
# Limit configured VLANs to those matching the given tags. Set to ['all'] for all VLANs (default).
tags: # default=['all']
- <str>
# Limit configured Network Services to those defined under these VRFs. Set to ['all'] for all VRFs (default).
# This list also limits VRFs included by `always_include_vrfs_in_tenants`.
allow_vrfs: # default=['all']
- <str>
# Prevent configuration of Network Services defined under these VRFs.
# This list prevents the given VRFs to be included by any other filtering mechanism.
deny_vrfs: # default=['all']
- <str>
# List of tenants where VRFs will be configured even if VLANs are not included in tags.
# Useful for L3 "border" leaf.
always_include_vrfs_in_tenants:
- <str>
# Only configure VLANs, SVIs, VRFs in use by connected endpoints or downstream L2 switches.
# Note! This feature only considers configuration managed by eos_designs.
# This excludes structured_config, custom_structured_configuration_, raw_eos_cli, eos_cli, custom templates, configlets etc.
only_vlans_in_use: <bool; default=False>
# Activate or deactivate IGMP snooping on device level.
igmp_snooping_enabled: <bool; default=True>
# Define variables related to all nodes part of this group.
node_groups:
# The Node Group Name is used for MLAG domain unless set with 'mlag_domain_id'.
# The Node Group Name is also used for peer description on downstream switches' uplinks.
- group: <str; required; unique>
# Define variables per node.
nodes:
# The Node Name is used as "hostname".
- name: <str; required; unique>
# Possibility to prevent configuration of Tenant VRFs and SVIs.
# Override node definition "network_services_l3" from node_type_keys.
# This allows support for centralized routing.
evpn_services_l2_only: <bool; default=False>
# Filter L3 and L2 network services based on tenant and tags (and operation filter).
# If filter is not defined it will default to all.
filter:
# Limit configured Network Services to those defined under these Tenants. Set to ['all'] for all Tenants (default).
# This list also limits Tenants included by `always_include_vrfs_in_tenants`.
tenants: # default=['all']
- <str>
# Limit configured VLANs to those matching the given tags. Set to ['all'] for all VLANs (default).
tags: # default=['all']
- <str>
# Limit configured Network Services to those defined under these VRFs. Set to ['all'] for all VRFs (default).
# This list also limits VRFs included by `always_include_vrfs_in_tenants`.
allow_vrfs: # default=['all']
- <str>
# Prevent configuration of Network Services defined under these VRFs.
# This list prevents the given VRFs to be included by any other filtering mechanism.
deny_vrfs: # default=['all']
- <str>
# List of tenants where VRFs will be configured even if VLANs are not included in tags.
# Useful for L3 "border" leaf.
always_include_vrfs_in_tenants:
- <str>
# Only configure VLANs, SVIs, VRFs in use by connected endpoints or downstream L2 switches.
# Note! This feature only considers configuration managed by eos_designs.
# This excludes structured_config, custom_structured_configuration_, raw_eos_cli, eos_cli, custom templates, configlets etc.
only_vlans_in_use: <bool; default=False>
# Activate or deactivate IGMP snooping on device level.
igmp_snooping_enabled: <bool; default=True>
# Possibility to prevent configuration of Tenant VRFs and SVIs.
# Override node definition "network_services_l3" from node_type_keys.
# This allows support for centralized routing.
evpn_services_l2_only: <bool; default=False>
# Filter L3 and L2 network services based on tenant and tags (and operation filter).
# If filter is not defined it will default to all.
filter:
# Limit configured Network Services to those defined under these Tenants. Set to ['all'] for all Tenants (default).
# This list also limits Tenants included by `always_include_vrfs_in_tenants`.
tenants: # default=['all']
- <str>
# Limit configured VLANs to those matching the given tags. Set to ['all'] for all VLANs (default).
tags: # default=['all']
- <str>
# Limit configured Network Services to those defined under these VRFs. Set to ['all'] for all VRFs (default).
# This list also limits VRFs included by `always_include_vrfs_in_tenants`.
allow_vrfs: # default=['all']
- <str>
# Prevent configuration of Network Services defined under these VRFs.
# This list prevents the given VRFs to be included by any other filtering mechanism.
deny_vrfs: # default=['all']
- <str>
# List of tenants where VRFs will be configured even if VLANs are not included in tags.
# Useful for L3 "border" leaf.
always_include_vrfs_in_tenants:
- <str>
# Only configure VLANs, SVIs, VRFs in use by connected endpoints or downstream L2 switches.
# Note! This feature only considers configuration managed by eos_designs.
# This excludes structured_config, custom_structured_configuration_, raw_eos_cli, eos_cli, custom templates, configlets etc.
only_vlans_in_use: <bool; default=False>
# Activate or deactivate IGMP snooping on device level.
igmp_snooping_enabled: <bool; default=True>
# Define variables per node.
nodes:
# The Node Name is used as "hostname".
- name: <str; required; unique>
# Possibility to prevent configuration of Tenant VRFs and SVIs.
# Override node definition "network_services_l3" from node_type_keys.
# This allows support for centralized routing.
evpn_services_l2_only: <bool; default=False>
# Filter L3 and L2 network services based on tenant and tags (and operation filter).
# If filter is not defined it will default to all.
filter:
# Limit configured Network Services to those defined under these Tenants. Set to ['all'] for all Tenants (default).
# This list also limits Tenants included by `always_include_vrfs_in_tenants`.
tenants: # default=['all']
- <str>
# Limit configured VLANs to those matching the given tags. Set to ['all'] for all VLANs (default).
tags: # default=['all']
- <str>
# Limit configured Network Services to those defined under these VRFs. Set to ['all'] for all VRFs (default).
# This list also limits VRFs included by `always_include_vrfs_in_tenants`.
allow_vrfs: # default=['all']
- <str>
# Prevent configuration of Network Services defined under these VRFs.
# This list prevents the given VRFs to be included by any other filtering mechanism.
deny_vrfs: # default=['all']
- <str>
# List of tenants where VRFs will be configured even if VLANs are not included in tags.
# Useful for L3 "border" leaf.
always_include_vrfs_in_tenants:
- <str>
# Only configure VLANs, SVIs, VRFs in use by connected endpoints or downstream L2 switches.
# Note! This feature only considers configuration managed by eos_designs.
# This excludes structured_config, custom_structured_configuration_, raw_eos_cli, eos_cli, custom templates, configlets etc.
only_vlans_in_use: <bool; default=False>
# Activate or deactivate IGMP snooping on device level.
igmp_snooping_enabled: <bool; default=True>
Node type EVPN gateway configuration¶
| Variable | Type | Required | Default | Value Restrictions | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| <node_type_keys.key> | Dictionary | ||||
| defaults | Dictionary | Define variables for all nodes of this type. | |||
| ipvpn_gateway | Dictionary | Node is acting as IP-VPN Gateway for EVPN to MPLS-IP-VPN Interworking. The BGP peer group used for this is “bgp_peer_groups.ipvpn_gateway_peers”. L3 Reachability is required for this to work, the preferred method to establish underlay connectivity is to use core_interfaces. |
|||
| enabled | Boolean | Required | |||
| evpn_domain_id | String | 65535:1 |
Domain ID to assign to EVPN address family for use with D-path. Format |
||
| ipvpn_domain_id | String | 65535:2 |
Domain ID to assign to IPVPN address families for use with D-path. Format |
||
| enable_d_path | Boolean | True |
Enable D-path for use with BGP bestpath selection algorithm. | ||
| maximum_routes | Integer | 0 |
Maximum routes to accept from IPVPN remote peers. | ||
| local_as | String | none |
Local BGP AS applied to peering with IPVPN remote peers. BGP AS <1-4294967295> or AS number in asdot notation “<1-65535>.<0-65535>”. For asdot notation in YAML inputs, the value must be put in quotes, to prevent it from being interpreted as a float number. |
||
| address_families | List, items: String | ['vpn-ipv4'] |
IPVPN address families to enable for remote peers. | ||
| - <str> | String | ||||
| remote_peers | List, items: Dictionary | ||||
| - hostname | String | Required | Hostname of remote IPVPN Peer. | ||
| ip_address | String | Required | Format: ipv4 | Peering IP of remote IPVPN Peer. | |
| bgp_as | String | Required | Remote IPVPN Peer’s BGP AS <1-4294967295> or AS number in asdot notation “<1-65535>.<0-65535>”. For asdot notation in YAML inputs, the value must be put in quotes, to prevent it from being interpreted as a float number. |
||
| node_groups | List, items: Dictionary | Define variables related to all nodes part of this group. | |||
| - group | String | Required, Unique | The Node Group Name is used for MLAG domain unless set with ‘mlag_domain_id’. The Node Group Name is also used for peer description on downstream switches’ uplinks. |
||
| nodes | List, items: Dictionary | Define variables per node. | |||
| - name | String | Required, Unique | The Node Name is used as “hostname”. | ||
| ipvpn_gateway | Dictionary | Node is acting as IP-VPN Gateway for EVPN to MPLS-IP-VPN Interworking. The BGP peer group used for this is “bgp_peer_groups.ipvpn_gateway_peers”. L3 Reachability is required for this to work, the preferred method to establish underlay connectivity is to use core_interfaces. |
|||
| enabled | Boolean | Required | |||
| evpn_domain_id | String | 65535:1 |
Domain ID to assign to EVPN address family for use with D-path. Format |
||
| ipvpn_domain_id | String | 65535:2 |
Domain ID to assign to IPVPN address families for use with D-path. Format |
||
| enable_d_path | Boolean | True |
Enable D-path for use with BGP bestpath selection algorithm. | ||
| maximum_routes | Integer | 0 |
Maximum routes to accept from IPVPN remote peers. | ||
| local_as | String | none |
Local BGP AS applied to peering with IPVPN remote peers. BGP AS <1-4294967295> or AS number in asdot notation “<1-65535>.<0-65535>”. For asdot notation in YAML inputs, the value must be put in quotes, to prevent it from being interpreted as a float number. |
||
| address_families | List, items: String | ['vpn-ipv4'] |
IPVPN address families to enable for remote peers. | ||
| - <str> | String | ||||
| remote_peers | List, items: Dictionary | ||||
| - hostname | String | Required | Hostname of remote IPVPN Peer. | ||
| ip_address | String | Required | Format: ipv4 | Peering IP of remote IPVPN Peer. | |
| bgp_as | String | Required | Remote IPVPN Peer’s BGP AS <1-4294967295> or AS number in asdot notation “<1-65535>.<0-65535>”. For asdot notation in YAML inputs, the value must be put in quotes, to prevent it from being interpreted as a float number. |
||
| ipvpn_gateway | Dictionary | Node is acting as IP-VPN Gateway for EVPN to MPLS-IP-VPN Interworking. The BGP peer group used for this is “bgp_peer_groups.ipvpn_gateway_peers”. L3 Reachability is required for this to work, the preferred method to establish underlay connectivity is to use core_interfaces. |
|||
| enabled | Boolean | Required | |||
| evpn_domain_id | String | 65535:1 |
Domain ID to assign to EVPN address family for use with D-path. Format |
||
| ipvpn_domain_id | String | 65535:2 |
Domain ID to assign to IPVPN address families for use with D-path. Format |
||
| enable_d_path | Boolean | True |
Enable D-path for use with BGP bestpath selection algorithm. | ||
| maximum_routes | Integer | 0 |
Maximum routes to accept from IPVPN remote peers. | ||
| local_as | String | none |
Local BGP AS applied to peering with IPVPN remote peers. BGP AS <1-4294967295> or AS number in asdot notation “<1-65535>.<0-65535>”. For asdot notation in YAML inputs, the value must be put in quotes, to prevent it from being interpreted as a float number. |
||
| address_families | List, items: String | ['vpn-ipv4'] |
IPVPN address families to enable for remote peers. | ||
| - <str> | String | ||||
| remote_peers | List, items: Dictionary | ||||
| - hostname | String | Required | Hostname of remote IPVPN Peer. | ||
| ip_address | String | Required | Format: ipv4 | Peering IP of remote IPVPN Peer. | |
| bgp_as | String | Required | Remote IPVPN Peer’s BGP AS <1-4294967295> or AS number in asdot notation “<1-65535>.<0-65535>”. For asdot notation in YAML inputs, the value must be put in quotes, to prevent it from being interpreted as a float number. |
||
| nodes | List, items: Dictionary | Define variables per node. | |||
| - name | String | Required, Unique | The Node Name is used as “hostname”. | ||
| ipvpn_gateway | Dictionary | Node is acting as IP-VPN Gateway for EVPN to MPLS-IP-VPN Interworking. The BGP peer group used for this is “bgp_peer_groups.ipvpn_gateway_peers”. L3 Reachability is required for this to work, the preferred method to establish underlay connectivity is to use core_interfaces. |
|||
| enabled | Boolean | Required | |||
| evpn_domain_id | String | 65535:1 |
Domain ID to assign to EVPN address family for use with D-path. Format |
||
| ipvpn_domain_id | String | 65535:2 |
Domain ID to assign to IPVPN address families for use with D-path. Format |
||
| enable_d_path | Boolean | True |
Enable D-path for use with BGP bestpath selection algorithm. | ||
| maximum_routes | Integer | 0 |
Maximum routes to accept from IPVPN remote peers. | ||
| local_as | String | none |
Local BGP AS applied to peering with IPVPN remote peers. BGP AS <1-4294967295> or AS number in asdot notation “<1-65535>.<0-65535>”. For asdot notation in YAML inputs, the value must be put in quotes, to prevent it from being interpreted as a float number. |
||
| address_families | List, items: String | ['vpn-ipv4'] |
IPVPN address families to enable for remote peers. | ||
| - <str> | String | ||||
| remote_peers | List, items: Dictionary | ||||
| - hostname | String | Required | Hostname of remote IPVPN Peer. | ||
| ip_address | String | Required | Format: ipv4 | Peering IP of remote IPVPN Peer. | |
| bgp_as | String | Required | Remote IPVPN Peer’s BGP AS <1-4294967295> or AS number in asdot notation “<1-65535>.<0-65535>”. For asdot notation in YAML inputs, the value must be put in quotes, to prevent it from being interpreted as a float number. |
<node_type_keys.key>:
# Define variables for all nodes of this type.
defaults:
# Node is acting as IP-VPN Gateway for EVPN to MPLS-IP-VPN Interworking. The BGP peer group used for this is "bgp_peer_groups.ipvpn_gateway_peers".
# L3 Reachability is required for this to work, the preferred method to establish underlay connectivity is to use core_interfaces.
ipvpn_gateway:
enabled: <bool; required>
# Domain ID to assign to EVPN address family for use with D-path. Format <nn>:<nn>.
evpn_domain_id: <str; default="65535:1">
# Domain ID to assign to IPVPN address families for use with D-path. Format <nn>:<nn>.
ipvpn_domain_id: <str; default="65535:2">
# Enable D-path for use with BGP bestpath selection algorithm.
enable_d_path: <bool; default=True>
# Maximum routes to accept from IPVPN remote peers.
maximum_routes: <int; default=0>
# Local BGP AS applied to peering with IPVPN remote peers.
# BGP AS <1-4294967295> or AS number in asdot notation "<1-65535>.<0-65535>".
# For asdot notation in YAML inputs, the value must be put in quotes, to prevent it from being interpreted as a float number.
local_as: <str; default="none">
# IPVPN address families to enable for remote peers.
address_families: # default=['vpn-ipv4']
- <str>
remote_peers:
# Hostname of remote IPVPN Peer.
- hostname: <str; required>
# Peering IP of remote IPVPN Peer.
ip_address: <str; required>
# Remote IPVPN Peer's BGP AS <1-4294967295> or AS number in asdot notation "<1-65535>.<0-65535>".
# For asdot notation in YAML inputs, the value must be put in quotes, to prevent it from being interpreted as a float number.
bgp_as: <str; required>
# Define variables related to all nodes part of this group.
node_groups:
# The Node Group Name is used for MLAG domain unless set with 'mlag_domain_id'.
# The Node Group Name is also used for peer description on downstream switches' uplinks.
- group: <str; required; unique>
# Define variables per node.
nodes:
# The Node Name is used as "hostname".
- name: <str; required; unique>
# Node is acting as IP-VPN Gateway for EVPN to MPLS-IP-VPN Interworking. The BGP peer group used for this is "bgp_peer_groups.ipvpn_gateway_peers".
# L3 Reachability is required for this to work, the preferred method to establish underlay connectivity is to use core_interfaces.
ipvpn_gateway:
enabled: <bool; required>
# Domain ID to assign to EVPN address family for use with D-path. Format <nn>:<nn>.
evpn_domain_id: <str; default="65535:1">
# Domain ID to assign to IPVPN address families for use with D-path. Format <nn>:<nn>.
ipvpn_domain_id: <str; default="65535:2">
# Enable D-path for use with BGP bestpath selection algorithm.
enable_d_path: <bool; default=True>
# Maximum routes to accept from IPVPN remote peers.
maximum_routes: <int; default=0>
# Local BGP AS applied to peering with IPVPN remote peers.
# BGP AS <1-4294967295> or AS number in asdot notation "<1-65535>.<0-65535>".
# For asdot notation in YAML inputs, the value must be put in quotes, to prevent it from being interpreted as a float number.
local_as: <str; default="none">
# IPVPN address families to enable for remote peers.
address_families: # default=['vpn-ipv4']
- <str>
remote_peers:
# Hostname of remote IPVPN Peer.
- hostname: <str; required>
# Peering IP of remote IPVPN Peer.
ip_address: <str; required>
# Remote IPVPN Peer's BGP AS <1-4294967295> or AS number in asdot notation "<1-65535>.<0-65535>".
# For asdot notation in YAML inputs, the value must be put in quotes, to prevent it from being interpreted as a float number.
bgp_as: <str; required>
# Node is acting as IP-VPN Gateway for EVPN to MPLS-IP-VPN Interworking. The BGP peer group used for this is "bgp_peer_groups.ipvpn_gateway_peers".
# L3 Reachability is required for this to work, the preferred method to establish underlay connectivity is to use core_interfaces.
ipvpn_gateway:
enabled: <bool; required>
# Domain ID to assign to EVPN address family for use with D-path. Format <nn>:<nn>.
evpn_domain_id: <str; default="65535:1">
# Domain ID to assign to IPVPN address families for use with D-path. Format <nn>:<nn>.
ipvpn_domain_id: <str; default="65535:2">
# Enable D-path for use with BGP bestpath selection algorithm.
enable_d_path: <bool; default=True>
# Maximum routes to accept from IPVPN remote peers.
maximum_routes: <int; default=0>
# Local BGP AS applied to peering with IPVPN remote peers.
# BGP AS <1-4294967295> or AS number in asdot notation "<1-65535>.<0-65535>".
# For asdot notation in YAML inputs, the value must be put in quotes, to prevent it from being interpreted as a float number.
local_as: <str; default="none">
# IPVPN address families to enable for remote peers.
address_families: # default=['vpn-ipv4']
- <str>
remote_peers:
# Hostname of remote IPVPN Peer.
- hostname: <str; required>
# Peering IP of remote IPVPN Peer.
ip_address: <str; required>
# Remote IPVPN Peer's BGP AS <1-4294967295> or AS number in asdot notation "<1-65535>.<0-65535>".
# For asdot notation in YAML inputs, the value must be put in quotes, to prevent it from being interpreted as a float number.
bgp_as: <str; required>
# Define variables per node.
nodes:
# The Node Name is used as "hostname".
- name: <str; required; unique>
# Node is acting as IP-VPN Gateway for EVPN to MPLS-IP-VPN Interworking. The BGP peer group used for this is "bgp_peer_groups.ipvpn_gateway_peers".
# L3 Reachability is required for this to work, the preferred method to establish underlay connectivity is to use core_interfaces.
ipvpn_gateway:
enabled: <bool; required>
# Domain ID to assign to EVPN address family for use with D-path. Format <nn>:<nn>.
evpn_domain_id: <str; default="65535:1">
# Domain ID to assign to IPVPN address families for use with D-path. Format <nn>:<nn>.
ipvpn_domain_id: <str; default="65535:2">
# Enable D-path for use with BGP bestpath selection algorithm.
enable_d_path: <bool; default=True>
# Maximum routes to accept from IPVPN remote peers.
maximum_routes: <int; default=0>
# Local BGP AS applied to peering with IPVPN remote peers.
# BGP AS <1-4294967295> or AS number in asdot notation "<1-65535>.<0-65535>".
# For asdot notation in YAML inputs, the value must be put in quotes, to prevent it from being interpreted as a float number.
local_as: <str; default="none">
# IPVPN address families to enable for remote peers.
address_families: # default=['vpn-ipv4']
- <str>
remote_peers:
# Hostname of remote IPVPN Peer.
- hostname: <str; required>
# Peering IP of remote IPVPN Peer.
ip_address: <str; required>
# Remote IPVPN Peer's BGP AS <1-4294967295> or AS number in asdot notation "<1-65535>.<0-65535>".
# For asdot notation in YAML inputs, the value must be put in quotes, to prevent it from being interpreted as a float number.
bgp_as: <str; required>
Node type EVPN multi-domain gateway configuration¶
| Variable | Type | Required | Default | Value Restrictions | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| <node_type_keys.key> | Dictionary | ||||
| defaults | Dictionary | Define variables for all nodes of this type. | |||
| evpn_gateway | Dictionary | Node is acting as EVPN Multi-Domain Gateway. New BGP peer-group is generated between EVPN GWs in different domains or between GWs and Route Servers. Name can be changed under “bgp_peer_groups.evpn_overlay_core” variable. L3 rechability for different EVPN GWs must be already in place, it is recommended to use DCI & L3 Edge if Route Servers and GWs are not defined under the same Ansible inventory. |
|||
| remote_peers | List, items: Dictionary | Define remote peers of the EVPN VXLAN Gateway. If the hostname can be found in the inventory, ip_address and BGP ASN will be automatically populated. Manual override takes precedence. If the peer’s hostname can not be found in the inventory, ip_address and bgp_as must be defined. |
|||
| - hostname | String | Hostname of remote EVPN GW server. | |||
| ip_address | String | Format: ipv4 | Peering IP of remote Route Server. | ||
| bgp_as | String | Remote Route Server’s BGP AS <1-4294967295> or AS number in asdot notation “<1-65535>.<0-65535>”. For asdot notation in YAML inputs, the value must be put in quotes, to prevent it from being interpreted as a float number. |
|||
| evpn_l2 | Dictionary | Enable EVPN Gateway functionality for route-types 2 (MAC-IP) and 3 (IMET). | |||
| enabled | Boolean | False |
|||
| evpn_l3 | Dictionary | Enable EVPN Gateway functionality for route-type 5 (IP-PREFIX). | |||
| enabled | Boolean | False |
|||
| inter_domain | Boolean | True |
|||
| node_groups | List, items: Dictionary | Define variables related to all nodes part of this group. | |||
| - group | String | Required, Unique | The Node Group Name is used for MLAG domain unless set with ‘mlag_domain_id’. The Node Group Name is also used for peer description on downstream switches’ uplinks. |
||
| nodes | List, items: Dictionary | Define variables per node. | |||
| - name | String | Required, Unique | The Node Name is used as “hostname”. | ||
| evpn_gateway | Dictionary | Node is acting as EVPN Multi-Domain Gateway. New BGP peer-group is generated between EVPN GWs in different domains or between GWs and Route Servers. Name can be changed under “bgp_peer_groups.evpn_overlay_core” variable. L3 rechability for different EVPN GWs must be already in place, it is recommended to use DCI & L3 Edge if Route Servers and GWs are not defined under the same Ansible inventory. |
|||
| remote_peers | List, items: Dictionary | Define remote peers of the EVPN VXLAN Gateway. If the hostname can be found in the inventory, ip_address and BGP ASN will be automatically populated. Manual override takes precedence. If the peer’s hostname can not be found in the inventory, ip_address and bgp_as must be defined. |
|||
| - hostname | String | Hostname of remote EVPN GW server. | |||
| ip_address | String | Format: ipv4 | Peering IP of remote Route Server. | ||
| bgp_as | String | Remote Route Server’s BGP AS <1-4294967295> or AS number in asdot notation “<1-65535>.<0-65535>”. For asdot notation in YAML inputs, the value must be put in quotes, to prevent it from being interpreted as a float number. |
|||
| evpn_l2 | Dictionary | Enable EVPN Gateway functionality for route-types 2 (MAC-IP) and 3 (IMET). | |||
| enabled | Boolean | False |
|||
| evpn_l3 | Dictionary | Enable EVPN Gateway functionality for route-type 5 (IP-PREFIX). | |||
| enabled | Boolean | False |
|||
| inter_domain | Boolean | True |
|||
| evpn_gateway | Dictionary | Node is acting as EVPN Multi-Domain Gateway. New BGP peer-group is generated between EVPN GWs in different domains or between GWs and Route Servers. Name can be changed under “bgp_peer_groups.evpn_overlay_core” variable. L3 rechability for different EVPN GWs must be already in place, it is recommended to use DCI & L3 Edge if Route Servers and GWs are not defined under the same Ansible inventory. |
|||
| remote_peers | List, items: Dictionary | Define remote peers of the EVPN VXLAN Gateway. If the hostname can be found in the inventory, ip_address and BGP ASN will be automatically populated. Manual override takes precedence. If the peer’s hostname can not be found in the inventory, ip_address and bgp_as must be defined. |
|||
| - hostname | String | Hostname of remote EVPN GW server. | |||
| ip_address | String | Format: ipv4 | Peering IP of remote Route Server. | ||
| bgp_as | String | Remote Route Server’s BGP AS <1-4294967295> or AS number in asdot notation “<1-65535>.<0-65535>”. For asdot notation in YAML inputs, the value must be put in quotes, to prevent it from being interpreted as a float number. |
|||
| evpn_l2 | Dictionary | Enable EVPN Gateway functionality for route-types 2 (MAC-IP) and 3 (IMET). | |||
| enabled | Boolean | False |
|||
| evpn_l3 | Dictionary | Enable EVPN Gateway functionality for route-type 5 (IP-PREFIX). | |||
| enabled | Boolean | False |
|||
| inter_domain | Boolean | True |
|||
| nodes | List, items: Dictionary | Define variables per node. | |||
| - name | String | Required, Unique | The Node Name is used as “hostname”. | ||
| evpn_gateway | Dictionary | Node is acting as EVPN Multi-Domain Gateway. New BGP peer-group is generated between EVPN GWs in different domains or between GWs and Route Servers. Name can be changed under “bgp_peer_groups.evpn_overlay_core” variable. L3 rechability for different EVPN GWs must be already in place, it is recommended to use DCI & L3 Edge if Route Servers and GWs are not defined under the same Ansible inventory. |
|||
| remote_peers | List, items: Dictionary | Define remote peers of the EVPN VXLAN Gateway. If the hostname can be found in the inventory, ip_address and BGP ASN will be automatically populated. Manual override takes precedence. If the peer’s hostname can not be found in the inventory, ip_address and bgp_as must be defined. |
|||
| - hostname | String | Hostname of remote EVPN GW server. | |||
| ip_address | String | Format: ipv4 | Peering IP of remote Route Server. | ||
| bgp_as | String | Remote Route Server’s BGP AS <1-4294967295> or AS number in asdot notation “<1-65535>.<0-65535>”. For asdot notation in YAML inputs, the value must be put in quotes, to prevent it from being interpreted as a float number. |
|||
| evpn_l2 | Dictionary | Enable EVPN Gateway functionality for route-types 2 (MAC-IP) and 3 (IMET). | |||
| enabled | Boolean | False |
|||
| evpn_l3 | Dictionary | Enable EVPN Gateway functionality for route-type 5 (IP-PREFIX). | |||
| enabled | Boolean | False |
|||
| inter_domain | Boolean | True |
<node_type_keys.key>:
# Define variables for all nodes of this type.
defaults:
# Node is acting as EVPN Multi-Domain Gateway.
# New BGP peer-group is generated between EVPN GWs in different domains or between GWs and Route Servers.
# Name can be changed under "bgp_peer_groups.evpn_overlay_core" variable.
# L3 rechability for different EVPN GWs must be already in place, it is recommended to use DCI & L3 Edge if Route Servers and GWs are not defined under the same Ansible inventory.
evpn_gateway:
# Define remote peers of the EVPN VXLAN Gateway.
# If the hostname can be found in the inventory, ip_address and BGP ASN will be automatically populated. Manual override takes precedence.
# If the peer's hostname can not be found in the inventory, ip_address and bgp_as must be defined.
remote_peers:
# Hostname of remote EVPN GW server.
- hostname: <str>
# Peering IP of remote Route Server.
ip_address: <str>
# Remote Route Server's BGP AS <1-4294967295> or AS number in asdot notation "<1-65535>.<0-65535>".
# For asdot notation in YAML inputs, the value must be put in quotes, to prevent it from being interpreted as a float number.
bgp_as: <str>
# Enable EVPN Gateway functionality for route-types 2 (MAC-IP) and 3 (IMET).
evpn_l2:
enabled: <bool; default=False>
# Enable EVPN Gateway functionality for route-type 5 (IP-PREFIX).
evpn_l3:
enabled: <bool; default=False>
inter_domain: <bool; default=True>
# Define variables related to all nodes part of this group.
node_groups:
# The Node Group Name is used for MLAG domain unless set with 'mlag_domain_id'.
# The Node Group Name is also used for peer description on downstream switches' uplinks.
- group: <str; required; unique>
# Define variables per node.
nodes:
# The Node Name is used as "hostname".
- name: <str; required; unique>
# Node is acting as EVPN Multi-Domain Gateway.
# New BGP peer-group is generated between EVPN GWs in different domains or between GWs and Route Servers.
# Name can be changed under "bgp_peer_groups.evpn_overlay_core" variable.
# L3 rechability for different EVPN GWs must be already in place, it is recommended to use DCI & L3 Edge if Route Servers and GWs are not defined under the same Ansible inventory.
evpn_gateway:
# Define remote peers of the EVPN VXLAN Gateway.
# If the hostname can be found in the inventory, ip_address and BGP ASN will be automatically populated. Manual override takes precedence.
# If the peer's hostname can not be found in the inventory, ip_address and bgp_as must be defined.
remote_peers:
# Hostname of remote EVPN GW server.
- hostname: <str>
# Peering IP of remote Route Server.
ip_address: <str>
# Remote Route Server's BGP AS <1-4294967295> or AS number in asdot notation "<1-65535>.<0-65535>".
# For asdot notation in YAML inputs, the value must be put in quotes, to prevent it from being interpreted as a float number.
bgp_as: <str>
# Enable EVPN Gateway functionality for route-types 2 (MAC-IP) and 3 (IMET).
evpn_l2:
enabled: <bool; default=False>
# Enable EVPN Gateway functionality for route-type 5 (IP-PREFIX).
evpn_l3:
enabled: <bool; default=False>
inter_domain: <bool; default=True>
# Node is acting as EVPN Multi-Domain Gateway.
# New BGP peer-group is generated between EVPN GWs in different domains or between GWs and Route Servers.
# Name can be changed under "bgp_peer_groups.evpn_overlay_core" variable.
# L3 rechability for different EVPN GWs must be already in place, it is recommended to use DCI & L3 Edge if Route Servers and GWs are not defined under the same Ansible inventory.
evpn_gateway:
# Define remote peers of the EVPN VXLAN Gateway.
# If the hostname can be found in the inventory, ip_address and BGP ASN will be automatically populated. Manual override takes precedence.
# If the peer's hostname can not be found in the inventory, ip_address and bgp_as must be defined.
remote_peers:
# Hostname of remote EVPN GW server.
- hostname: <str>
# Peering IP of remote Route Server.
ip_address: <str>
# Remote Route Server's BGP AS <1-4294967295> or AS number in asdot notation "<1-65535>.<0-65535>".
# For asdot notation in YAML inputs, the value must be put in quotes, to prevent it from being interpreted as a float number.
bgp_as: <str>
# Enable EVPN Gateway functionality for route-types 2 (MAC-IP) and 3 (IMET).
evpn_l2:
enabled: <bool; default=False>
# Enable EVPN Gateway functionality for route-type 5 (IP-PREFIX).
evpn_l3:
enabled: <bool; default=False>
inter_domain: <bool; default=True>
# Define variables per node.
nodes:
# The Node Name is used as "hostname".
- name: <str; required; unique>
# Node is acting as EVPN Multi-Domain Gateway.
# New BGP peer-group is generated between EVPN GWs in different domains or between GWs and Route Servers.
# Name can be changed under "bgp_peer_groups.evpn_overlay_core" variable.
# L3 rechability for different EVPN GWs must be already in place, it is recommended to use DCI & L3 Edge if Route Servers and GWs are not defined under the same Ansible inventory.
evpn_gateway:
# Define remote peers of the EVPN VXLAN Gateway.
# If the hostname can be found in the inventory, ip_address and BGP ASN will be automatically populated. Manual override takes precedence.
# If the peer's hostname can not be found in the inventory, ip_address and bgp_as must be defined.
remote_peers:
# Hostname of remote EVPN GW server.
- hostname: <str>
# Peering IP of remote Route Server.
ip_address: <str>
# Remote Route Server's BGP AS <1-4294967295> or AS number in asdot notation "<1-65535>.<0-65535>".
# For asdot notation in YAML inputs, the value must be put in quotes, to prevent it from being interpreted as a float number.
bgp_as: <str>
# Enable EVPN Gateway functionality for route-types 2 (MAC-IP) and 3 (IMET).
evpn_l2:
enabled: <bool; default=False>
# Enable EVPN Gateway functionality for route-type 5 (IP-PREFIX).
evpn_l3:
enabled: <bool; default=False>
inter_domain: <bool; default=True>
Node type ISIS Configuration¶
| Variable | Type | Required | Default | Value Restrictions | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| <node_type_keys.key> | Dictionary | ||||
| defaults | Dictionary | Define variables for all nodes of this type. | |||
| isis_system_id_prefix | String | Pattern: [0-9a-f]{4}.[0-9a-f]{4} | (4.4 hexadecimal). | ||
| isis_maximum_paths | Integer | Number of path to configure in ECMP for ISIS. | |||
| is_type | String | level-2 |
Valid Values: - level-1-2- level-1- level-2 |
||
| node_sid_base | Integer | 0 |
Node-SID base for isis-sr underlay variants. Combined with node id to generate ISIS-SR node-SID. | ||
| node_groups | List, items: Dictionary | Define variables related to all nodes part of this group. | |||
| - group | String | Required, Unique | The Node Group Name is used for MLAG domain unless set with ‘mlag_domain_id’. The Node Group Name is also used for peer description on downstream switches’ uplinks. |
||
| nodes | List, items: Dictionary | Define variables per node. | |||
| - name | String | Required, Unique | The Node Name is used as “hostname”. | ||
| isis_system_id_prefix | String | Pattern: [0-9a-f]{4}.[0-9a-f]{4} | (4.4 hexadecimal). | ||
| isis_maximum_paths | Integer | Number of path to configure in ECMP for ISIS. | |||
| is_type | String | level-2 |
Valid Values: - level-1-2- level-1- level-2 |
||
| node_sid_base | Integer | 0 |
Node-SID base for isis-sr underlay variants. Combined with node id to generate ISIS-SR node-SID. | ||
| isis_system_id_prefix | String | Pattern: [0-9a-f]{4}.[0-9a-f]{4} | (4.4 hexadecimal). | ||
| isis_maximum_paths | Integer | Number of path to configure in ECMP for ISIS. | |||
| is_type | String | level-2 |
Valid Values: - level-1-2- level-1- level-2 |
||
| node_sid_base | Integer | 0 |
Node-SID base for isis-sr underlay variants. Combined with node id to generate ISIS-SR node-SID. | ||
| nodes | List, items: Dictionary | Define variables per node. | |||
| - name | String | Required, Unique | The Node Name is used as “hostname”. | ||
| isis_system_id_prefix | String | Pattern: [0-9a-f]{4}.[0-9a-f]{4} | (4.4 hexadecimal). | ||
| isis_maximum_paths | Integer | Number of path to configure in ECMP for ISIS. | |||
| is_type | String | level-2 |
Valid Values: - level-1-2- level-1- level-2 |
||
| node_sid_base | Integer | 0 |
Node-SID base for isis-sr underlay variants. Combined with node id to generate ISIS-SR node-SID. |
<node_type_keys.key>:
# Define variables for all nodes of this type.
defaults:
# (4.4 hexadecimal).
isis_system_id_prefix: <str>
# Number of path to configure in ECMP for ISIS.
isis_maximum_paths: <int>
is_type: <str; "level-1-2" | "level-1" | "level-2"; default="level-2">
# Node-SID base for isis-sr underlay variants. Combined with node id to generate ISIS-SR node-SID.
node_sid_base: <int; default=0>
# Define variables related to all nodes part of this group.
node_groups:
# The Node Group Name is used for MLAG domain unless set with 'mlag_domain_id'.
# The Node Group Name is also used for peer description on downstream switches' uplinks.
- group: <str; required; unique>
# Define variables per node.
nodes:
# The Node Name is used as "hostname".
- name: <str; required; unique>
# (4.4 hexadecimal).
isis_system_id_prefix: <str>
# Number of path to configure in ECMP for ISIS.
isis_maximum_paths: <int>
is_type: <str; "level-1-2" | "level-1" | "level-2"; default="level-2">
# Node-SID base for isis-sr underlay variants. Combined with node id to generate ISIS-SR node-SID.
node_sid_base: <int; default=0>
# (4.4 hexadecimal).
isis_system_id_prefix: <str>
# Number of path to configure in ECMP for ISIS.
isis_maximum_paths: <int>
is_type: <str; "level-1-2" | "level-1" | "level-2"; default="level-2">
# Node-SID base for isis-sr underlay variants. Combined with node id to generate ISIS-SR node-SID.
node_sid_base: <int; default=0>
# Define variables per node.
nodes:
# The Node Name is used as "hostname".
- name: <str; required; unique>
# (4.4 hexadecimal).
isis_system_id_prefix: <str>
# Number of path to configure in ECMP for ISIS.
isis_maximum_paths: <int>
is_type: <str; "level-1-2" | "level-1" | "level-2"; default="level-2">
# Node-SID base for isis-sr underlay variants. Combined with node id to generate ISIS-SR node-SID.
node_sid_base: <int; default=0>
Node type MPLS configuration¶
| Variable | Type | Required | Default | Value Restrictions | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| <node_type_keys.key> | Dictionary | ||||
| defaults | Dictionary | Define variables for all nodes of this type. | |||
| mpls_overlay_role | String | Valid Values: - client- server- none |
Set the default mpls overlay role. Acting role in overlay control plane. |
||
| overlay_address_families | List, items: String | Set the default overlay address families. |
|||
| - <str> | String | Valid Values: - evpn- vpn-ipv4- vpn-ipv6 |
|||
| mpls_route_reflectors | List, items: String | List of inventory hostname acting as MPLS route-reflectors. | |||
| - <str> | String | Inventory_hostname_of_mpls_route_reflectors. | |||
| bgp_cluster_id | String | Set BGP cluster id. | |||
| node_groups | List, items: Dictionary | Define variables related to all nodes part of this group. | |||
| - group | String | Required, Unique | The Node Group Name is used for MLAG domain unless set with ‘mlag_domain_id’. The Node Group Name is also used for peer description on downstream switches’ uplinks. |
||
| nodes | List, items: Dictionary | Define variables per node. | |||
| - name | String | Required, Unique | The Node Name is used as “hostname”. | ||
| mpls_overlay_role | String | Valid Values: - client- server- none |
Set the default mpls overlay role. Acting role in overlay control plane. |
||
| overlay_address_families | List, items: String | Set the default overlay address families. |
|||
| - <str> | String | Valid Values: - evpn- vpn-ipv4- vpn-ipv6 |
|||
| mpls_route_reflectors | List, items: String | List of inventory hostname acting as MPLS route-reflectors. | |||
| - <str> | String | Inventory_hostname_of_mpls_route_reflectors. | |||
| bgp_cluster_id | String | Set BGP cluster id. | |||
| mpls_overlay_role | String | Valid Values: - client- server- none |
Set the default mpls overlay role. Acting role in overlay control plane. |
||
| overlay_address_families | List, items: String | Set the default overlay address families. |
|||
| - <str> | String | Valid Values: - evpn- vpn-ipv4- vpn-ipv6 |
|||
| mpls_route_reflectors | List, items: String | List of inventory hostname acting as MPLS route-reflectors. | |||
| - <str> | String | Inventory_hostname_of_mpls_route_reflectors. | |||
| bgp_cluster_id | String | Set BGP cluster id. | |||
| nodes | List, items: Dictionary | Define variables per node. | |||
| - name | String | Required, Unique | The Node Name is used as “hostname”. | ||
| mpls_overlay_role | String | Valid Values: - client- server- none |
Set the default mpls overlay role. Acting role in overlay control plane. |
||
| overlay_address_families | List, items: String | Set the default overlay address families. |
|||
| - <str> | String | Valid Values: - evpn- vpn-ipv4- vpn-ipv6 |
|||
| mpls_route_reflectors | List, items: String | List of inventory hostname acting as MPLS route-reflectors. | |||
| - <str> | String | Inventory_hostname_of_mpls_route_reflectors. | |||
| bgp_cluster_id | String | Set BGP cluster id. |
<node_type_keys.key>:
# Define variables for all nodes of this type.
defaults:
# Set the default mpls overlay role.
# Acting role in overlay control plane.
mpls_overlay_role: <str; "client" | "server" | "none">
# Set the default overlay address families.
overlay_address_families:
- <str; "evpn" | "vpn-ipv4" | "vpn-ipv6">
# List of inventory hostname acting as MPLS route-reflectors.
mpls_route_reflectors:
# Inventory_hostname_of_mpls_route_reflectors.
- <str>
# Set BGP cluster id.
bgp_cluster_id: <str>
# Define variables related to all nodes part of this group.
node_groups:
# The Node Group Name is used for MLAG domain unless set with 'mlag_domain_id'.
# The Node Group Name is also used for peer description on downstream switches' uplinks.
- group: <str; required; unique>
# Define variables per node.
nodes:
# The Node Name is used as "hostname".
- name: <str; required; unique>
# Set the default mpls overlay role.
# Acting role in overlay control plane.
mpls_overlay_role: <str; "client" | "server" | "none">
# Set the default overlay address families.
overlay_address_families:
- <str; "evpn" | "vpn-ipv4" | "vpn-ipv6">
# List of inventory hostname acting as MPLS route-reflectors.
mpls_route_reflectors:
# Inventory_hostname_of_mpls_route_reflectors.
- <str>
# Set BGP cluster id.
bgp_cluster_id: <str>
# Set the default mpls overlay role.
# Acting role in overlay control plane.
mpls_overlay_role: <str; "client" | "server" | "none">
# Set the default overlay address families.
overlay_address_families:
- <str; "evpn" | "vpn-ipv4" | "vpn-ipv6">
# List of inventory hostname acting as MPLS route-reflectors.
mpls_route_reflectors:
# Inventory_hostname_of_mpls_route_reflectors.
- <str>
# Set BGP cluster id.
bgp_cluster_id: <str>
# Define variables per node.
nodes:
# The Node Name is used as "hostname".
- name: <str; required; unique>
# Set the default mpls overlay role.
# Acting role in overlay control plane.
mpls_overlay_role: <str; "client" | "server" | "none">
# Set the default overlay address families.
overlay_address_families:
- <str; "evpn" | "vpn-ipv4" | "vpn-ipv6">
# List of inventory hostname acting as MPLS route-reflectors.
mpls_route_reflectors:
# Inventory_hostname_of_mpls_route_reflectors.
- <str>
# Set BGP cluster id.
bgp_cluster_id: <str>
Node type WAN configuration¶
| Variable | Type | Required | Default | Value Restrictions | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| <node_type_keys.key> | Dictionary | ||||
| defaults | Dictionary | Define variables for all nodes of this type. | |||
| wan_role | String | Valid Values: - client- server |
Override the default WAN role. This is used both for AutoVPN and Pathfinder designs. That means if wan_mode root key is set to autovpn or cv-pathfinder.server indicates that the router is a route-reflector.Only supported if overlay_routing_protocol is set to ibgp. |
||
| cv_pathfinder_transit_mode | String | Valid Values: - region- zone |
Configure the transit mode for a WAN client for CV Pathfinder designs only when the wan_mode root key is set to cv_pathfinder.‘zone’ is currently not supported. |
||
| cv_pathfinder_region | String | The CV Pathfinder region name. This key is required for WAN routers but optional for pathfinders. The region name must be defined under ‘cv_pathfinder_regions’. |
|||
| cv_pathfinder_site | String | The CV Pathfinder site name. This key is required for WAN routers but ignored for pathfinders. The site name must be defined for the relevant region under ‘cv_pathfinder_regions’. |
|||
| wan_ha | Dictionary | PREVIEW: This key is currently not supported The key is supported only if wan_mode == cv-pathfinder.AutoVPN support is still to be determined. Maximum 2 devices supported by group for HA. |
|||
| enabled | Boolean | True |
Enable / Disable auto CV-Pathfinder HA, when two nodes are defined in the same node_group. | ||
| ipsec | Boolean | True |
Enable / Disable IPsec over HA path-group when HA is enabled. | ||
| dps_mss_ipv4 | String | auto |
IPv4 MSS value configured under “router path-selection” on WAN Devices. | ||
| node_groups | List, items: Dictionary | Define variables related to all nodes part of this group. | |||
| - group | String | Required, Unique | The Node Group Name is used for MLAG domain unless set with ‘mlag_domain_id’. The Node Group Name is also used for peer description on downstream switches’ uplinks. |
||
| nodes | List, items: Dictionary | Define variables per node. | |||
| - name | String | Required, Unique | The Node Name is used as “hostname”. | ||
| wan_role | String | Valid Values: - client- server |
Override the default WAN role. This is used both for AutoVPN and Pathfinder designs. That means if wan_mode root key is set to autovpn or cv-pathfinder.server indicates that the router is a route-reflector.Only supported if overlay_routing_protocol is set to ibgp. |
||
| cv_pathfinder_transit_mode | String | Valid Values: - region- zone |
Configure the transit mode for a WAN client for CV Pathfinder designs only when the wan_mode root key is set to cv_pathfinder.‘zone’ is currently not supported. |
||
| cv_pathfinder_region | String | The CV Pathfinder region name. This key is required for WAN routers but optional for pathfinders. The region name must be defined under ‘cv_pathfinder_regions’. |
|||
| cv_pathfinder_site | String | The CV Pathfinder site name. This key is required for WAN routers but ignored for pathfinders. The site name must be defined for the relevant region under ‘cv_pathfinder_regions’. |
|||
| wan_ha | Dictionary | PREVIEW: This key is currently not supported The key is supported only if wan_mode == cv-pathfinder.AutoVPN support is still to be determined. Maximum 2 devices supported by group for HA. |
|||
| enabled | Boolean | True |
Enable / Disable auto CV-Pathfinder HA, when two nodes are defined in the same node_group. | ||
| ipsec | Boolean | True |
Enable / Disable IPsec over HA path-group when HA is enabled. | ||
| dps_mss_ipv4 | String | auto |
IPv4 MSS value configured under “router path-selection” on WAN Devices. | ||
| wan_role | String | Valid Values: - client- server |
Override the default WAN role. This is used both for AutoVPN and Pathfinder designs. That means if wan_mode root key is set to autovpn or cv-pathfinder.server indicates that the router is a route-reflector.Only supported if overlay_routing_protocol is set to ibgp. |
||
| cv_pathfinder_transit_mode | String | Valid Values: - region- zone |
Configure the transit mode for a WAN client for CV Pathfinder designs only when the wan_mode root key is set to cv_pathfinder.‘zone’ is currently not supported. |
||
| cv_pathfinder_region | String | The CV Pathfinder region name. This key is required for WAN routers but optional for pathfinders. The region name must be defined under ‘cv_pathfinder_regions’. |
|||
| cv_pathfinder_site | String | The CV Pathfinder site name. This key is required for WAN routers but ignored for pathfinders. The site name must be defined for the relevant region under ‘cv_pathfinder_regions’. |
|||
| wan_ha | Dictionary | PREVIEW: This key is currently not supported The key is supported only if wan_mode == cv-pathfinder.AutoVPN support is still to be determined. Maximum 2 devices supported by group for HA. |
|||
| enabled | Boolean | True |
Enable / Disable auto CV-Pathfinder HA, when two nodes are defined in the same node_group. | ||
| ipsec | Boolean | True |
Enable / Disable IPsec over HA path-group when HA is enabled. | ||
| dps_mss_ipv4 | String | auto |
IPv4 MSS value configured under “router path-selection” on WAN Devices. | ||
| nodes | List, items: Dictionary | Define variables per node. | |||
| - name | String | Required, Unique | The Node Name is used as “hostname”. | ||
| wan_role | String | Valid Values: - client- server |
Override the default WAN role. This is used both for AutoVPN and Pathfinder designs. That means if wan_mode root key is set to autovpn or cv-pathfinder.server indicates that the router is a route-reflector.Only supported if overlay_routing_protocol is set to ibgp. |
||
| cv_pathfinder_transit_mode | String | Valid Values: - region- zone |
Configure the transit mode for a WAN client for CV Pathfinder designs only when the wan_mode root key is set to cv_pathfinder.‘zone’ is currently not supported. |
||
| cv_pathfinder_region | String | The CV Pathfinder region name. This key is required for WAN routers but optional for pathfinders. The region name must be defined under ‘cv_pathfinder_regions’. |
|||
| cv_pathfinder_site | String | The CV Pathfinder site name. This key is required for WAN routers but ignored for pathfinders. The site name must be defined for the relevant region under ‘cv_pathfinder_regions’. |
|||
| wan_ha | Dictionary | PREVIEW: This key is currently not supported The key is supported only if wan_mode == cv-pathfinder.AutoVPN support is still to be determined. Maximum 2 devices supported by group for HA. |
|||
| enabled | Boolean | True |
Enable / Disable auto CV-Pathfinder HA, when two nodes are defined in the same node_group. | ||
| ipsec | Boolean | True |
Enable / Disable IPsec over HA path-group when HA is enabled. | ||
| dps_mss_ipv4 | String | auto |
IPv4 MSS value configured under “router path-selection” on WAN Devices. |
<node_type_keys.key>:
# Define variables for all nodes of this type.
defaults:
# Override the default WAN role.
#
# This is used both for AutoVPN and Pathfinder designs.
# That means if `wan_mode` root key is set to `autovpn` or `cv-pathfinder`.
# `server` indicates that the router is a route-reflector.
#
# Only supported if `overlay_routing_protocol` is set to `ibgp`.
wan_role: <str; "client" | "server">
# Configure the transit mode for a WAN client for CV Pathfinder designs
# only when the `wan_mode` root key is set to `cv_pathfinder`.
#
# 'zone' is currently not supported.
cv_pathfinder_transit_mode: <str; "region" | "zone">
# The CV Pathfinder region name.
# This key is required for WAN routers but optional for pathfinders.
# The region name must be defined under 'cv_pathfinder_regions'.
cv_pathfinder_region: <str>
# The CV Pathfinder site name.
# This key is required for WAN routers but ignored for pathfinders.
# The site name must be defined for the relevant region under 'cv_pathfinder_regions'.
cv_pathfinder_site: <str>
# PREVIEW: This key is currently not supported
#
# The key is supported only if `wan_mode` == `cv-pathfinder`.
# AutoVPN support is still to be determined.
#
# Maximum 2 devices supported by group for HA.
wan_ha:
# Enable / Disable auto CV-Pathfinder HA, when two nodes are defined in the same node_group.
enabled: <bool; default=True>
# Enable / Disable IPsec over HA path-group when HA is enabled.
ipsec: <bool; default=True>
# IPv4 MSS value configured under "router path-selection" on WAN Devices.
dps_mss_ipv4: <str; default="auto">
# Define variables related to all nodes part of this group.
node_groups:
# The Node Group Name is used for MLAG domain unless set with 'mlag_domain_id'.
# The Node Group Name is also used for peer description on downstream switches' uplinks.
- group: <str; required; unique>
# Define variables per node.
nodes:
# The Node Name is used as "hostname".
- name: <str; required; unique>
# Override the default WAN role.
#
# This is used both for AutoVPN and Pathfinder designs.
# That means if `wan_mode` root key is set to `autovpn` or `cv-pathfinder`.
# `server` indicates that the router is a route-reflector.
#
# Only supported if `overlay_routing_protocol` is set to `ibgp`.
wan_role: <str; "client" | "server">
# Configure the transit mode for a WAN client for CV Pathfinder designs
# only when the `wan_mode` root key is set to `cv_pathfinder`.
#
# 'zone' is currently not supported.
cv_pathfinder_transit_mode: <str; "region" | "zone">
# The CV Pathfinder region name.
# This key is required for WAN routers but optional for pathfinders.
# The region name must be defined under 'cv_pathfinder_regions'.
cv_pathfinder_region: <str>
# The CV Pathfinder site name.
# This key is required for WAN routers but ignored for pathfinders.
# The site name must be defined for the relevant region under 'cv_pathfinder_regions'.
cv_pathfinder_site: <str>
# PREVIEW: This key is currently not supported
#
# The key is supported only if `wan_mode` == `cv-pathfinder`.
# AutoVPN support is still to be determined.
#
# Maximum 2 devices supported by group for HA.
wan_ha:
# Enable / Disable auto CV-Pathfinder HA, when two nodes are defined in the same node_group.
enabled: <bool; default=True>
# Enable / Disable IPsec over HA path-group when HA is enabled.
ipsec: <bool; default=True>
# IPv4 MSS value configured under "router path-selection" on WAN Devices.
dps_mss_ipv4: <str; default="auto">
# Override the default WAN role.
#
# This is used both for AutoVPN and Pathfinder designs.
# That means if `wan_mode` root key is set to `autovpn` or `cv-pathfinder`.
# `server` indicates that the router is a route-reflector.
#
# Only supported if `overlay_routing_protocol` is set to `ibgp`.
wan_role: <str; "client" | "server">
# Configure the transit mode for a WAN client for CV Pathfinder designs
# only when the `wan_mode` root key is set to `cv_pathfinder`.
#
# 'zone' is currently not supported.
cv_pathfinder_transit_mode: <str; "region" | "zone">
# The CV Pathfinder region name.
# This key is required for WAN routers but optional for pathfinders.
# The region name must be defined under 'cv_pathfinder_regions'.
cv_pathfinder_region: <str>
# The CV Pathfinder site name.
# This key is required for WAN routers but ignored for pathfinders.
# The site name must be defined for the relevant region under 'cv_pathfinder_regions'.
cv_pathfinder_site: <str>
# PREVIEW: This key is currently not supported
#
# The key is supported only if `wan_mode` == `cv-pathfinder`.
# AutoVPN support is still to be determined.
#
# Maximum 2 devices supported by group for HA.
wan_ha:
# Enable / Disable auto CV-Pathfinder HA, when two nodes are defined in the same node_group.
enabled: <bool; default=True>
# Enable / Disable IPsec over HA path-group when HA is enabled.
ipsec: <bool; default=True>
# IPv4 MSS value configured under "router path-selection" on WAN Devices.
dps_mss_ipv4: <str; default="auto">
# Define variables per node.
nodes:
# The Node Name is used as "hostname".
- name: <str; required; unique>
# Override the default WAN role.
#
# This is used both for AutoVPN and Pathfinder designs.
# That means if `wan_mode` root key is set to `autovpn` or `cv-pathfinder`.
# `server` indicates that the router is a route-reflector.
#
# Only supported if `overlay_routing_protocol` is set to `ibgp`.
wan_role: <str; "client" | "server">
# Configure the transit mode for a WAN client for CV Pathfinder designs
# only when the `wan_mode` root key is set to `cv_pathfinder`.
#
# 'zone' is currently not supported.
cv_pathfinder_transit_mode: <str; "region" | "zone">
# The CV Pathfinder region name.
# This key is required for WAN routers but optional for pathfinders.
# The region name must be defined under 'cv_pathfinder_regions'.
cv_pathfinder_region: <str>
# The CV Pathfinder site name.
# This key is required for WAN routers but ignored for pathfinders.
# The site name must be defined for the relevant region under 'cv_pathfinder_regions'.
cv_pathfinder_site: <str>
# PREVIEW: This key is currently not supported
#
# The key is supported only if `wan_mode` == `cv-pathfinder`.
# AutoVPN support is still to be determined.
#
# Maximum 2 devices supported by group for HA.
wan_ha:
# Enable / Disable auto CV-Pathfinder HA, when two nodes are defined in the same node_group.
enabled: <bool; default=True>
# Enable / Disable IPsec over HA path-group when HA is enabled.
ipsec: <bool; default=True>
# IPv4 MSS value configured under "router path-selection" on WAN Devices.
dps_mss_ipv4: <str; default="auto">
Node type PTP configuration¶
| Variable | Type | Required | Default | Value Restrictions | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| <node_type_keys.key> | Dictionary | ||||
| defaults | Dictionary | Define variables for all nodes of this type. | |||
| ptp | Dictionary | ||||
| enabled | Boolean | False |
|||
| profile | String | aes67-r16-2016 |
Valid Values: - aes67- smpte2059-2- aes67-r16-2016 |
||
| mlag | Boolean | False |
Configure PTP on the MLAG peer-link port-channel when PTP is enabled. By default PTP will not be configured on the MLAG peer-link port-channel. | ||
| domain | Integer | 127 |
Min: 0 Max: 255 |
||
| priority1 | Integer | Min: 0 Max: 255 |
default -> automatically set based on node_type. |
||
| priority2 | Integer | Min: 0 Max: 255 |
default -> (node_id modulus 256). |
||
| auto_clock_identity | Boolean | True |
If you prefer to have PTP clock identity be the system MAC-address of the switch, which is the default EOS behaviour, simply disable the automatic PTP clock identity. default -> (clock_identity_prefix = 00:1C:73 (default)) + (PTP priority 1 as HEX) + “:00:” + (PTP priority 2 as HEX). |
||
| clock_identity_prefix | String | PTP clock idetentiy 3-byte prefix. i.e. “01:02:03”. By default the 3-byte prefix is “00:1C:73”. This can be overridden if auto_clock_identity is set to true (which is the default). |
|||
| clock_identity | String | Set PTP clock identity manually. 6-byte value i.e. “01:02:03:04:05:06”. |
|||
| source_ip | String | By default in EOS, PTP packets are sourced with an IP address from the routed port or from the relevant SVI, which is the recommended behaviour. This can be set manually if required, for example, to a value of “10.1.2.3”. |
|||
| mode | String | boundary |
Valid Values: - boundary |
||
| mode_one_step | Boolean | False |
|||
| ttl | Integer | ||||
| forward_unicast | Boolean | False |
Enable PTP unicast forwarding. |
||
| dscp | Dictionary | ||||
| general_messages | Integer | ||||
| event_messages | Integer | ||||
| monitor | Dictionary | ||||
| enabled | Boolean | True |
|||
| threshold | Dictionary | ||||
| offset_from_master | Integer | 250 |
Min: 0 Max: 1000000000 |
||
| mean_path_delay | Integer | 1500 |
Min: 0 Max: 1000000000 |
||
| drop | Dictionary | ||||
| offset_from_master | Integer | Min: 0 Max: 1000000000 |
|||
| mean_path_delay | Integer | Min: 0 Max: 1000000000 |
|||
| missing_message | Dictionary | ||||
| intervals | Dictionary | ||||
| announce | Integer | Min: 2 Max: 255 |
|||
| follow_up | Integer | Min: 2 Max: 255 |
|||
| sync | Integer | Min: 2 Max: 255 |
|||
| sequence_ids | Dictionary | ||||
| enabled | Boolean | True |
|||
| announce | Integer | 3 |
Min: 2 Max: 255 |
||
| delay_resp | Integer | 3 |
Min: 2 Max: 255 |
||
| follow_up | Integer | 3 |
Min: 2 Max: 255 |
||
| sync | Integer | 3 |
Min: 2 Max: 255 |
||
| node_groups | List, items: Dictionary | Define variables related to all nodes part of this group. | |||
| - group | String | Required, Unique | The Node Group Name is used for MLAG domain unless set with ‘mlag_domain_id’. The Node Group Name is also used for peer description on downstream switches’ uplinks. |
||
| nodes | List, items: Dictionary | Define variables per node. | |||
| - name | String | Required, Unique | The Node Name is used as “hostname”. | ||
| ptp | Dictionary | ||||
| enabled | Boolean | False |
|||
| profile | String | aes67-r16-2016 |
Valid Values: - aes67- smpte2059-2- aes67-r16-2016 |
||
| mlag | Boolean | False |
Configure PTP on the MLAG peer-link port-channel when PTP is enabled. By default PTP will not be configured on the MLAG peer-link port-channel. | ||
| domain | Integer | 127 |
Min: 0 Max: 255 |
||
| priority1 | Integer | Min: 0 Max: 255 |
default -> automatically set based on node_type. |
||
| priority2 | Integer | Min: 0 Max: 255 |
default -> (node_id modulus 256). |
||
| auto_clock_identity | Boolean | True |
If you prefer to have PTP clock identity be the system MAC-address of the switch, which is the default EOS behaviour, simply disable the automatic PTP clock identity. default -> (clock_identity_prefix = 00:1C:73 (default)) + (PTP priority 1 as HEX) + “:00:” + (PTP priority 2 as HEX). |
||
| clock_identity_prefix | String | PTP clock idetentiy 3-byte prefix. i.e. “01:02:03”. By default the 3-byte prefix is “00:1C:73”. This can be overridden if auto_clock_identity is set to true (which is the default). |
|||
| clock_identity | String | Set PTP clock identity manually. 6-byte value i.e. “01:02:03:04:05:06”. |
|||
| source_ip | String | By default in EOS, PTP packets are sourced with an IP address from the routed port or from the relevant SVI, which is the recommended behaviour. This can be set manually if required, for example, to a value of “10.1.2.3”. |
|||
| mode | String | boundary |
Valid Values: - boundary |
||
| mode_one_step | Boolean | False |
|||
| ttl | Integer | ||||
| forward_unicast | Boolean | False |
Enable PTP unicast forwarding. |
||
| dscp | Dictionary | ||||
| general_messages | Integer | ||||
| event_messages | Integer | ||||
| monitor | Dictionary | ||||
| enabled | Boolean | True |
|||
| threshold | Dictionary | ||||
| offset_from_master | Integer | 250 |
Min: 0 Max: 1000000000 |
||
| mean_path_delay | Integer | 1500 |
Min: 0 Max: 1000000000 |
||
| drop | Dictionary | ||||
| offset_from_master | Integer | Min: 0 Max: 1000000000 |
|||
| mean_path_delay | Integer | Min: 0 Max: 1000000000 |
|||
| missing_message | Dictionary | ||||
| intervals | Dictionary | ||||
| announce | Integer | Min: 2 Max: 255 |
|||
| follow_up | Integer | Min: 2 Max: 255 |
|||
| sync | Integer | Min: 2 Max: 255 |
|||
| sequence_ids | Dictionary | ||||
| enabled | Boolean | True |
|||
| announce | Integer | 3 |
Min: 2 Max: 255 |
||
| delay_resp | Integer | 3 |
Min: 2 Max: 255 |
||
| follow_up | Integer | 3 |
Min: 2 Max: 255 |
||
| sync | Integer | 3 |
Min: 2 Max: 255 |
||
| ptp | Dictionary | ||||
| enabled | Boolean | False |
|||
| profile | String | aes67-r16-2016 |
Valid Values: - aes67- smpte2059-2- aes67-r16-2016 |
||
| mlag | Boolean | False |
Configure PTP on the MLAG peer-link port-channel when PTP is enabled. By default PTP will not be configured on the MLAG peer-link port-channel. | ||
| domain | Integer | 127 |
Min: 0 Max: 255 |
||
| priority1 | Integer | Min: 0 Max: 255 |
default -> automatically set based on node_type. |
||
| priority2 | Integer | Min: 0 Max: 255 |
default -> (node_id modulus 256). |
||
| auto_clock_identity | Boolean | True |
If you prefer to have PTP clock identity be the system MAC-address of the switch, which is the default EOS behaviour, simply disable the automatic PTP clock identity. default -> (clock_identity_prefix = 00:1C:73 (default)) + (PTP priority 1 as HEX) + “:00:” + (PTP priority 2 as HEX). |
||
| clock_identity_prefix | String | PTP clock idetentiy 3-byte prefix. i.e. “01:02:03”. By default the 3-byte prefix is “00:1C:73”. This can be overridden if auto_clock_identity is set to true (which is the default). |
|||
| clock_identity | String | Set PTP clock identity manually. 6-byte value i.e. “01:02:03:04:05:06”. |
|||
| source_ip | String | By default in EOS, PTP packets are sourced with an IP address from the routed port or from the relevant SVI, which is the recommended behaviour. This can be set manually if required, for example, to a value of “10.1.2.3”. |
|||
| mode | String | boundary |
Valid Values: - boundary |
||
| mode_one_step | Boolean | False |
|||
| ttl | Integer | ||||
| forward_unicast | Boolean | False |
Enable PTP unicast forwarding. |
||
| dscp | Dictionary | ||||
| general_messages | Integer | ||||
| event_messages | Integer | ||||
| monitor | Dictionary | ||||
| enabled | Boolean | True |
|||
| threshold | Dictionary | ||||
| offset_from_master | Integer | 250 |
Min: 0 Max: 1000000000 |
||
| mean_path_delay | Integer | 1500 |
Min: 0 Max: 1000000000 |
||
| drop | Dictionary | ||||
| offset_from_master | Integer | Min: 0 Max: 1000000000 |
|||
| mean_path_delay | Integer | Min: 0 Max: 1000000000 |
|||
| missing_message | Dictionary | ||||
| intervals | Dictionary | ||||
| announce | Integer | Min: 2 Max: 255 |
|||
| follow_up | Integer | Min: 2 Max: 255 |
|||
| sync | Integer | Min: 2 Max: 255 |
|||
| sequence_ids | Dictionary | ||||
| enabled | Boolean | True |
|||
| announce | Integer | 3 |
Min: 2 Max: 255 |
||
| delay_resp | Integer | 3 |
Min: 2 Max: 255 |
||
| follow_up | Integer | 3 |
Min: 2 Max: 255 |
||
| sync | Integer | 3 |
Min: 2 Max: 255 |
||
| nodes | List, items: Dictionary | Define variables per node. | |||
| - name | String | Required, Unique | The Node Name is used as “hostname”. | ||
| ptp | Dictionary | ||||
| enabled | Boolean | False |
|||
| profile | String | aes67-r16-2016 |
Valid Values: - aes67- smpte2059-2- aes67-r16-2016 |
||
| mlag | Boolean | False |
Configure PTP on the MLAG peer-link port-channel when PTP is enabled. By default PTP will not be configured on the MLAG peer-link port-channel. | ||
| domain | Integer | 127 |
Min: 0 Max: 255 |
||
| priority1 | Integer | Min: 0 Max: 255 |
default -> automatically set based on node_type. |
||
| priority2 | Integer | Min: 0 Max: 255 |
default -> (node_id modulus 256). |
||
| auto_clock_identity | Boolean | True |
If you prefer to have PTP clock identity be the system MAC-address of the switch, which is the default EOS behaviour, simply disable the automatic PTP clock identity. default -> (clock_identity_prefix = 00:1C:73 (default)) + (PTP priority 1 as HEX) + “:00:” + (PTP priority 2 as HEX). |
||
| clock_identity_prefix | String | PTP clock idetentiy 3-byte prefix. i.e. “01:02:03”. By default the 3-byte prefix is “00:1C:73”. This can be overridden if auto_clock_identity is set to true (which is the default). |
|||
| clock_identity | String | Set PTP clock identity manually. 6-byte value i.e. “01:02:03:04:05:06”. |
|||
| source_ip | String | By default in EOS, PTP packets are sourced with an IP address from the routed port or from the relevant SVI, which is the recommended behaviour. This can be set manually if required, for example, to a value of “10.1.2.3”. |
|||
| mode | String | boundary |
Valid Values: - boundary |
||
| mode_one_step | Boolean | False |
|||
| ttl | Integer | ||||
| forward_unicast | Boolean | False |
Enable PTP unicast forwarding. |
||
| dscp | Dictionary | ||||
| general_messages | Integer | ||||
| event_messages | Integer | ||||
| monitor | Dictionary | ||||
| enabled | Boolean | True |
|||
| threshold | Dictionary | ||||
| offset_from_master | Integer | 250 |
Min: 0 Max: 1000000000 |
||
| mean_path_delay | Integer | 1500 |
Min: 0 Max: 1000000000 |
||
| drop | Dictionary | ||||
| offset_from_master | Integer | Min: 0 Max: 1000000000 |
|||
| mean_path_delay | Integer | Min: 0 Max: 1000000000 |
|||
| missing_message | Dictionary | ||||
| intervals | Dictionary | ||||
| announce | Integer | Min: 2 Max: 255 |
|||
| follow_up | Integer | Min: 2 Max: 255 |
|||
| sync | Integer | Min: 2 Max: 255 |
|||
| sequence_ids | Dictionary | ||||
| enabled | Boolean | True |
|||
| announce | Integer | 3 |
Min: 2 Max: 255 |
||
| delay_resp | Integer | 3 |
Min: 2 Max: 255 |
||
| follow_up | Integer | 3 |
Min: 2 Max: 255 |
||
| sync | Integer | 3 |
Min: 2 Max: 255 |
<node_type_keys.key>:
# Define variables for all nodes of this type.
defaults:
ptp:
enabled: <bool; default=False>
profile: <str; "aes67" | "smpte2059-2" | "aes67-r16-2016"; default="aes67-r16-2016">
# Configure PTP on the MLAG peer-link port-channel when PTP is enabled. By default PTP will not be configured on the MLAG peer-link port-channel.
mlag: <bool; default=False>
domain: <int; 0-255; default=127>
# default -> automatically set based on node_type.
priority1: <int; 0-255>
# default -> (node_id modulus 256).
priority2: <int; 0-255>
# If you prefer to have PTP clock identity be the system MAC-address of the switch, which is the default EOS behaviour, simply disable the automatic PTP clock identity.
# default -> (clock_identity_prefix = 00:1C:73 (default)) + (PTP priority 1 as HEX) + ":00:" + (PTP priority 2 as HEX).
auto_clock_identity: <bool; default=True>
# PTP clock idetentiy 3-byte prefix. i.e. "01:02:03".
# By default the 3-byte prefix is "00:1C:73".
# This can be overridden if auto_clock_identity is set to true (which is the default).
clock_identity_prefix: <str>
# Set PTP clock identity manually. 6-byte value i.e. "01:02:03:04:05:06".
clock_identity: <str>
# By default in EOS, PTP packets are sourced with an IP address from the routed port or from the relevant SVI, which is the recommended behaviour.
# This can be set manually if required, for example, to a value of "10.1.2.3".
source_ip: <str>
mode: <str; "boundary"; default="boundary">
mode_one_step: <bool; default=False>
ttl: <int>
# Enable PTP unicast forwarding.
forward_unicast: <bool; default=False>
dscp:
general_messages: <int>
event_messages: <int>
monitor:
enabled: <bool; default=True>
threshold:
offset_from_master: <int; 0-1000000000; default=250>
mean_path_delay: <int; 0-1000000000; default=1500>
drop:
offset_from_master: <int; 0-1000000000>
mean_path_delay: <int; 0-1000000000>
missing_message:
intervals:
announce: <int; 2-255>
follow_up: <int; 2-255>
sync: <int; 2-255>
sequence_ids:
enabled: <bool; default=True>
announce: <int; 2-255; default=3>
delay_resp: <int; 2-255; default=3>
follow_up: <int; 2-255; default=3>
sync: <int; 2-255; default=3>
# Define variables related to all nodes part of this group.
node_groups:
# The Node Group Name is used for MLAG domain unless set with 'mlag_domain_id'.
# The Node Group Name is also used for peer description on downstream switches' uplinks.
- group: <str; required; unique>
# Define variables per node.
nodes:
# The Node Name is used as "hostname".
- name: <str; required; unique>
ptp:
enabled: <bool; default=False>
profile: <str; "aes67" | "smpte2059-2" | "aes67-r16-2016"; default="aes67-r16-2016">
# Configure PTP on the MLAG peer-link port-channel when PTP is enabled. By default PTP will not be configured on the MLAG peer-link port-channel.
mlag: <bool; default=False>
domain: <int; 0-255; default=127>
# default -> automatically set based on node_type.
priority1: <int; 0-255>
# default -> (node_id modulus 256).
priority2: <int; 0-255>
# If you prefer to have PTP clock identity be the system MAC-address of the switch, which is the default EOS behaviour, simply disable the automatic PTP clock identity.
# default -> (clock_identity_prefix = 00:1C:73 (default)) + (PTP priority 1 as HEX) + ":00:" + (PTP priority 2 as HEX).
auto_clock_identity: <bool; default=True>
# PTP clock idetentiy 3-byte prefix. i.e. "01:02:03".
# By default the 3-byte prefix is "00:1C:73".
# This can be overridden if auto_clock_identity is set to true (which is the default).
clock_identity_prefix: <str>
# Set PTP clock identity manually. 6-byte value i.e. "01:02:03:04:05:06".
clock_identity: <str>
# By default in EOS, PTP packets are sourced with an IP address from the routed port or from the relevant SVI, which is the recommended behaviour.
# This can be set manually if required, for example, to a value of "10.1.2.3".
source_ip: <str>
mode: <str; "boundary"; default="boundary">
mode_one_step: <bool; default=False>
ttl: <int>
# Enable PTP unicast forwarding.
forward_unicast: <bool; default=False>
dscp:
general_messages: <int>
event_messages: <int>
monitor:
enabled: <bool; default=True>
threshold:
offset_from_master: <int; 0-1000000000; default=250>
mean_path_delay: <int; 0-1000000000; default=1500>
drop:
offset_from_master: <int; 0-1000000000>
mean_path_delay: <int; 0-1000000000>
missing_message:
intervals:
announce: <int; 2-255>
follow_up: <int; 2-255>
sync: <int; 2-255>
sequence_ids:
enabled: <bool; default=True>
announce: <int; 2-255; default=3>
delay_resp: <int; 2-255; default=3>
follow_up: <int; 2-255; default=3>
sync: <int; 2-255; default=3>
ptp:
enabled: <bool; default=False>
profile: <str; "aes67" | "smpte2059-2" | "aes67-r16-2016"; default="aes67-r16-2016">
# Configure PTP on the MLAG peer-link port-channel when PTP is enabled. By default PTP will not be configured on the MLAG peer-link port-channel.
mlag: <bool; default=False>
domain: <int; 0-255; default=127>
# default -> automatically set based on node_type.
priority1: <int; 0-255>
# default -> (node_id modulus 256).
priority2: <int; 0-255>
# If you prefer to have PTP clock identity be the system MAC-address of the switch, which is the default EOS behaviour, simply disable the automatic PTP clock identity.
# default -> (clock_identity_prefix = 00:1C:73 (default)) + (PTP priority 1 as HEX) + ":00:" + (PTP priority 2 as HEX).
auto_clock_identity: <bool; default=True>
# PTP clock idetentiy 3-byte prefix. i.e. "01:02:03".
# By default the 3-byte prefix is "00:1C:73".
# This can be overridden if auto_clock_identity is set to true (which is the default).
clock_identity_prefix: <str>
# Set PTP clock identity manually. 6-byte value i.e. "01:02:03:04:05:06".
clock_identity: <str>
# By default in EOS, PTP packets are sourced with an IP address from the routed port or from the relevant SVI, which is the recommended behaviour.
# This can be set manually if required, for example, to a value of "10.1.2.3".
source_ip: <str>
mode: <str; "boundary"; default="boundary">
mode_one_step: <bool; default=False>
ttl: <int>
# Enable PTP unicast forwarding.
forward_unicast: <bool; default=False>
dscp:
general_messages: <int>
event_messages: <int>
monitor:
enabled: <bool; default=True>
threshold:
offset_from_master: <int; 0-1000000000; default=250>
mean_path_delay: <int; 0-1000000000; default=1500>
drop:
offset_from_master: <int; 0-1000000000>
mean_path_delay: <int; 0-1000000000>
missing_message:
intervals:
announce: <int; 2-255>
follow_up: <int; 2-255>
sync: <int; 2-255>
sequence_ids:
enabled: <bool; default=True>
announce: <int; 2-255; default=3>
delay_resp: <int; 2-255; default=3>
follow_up: <int; 2-255; default=3>
sync: <int; 2-255; default=3>
# Define variables per node.
nodes:
# The Node Name is used as "hostname".
- name: <str; required; unique>
ptp:
enabled: <bool; default=False>
profile: <str; "aes67" | "smpte2059-2" | "aes67-r16-2016"; default="aes67-r16-2016">
# Configure PTP on the MLAG peer-link port-channel when PTP is enabled. By default PTP will not be configured on the MLAG peer-link port-channel.
mlag: <bool; default=False>
domain: <int; 0-255; default=127>
# default -> automatically set based on node_type.
priority1: <int; 0-255>
# default -> (node_id modulus 256).
priority2: <int; 0-255>
# If you prefer to have PTP clock identity be the system MAC-address of the switch, which is the default EOS behaviour, simply disable the automatic PTP clock identity.
# default -> (clock_identity_prefix = 00:1C:73 (default)) + (PTP priority 1 as HEX) + ":00:" + (PTP priority 2 as HEX).
auto_clock_identity: <bool; default=True>
# PTP clock idetentiy 3-byte prefix. i.e. "01:02:03".
# By default the 3-byte prefix is "00:1C:73".
# This can be overridden if auto_clock_identity is set to true (which is the default).
clock_identity_prefix: <str>
# Set PTP clock identity manually. 6-byte value i.e. "01:02:03:04:05:06".
clock_identity: <str>
# By default in EOS, PTP packets are sourced with an IP address from the routed port or from the relevant SVI, which is the recommended behaviour.
# This can be set manually if required, for example, to a value of "10.1.2.3".
source_ip: <str>
mode: <str; "boundary"; default="boundary">
mode_one_step: <bool; default=False>
ttl: <int>
# Enable PTP unicast forwarding.
forward_unicast: <bool; default=False>
dscp:
general_messages: <int>
event_messages: <int>
monitor:
enabled: <bool; default=True>
threshold:
offset_from_master: <int; 0-1000000000; default=250>
mean_path_delay: <int; 0-1000000000; default=1500>
drop:
offset_from_master: <int; 0-1000000000>
mean_path_delay: <int; 0-1000000000>
missing_message:
intervals:
announce: <int; 2-255>
follow_up: <int; 2-255>
sync: <int; 2-255>
sequence_ids:
enabled: <bool; default=True>
announce: <int; 2-255; default=3>
delay_resp: <int; 2-255; default=3>
follow_up: <int; 2-255; default=3>
sync: <int; 2-255; default=3>
Default interface settings¶
- Set default uplink, downlink, and MLAG interfaces, which will be used if these interfaces are not defined on a device (either directly or through inheritance).
- These are defined based on the combination of node_type (e.g., l3leaf or spine) and a regex for matching the platform.
- A list of interfaces or interface ranges can be specified.
- Each list item supports range syntax that can be expanded into a list of interfaces. Interface range examples:
- Ethernet49-52/1: Expands to [ Ethernet49/1, Ethernet50/1, Ethernet51/1, Ethernet52/1 ]
- Ethernet1/31-34/1: Expands to [ Ethernet1/31/1, Ethernet1/32/1, Ethernet1/33/1, Ethernet1/34/1 ]
- Ethernet49-50,53-54: Expands to [ Ethernet49, Ethernet50, Ethernet53, Ethernet54 ]
- Ethernet1-2/1-4: Expands to [ Ethernet1/1, Ethernet1/2, Ethernet1/3, Ethernet1/4, Ethernet2/1, Ethernet2/2, Ethernet2/3, Ethernet2/4 ]
uplink_interfacesandmlag_interfacesunderdefault_interfacesare directly inherited byuplink_interfacesandmlag_interfaces.downlink_interfacesare referenced by the child switch (e.g., the leaf in a leaf/spine network). The child switch leverages an upstream switch’sdefault_downlink_interfacesusing the child switch ID. This is then used to builduplink_switch_interfacesfor that child.- In the case of
max_parallel_uplinks> 1 thedefault_downlink_interfacesare mapped with consecutive downlinks per child ID. - Example for
max_parallel_uplinks: 2, downlink interfaces will be mapped as[ <downlink1 to leaf-id1>, <downlink2 to leaf-id1>, <downlink1 to leaf-id2>, <downlink2 to leaf-id2> ...]
- In the case of
- Please note that no default interfaces are defined in AVD itself. You will need to create your own based on the example below.
Default interfaces example
| Variable | Type | Required | Default | Value Restrictions | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| default_interfaces | List, items: Dictionary | Default uplink, downlink, and MLAG interfaces, which will be used if these interfaces are not defined on a device (either directly or through inheritance). |
|||
| - types | List, items: String | Required | List of node type keys. | ||
| - <str> | String | ||||
| platforms | List, items: String | Required | List of platform families. This is defined as a Python regular expression that matches the full platform type. |
||
| - <str> | String | Arista platform family regular expression. | |||
| uplink_interfaces | List, items: String | List of uplink interfaces or uplink interface ranges. | |||
| - <str> | String | Interface range or interface. | |||
| mlag_interfaces | List, items: String | List of MLAG interfaces or MLAG interface ranges. | |||
| - <str> | String | Interface range or interface. | |||
| downlink_interfaces | List, items: String | List of downlink interfaces or downlink interface ranges. | |||
| - <str> | String | Interface range or interface. |
# Default uplink, downlink, and MLAG interfaces, which will be used if these interfaces are not defined on a device (either directly or through inheritance).
default_interfaces:
# List of node type keys.
- types: # required
- <str>
# List of platform families.
# This is defined as a Python regular expression that matches the full platform type.
platforms: # required
# Arista platform family regular expression.
- <str>
# List of uplink interfaces or uplink interface ranges.
uplink_interfaces:
# Interface range or interface.
- <str>
# List of MLAG interfaces or MLAG interface ranges.
mlag_interfaces:
# Interface range or interface.
- <str>
# List of downlink interfaces or downlink interface ranges.
downlink_interfaces:
# Interface range or interface.
- <str>
L3 edge and DCI settings¶
The l3_edge data model can be used to configure extra L3 P2P links anywhere in the fabric. It can be between two switches that are already part of the fabric inventory, or it can be towards another device, where only one end of the link is on a switch in the fabric.
The data model supports using IP pools, Subnet per link, specifying the IP addresses manually or using ipv6 with rfc5549. One of these options must be set.
For BGP peerings the AS number must be specified. If the AS number is different than the AS number configured for the node, the local-as will be replaced on this BGP peering (neighbor <ip> local-as <as> no-prepend replace-as).
Make sure to configure the variables in a group_vars file covering all devices mentioned in the data model.
| Variable | Type | Required | Default | Value Restrictions | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| l3_edge | Dictionary | ||||
| p2p_links_ip_pools | List, items: Dictionary | ||||
| - name | String | Required, Unique | P2P pool name. | ||
| ipv4_pool | String | IPv4 address/Mask. | |||
| prefix_size | Integer | 31 |
Min: 8 Max: 31 |
Subnet mask size. | |
| p2p_links_profiles | List, items: Dictionary | ||||
| - name | String | Required, Unique | P2P profile name. Any variable supported under p2p_links can be inherited from a profile. |
||
| id | Integer | Unique id per subnet_summary. Used to calculate ip addresses. Required with ip_pool. ID starting from 1. |
|||
| speed | String | Speed should be set in the format <interface_speed> or forced <interface_speed> or auto <interface_speed>. |
|||
| ip_pool | String | P2P pool name. IP Pool defined under p2p_links_ip_pools. A /31 will be taken from the pool per P2P link. | |||
| subnet | String | IPv4 address/Mask. Subnet used on this P2P link. | |||
| ip | List, items: String | Specific IP addresses used on this P2P link. | |||
| - <str> | String | Node IPv4 address/Mask. | |||
| ipv6_enable | Boolean | False |
Allows turning on ipv6 for the link or profile (also autodetected based on underlay_rfc5549 and include_in_underlay_protocol). | ||
| nodes | List, items: String | Nodes where this link should be configured. | |||
| - <str> | String | The values can be < node_a >, < node_b >. ex.- [ core-1-isis-sr-ldp, core-2-ospf-ldp ]. |
|||
| interfaces | List, items: String | Interfaces where this link should be configured and Required unless using port-channels. | |||
| - <str> | String | The value can be like < node_a_interface >, < node_b_interface >. ex. - [ Ethernet2, Ethernet2 ]. |
|||
| as | List, items: String | AS numbers for BGP. Required with bgp peering. |
|||
| - <str> | String | The values can be like [“node_a_as”, “node_b_as”]. | |||
| descriptions | List, items: String | Interface description. | |||
| - <str> | String | ||||
| include_in_underlay_protocol | Boolean | True |
Add this interface to underlay routing protocol. | ||
| isis_hello_padding | Boolean | False |
|||
| isis_metric | Integer | ||||
| isis_circuit_type | String | Valid Values: - level-1- level-2- level-1-2 |
|||
| isis_authentication_mode | String | Valid Values: - md5- text |
|||
| isis_authentication_key | String | Type-7 encrypted password. | |||
| mpls_ip | Boolean | MPLS parameters. Default value is true if switch.mpls_lsr is true. | |||
| mpls_ldp | Boolean | MPLS parameters. Default value is true for ldp underlay variants, otherwise false. | |||
| mtu | Integer | MTU for this P2P link. Default value same as p2p_uplinks_mtu. | |||
| bfd | Boolean | False |
Enable BFD (only considered for BGP). | ||
| ptp | Dictionary | PTP parameters. | |||
| enabled | Boolean | False |
Enable PTP. | ||
| sflow | Boolean | Enable sFlow. Overrides fabric_sflow setting. |
|||
| underlay_multicast | Boolean | False |
Enable PIM sparse mode. Requires include_in_underlay_protocol and the global underlay_multicast to be true. |
||
| flow_tracking | Dictionary | Enable flow-tracking. Overrides fabric_flow_tracking setting. |
|||
| enabled | Boolean | ||||
| name | String | Flow tracker name as defined in flow_tracking_settings. | |||
| qos_profile | String | QOS service profile. | |||
| macsec_profile | String | MAC security profile. | |||
| port_channel | Dictionary | Port-channel parameters. | |||
| mode | String | active |
|||
| nodes_child_interfaces | List, items: Dictionary | ||||
| - node | String | Required, Unique | |||
| interfaces | List, items: String | List of node interfaces. Ex.- [ ‘node1 interface1’, ‘node1 interface2’ ]. | |||
| - <str> | String | ||||
| channel_id | Integer | Port-Channel ID. If no channel_id is specified, an id is generated from the first switch port in the port channel. | |||
| raw_eos_cli | String | EOS CLI rendered directly on the point-to-point interface in the final EOS configuration. | |||
| routing_protocol | String | Valid Values: - ebgp |
Enables deviation of the routing protocol used on this link from the fabric underlay default. - ebgp: Enforce plain IPv4 BGP peering |
||
| structured_config | Dictionary | Custom structured config for interfaces. Note! The content of this dictionary is not validated by the schema, since it can be either ethernet_interfaces or port_channel_interfaces. |
|||
| p2p_links | List, items: Dictionary | ||||
| - nodes | List, items: String | Required | Nodes where this link should be configured. | ||
| - <str> | String | The values can be < node_a >, < node_b >. ex.- [ core-1-isis-sr-ldp, core-2-ospf-ldp ]. |
|||
| profile | String | P2P profile name. Profile defined under p2p_profiles. | |||
| id | Integer | Unique id per subnet_summary. Used to calculate ip addresses. Required with ip_pool. ID starting from 1. |
|||
| speed | String | Speed should be set in the format <interface_speed> or forced <interface_speed> or auto <interface_speed>. |
|||
| ip_pool | String | P2P pool name. IP Pool defined under p2p_links_ip_pools. A /31 will be taken from the pool per P2P link. | |||
| subnet | String | IPv4 address/Mask. Subnet used on this P2P link. | |||
| ip | List, items: String | Specific IP addresses used on this P2P link. | |||
| - <str> | String | Node IPv4 address/Mask. | |||
| ipv6_enable | Boolean | False |
Allows turning on ipv6 for the link or profile (also autodetected based on underlay_rfc5549 and include_in_underlay_protocol). | ||
| interfaces | List, items: String | Interfaces where this link should be configured and Required unless using port-channels. | |||
| - <str> | String | The value can be like < node_a_interface >, < node_b_interface >. ex. - [ Ethernet2, Ethernet2 ]. |
|||
| as | List, items: String | AS numbers for BGP. Required with bgp peering. |
|||
| - <str> | String | The values can be like [“node_a_as”, “node_b_as”]. | |||
| descriptions | List, items: String | Interface description. | |||
| - <str> | String | ||||
| include_in_underlay_protocol | Boolean | True |
Add this interface to underlay routing protocol. | ||
| isis_hello_padding | Boolean | False |
|||
| isis_metric | Integer | ||||
| isis_circuit_type | String | Valid Values: - level-1- level-2- level-1-2 |
|||
| isis_authentication_mode | String | Valid Values: - md5- text |
|||
| isis_authentication_key | String | Type-7 encrypted password. | |||
| mpls_ip | Boolean | MPLS parameters. Default value is true if switch.mpls_lsr is true. | |||
| mpls_ldp | Boolean | MPLS parameters. Default value is true for ldp underlay variants, otherwise false. | |||
| mtu | Integer | MTU for this P2P link. Default value same as p2p_uplinks_mtu. | |||
| bfd | Boolean | False |
Enable BFD (only considered for BGP). | ||
| ptp | Dictionary | PTP parameters. | |||
| enabled | Boolean | False |
Enable PTP. | ||
| sflow | Boolean | Enable sFlow. Overrides fabric_sflow setting. |
|||
| underlay_multicast | Boolean | False |
Enable PIM sparse mode. Requires include_in_underlay_protocol and the global underlay_multicast to be true. |
||
| flow_tracking | Dictionary | Enable flow-tracking. Overrides fabric_flow_tracking setting. |
|||
| enabled | Boolean | ||||
| name | String | Flow tracker name as defined in flow_tracking_settings. | |||
| qos_profile | String | QOS service profile. | |||
| macsec_profile | String | MAC security profile. | |||
| port_channel | Dictionary | Port-channel parameters. | |||
| mode | String | active |
|||
| nodes_child_interfaces | List, items: Dictionary | ||||
| - node | String | Required, Unique | |||
| interfaces | List, items: String | List of node interfaces. Ex.- [ ‘node1 interface1’, ‘node1 interface2’ ]. | |||
| - <str> | String | ||||
| channel_id | Integer | Port-Channel ID. If no channel_id is specified, an id is generated from the first switch port in the port channel. | |||
| raw_eos_cli | String | EOS CLI rendered directly on the point-to-point interface in the final EOS configuration. | |||
| routing_protocol | String | Valid Values: - ebgp |
Enables deviation of the routing protocol used on this link from the fabric underlay default. - ebgp: Enforce plain IPv4 BGP peering |
||
| structured_config | Dictionary | Custom structured config for interfaces. Note! The content of this dictionary is not validated by the schema, since it can be either ethernet_interfaces or port_channel_interfaces. |
l3_edge:
p2p_links_ip_pools:
# P2P pool name.
- name: <str; required; unique>
# IPv4 address/Mask.
ipv4_pool: <str>
# Subnet mask size.
prefix_size: <int; 8-31; default=31>
p2p_links_profiles:
# P2P profile name. Any variable supported under `p2p_links` can be inherited from a profile.
- name: <str; required; unique>
# Unique id per subnet_summary. Used to calculate ip addresses.
# Required with ip_pool. ID starting from 1.
id: <int>
# Speed should be set in the format `<interface_speed>` or `forced <interface_speed>` or `auto <interface_speed>`.
speed: <str>
# P2P pool name. IP Pool defined under p2p_links_ip_pools. A /31 will be taken from the pool per P2P link.
ip_pool: <str>
# IPv4 address/Mask. Subnet used on this P2P link.
subnet: <str>
# Specific IP addresses used on this P2P link.
ip:
# Node IPv4 address/Mask.
- <str>
# Allows turning on ipv6 for the link or profile (also autodetected based on underlay_rfc5549 and include_in_underlay_protocol).
ipv6_enable: <bool; default=False>
# Nodes where this link should be configured.
nodes:
# The values can be < node_a >, < node_b >.
# ex.- [ core-1-isis-sr-ldp, core-2-ospf-ldp ].
- <str>
# Interfaces where this link should be configured and Required unless using port-channels.
interfaces:
# The value can be like < node_a_interface >, < node_b_interface >.
# ex. - [ Ethernet2, Ethernet2 ].
- <str>
# AS numbers for BGP.
# Required with bgp peering.
as:
# The values can be like ["node_a_as", "node_b_as"].
- <str>
# Interface description.
descriptions:
- <str>
# Add this interface to underlay routing protocol.
include_in_underlay_protocol: <bool; default=True>
isis_hello_padding: <bool; default=False>
isis_metric: <int>
isis_circuit_type: <str; "level-1" | "level-2" | "level-1-2">
isis_authentication_mode: <str; "md5" | "text">
# Type-7 encrypted password.
isis_authentication_key: <str>
# MPLS parameters. Default value is true if switch.mpls_lsr is true.
mpls_ip: <bool>
# MPLS parameters. Default value is true for ldp underlay variants, otherwise false.
mpls_ldp: <bool>
# MTU for this P2P link. Default value same as p2p_uplinks_mtu.
mtu: <int>
# Enable BFD (only considered for BGP).
bfd: <bool; default=False>
# PTP parameters.
ptp:
# Enable PTP.
enabled: <bool; default=False>
# Enable sFlow. Overrides `fabric_sflow` setting.
sflow: <bool>
# Enable PIM sparse mode. Requires `include_in_underlay_protocol` and the global `underlay_multicast` to be `true`.
underlay_multicast: <bool; default=False>
# Enable flow-tracking. Overrides `fabric_flow_tracking` setting.
flow_tracking:
enabled: <bool>
# Flow tracker name as defined in flow_tracking_settings.
name: <str>
# QOS service profile.
qos_profile: <str>
# MAC security profile.
macsec_profile: <str>
# Port-channel parameters.
port_channel:
mode: <str; default="active">
nodes_child_interfaces:
- node: <str; required; unique>
# List of node interfaces. Ex.- [ 'node1 interface1', 'node1 interface2' ].
interfaces:
- <str>
# Port-Channel ID. If no channel_id is specified, an id is generated from the first switch port in the port channel.
channel_id: <int>
# EOS CLI rendered directly on the point-to-point interface in the final EOS configuration.
raw_eos_cli: <str>
# Enables deviation of the routing protocol used on this link from the fabric underlay default.
# - ebgp: Enforce plain IPv4 BGP peering
routing_protocol: <str; "ebgp">
# Custom structured config for interfaces.
# Note! The content of this dictionary is _not_ validated by the schema, since it can be either ethernet_interfaces or port_channel_interfaces.
structured_config: <dict>
p2p_links:
# Nodes where this link should be configured.
- nodes: # required
# The values can be < node_a >, < node_b >.
# ex.- [ core-1-isis-sr-ldp, core-2-ospf-ldp ].
- <str>
# P2P profile name. Profile defined under p2p_profiles.
profile: <str>
# Unique id per subnet_summary. Used to calculate ip addresses.
# Required with ip_pool. ID starting from 1.
id: <int>
# Speed should be set in the format `<interface_speed>` or `forced <interface_speed>` or `auto <interface_speed>`.
speed: <str>
# P2P pool name. IP Pool defined under p2p_links_ip_pools. A /31 will be taken from the pool per P2P link.
ip_pool: <str>
# IPv4 address/Mask. Subnet used on this P2P link.
subnet: <str>
# Specific IP addresses used on this P2P link.
ip:
# Node IPv4 address/Mask.
- <str>
# Allows turning on ipv6 for the link or profile (also autodetected based on underlay_rfc5549 and include_in_underlay_protocol).
ipv6_enable: <bool; default=False>
# Interfaces where this link should be configured and Required unless using port-channels.
interfaces:
# The value can be like < node_a_interface >, < node_b_interface >.
# ex. - [ Ethernet2, Ethernet2 ].
- <str>
# AS numbers for BGP.
# Required with bgp peering.
as:
# The values can be like ["node_a_as", "node_b_as"].
- <str>
# Interface description.
descriptions:
- <str>
# Add this interface to underlay routing protocol.
include_in_underlay_protocol: <bool; default=True>
isis_hello_padding: <bool; default=False>
isis_metric: <int>
isis_circuit_type: <str; "level-1" | "level-2" | "level-1-2">
isis_authentication_mode: <str; "md5" | "text">
# Type-7 encrypted password.
isis_authentication_key: <str>
# MPLS parameters. Default value is true if switch.mpls_lsr is true.
mpls_ip: <bool>
# MPLS parameters. Default value is true for ldp underlay variants, otherwise false.
mpls_ldp: <bool>
# MTU for this P2P link. Default value same as p2p_uplinks_mtu.
mtu: <int>
# Enable BFD (only considered for BGP).
bfd: <bool; default=False>
# PTP parameters.
ptp:
# Enable PTP.
enabled: <bool; default=False>
# Enable sFlow. Overrides `fabric_sflow` setting.
sflow: <bool>
# Enable PIM sparse mode. Requires `include_in_underlay_protocol` and the global `underlay_multicast` to be `true`.
underlay_multicast: <bool; default=False>
# Enable flow-tracking. Overrides `fabric_flow_tracking` setting.
flow_tracking:
enabled: <bool>
# Flow tracker name as defined in flow_tracking_settings.
name: <str>
# QOS service profile.
qos_profile: <str>
# MAC security profile.
macsec_profile: <str>
# Port-channel parameters.
port_channel:
mode: <str; default="active">
nodes_child_interfaces:
- node: <str; required; unique>
# List of node interfaces. Ex.- [ 'node1 interface1', 'node1 interface2' ].
interfaces:
- <str>
# Port-Channel ID. If no channel_id is specified, an id is generated from the first switch port in the port channel.
channel_id: <int>
# EOS CLI rendered directly on the point-to-point interface in the final EOS configuration.
raw_eos_cli: <str>
# Enables deviation of the routing protocol used on this link from the fabric underlay default.
# - ebgp: Enforce plain IPv4 BGP peering
routing_protocol: <str; "ebgp">
# Custom structured config for interfaces.
# Note! The content of this dictionary is _not_ validated by the schema, since it can be either ethernet_interfaces or port_channel_interfaces.
structured_config: <dict>
Core interfaces settings¶
The core_interfaces data model can be used to configure L3 P2P links anywhere in the fabric. It can be between two switches that are already part of the fabric inventory, or it can be towards another device, where only one end of the link is on a switch in the fabric.
The data model supports using IP pools, Subnet per link or specifying the IP addresses manually.
For BGP peerings the AS number must be specified. If the AS number is different than the AS number configured for the node, the local-as will be replaced on this BGP peering (neighbor <ip> local-as <as> no-prepend replace-as).
Make sure to configure the variables in a group_vars file covering all devices mentioned in the data model.
| Variable | Type | Required | Default | Value Restrictions | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| core_interfaces | Dictionary | ||||
| p2p_links_ip_pools | List, items: Dictionary | ||||
| - name | String | Required, Unique | P2P pool name. | ||
| ipv4_pool | String | IPv4 address/Mask. | |||
| prefix_size | Integer | 31 |
Min: 8 Max: 31 |
Subnet mask size. | |
| p2p_links_profiles | List, items: Dictionary | ||||
| - name | String | Required, Unique | P2P profile name. Any variable supported under p2p_links can be inherited from a profile. |
||
| id | Integer | Unique id per subnet_summary. Used to calculate ip addresses. Required with ip_pool. ID starting from 1. |
|||
| speed | String | Speed should be set in the format <interface_speed> or forced <interface_speed> or auto <interface_speed>. |
|||
| ip_pool | String | P2P pool name. IP Pool defined under p2p_links_ip_pools. A /31 will be taken from the pool per P2P link. | |||
| subnet | String | IPv4 address/Mask. Subnet used on this P2P link. | |||
| ip | List, items: String | Specific IP addresses used on this P2P link. | |||
| - <str> | String | Node IPv4 address/Mask. | |||
| ipv6_enable | Boolean | False |
Allows turning on ipv6 for the link or profile (also autodetected based on underlay_rfc5549 and include_in_underlay_protocol). | ||
| nodes | List, items: String | Nodes where this link should be configured. | |||
| - <str> | String | The values can be < node_a >, < node_b >. ex.- [ core-1-isis-sr-ldp, core-2-ospf-ldp ]. |
|||
| interfaces | List, items: String | Interfaces where this link should be configured and Required unless using port-channels. | |||
| - <str> | String | The value can be like < node_a_interface >, < node_b_interface >. ex. - [ Ethernet2, Ethernet2 ]. |
|||
| as | List, items: String | AS numbers for BGP. Required with bgp peering. |
|||
| - <str> | String | The values can be like [“node_a_as”, “node_b_as”]. | |||
| descriptions | List, items: String | Interface description. | |||
| - <str> | String | ||||
| include_in_underlay_protocol | Boolean | True |
Add this interface to underlay routing protocol. | ||
| isis_hello_padding | Boolean | False |
|||
| isis_metric | Integer | ||||
| isis_circuit_type | String | Valid Values: - level-1- level-2- level-1-2 |
|||
| isis_authentication_mode | String | Valid Values: - md5- text |
|||
| isis_authentication_key | String | Type-7 encrypted password. | |||
| mpls_ip | Boolean | MPLS parameters. Default value is true if switch.mpls_lsr is true. | |||
| mpls_ldp | Boolean | MPLS parameters. Default value is true for ldp underlay variants, otherwise false. | |||
| mtu | Integer | MTU for this P2P link. Default value same as p2p_uplinks_mtu. | |||
| bfd | Boolean | False |
Enable BFD (only considered for BGP). | ||
| ptp | Dictionary | PTP parameters. | |||
| enabled | Boolean | False |
Enable PTP. | ||
| sflow | Boolean | Enable sFlow. Overrides fabric_sflow setting. |
|||
| underlay_multicast | Boolean | False |
Enable PIM sparse mode. Requires include_in_underlay_protocol and the global underlay_multicast to be true. |
||
| flow_tracking | Dictionary | Enable flow-tracking. Overrides fabric_flow_tracking setting. |
|||
| enabled | Boolean | ||||
| name | String | Flow tracker name as defined in flow_tracking_settings. | |||
| qos_profile | String | QOS service profile. | |||
| macsec_profile | String | MAC security profile. | |||
| port_channel | Dictionary | Port-channel parameters. | |||
| mode | String | active |
|||
| nodes_child_interfaces | List, items: Dictionary | ||||
| - node | String | Required, Unique | |||
| interfaces | List, items: String | List of node interfaces. Ex.- [ ‘node1 interface1’, ‘node1 interface2’ ]. | |||
| - <str> | String | ||||
| channel_id | Integer | Port-Channel ID. If no channel_id is specified, an id is generated from the first switch port in the port channel. | |||
| raw_eos_cli | String | EOS CLI rendered directly on the point-to-point interface in the final EOS configuration. | |||
| routing_protocol | String | Valid Values: - ebgp |
Enables deviation of the routing protocol used on this link from the fabric underlay default. - ebgp: Enforce plain IPv4 BGP peering |
||
| structured_config | Dictionary | Custom structured config for interfaces. Note! The content of this dictionary is not validated by the schema, since it can be either ethernet_interfaces or port_channel_interfaces. |
|||
| p2p_links | List, items: Dictionary | ||||
| - nodes | List, items: String | Required | Nodes where this link should be configured. | ||
| - <str> | String | The values can be < node_a >, < node_b >. ex.- [ core-1-isis-sr-ldp, core-2-ospf-ldp ]. |
|||
| profile | String | P2P profile name. Profile defined under p2p_profiles. | |||
| id | Integer | Unique id per subnet_summary. Used to calculate ip addresses. Required with ip_pool. ID starting from 1. |
|||
| speed | String | Speed should be set in the format <interface_speed> or forced <interface_speed> or auto <interface_speed>. |
|||
| ip_pool | String | P2P pool name. IP Pool defined under p2p_links_ip_pools. A /31 will be taken from the pool per P2P link. | |||
| subnet | String | IPv4 address/Mask. Subnet used on this P2P link. | |||
| ip | List, items: String | Specific IP addresses used on this P2P link. | |||
| - <str> | String | Node IPv4 address/Mask. | |||
| ipv6_enable | Boolean | False |
Allows turning on ipv6 for the link or profile (also autodetected based on underlay_rfc5549 and include_in_underlay_protocol). | ||
| interfaces | List, items: String | Interfaces where this link should be configured and Required unless using port-channels. | |||
| - <str> | String | The value can be like < node_a_interface >, < node_b_interface >. ex. - [ Ethernet2, Ethernet2 ]. |
|||
| as | List, items: String | AS numbers for BGP. Required with bgp peering. |
|||
| - <str> | String | The values can be like [“node_a_as”, “node_b_as”]. | |||
| descriptions | List, items: String | Interface description. | |||
| - <str> | String | ||||
| include_in_underlay_protocol | Boolean | True |
Add this interface to underlay routing protocol. | ||
| isis_hello_padding | Boolean | False |
|||
| isis_metric | Integer | ||||
| isis_circuit_type | String | Valid Values: - level-1- level-2- level-1-2 |
|||
| isis_authentication_mode | String | Valid Values: - md5- text |
|||
| isis_authentication_key | String | Type-7 encrypted password. | |||
| mpls_ip | Boolean | MPLS parameters. Default value is true if switch.mpls_lsr is true. | |||
| mpls_ldp | Boolean | MPLS parameters. Default value is true for ldp underlay variants, otherwise false. | |||
| mtu | Integer | MTU for this P2P link. Default value same as p2p_uplinks_mtu. | |||
| bfd | Boolean | False |
Enable BFD (only considered for BGP). | ||
| ptp | Dictionary | PTP parameters. | |||
| enabled | Boolean | False |
Enable PTP. | ||
| sflow | Boolean | Enable sFlow. Overrides fabric_sflow setting. |
|||
| underlay_multicast | Boolean | False |
Enable PIM sparse mode. Requires include_in_underlay_protocol and the global underlay_multicast to be true. |
||
| flow_tracking | Dictionary | Enable flow-tracking. Overrides fabric_flow_tracking setting. |
|||
| enabled | Boolean | ||||
| name | String | Flow tracker name as defined in flow_tracking_settings. | |||
| qos_profile | String | QOS service profile. | |||
| macsec_profile | String | MAC security profile. | |||
| port_channel | Dictionary | Port-channel parameters. | |||
| mode | String | active |
|||
| nodes_child_interfaces | List, items: Dictionary | ||||
| - node | String | Required, Unique | |||
| interfaces | List, items: String | List of node interfaces. Ex.- [ ‘node1 interface1’, ‘node1 interface2’ ]. | |||
| - <str> | String | ||||
| channel_id | Integer | Port-Channel ID. If no channel_id is specified, an id is generated from the first switch port in the port channel. | |||
| raw_eos_cli | String | EOS CLI rendered directly on the point-to-point interface in the final EOS configuration. | |||
| routing_protocol | String | Valid Values: - ebgp |
Enables deviation of the routing protocol used on this link from the fabric underlay default. - ebgp: Enforce plain IPv4 BGP peering |
||
| structured_config | Dictionary | Custom structured config for interfaces. Note! The content of this dictionary is not validated by the schema, since it can be either ethernet_interfaces or port_channel_interfaces. |
core_interfaces:
p2p_links_ip_pools:
# P2P pool name.
- name: <str; required; unique>
# IPv4 address/Mask.
ipv4_pool: <str>
# Subnet mask size.
prefix_size: <int; 8-31; default=31>
p2p_links_profiles:
# P2P profile name. Any variable supported under `p2p_links` can be inherited from a profile.
- name: <str; required; unique>
# Unique id per subnet_summary. Used to calculate ip addresses.
# Required with ip_pool. ID starting from 1.
id: <int>
# Speed should be set in the format `<interface_speed>` or `forced <interface_speed>` or `auto <interface_speed>`.
speed: <str>
# P2P pool name. IP Pool defined under p2p_links_ip_pools. A /31 will be taken from the pool per P2P link.
ip_pool: <str>
# IPv4 address/Mask. Subnet used on this P2P link.
subnet: <str>
# Specific IP addresses used on this P2P link.
ip:
# Node IPv4 address/Mask.
- <str>
# Allows turning on ipv6 for the link or profile (also autodetected based on underlay_rfc5549 and include_in_underlay_protocol).
ipv6_enable: <bool; default=False>
# Nodes where this link should be configured.
nodes:
# The values can be < node_a >, < node_b >.
# ex.- [ core-1-isis-sr-ldp, core-2-ospf-ldp ].
- <str>
# Interfaces where this link should be configured and Required unless using port-channels.
interfaces:
# The value can be like < node_a_interface >, < node_b_interface >.
# ex. - [ Ethernet2, Ethernet2 ].
- <str>
# AS numbers for BGP.
# Required with bgp peering.
as:
# The values can be like ["node_a_as", "node_b_as"].
- <str>
# Interface description.
descriptions:
- <str>
# Add this interface to underlay routing protocol.
include_in_underlay_protocol: <bool; default=True>
isis_hello_padding: <bool; default=False>
isis_metric: <int>
isis_circuit_type: <str; "level-1" | "level-2" | "level-1-2">
isis_authentication_mode: <str; "md5" | "text">
# Type-7 encrypted password.
isis_authentication_key: <str>
# MPLS parameters. Default value is true if switch.mpls_lsr is true.
mpls_ip: <bool>
# MPLS parameters. Default value is true for ldp underlay variants, otherwise false.
mpls_ldp: <bool>
# MTU for this P2P link. Default value same as p2p_uplinks_mtu.
mtu: <int>
# Enable BFD (only considered for BGP).
bfd: <bool; default=False>
# PTP parameters.
ptp:
# Enable PTP.
enabled: <bool; default=False>
# Enable sFlow. Overrides `fabric_sflow` setting.
sflow: <bool>
# Enable PIM sparse mode. Requires `include_in_underlay_protocol` and the global `underlay_multicast` to be `true`.
underlay_multicast: <bool; default=False>
# Enable flow-tracking. Overrides `fabric_flow_tracking` setting.
flow_tracking:
enabled: <bool>
# Flow tracker name as defined in flow_tracking_settings.
name: <str>
# QOS service profile.
qos_profile: <str>
# MAC security profile.
macsec_profile: <str>
# Port-channel parameters.
port_channel:
mode: <str; default="active">
nodes_child_interfaces:
- node: <str; required; unique>
# List of node interfaces. Ex.- [ 'node1 interface1', 'node1 interface2' ].
interfaces:
- <str>
# Port-Channel ID. If no channel_id is specified, an id is generated from the first switch port in the port channel.
channel_id: <int>
# EOS CLI rendered directly on the point-to-point interface in the final EOS configuration.
raw_eos_cli: <str>
# Enables deviation of the routing protocol used on this link from the fabric underlay default.
# - ebgp: Enforce plain IPv4 BGP peering
routing_protocol: <str; "ebgp">
# Custom structured config for interfaces.
# Note! The content of this dictionary is _not_ validated by the schema, since it can be either ethernet_interfaces or port_channel_interfaces.
structured_config: <dict>
p2p_links:
# Nodes where this link should be configured.
- nodes: # required
# The values can be < node_a >, < node_b >.
# ex.- [ core-1-isis-sr-ldp, core-2-ospf-ldp ].
- <str>
# P2P profile name. Profile defined under p2p_profiles.
profile: <str>
# Unique id per subnet_summary. Used to calculate ip addresses.
# Required with ip_pool. ID starting from 1.
id: <int>
# Speed should be set in the format `<interface_speed>` or `forced <interface_speed>` or `auto <interface_speed>`.
speed: <str>
# P2P pool name. IP Pool defined under p2p_links_ip_pools. A /31 will be taken from the pool per P2P link.
ip_pool: <str>
# IPv4 address/Mask. Subnet used on this P2P link.
subnet: <str>
# Specific IP addresses used on this P2P link.
ip:
# Node IPv4 address/Mask.
- <str>
# Allows turning on ipv6 for the link or profile (also autodetected based on underlay_rfc5549 and include_in_underlay_protocol).
ipv6_enable: <bool; default=False>
# Interfaces where this link should be configured and Required unless using port-channels.
interfaces:
# The value can be like < node_a_interface >, < node_b_interface >.
# ex. - [ Ethernet2, Ethernet2 ].
- <str>
# AS numbers for BGP.
# Required with bgp peering.
as:
# The values can be like ["node_a_as", "node_b_as"].
- <str>
# Interface description.
descriptions:
- <str>
# Add this interface to underlay routing protocol.
include_in_underlay_protocol: <bool; default=True>
isis_hello_padding: <bool; default=False>
isis_metric: <int>
isis_circuit_type: <str; "level-1" | "level-2" | "level-1-2">
isis_authentication_mode: <str; "md5" | "text">
# Type-7 encrypted password.
isis_authentication_key: <str>
# MPLS parameters. Default value is true if switch.mpls_lsr is true.
mpls_ip: <bool>
# MPLS parameters. Default value is true for ldp underlay variants, otherwise false.
mpls_ldp: <bool>
# MTU for this P2P link. Default value same as p2p_uplinks_mtu.
mtu: <int>
# Enable BFD (only considered for BGP).
bfd: <bool; default=False>
# PTP parameters.
ptp:
# Enable PTP.
enabled: <bool; default=False>
# Enable sFlow. Overrides `fabric_sflow` setting.
sflow: <bool>
# Enable PIM sparse mode. Requires `include_in_underlay_protocol` and the global `underlay_multicast` to be `true`.
underlay_multicast: <bool; default=False>
# Enable flow-tracking. Overrides `fabric_flow_tracking` setting.
flow_tracking:
enabled: <bool>
# Flow tracker name as defined in flow_tracking_settings.
name: <str>
# QOS service profile.
qos_profile: <str>
# MAC security profile.
macsec_profile: <str>
# Port-channel parameters.
port_channel:
mode: <str; default="active">
nodes_child_interfaces:
- node: <str; required; unique>
# List of node interfaces. Ex.- [ 'node1 interface1', 'node1 interface2' ].
interfaces:
- <str>
# Port-Channel ID. If no channel_id is specified, an id is generated from the first switch port in the port channel.
channel_id: <int>
# EOS CLI rendered directly on the point-to-point interface in the final EOS configuration.
raw_eos_cli: <str>
# Enables deviation of the routing protocol used on this link from the fabric underlay default.
# - ebgp: Enforce plain IPv4 BGP peering
routing_protocol: <str; "ebgp">
# Custom structured config for interfaces.
# Note! The content of this dictionary is _not_ validated by the schema, since it can be either ethernet_interfaces or port_channel_interfaces.
structured_config: <dict>
Flagging a device as not deployed¶
- It is possible to provision configurations for a complete topology but flag devices as undeployed using the host level variable
is_deployed: false. - By default, this will have no impact within the
eos_designsrole. Configs will still be generated by theeos_cli_config_genrole and will still be pushed by theeos_config_deploy_eapidirectly to devices if used. - However, if the
eos_config_deploy_cvprole is used to push configurations, CloudVision will ignore the devices flagged asis_deployed: falseand not attempt to configure them. - If the device is not present in the network due to CloudVision not configuring the device,
eos_validate_staterole will fail lldp_toplogy and interface tests on peers of the undeployed device trying to verify that interfaces are up. - To overcome this and shutdown interfaces towards undeployed peers, the variable
shutdown_interfaces_towards_undeployed_peerscan be used, satisfying theeos_validate_staterole interface and lldp_topology tests. Again, this is only an issue ifeos_config_deploy_cvpis used and the devices are not present in the network.
| Variable | Type | Required | Default | Value Restrictions | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| is_deployed | Boolean | True |
If the device is already deployed in the fabric. When set to false, interfaces toward this device may be shutdown depending on the shutdown_interfaces_towards_undeployed_peers setting.Furthermore eos_config_deploy_cvp will not attempt to move or apply configurations to the device. |
# If the device is already deployed in the fabric.
# When set to false, interfaces toward this device may be shutdown depending on the `shutdown_interfaces_towards_undeployed_peers` setting.
# Furthermore `eos_config_deploy_cvp` will not attempt to move or apply configurations to the device.
is_deployed: <bool; default=True>
Fabric settings¶
The following underlay routing protocols are supported:
- EBGP (default for l3ls-evpn)
- OSPF.
- ISIS.
- ISIS-SR*.
- ISIS-LDP*.
- ISIS-SR-LDP*.
- OSPF-LDP*.
- none**.
* Only supported with core_interfaces data model.
** For use with design type “l2ls” or other designs where there is no requirement for a routing protocol for underlay and/or overlay on l3 devices.
Details on enable_trunk_groups
Enabling the use of trunk groups will change the behavior of several components in AVD.
Changes:
- Requires Trunk Groups to be defined on all trunks towards connected endpoints
MLAGTrunk Group will be configured on all vlans on MLAG switches- Use Trunk Groups for uplinks to L2 switches instead of “switchport trunk allow vlan” lists.
- On the parent switch a Trunk Group with the name of the L2 switch will be assigned on all vlans that are allowed towards the L2 switch.
- The port-channel towards the L2 switch will be assigned to this trunk group only
- Add
UPLINKTrunk Group to all vlans on the L2 Switch and assign this to the uplink port-channel
While it is recommended for consistency to set enable_trunk_groups for all devices in the fabric,
it can also be set in group_vars or host_vars since trunk-groups are only local to a switch.
Warning
Because of the nature of the EOS Trunk Group feature, enabling this is “all or nothing”. All vlans and all trunks towards connected endpoints must be using trunk groups as well. If trunk groups are not assigned to a trunk, no vlans will be enabled on that trunk.
Details on only_local_vlan_trunk_groups
Enabling this feature will prevent unneeded trunk groups from being configured on vlans.
Using the figure under Details on enable_trunk_groups as basis
enabling with feature would remove the unmatched trunk groups like this:
| Variable | Type | Required | Default | Value Restrictions | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| enable_trunk_groups | Boolean | False |
Enable Trunk Group support across eos_designs. Warning: Because of the nature of the EOS Trunk Group feature, enabling this is “all or nothing”. All vlans and all trunks towards connected endpoints must be using trunk groups as well. If trunk groups are not assigned to a trunk, no vlans will be enabled on that trunk. See “Details on enable_trunk_groups” below before enabling this feature. |
||
| mlag_on_orphan_port_channel_downlink | Boolean | True |
If true (default) an MLAG ID will always be configured on a Port-Channel downlink even if the downlink is only on one node in the MLAG pair.If false an MLAG ID will only be configured on Port-Channel downlinks dual-homed to two MLAG switches.Note the default value will change to false in AVD version 5.0 |
||
| only_local_vlan_trunk_groups | Boolean | False |
A vlan can have many trunk_groups assigned. To avoid unneeded configuration changes on all leaf switches when a new trunk group is added, this feature will only configure the vlan trunk groups matched with local connected_endpoints. See “Details on only_local_vlan_trunk_groups” below. Requires “enable_trunk_groups: true”. |
||
| p2p_uplinks_mtu | Integer | 9214 |
Min: 68 Max: 65535 |
Point to Point Links MTU. | |
| p2p_uplinks_qos_profile | String | QOS Profile assigned on all infrastructure links. | |||
| shutdown_interfaces_towards_undeployed_peers | Boolean | False |
- It is possible to provision configurations for a complete topology but flag devices as undeployed using the host level variable is_deployed: false.yaml<br># Use at the host level<br>is_deployed: < true or false or default -> true ><br>- By default, this will have no impact within the eos_designs role. Configs will still be generated by the eos_cli_config_gen role and will still be pushed by the eos_config_deploy_eapi directly to devices if used.- However, if the eos_config_deploy_cvp role is used to push configurations, CloudVision will ignore the devices flagged as is_deployed: false and not attempt to configure them.- If the device is not present in the network due to CloudVision not configuring the device, eos_validate_state role will fail tests on peers of the undeployed device trying to verify that interfaces are up.- To overcome this and shutdown interfaces towards undeployed peers, the variable shutdown_interfaces_towards_undeployed_peers can be used, satisfying the eos_validate_state role interface tests.- Again, this is only an issue if eos_config_deploy_cvp is used and the devices are not present in the network. |
||
| trunk_groups | Dictionary | ||||
| mlag | Dictionary | Trunk Group used for MLAG VLAN (Typically VLAN 4094). |
|||
| name | String | MLAG |
|||
| mlag_l3 | Dictionary | Trunk Group used for MLAG L3 peering VLAN and for VRF L3 peering VLANs (Typically VLAN 4093). |
|||
| name | String | LEAF_PEER_L3 |
|||
| uplink | Dictionary | Trunk Group used on L2 Leaf switches when “enable_trunk_groups” is set. |
|||
| name | String | UPLINK |
|||
| underlay_filter_peer_as | Boolean | False |
Configure route-map on eBGP sessions towards underlay peers, where prefixes with the peer’s ASN in the AS Path are filtered away. This is very useful in very large scale networks not using EVPN overlays, where convergence will be quicker by not having to return all updates received from Spine-1 to Spine-2 just for Spine-2 to throw them away because of AS Path loop detection. Note that this setting cannot be used while there are EVPN services present in the default VRF. |
||
| underlay_filter_redistribute_connected | Boolean | True |
Filter redistribution of connected into the underlay routing protocol. Only applicable when overlay_routing_protocol != ‘none’ and underlay_routing_protocol == BGP. Creates a route-map and prefix-list assigned to redistribute connected permitting only loopbacks and inband management subnets. |
||
| underlay_ipv6 | Boolean | False |
This feature allows IPv6 underlay routing protocol with RFC5549 addresses to be used along with IPv4 advertisements as VXLAN tunnel endpoints. Requires “underlay_rfc5549: true” and “loopback_ipv6_pool” under the node type settings. |
||
| underlay_multicast | Boolean | False |
Enable Multicast in the underlay on all p2p uplink interfaces and mlag l3 peer interface. Specifically PIM Sparse-Mode will be configured on all routed underlay interfaces. No other configuration is added, so the underlay will only support Source-Specific Multicast (SSM). The configuration is intended to be used as multicast underlay for EVPN OISM overlay. |
||
| underlay_multicast_anycast_rp | Dictionary | If multiple nodes are configured under ‘underlay_multicast_rps.[].nodes’ for the same RP address, they will be configured with one of the following methods: - Anycast RP using PIM (RFC4610). - Anycast RP using MSDP (RFC4611). NOTE: When using MSDP, all nodes across all MSDP enabled RPs will be added to a single MSDP mesh group named “ANYCAST-RP”. |
|||
| mode | String | pim |
Valid Values: - pim- msdp |
||
| underlay_multicast_rps | List, items: Dictionary | List of PIM Sparse-Mode Rendevouz Points configured for underlay multicast on all devices. The device(s) listed under ‘nodes’, will be configured as the Rendevouz point router(s). If multiple nodes are configured under ‘nodes’ for the same RP address, they will be configured according to the ‘underlay_multicast_anycast_rp.mode’ setting. Requires ‘underlay_multicast: true’. |
|||
| - rp | String | Required, Unique | RP IPv4 address. | ||
| nodes | List, items: Dictionary | List of nodes where a Loopback interface with the RP address will be configured. |
|||
| - name | String | Required, Unique | Hostname. | ||
| loopback_number | Integer | Required | |||
| description | String | PIM RP |
Interface description. | ||
| groups | List, items: String | List of groups to associate with the RP address set in ‘rp’. If access_list_name is set, a standard access-list will be configured matching these groups. Otherwise the groups are configured directly on the RP command. |
|||
| - <str> | String | Multicast Group IPv4 prefix/mask. | |||
| access_list_name | String | Name of standard Access-List. |
|||
| underlay_rfc5549 | Boolean | False |
Point to Point Underlay with RFC 5549(eBGP), i.e. IPv6 Unnumbered. Requires “underlay_routing_protocol: ebgp”. |
||
| underlay_routing_protocol | String | Value is converted to lower case. Valid Values: - ebgp- ospf- ospf-ldp- isis- isis-sr- isis-ldp- isis-sr-ldp- none |
- The following underlay routing protocols are supported: - EBGP (default for l3ls-evpn) - OSPF. - OSPF-LDP*. - ISIS. - ISIS-SR*. - ISIS-LDP*. - ISIS-SR-LDP*. - No underlay routing protocol (none) - The variables should be applied to all devices in the fabric. *Only supported with core_interfaces data model. |
||
| uplink_ptp | Dictionary | Enable PTP on all infrastructure links. | |||
| enable | Boolean | False |
# Enable Trunk Group support across eos_designs.
# Warning: Because of the nature of the EOS Trunk Group feature, enabling this is "all or nothing".
# *All* vlans and *all* trunks towards connected endpoints must be using trunk groups as well.
# If trunk groups are not assigned to a trunk, no vlans will be enabled on that trunk.
# See "Details on enable_trunk_groups" below before enabling this feature.
enable_trunk_groups: <bool; default=False>
# If `true` (default) an MLAG ID will always be configured on a Port-Channel downlink even if the downlink is only on one node in the MLAG pair.
# If `false` an MLAG ID will only be configured on Port-Channel downlinks dual-homed to two MLAG switches.
# Note the default value will change to `false` in AVD version 5.0
mlag_on_orphan_port_channel_downlink: <bool; default=True>
# A vlan can have many trunk_groups assigned.
# To avoid unneeded configuration changes on all leaf switches when a new trunk group is added,
# this feature will only configure the vlan trunk groups matched with local connected_endpoints.
# See "Details on only_local_vlan_trunk_groups" below.
# Requires "enable_trunk_groups: true".
only_local_vlan_trunk_groups: <bool; default=False>
# Point to Point Links MTU.
p2p_uplinks_mtu: <int; 68-65535; default=9214>
# QOS Profile assigned on all infrastructure links.
p2p_uplinks_qos_profile: <str>
# - It is possible to provision configurations for a complete topology but flag devices as undeployed using the host level variable `is_deployed: false`.
#
# ```yaml
# # Use at the host level
# is_deployed: < true or false or default -> true >
# ```
#
# - By default, this will have no impact within the `eos_designs` role. Configs will still be generated by the `eos_cli_config_gen` role and will still be pushed by the `eos_config_deploy_eapi` directly to devices if used.
# - However, if the `eos_config_deploy_cvp` role is used to push configurations, CloudVision will ignore the devices flagged as `is_deployed: false` and not attempt to configure them.
# - If the device is not present in the network due to CloudVision not configuring the device, `eos_validate_state` role will fail tests on peers of the undeployed device trying to verify that interfaces are up.
# - To overcome this and shutdown interfaces towards undeployed peers, the variable `shutdown_interfaces_towards_undeployed_peers` can be used, satisfying the `eos_validate_state` role interface tests.
# - Again, this is only an issue if `eos_config_deploy_cvp` is used and the devices are not present in the network.
shutdown_interfaces_towards_undeployed_peers: <bool; default=False>
trunk_groups:
# Trunk Group used for MLAG VLAN (Typically VLAN 4094).
mlag:
name: <str; default="MLAG">
# Trunk Group used for MLAG L3 peering VLAN and for VRF L3 peering VLANs (Typically VLAN 4093).
mlag_l3:
name: <str; default="LEAF_PEER_L3">
# Trunk Group used on L2 Leaf switches when "enable_trunk_groups" is set.
uplink:
name: <str; default="UPLINK">
# Configure route-map on eBGP sessions towards underlay peers, where prefixes with the peer's ASN in the AS Path are filtered away.
# This is very useful in very large scale networks not using EVPN overlays, where convergence will be quicker by not having to return
# all updates received from Spine-1 to Spine-2 just for Spine-2 to throw them away because of AS Path loop detection.
# Note that this setting cannot be used while there are EVPN services present in the default VRF.
underlay_filter_peer_as: <bool; default=False>
# Filter redistribution of connected into the underlay routing protocol.
# Only applicable when overlay_routing_protocol != 'none' and underlay_routing_protocol == BGP.
# Creates a route-map and prefix-list assigned to redistribute connected permitting only loopbacks and inband management subnets.
underlay_filter_redistribute_connected: <bool; default=True>
# This feature allows IPv6 underlay routing protocol with RFC5549 addresses to be used along with IPv4 advertisements as VXLAN tunnel endpoints.
# Requires "underlay_rfc5549: true" and "loopback_ipv6_pool" under the node type settings.
underlay_ipv6: <bool; default=False>
# Enable Multicast in the underlay on all p2p uplink interfaces and mlag l3 peer interface.
# Specifically PIM Sparse-Mode will be configured on all routed underlay interfaces.
# No other configuration is added, so the underlay will only support Source-Specific Multicast (SSM).
# The configuration is intended to be used as multicast underlay for EVPN OISM overlay.
underlay_multicast: <bool; default=False>
# If multiple nodes are configured under 'underlay_multicast_rps.[].nodes' for the same RP address, they will be configured
# with one of the following methods:
# - Anycast RP using PIM (RFC4610).
# - Anycast RP using MSDP (RFC4611).
#
# NOTE: When using MSDP, all nodes across all MSDP enabled RPs will be added to a single MSDP mesh group named "ANYCAST-RP".
underlay_multicast_anycast_rp:
mode: <str; "pim" | "msdp"; default="pim">
# List of PIM Sparse-Mode Rendevouz Points configured for underlay multicast on all devices.
# The device(s) listed under 'nodes', will be configured as the Rendevouz point router(s).
# If multiple nodes are configured under 'nodes' for the same RP address, they will be configured
# according to the 'underlay_multicast_anycast_rp.mode' setting.
#
# Requires 'underlay_multicast: true'.
underlay_multicast_rps:
# RP IPv4 address.
- rp: <str; required; unique>
# List of nodes where a Loopback interface with the RP address will be configured.
nodes:
# Hostname.
- name: <str; required; unique>
loopback_number: <int; required>
# Interface description.
description: <str; default="PIM RP">
# List of groups to associate with the RP address set in 'rp'.
# If access_list_name is set, a standard access-list will be configured matching these groups.
# Otherwise the groups are configured directly on the RP command.
groups:
# Multicast Group IPv4 prefix/mask.
- <str>
# Name of standard Access-List.
access_list_name: <str>
# Point to Point Underlay with RFC 5549(eBGP), i.e. IPv6 Unnumbered.
# Requires "underlay_routing_protocol: ebgp".
underlay_rfc5549: <bool; default=False>
# - The following underlay routing protocols are supported:
# - EBGP (default for l3ls-evpn)
# - OSPF.
# - OSPF-LDP*.
# - ISIS.
# - ISIS-SR*.
# - ISIS-LDP*.
# - ISIS-SR-LDP*.
# - No underlay routing protocol (none)
# - The variables should be applied to all devices in the fabric.
# *Only supported with core_interfaces data model.
underlay_routing_protocol: <str; "ebgp" | "ospf" | "ospf-ldp" | "isis" | "isis-sr" | "isis-ldp" | "isis-sr-ldp" | "none">
# Enable PTP on all infrastructure links.
uplink_ptp:
enable: <bool; default=False>
Management interface settings¶
| Variable | Type | Required | Default | Value Restrictions | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| default_mgmt_method | String | oob |
Valid Values: - oob- inband- none |
default_mgmt_method controls the default VRF and source interface used for the following management and monitoring protocols configured with eos_designs:- cv_settings- dns_settings- ntp_settings- sflow_settingsoob means the protocols will be configured with the VRF set by mgmt_interface_vrf and mgmt_interface as the source interface.inband means the protocols will be configured with the VRF set by inband_mgmt_vrf and inband_mgmt_interface as the source interface.none means the VRF and or interface must be manually set for each protocol.This can be overridden under the settings for each protocol. |
|
| mgmt_destination_networks | List, items: String | List of IPv4 prefixes to configure as static routes towards the OOB Management interface gateway. Replaces the default route. |
|||
| - <str> | String | IPv4_address/Mask. | |||
| mgmt_gateway | String | OOB Management interface gateway in IPv4 format. Used as next-hop for default gateway or static routes defined under ‘mgmt_destination_networks’. |
|||
| mgmt_interface | String | Management1 |
OOB Management interface. | ||
| mgmt_interface_description | String | oob_management |
Management interface description. |
||
| mgmt_interface_vrf | String | MGMT |
OOB Management VRF. | ||
| mgmt_vrf_routing | Boolean | False |
Configure IP routing for the OOB Management VRF. |
# `default_mgmt_method` controls the default VRF and source interface used for the following management and monitoring protocols configured with `eos_designs`:
# - `cv_settings`
# - `dns_settings`
# - `ntp_settings`
# - `sflow_settings`
#
# `oob` means the protocols will be configured with the VRF set by `mgmt_interface_vrf` and `mgmt_interface` as the source interface.
# `inband` means the protocols will be configured with the VRF set by `inband_mgmt_vrf` and `inband_mgmt_interface` as the source interface.
# `none` means the VRF and or interface must be manually set for each protocol.
# This can be overridden under the settings for each protocol.
default_mgmt_method: <str; "oob" | "inband" | "none"; default="oob">
# List of IPv4 prefixes to configure as static routes towards the OOB Management interface gateway.
# Replaces the default route.
mgmt_destination_networks:
# IPv4_address/Mask.
- <str>
# OOB Management interface gateway in IPv4 format.
# Used as next-hop for default gateway or static routes defined under 'mgmt_destination_networks'.
mgmt_gateway: <str>
# OOB Management interface.
mgmt_interface: <str; default="Management1">
# Management interface description.
mgmt_interface_description: <str; default="oob_management">
# OOB Management VRF.
mgmt_interface_vrf: <str; default="MGMT">
# Configure IP routing for the OOB Management VRF.
mgmt_vrf_routing: <bool; default=False>
BFD settings¶
| Variable | Type | Required | Default | Value Restrictions | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| bfd_multihop | Dictionary | See (+) on YAML tab | BFD Multihop tuning. | ||
| interval | Integer | Required | Min: 50 Max: 60000 |
||
| min_rx | Integer | Required | Min: 50 Max: 60000 |
||
| multiplier | Integer | Required | Min: 3 Max: 50 |
BGP settings¶
| Variable | Type | Required | Default | Value Restrictions | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| bgp_as | String | BGP AS <1-4294967295> or AS number in asdot notation “<1-65535>.<0-65535>” to use to configure overlay when “overlay_routing_protocol” == ibgp. For asdot notation in YAML inputs, the value must be put in quotes, to prevent it from being interpreted as a float number. |
|||
| bgp_default_ipv4_unicast | Boolean | False |
Default activation of IPv4 unicast address-family on all IPv4 neighbors. It is best practice to disable activation. |
||
| bgp_distance | Dictionary | ||||
| external_routes | Integer | Required | Min: 1 Max: 255 |
||
| internal_routes | Integer | Required | Min: 1 Max: 255 |
||
| local_routes | Integer | Required | Min: 1 Max: 255 |
||
| bgp_ecmp | Integer | Maximum ECMP for BGP multi-path. The default value is 4 except for WAN Routers where the default value is unset (falls back to EOS default). |
|||
| bgp_graceful_restart | Dictionary | BGP graceful-restart allows a BGP speaker with separate control plane and data plane processing to continue forwarding traffic during a BGP restart. Its neighbors (receiving speakers) may retain routing information from the restarting speaker while a BGP session with it is being re-established, reducing route flapping. |
|||
| enabled | Boolean | Required | False |
Enable or disable graceful-restart for all BGP peers. | |
| restart_time | Integer | 300 |
Min: 1 Max: 3600 |
Restart time in seconds. | |
| bgp_maximum_paths | Integer | Min: 1 Max: 512 |
Maximum Paths for BGP multi-path. The default value is 4 except for WAN Routers where the default value is 16. |
||
| bgp_peer_groups | Dictionary | Leverage an Arista EOS switch to generate the encrypted password using the correct peer group name. Note that the name of the peer groups use ‘-’ instead of ‘_’ in EOS configuration. |
|||
| ipv4_underlay_peers | Dictionary | ||||
| name | String | IPv4-UNDERLAY-PEERS |
Name of peer group. | ||
| password | String | Type 7 encrypted password. | |||
| bfd | Boolean | False |
|||
| structured_config | Dictionary | Custom structured config added under router_bgp.peer_groups.[name= |
|||
| mlag_ipv4_underlay_peer | Dictionary | ||||
| name | String | MLAG-IPv4-UNDERLAY-PEER |
Name of peer group. | ||
| password | String | Type 7 encrypted password. | |||
| bfd | Boolean | False |
|||
| structured_config | Dictionary | Custom structured config added under router_bgp.peer_groups.[name= |
|||
| evpn_overlay_peers | Dictionary | ||||
| name | String | EVPN-OVERLAY-PEERS |
Name of peer group. | ||
| password | String | Type 7 encrypted password. | |||
| bfd | Boolean | True |
|||
| structured_config | Dictionary | Custom structured config added under router_bgp.peer_groups.[name= |
|||
| evpn_overlay_core | Dictionary | ||||
| name | String | EVPN-OVERLAY-CORE |
Name of peer group. | ||
| password | String | Type 7 encrypted password. | |||
| bfd | Boolean | True |
|||
| structured_config | Dictionary | Custom structured config added under router_bgp.peer_groups.[name= |
|||
| mpls_overlay_peers | Dictionary | ||||
| name | String | MPLS-OVERLAY-PEERS |
Name of peer group. | ||
| password | String | Type 7 encrypted password. | |||
| bfd | Boolean | True |
|||
| structured_config | Dictionary | Custom structured config added under router_bgp.peer_groups.[name= |
|||
| rr_overlay_peers | Dictionary | ||||
| name | String | RR-OVERLAY-PEERS |
Name of peer group. | ||
| password | String | Type 7 encrypted password. | |||
| bfd | Boolean | True |
|||
| structured_config | Dictionary | Custom structured config added under router_bgp.peer_groups.[name= |
|||
| ipvpn_gateway_peers | Dictionary | ||||
| name | String | IPVPN-GATEWAY-PEERS |
Name of peer group. | ||
| password | String | Type 7 encrypted password. | |||
| bfd | Boolean | True |
|||
| structured_config | Dictionary | Custom structured config added under router_bgp.peer_groups.[name= |
|||
| wan_overlay_peers | Dictionary | ||||
| name | String | WAN-OVERLAY-PEERS |
Name of peer group. | ||
| password | String | Type 7 encrypted password. | |||
| bfd | Boolean | True |
|||
| bfd_timers | Dictionary | Specify the BFD timers to override the default values. It is recommended to keep BFD total timeout longer than the DPS timeout. The Default BFD timeout is 10 x 1 seconds and the default DPS timeout is 5 x 1 seconds. |
|||
| interval | Integer | Required | 1000 |
Min: 50 Max: 60000 |
Interval in milliseconds. |
| min_rx | Integer | Required | 1000 |
Min: 50 Max: 60000 |
Rate in milliseconds. |
| multiplier | Integer | Required | 10 |
Min: 3 Max: 50 |
|
| listen_range_prefixes | List, items: String | Only used for nodes where wan_role is server like AutoVPN RRs and Pathfinders.For clients, AVD will raise an error if the Loopback0 IP is not in any listen range. |
|||
| - <str> | String | The prefixes to use in listen_range. | |||
| ttl_maximum_hops | Integer | 1 |
|||
| structured_config | Dictionary | Custom structured config added under router_bgp.peer_groups.[name= |
|||
| wan_rr_overlay_peers | Dictionary | Configuration options for the peer-group created to peer between AutoVPN RRs or CV Pathfinders. | |||
| name | String | WAN-RR-OVERLAY-PEERS |
Name of peer group. | ||
| password | String | Type 7 encrypted password. | |||
| bfd | Boolean | True |
|||
| bfd_timers | Dictionary | Specify the BFD timers to override the default values. It is recommended to keep BFD total timeout longer than the DPS timeout. The Default BFD timeout is 10 x 1 seconds and the default DPS timeout is 5 x 1 seconds. |
|||
| interval | Integer | Required | 1000 |
Min: 50 Max: 60000 |
Interval in milliseconds. |
| min_rx | Integer | Required | 1000 |
Min: 50 Max: 60000 |
Rate in milliseconds. |
| multiplier | Integer | Required | 10 |
Min: 3 Max: 50 |
|
| ttl_maximum_hops | Integer | 1 |
|||
| structured_config | Dictionary | Custom structured config added under router_bgp.peer_groups.[name= |
|||
| IPv4_UNDERLAY_PEERS removed | Dictionary | This key was removed. Support was removed in AVD version 4.0.0. Use bgp_peer_groups.ipv4_underlay_peers instead. | |||
| MLAG_IPv4_UNDERLAY_PEER removed | Dictionary | This key was removed. Support was removed in AVD version 4.0.0. Use bgp_peer_groups.mlag_ipv4_underlay_peer instead. | |||
| EVPN_OVERLAY_PEERS removed | Dictionary | This key was removed. Support was removed in AVD version 4.0.0. Use bgp_peer_groups.evpn_overlay_peers instead. | |||
| bgp_update_wait_install | Boolean | Do not advertise reachability to a prefix until that prefix has been installed in hardware. This will eliminate any temporary black holes due to a BGP speaker advertising reachability to a prefix that may not yet be installed into the forwarding plane. |
|||
| bgp_update_wait_for_convergence | Boolean | Disables FIB updates and route advertisement when the BGP instance is initiated until the BGP convergence state is reached. |
# BGP AS <1-4294967295> or AS number in asdot notation "<1-65535>.<0-65535>" to use to configure overlay when "overlay_routing_protocol" == ibgp.
# For asdot notation in YAML inputs, the value must be put in quotes, to prevent it from being interpreted as a float number.
bgp_as: <str>
# Default activation of IPv4 unicast address-family on all IPv4 neighbors.
# It is best practice to disable activation.
bgp_default_ipv4_unicast: <bool; default=False>
bgp_distance:
external_routes: <int; 1-255; required>
internal_routes: <int; 1-255; required>
local_routes: <int; 1-255; required>
# Maximum ECMP for BGP multi-path.
# The default value is 4 except for WAN Routers where the default value is unset (falls back to EOS default).
bgp_ecmp: <int>
# BGP graceful-restart allows a BGP speaker with separate control plane and data plane processing to continue forwarding traffic during a BGP restart.
# Its neighbors (receiving speakers) may retain routing information from the restarting speaker while a BGP session with it is being re-established, reducing route flapping.
bgp_graceful_restart:
# Enable or disable graceful-restart for all BGP peers.
enabled: <bool; default=False; required>
# Restart time in seconds.
restart_time: <int; 1-3600; default=300>
# Maximum Paths for BGP multi-path.
# The default value is 4 except for WAN Routers where the default value is 16.
bgp_maximum_paths: <int; 1-512>
# Leverage an Arista EOS switch to generate the encrypted password using the correct peer group name.
# Note that the name of the peer groups use '-' instead of '_' in EOS configuration.
bgp_peer_groups:
ipv4_underlay_peers:
# Name of peer group.
name: <str; default="IPv4-UNDERLAY-PEERS">
# Type 7 encrypted password.
password: <str>
bfd: <bool; default=False>
# Custom structured config added under router_bgp.peer_groups.[name=<name>] for eos_cli_config_gen.
structured_config: <dict>
mlag_ipv4_underlay_peer:
# Name of peer group.
name: <str; default="MLAG-IPv4-UNDERLAY-PEER">
# Type 7 encrypted password.
password: <str>
bfd: <bool; default=False>
# Custom structured config added under router_bgp.peer_groups.[name=<name>] for eos_cli_config_gen.
structured_config: <dict>
evpn_overlay_peers:
# Name of peer group.
name: <str; default="EVPN-OVERLAY-PEERS">
# Type 7 encrypted password.
password: <str>
bfd: <bool; default=True>
# Custom structured config added under router_bgp.peer_groups.[name=<name>] for eos_cli_config_gen.
structured_config: <dict>
evpn_overlay_core:
# Name of peer group.
name: <str; default="EVPN-OVERLAY-CORE">
# Type 7 encrypted password.
password: <str>
bfd: <bool; default=True>
# Custom structured config added under router_bgp.peer_groups.[name=<name>] for eos_cli_config_gen.
structured_config: <dict>
mpls_overlay_peers:
# Name of peer group.
name: <str; default="MPLS-OVERLAY-PEERS">
# Type 7 encrypted password.
password: <str>
bfd: <bool; default=True>
# Custom structured config added under router_bgp.peer_groups.[name=<name>] for eos_cli_config_gen.
structured_config: <dict>
rr_overlay_peers:
# Name of peer group.
name: <str; default="RR-OVERLAY-PEERS">
# Type 7 encrypted password.
password: <str>
bfd: <bool; default=True>
# Custom structured config added under router_bgp.peer_groups.[name=<name>] for eos_cli_config_gen.
structured_config: <dict>
ipvpn_gateway_peers:
# Name of peer group.
name: <str; default="IPVPN-GATEWAY-PEERS">
# Type 7 encrypted password.
password: <str>
bfd: <bool; default=True>
# Custom structured config added under router_bgp.peer_groups.[name=<name>] for eos_cli_config_gen.
structured_config: <dict>
wan_overlay_peers:
# Name of peer group.
name: <str; default="WAN-OVERLAY-PEERS">
# Type 7 encrypted password.
password: <str>
bfd: <bool; default=True>
# Specify the BFD timers to override the default values.
# It is recommended to keep BFD total timeout longer than the DPS timeout.
# The Default BFD timeout is 10 x 1 seconds and the default DPS timeout is 5 x 1 seconds.
bfd_timers:
# Interval in milliseconds.
interval: <int; 50-60000; default=1000; required>
# Rate in milliseconds.
min_rx: <int; 50-60000; default=1000; required>
multiplier: <int; 3-50; default=10; required>
# Only used for nodes where `wan_role` is `server` like AutoVPN RRs and Pathfinders.
# For clients, AVD will raise an error if the Loopback0 IP is not in any listen range.
listen_range_prefixes:
# The prefixes to use in listen_range.
- <str>
ttl_maximum_hops: <int; default=1>
# Custom structured config added under router_bgp.peer_groups.[name=<name>] for eos_cli_config_gen.
structured_config: <dict>
# Configuration options for the peer-group created to peer between AutoVPN RRs or CV Pathfinders.
wan_rr_overlay_peers:
# Name of peer group.
name: <str; default="WAN-RR-OVERLAY-PEERS">
# Type 7 encrypted password.
password: <str>
bfd: <bool; default=True>
# Specify the BFD timers to override the default values.
# It is recommended to keep BFD total timeout longer than the DPS timeout.
# The Default BFD timeout is 10 x 1 seconds and the default DPS timeout is 5 x 1 seconds.
bfd_timers:
# Interval in milliseconds.
interval: <int; 50-60000; default=1000; required>
# Rate in milliseconds.
min_rx: <int; 50-60000; default=1000; required>
multiplier: <int; 3-50; default=10; required>
ttl_maximum_hops: <int; default=1>
# Custom structured config added under router_bgp.peer_groups.[name=<name>] for eos_cli_config_gen.
structured_config: <dict>
# Do not advertise reachability to a prefix until that prefix has been installed in hardware.
# This will eliminate any temporary black holes due to a BGP speaker advertising reachability to a prefix that may not yet be installed into the forwarding plane.
bgp_update_wait_install: <bool>
# Disables FIB updates and route advertisement when the BGP instance is initiated until the BGP convergence state is reached.
bgp_update_wait_for_convergence: <bool>
OSPF settings¶
| Variable | Type | Required | Default | Value Restrictions | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| underlay_ospf_area | String | 0.0.0.0 |
Format: ipv4 | ||
| underlay_ospf_bfd_enable | Boolean | False |
|||
| underlay_ospf_max_lsa | Integer | 12000 |
|||
| underlay_ospf_process_id | Integer | 100 |
ISIS settings¶
| Variable | Type | Required | Default | Value Restrictions | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| isis_advertise_passive_only | Boolean | False |
|||
| isis_area_id | String | 49.0001 |
|||
| isis_default_circuit_type | String | level-2 |
Valid Values: - level-1-2- level-1- level-2 |
These fabric level parameters can be used with core_interfaces running ISIS, and may be overridden on link profile or link level. |
|
| isis_default_is_type | String | level-2 |
Valid Values: - level-1-2- level-1- level-2 |
||
| isis_default_metric | Integer | 50 |
These fabric level parameters can be used with core_interfaces running ISIS, and may be overridden at link profile or link level. |
||
| isis_maximum_paths | Integer | Number of path to configure in ECMP for ISIS. | |||
| isis_system_id_format | String | node_id |
Valid Values: - node_id- underlay_loopback |
Configures source for the system-id within the ISIS net id. By default the id and isis_system_id_prefix fields configured under the node attributes are used to generate the system-id.If underlay_loopback is selected then all node isis_system_id_prefix settings will be ignored and the loopback address will be used to generate the system-id. |
|
| isis_ti_lfa | Dictionary | ||||
| enabled | Boolean | False |
|||
| protection | String | Valid Values: - link- node |
|||
| local_convergence_delay | Integer | 10000 |
Local convergence delay in milliseconds. | ||
| underlay_isis_instance_name | String | Default -> “EVPN_UNDERLAY” for l3ls, “CORE” for mpls. |
isis_advertise_passive_only: <bool; default=False>
isis_area_id: <str; default="49.0001">
# These fabric level parameters can be used with core_interfaces running ISIS, and may be overridden on link profile or link level.
isis_default_circuit_type: <str; "level-1-2" | "level-1" | "level-2"; default="level-2">
isis_default_is_type: <str; "level-1-2" | "level-1" | "level-2"; default="level-2">
# These fabric level parameters can be used with core_interfaces running ISIS, and may be overridden at link profile or link level.
isis_default_metric: <int; default=50>
# Number of path to configure in ECMP for ISIS.
isis_maximum_paths: <int>
# Configures source for the system-id within the ISIS net id.
# By default the `id` and `isis_system_id_prefix` fields configured under the node attributes are used to generate the system-id.
#
# If `underlay_loopback` is selected then all node `isis_system_id_prefix` settings will be ignored and the loopback address will be used to generate the system-id.
isis_system_id_format: <str; "node_id" | "underlay_loopback"; default="node_id">
isis_ti_lfa:
enabled: <bool; default=False>
protection: <str; "link" | "node">
# Local convergence delay in milliseconds.
local_convergence_delay: <int; default=10000>
# Default -> "EVPN_UNDERLAY" for l3ls, "CORE" for mpls.
underlay_isis_instance_name: <str>
Overlay settings¶
The following overlay routing protocols are supported:
- EBGP (default for l3ls-evpn)
- IBGP (only with OSPF or ISIS variants in underlay)
- none*
- HER (Head-End Replication)**
- CVX (CloudVision eXchange)
* For use with design type “l2ls” or other designs where there is no requirement for a routing protocol for underlay and/or overlay on l3 devices.
** By setting overlay_routing_protocol:HER, eos_designs will configure static VXLAN flood-lists instead of using a dynamic overlay protocol.
| Variable | Type | Required | Default | Value Restrictions | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| bgp_mesh_pes | Boolean | False |
Configure an iBGP full mesh between PEs, either because there is no RR used or other reasons. Only supported in combination with MPLS overlay. |
||
| mlag_ibgp_peering_vrfs | Dictionary | On mlag leafs, an SVI interface is defined per vrf, to establish iBGP peering (required when there are MLAG leafs in topology). The SVI id will be derived from the base vlan defined: mlag_ibgp_peering_vrfs.base_vlan + (vrf_id or vrf_vni) - 1. Depending on the values of vrf_id / vrf_vni it may be required to adjust the base_vlan to avoid overlaps or invalid vlan ids. The SVI ip address derived from mlag_l3_peer_ipv4_pool is re-used across all iBGP peerings. |
|||
| base_vlan | Integer | 3000 |
Min: 1 Max: 4093 |
||
| overlay_cvx_servers | List, items: String | List of CVX vxlan overlay controllers. Required if overlay_routing_protocol == CVX. CVX servers (VMs) are peering using their management interface, so mgmt_ip must be set for all CVX servers. |
|||
| - <str> | String | ‘inventory_hostname’ of CVX server. |
|||
| overlay_her_flood_list_per_vni | Boolean | False |
When using Head-End Replication, configure flood-lists per VNI. By default HER will be configured with a common flood-list containing all VTEPs. This behavior can be changed to per-VNI flood-lists by setting overlay_her_flood_list_per_vni: true.This will make eos_designs consider configured VLANs per VTEP, and only include the relevant VTEPs to each VNI’s flood-list. |
||
| overlay_her_flood_list_scope | String | fabric |
Valid Values: - fabric- dc |
When using Head-End Replication, set the scope of flood-lists to Fabric or DC. By default all VTEPs in the Fabric (part of the inventory group referenced by “fabric_name”) are added to the flood-lists. This can be changed to all VTEPs in the DC (sharing the same “dc_name” value). This is useful if Border Leaf switches are dividing the VXLAN overlay into separate domains. |
|
| overlay_loopback_description | String | Customize the description on overlay interface Loopback0. | |||
| overlay_mlag_rfc5549 | Boolean | False |
IPv6 Unnumbered for MLAG iBGP connections. Requires “underlay_rfc5549: true”. |
||
| overlay_rd_type | Dictionary | Configuration options for the Administrator subfield (first part of RD) and the Assigned Number subfield (second part of RD). By default Route Distinguishers (RD) are set to: - <overlay_loopback>:<mac_vrf_id_base + vlan_id or mac_vrf_vni_base + vlan_id> for VLANs and VLAN-Aware Bundles with L2 vlans.- <overlay_loopback>:<vlan_aware_bundle_number_base + vrf_id> for VLAN-Aware Bundles with SVIs.- <overlay_loopback>:<vlan_aware_bundle_number_base + id> for VLAN-Aware Bundles defined under ‘evpn_vlan_bundles’.- <overlay_loopback>:<vrf_id> for VRFs.Note: RD is a 48-bit value which is split into <16-bit>:<32-bit> or <32-bit>:<16-bit>. When using loopback or 32-bit ASN/number the assigned number can only be a 16-bit number. This may be a problem with large VNIs. For 16-bit ASN/number the assigned number can be a 32-bit number. |
|||
| admin_subfield | String | overlay_loopback_ip |
The method for deriving RD Administrator subfield (first part of RD): - ‘overlay_loopback_ip’ means the IP address of Loopback0. - ‘vtep_loopback’ means the IP address of the VTEP loopback interface. - ‘bgp_as’ means the AS number of the device. - ‘switch_id’ means the ‘id’ value of the device. - Any - Integer between <0-65535>. - Integer between <0-4294967295>. |
||
| admin_subfield_offset | String | Offset can only be used if admin_subfield is an integer between <0-4294967295> or ‘switch_id’. Total value of admin_subfield + admin_subfield_offset must be <= 4294967295. |
|||
| vrf_admin_subfield | String | The method for deriving RD Administrator subfield (first part of RD) for VRF services: - ‘overlay_loopback_ip’ means the IP address of Loopback0. - ‘vtep_loopback’ means the IP address of the VTEP loopback interface. - ‘bgp_as’ means the AS number of the device. - ‘switch_id’ means the ‘id’ value of the device. - Any - Integer between <0-65535>. - Integer between <0-4294967295>. ‘vrf_admin_subfield’ takes precedence for VRF RDs if set. Otherwise the ‘admin_subfield’ value will be used. |
|||
| vrf_admin_subfield_offset | String | Offset can only be used if ‘vrf_admin_subfield’ is an integer between <0-4294967295> or ‘switch_id’. Total value of ‘vrf_admin_subfield’ + ‘vrf_admin_subfield_offset’ must be <= 4294967295. |
|||
| vlan_assigned_number_subfield | String | mac_vrf_id |
Valid Values: - mac_vrf_id- mac_vrf_vni- vlan_id |
The method for deriving RD Assigned Number subfield for VLAN services (second part of RD): - ‘mac_vrf_id’ means (mac_vrf_id_base or mac_vrf_vni_base) + vlan_id.- ‘mac_vrf_vni’ means (mac_vrf_vni_base or mac_vrf_id_base) + vlan_id.- ‘vlan_id’ will only use the ‘vlan_id’ and ignores all base values. These methods can be overridden per VLAN if either ‘rd_override’, ‘rt_override’ or ‘vni_override’ is set (preferred in this order). |
|
| overlay_routing_protocol | String | ebgp |
Value is converted to lower case. Valid Values: - ebgp- ibgp- cvx- her- none |
- The following overlay routing protocols are supported: - eBGP: Configures fabric with eBGP, default for l3ls-evpn design. - iBGP: Configured fabric with iBGP, only supported with OSPF or ISIS variants in underlay, default for mpls design. - CVX: Configures fabric to leverage CloudVision eXchange as the overlay controller. - HER: Configures fabric with Head-End Replication, configures static VXLAN flood-lists instead of using a dynamic overlay protocol. - none: No overlay configuration will be generated, default for l2ls design. |
|
| overlay_routing_protocol_address_family | String | ipv4 |
Valid Values: - ipv4- ipv6 |
When set to ipv6, enable overlay EVPN peering with IPv6 addresses.This feature depends on underlay_ipv6 variable. As of today, only RFC5549 is capable to transport IPv6 in the underlay. |
|
| overlay_rt_type | Dictionary | Configuration options for the Administrator subfield (first part of RT) and the Assigned Number subfield (second part of RT). By default Route Targets (RT) are set to: - <(mac_vrf_id_base or mac_vrf_vni_base) + vlan_id>:<(mac_vrf_id_base or mac_vrf_vni_base) + vlan_id> for VLANs and VLAN-Aware Bundles with L2 vlans.- <vlan_aware_bundle_number_base + vrf_id>:<vlan_aware_bundle_number_base + vrf_id> for VLAN-Aware Bundles with SVIs.- <vlan_aware_bundle_number_base + id>:<vlan_aware_bundle_number_base + id> for VLAN-Aware Bundles defined under ‘evpn_vlan_bundles’.- <vrf_id>:<vrf_id> for VRFs.Notes: RT is a 48-bit value which is split into <16-bit>:<32-bit> or <32-bit>:<16-bit>. When using 32-bit ASN/number the VNI can only be a 16-bit number. Alternatively use vlan_id/vrf_id as assigned number. For 16-bit ASN/number the assigned number can be a 32-bit number. |
|||
| admin_subfield | String | vrf_id |
The method for deriving RT Administrator subfield (first part of RT): - ‘vrf_id’ means (mac_vrf_id_base or mac_vrf_vni_base) + vlan_id for VLANs, (vrf_id or vrf_vni) for VRFs and id for bundles defined under ‘evpn_vlan_bundles’.- ‘vrf_vni’ means (mac_vrf_vni_base or mac_vrf_id_base) + vlan_id for VLANs, (vrf_vni or vrf_id) for VRFs and id for bundles defined under ‘evpn_vlan_bundles’.- ‘id’ means vlan_id for VLANs, (vrf_id or vrf_vni) for VRFs and id for bundles defined under ‘evpn_vlan_bundles’.- ‘bgp_as’ means the AS number of the device. - Integer between <0-65535>. - Integer between <0-4294967295>. The ‘vrf_id’ and ‘vrf_vni’ methods can be overridden per VLAN if either ‘rt_override’ or ‘vni_override’ is set (preferred in this order). The ‘vrf_id’, ‘vrf_vni’ and ‘id’ methods can be overridden per bundle defined under evpn_vlan_bundles using ‘rt_override’. |
||
| vrf_admin_subfield | String | vrf_id |
The method for deriving RT Administrator subfield (first part of RT) for VRF services: - ‘id’ means (vrf_id or vrf_vni).- ‘vrf_id’ means (vrf_id or vrf_vni).- ‘vrf_vni’ means (vrf_vni or vrf_id).- ‘bgp_as’ means the AS number of the device. - Integer between <0-65535>. - Integer between <0-4294967295>. ‘vrf_admin_subfield’ takes precedence for VRF RDs if set. Otherwise the ‘admin_subfield’ value will be used. |
||
| vlan_assigned_number_subfield | String | mac_vrf_id |
Valid Values: - mac_vrf_id- mac_vrf_vni- vlan_id |
The method for deriving RT Assigned Number subfield for VLAN services (second part of RT): - ‘mac_vrf_id’ means (mac_vrf_id_base or mac_vrf_vni_base) + vlan_id.- ‘mac_vrf_vni’ means (mac_vrf_vni_base or mac_vrf_id_base) + vlan_id.- ‘vlan_id’ will only use the ‘vlan_id’ and ignores all base values. These methods can be overridden per VLAN if either ‘rt_override’ or ‘vni_override’ is set (preferred in this order). |
|
| vtep_vvtep_ip | String | IP Address used as Virtual VTEP. Will be configured as secondary IP on Loopback1. This is only needed for centralized routing designs. |
# Configure an iBGP full mesh between PEs, either because there is no RR used or other reasons.
# Only supported in combination with MPLS overlay.
bgp_mesh_pes: <bool; default=False>
# On mlag leafs, an SVI interface is defined per vrf, to establish iBGP peering (required when there are MLAG leafs in topology).
# The SVI id will be derived from the base vlan defined: mlag_ibgp_peering_vrfs.base_vlan + (vrf_id or vrf_vni) - 1.
# Depending on the values of vrf_id / vrf_vni it may be required to adjust the base_vlan to avoid overlaps or invalid vlan ids.
# The SVI ip address derived from mlag_l3_peer_ipv4_pool is re-used across all iBGP peerings.
mlag_ibgp_peering_vrfs:
base_vlan: <int; 1-4093; default=3000>
# List of CVX vxlan overlay controllers.
# Required if overlay_routing_protocol == CVX.
# CVX servers (VMs) are peering using their management interface, so mgmt_ip must be set for all CVX servers.
overlay_cvx_servers:
# 'inventory_hostname' of CVX server.
- <str>
# When using Head-End Replication, configure flood-lists per VNI.
# By default HER will be configured with a common flood-list containing all VTEPs.
# This behavior can be changed to per-VNI flood-lists by setting `overlay_her_flood_list_per_vni: true`.
# This will make `eos_designs` consider configured VLANs per VTEP, and only include the relevant VTEPs to each VNI's flood-list.
overlay_her_flood_list_per_vni: <bool; default=False>
# When using Head-End Replication, set the scope of flood-lists to Fabric or DC.
# By default all VTEPs in the Fabric (part of the inventory group referenced by "fabric_name") are added to the flood-lists.
# This can be changed to all VTEPs in the DC (sharing the same "dc_name" value).
# This is useful if Border Leaf switches are dividing the VXLAN overlay into separate domains.
overlay_her_flood_list_scope: <str; "fabric" | "dc"; default="fabric">
# Customize the description on overlay interface Loopback0.
overlay_loopback_description: <str>
# IPv6 Unnumbered for MLAG iBGP connections.
# Requires "underlay_rfc5549: true".
overlay_mlag_rfc5549: <bool; default=False>
# Configuration options for the Administrator subfield (first part of RD) and the Assigned Number subfield (second part of RD).
#
# By default Route Distinguishers (RD) are set to:
# - `<overlay_loopback>:<mac_vrf_id_base + vlan_id or mac_vrf_vni_base + vlan_id>` for VLANs and VLAN-Aware Bundles with L2 vlans.
# - `<overlay_loopback>:<vlan_aware_bundle_number_base + vrf_id>` for VLAN-Aware Bundles with SVIs.
# - `<overlay_loopback>:<vlan_aware_bundle_number_base + id>` for VLAN-Aware Bundles defined under 'evpn_vlan_bundles'.
# - `<overlay_loopback>:<vrf_id>` for VRFs.
#
# Note:
# RD is a 48-bit value which is split into <16-bit>:<32-bit> or <32-bit>:<16-bit>.
# When using loopback or 32-bit ASN/number the assigned number can only be a 16-bit number. This may be a problem with large VNIs.
# For 16-bit ASN/number the assigned number can be a 32-bit number.
overlay_rd_type:
# The method for deriving RD Administrator subfield (first part of RD):
# - 'overlay_loopback_ip' means the IP address of Loopback0.
# - 'vtep_loopback' means the IP address of the VTEP loopback interface.
# - 'bgp_as' means the AS number of the device.
# - 'switch_id' means the 'id' value of the device.
# - Any <IPv4 Address> without mask.
# - Integer between <0-65535>.
# - Integer between <0-4294967295>.
admin_subfield: <str; default="overlay_loopback_ip">
# Offset can only be used if admin_subfield is an integer between <0-4294967295> or 'switch_id'.
# Total value of admin_subfield + admin_subfield_offset must be <= 4294967295.
admin_subfield_offset: <str>
# The method for deriving RD Administrator subfield (first part of RD) for VRF services:
# - 'overlay_loopback_ip' means the IP address of Loopback0.
# - 'vtep_loopback' means the IP address of the VTEP loopback interface.
# - 'bgp_as' means the AS number of the device.
# - 'switch_id' means the 'id' value of the device.
# - Any <IPv4 Address> without mask.
# - Integer between <0-65535>.
# - Integer between <0-4294967295>.
#
# 'vrf_admin_subfield' takes precedence for VRF RDs if set. Otherwise the 'admin_subfield' value will be used.
vrf_admin_subfield: <str>
# Offset can only be used if 'vrf_admin_subfield' is an integer between <0-4294967295> or 'switch_id'.
# Total value of 'vrf_admin_subfield' + 'vrf_admin_subfield_offset' must be <= 4294967295.
vrf_admin_subfield_offset: <str>
# The method for deriving RD Assigned Number subfield for VLAN services (second part of RD):
# - 'mac_vrf_id' means `(mac_vrf_id_base or mac_vrf_vni_base) + vlan_id`.
# - 'mac_vrf_vni' means `(mac_vrf_vni_base or mac_vrf_id_base) + vlan_id`.
# - 'vlan_id' will only use the 'vlan_id' and ignores all base values.
#
# These methods can be overridden per VLAN if either 'rd_override', 'rt_override' or 'vni_override' is set (preferred in this order).
vlan_assigned_number_subfield: <str; "mac_vrf_id" | "mac_vrf_vni" | "vlan_id"; default="mac_vrf_id">
# - The following overlay routing protocols are supported:
# - eBGP: Configures fabric with eBGP, default for l3ls-evpn design.
# - iBGP: Configured fabric with iBGP, only supported with OSPF or ISIS variants in underlay, default for mpls design.
# - CVX: Configures fabric to leverage CloudVision eXchange as the overlay controller.
# - HER: Configures fabric with Head-End Replication, configures static VXLAN flood-lists instead of using a dynamic overlay protocol.
# - none: No overlay configuration will be generated, default for l2ls design.
overlay_routing_protocol: <str; "ebgp" | "ibgp" | "cvx" | "her" | "none"; default="ebgp">
# When set to `ipv6`, enable overlay EVPN peering with IPv6 addresses.
# This feature depends on underlay_ipv6 variable. As of today, only RFC5549 is capable to transport IPv6 in the underlay.
overlay_routing_protocol_address_family: <str; "ipv4" | "ipv6"; default="ipv4">
# Configuration options for the Administrator subfield (first part of RT) and the Assigned Number subfield (second part of RT).
#
# By default Route Targets (RT) are set to:
# - `<(mac_vrf_id_base or mac_vrf_vni_base) + vlan_id>:<(mac_vrf_id_base or mac_vrf_vni_base) + vlan_id>` for VLANs and VLAN-Aware Bundles with L2 vlans.
# - `<vlan_aware_bundle_number_base + vrf_id>:<vlan_aware_bundle_number_base + vrf_id>` for VLAN-Aware Bundles with SVIs.
# - `<vlan_aware_bundle_number_base + id>:<vlan_aware_bundle_number_base + id>` for VLAN-Aware Bundles defined under 'evpn_vlan_bundles'.
# - `<vrf_id>:<vrf_id>` for VRFs.
#
# Notes:
# RT is a 48-bit value which is split into <16-bit>:<32-bit> or <32-bit>:<16-bit>.
# When using 32-bit ASN/number the VNI can only be a 16-bit number. Alternatively use vlan_id/vrf_id as assigned number.
# For 16-bit ASN/number the assigned number can be a 32-bit number.
overlay_rt_type:
# The method for deriving RT Administrator subfield (first part of RT):
# - 'vrf_id' means `(mac_vrf_id_base or mac_vrf_vni_base) + vlan_id` for VLANs, `(vrf_id or vrf_vni)` for VRFs and `id` for bundles defined under 'evpn_vlan_bundles'.
# - 'vrf_vni' means `(mac_vrf_vni_base or mac_vrf_id_base) + vlan_id` for VLANs, `(vrf_vni or vrf_id)` for VRFs and `id` for bundles defined under 'evpn_vlan_bundles'.
# - 'id' means `vlan_id` for VLANs, `(vrf_id or vrf_vni)` for VRFs and `id` for bundles defined under 'evpn_vlan_bundles'.
# - 'bgp_as' means the AS number of the device.
# - Integer between <0-65535>.
# - Integer between <0-4294967295>.
#
# The 'vrf_id' and 'vrf_vni' methods can be overridden per VLAN if either 'rt_override' or 'vni_override' is set (preferred in this order).
# The 'vrf_id', 'vrf_vni' and 'id' methods can be overridden per bundle defined under `evpn_vlan_bundles` using 'rt_override'.
admin_subfield: <str; default="vrf_id">
# The method for deriving RT Administrator subfield (first part of RT) for VRF services:
# - 'id' means `(vrf_id or vrf_vni)`.
# - 'vrf_id' means `(vrf_id or vrf_vni)`.
# - 'vrf_vni' means `(vrf_vni or vrf_id)`.
# - 'bgp_as' means the AS number of the device.
# - Integer between <0-65535>.
# - Integer between <0-4294967295>.
#
# 'vrf_admin_subfield' takes precedence for VRF RDs if set. Otherwise the 'admin_subfield' value will be used.
vrf_admin_subfield: <str; default="vrf_id">
# The method for deriving RT Assigned Number subfield for VLAN services (second part of RT):
# - 'mac_vrf_id' means `(mac_vrf_id_base or mac_vrf_vni_base) + vlan_id`.
# - 'mac_vrf_vni' means `(mac_vrf_vni_base or mac_vrf_id_base) + vlan_id`.
# - 'vlan_id' will only use the 'vlan_id' and ignores all base values.
#
# These methods can be overridden per VLAN if either 'rt_override' or 'vni_override' is set (preferred in this order).
vlan_assigned_number_subfield: <str; "mac_vrf_id" | "mac_vrf_vni" | "vlan_id"; default="mac_vrf_id">
# IP Address used as Virtual VTEP. Will be configured as secondary IP on Loopback1.
# This is only needed for centralized routing designs.
vtep_vvtep_ip: <str>
EVPN settings¶
| Variable | Type | Required | Default | Value Restrictions | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| evpn_ebgp_gateway_inter_domain | Boolean | ||||
| evpn_ebgp_gateway_multihop | Integer | 15 |
Default of 15, considering a large value to avoid BGP reachability issues in very complex DCI networks. Adapt the value for your specific topology. |
||
| evpn_ebgp_multihop | Integer | 3 |
Default of 3, the recommended value for a 3 stage spine and leaf topology. Set to a higher value to allow for very large and complex topologies. |
||
| evpn_hostflap_detection | Dictionary | ||||
| enabled | Boolean | True |
If set to false it will disable EVPN host-flap detection. | ||
| threshold | Integer | 5 |
Minimum number of MAC moves that indicate a MAC duplication issue. | ||
| window | Integer | 180 |
Time (in seconds) to detect a MAC duplication issue. | ||
| expiry_timeout | Integer | Time (in seconds) to purge a MAC duplication issue. | |||
| evpn_import_pruning | Boolean | False |
Enable VPN import pruning (Min. EOS 4.24.2F). The Route Target extended communities carried by incoming VPN paths will be examined. If none of those Route Targets have been configured for import, the path will be immediately discarded. |
||
| evpn_multicast | Boolean | False |
General Configuration required for EVPN Multicast. “evpn_l2_multicast” or “evpn_l3_multicast” must also be configured under the Network Services (tenants). Requires “underlay_multicast: true” and IGMP snooping enabled globally (default). For MLAG devices Route Distinguisher must be unique since this feature will create multi-vtep configuration. Warning !!! For Trident3 based platforms i.e 7050X3, 7300X3, 720XP and 722XP The Following default platform setting will be configured: “platform trident forwarding-table partition flexible exact-match 16384 l2-shared 98304 l3-shared 131072” All forwarding agents will be restarted when this configuration is applied. You can tune the settings by overriding the default variable: “platform_settings[platforms].trident_forwarding_table_partition:” Please contact an Arista representative for help with determining the appropriate values for your environment. |
||
| evpn_overlay_bgp_rtc | Boolean | False |
Enable Route Target Membership Constraint Address Family on EVPN overlay BGP peerings (Min. EOS 4.25.1F). Requires use eBGP as overlay protocol. |
||
| evpn_prevent_readvertise_to_server | Boolean | False |
Configure route-map on eBGP sessions towards route-servers, where prefixes with the peer’s ASN in the AS Path are filtered away. This is very useful in large-scale networks, where convergence will be quicker by not returning all updates received from Route-server-1 to Router-server-2 just for Route-server-2 to throw them away because of AS Path loop detection. |
||
| evpn_rd_type removed | Dictionary | This key was removed. Support was removed in AVD version 4.0.0. Use overlay_rd_type instead. | |||
| evpn_rt_type removed | Dictionary | This key was removed. Support was removed in AVD version 4.0.0. Use overlay_rt_type instead. | |||
| evpn_short_esi_prefix | String | 0000:0000: |
Configure prefix for “short_esi” values. | ||
| evpn_vlan_aware_bundles | Boolean | False |
Enable VLAN aware bundles for every EVPN MAC-VRF. If set to true all SVIs in a VRF are configured in a vlan-aware-bundle using the VRF name as the bundle name. l2vlans are bundled in vlan-aware-bundles using the VLAN name as the bundle name.The evpn_vlan_bundle option under svis and l2vlans takes precedence and overrides this behavior. Per svi/l2vlan evpn_vlan_bundle also works when this setting is disabled which allow mixing vlan-aware-bundles with regular MAC-VRFs. |
||
| fabric_evpn_encapsulation | String | vxlan |
Valid Values: - vxlan- mpls |
Should be set to mpls for evpn-mpls scenario. | |
| vxlan_vlan_aware_bundles removed | Boolean | False |
This key was removed. Support was removed in AVD version 4.0.0. Use evpn_vlan_aware_bundles instead. |
evpn_ebgp_gateway_inter_domain: <bool>
# Default of 15, considering a large value to avoid BGP reachability issues in very complex DCI networks.
# Adapt the value for your specific topology.
evpn_ebgp_gateway_multihop: <int; default=15>
# Default of 3, the recommended value for a 3 stage spine and leaf topology.
# Set to a higher value to allow for very large and complex topologies.
evpn_ebgp_multihop: <int; default=3>
evpn_hostflap_detection:
# If set to false it will disable EVPN host-flap detection.
enabled: <bool; default=True>
# Minimum number of MAC moves that indicate a MAC duplication issue.
threshold: <int; default=5>
# Time (in seconds) to detect a MAC duplication issue.
window: <int; default=180>
# Time (in seconds) to purge a MAC duplication issue.
expiry_timeout: <int>
# Enable VPN import pruning (Min. EOS 4.24.2F).
# The Route Target extended communities carried by incoming VPN paths will be examined.
# If none of those Route Targets have been configured for import, the path will be immediately discarded.
evpn_import_pruning: <bool; default=False>
# General Configuration required for EVPN Multicast. "evpn_l2_multicast" or "evpn_l3_multicast" must also be configured under the Network Services (tenants).
# Requires "underlay_multicast: true" and IGMP snooping enabled globally (default).
# For MLAG devices Route Distinguisher must be unique since this feature will create multi-vtep configuration.
# Warning !!! For Trident3 based platforms i.e 7050X3, 7300X3, 720XP and 722XP
# The Following default platform setting will be configured: "platform trident forwarding-table partition flexible exact-match 16384 l2-shared 98304 l3-shared 131072"
# All forwarding agents will be restarted when this configuration is applied.
# You can tune the settings by overriding the default variable: "platform_settings[platforms].trident_forwarding_table_partition:"
# Please contact an Arista representative for help with determining the appropriate values for your environment.
evpn_multicast: <bool; default=False>
# Enable Route Target Membership Constraint Address Family on EVPN overlay BGP peerings (Min. EOS 4.25.1F).
# Requires use eBGP as overlay protocol.
evpn_overlay_bgp_rtc: <bool; default=False>
# Configure route-map on eBGP sessions towards route-servers, where prefixes with the peer's ASN in the AS Path are filtered away.
# This is very useful in large-scale networks, where convergence will be quicker by not returning all updates received
# from Route-server-1 to Router-server-2 just for Route-server-2 to throw them away because of AS Path loop detection.
evpn_prevent_readvertise_to_server: <bool; default=False>
# Configure prefix for "short_esi" values.
evpn_short_esi_prefix: <str; default="0000:0000:">
# Enable VLAN aware bundles for every EVPN MAC-VRF.
# If set to `true` all SVIs in a VRF are configured in a vlan-aware-bundle using the VRF name as the bundle name. `l2vlans` are bundled in vlan-aware-bundles using the VLAN name as the bundle name.
#
# The `evpn_vlan_bundle` option under `svis` and `l2vlans` takes precedence and overrides this behavior. Per svi/l2vlan `evpn_vlan_bundle` also works when this setting is disabled which allow mixing vlan-aware-bundles with regular MAC-VRFs.
evpn_vlan_aware_bundles: <bool; default=False>
# Should be set to mpls for evpn-mpls scenario.
fabric_evpn_encapsulation: <str; "vxlan" | "mpls"; default="vxlan">
WAN Settings¶
WAN generic settings¶
| Variable | Type | Required | Default | Value Restrictions | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| wan_ha | Dictionary | PREVIEW: The wan_ha key is currently not supported. |
|||
| lan_ha_path_group_name | String | LAN_HA |
When WAN HA is enabled for a site if wan_mode: cv-pathfinder, a default path-group is injected to form DPS tunnels over LAN.This key allows to overwrite the default LAN HA path-group name. |
||
| wan_ipsec_profiles | Dictionary | Define IPsec profiles parameters for WAN configuration. | |||
| control_plane | Dictionary | Required | |||
| ike_policy_name | String | CP-IKE-POLICY |
Name of the IKE policy. | ||
| sa_policy_name | String | CP-SA-POLICY |
Name of the SA policy. | ||
| profile_name | String | CP-PROFILE |
Name of the IPSec profile. | ||
| shared_key | String | Required | The IPSec shared key. This variable is sensitive and SHOULD be configured using some vault mechanism. |
||
| data_plane | Dictionary | If data_plane is not defined, control_plane information is used for both. |
|||
| ike_policy_name | String | DP-IKE-POLICY |
Name of the IKE policy. | ||
| sa_policy_name | String | DP-SA-POLICY |
Name of the SA policy. | ||
| profile_name | String | DP-PROFILE |
Name of the IPSec profile. | ||
| shared_key | String | Required | The type 7 encrypted IPSec shared key. This variable is sensitive and should be configured using some vault mechanism. |
||
| wan_mode | String | cv-pathfinder |
Valid Values: - autovpn- cv-pathfinder |
Select if the WAN should be run using CV Pathfinder or AutoVPN only. | |
| wan_stun_dtls_disable | Boolean | False |
WAN STUN connections are authenticated and secured with DTLS by default. For CV Pathfinder deployments CloudVision will automatically deploy certificates on the devices. In case of AutoVPN the certificates must be deployed manually to all devices. For LAB environments this can be disabled, if there are no certificates available. This should NOT be disabled for a WAN network connected to the internet, since it will leave the STUN service exposed with no authentication. |
||
| wan_stun_dtls_profile_name | String | STUN-DTLS |
Name of the SSL profile used for DTLS on WAN STUN connections. When using automatic ceritficate deployment via CloudVision this name must be the same on all WAN routers. |
# PREVIEW: The `wan_ha` key is currently not supported.
wan_ha:
# When WAN HA is enabled for a site if `wan_mode: cv-pathfinder`, a default path-group is injected to form DPS tunnels over LAN.
# This key allows to overwrite the default LAN HA path-group name.
lan_ha_path_group_name: <str; default="LAN_HA">
# Define IPsec profiles parameters for WAN configuration.
wan_ipsec_profiles:
control_plane: # required
# Name of the IKE policy.
ike_policy_name: <str; default="CP-IKE-POLICY">
# Name of the SA policy.
sa_policy_name: <str; default="CP-SA-POLICY">
# Name of the IPSec profile.
profile_name: <str; default="CP-PROFILE">
# The IPSec shared key.
# This variable is sensitive and SHOULD be configured using some vault mechanism.
shared_key: <str; required>
# If `data_plane` is not defined, `control_plane` information is used for both.
data_plane:
# Name of the IKE policy.
ike_policy_name: <str; default="DP-IKE-POLICY">
# Name of the SA policy.
sa_policy_name: <str; default="DP-SA-POLICY">
# Name of the IPSec profile.
profile_name: <str; default="DP-PROFILE">
# The type 7 encrypted IPSec shared key.
# This variable is sensitive and should be configured using some vault mechanism.
shared_key: <str; required>
# Select if the WAN should be run using CV Pathfinder or AutoVPN only.
wan_mode: <str; "autovpn" | "cv-pathfinder"; default="cv-pathfinder">
# WAN STUN connections are authenticated and secured with DTLS by default.
# For CV Pathfinder deployments CloudVision will automatically deploy certificates on the devices.
# In case of AutoVPN the certificates must be deployed manually to all devices.
#
# For LAB environments this can be disabled, if there are no certificates available.
# This should NOT be disabled for a WAN network connected to the internet, since it will leave the STUN service exposed with no authentication.
wan_stun_dtls_disable: <bool; default=False>
# Name of the SSL profile used for DTLS on WAN STUN connections.
# When using automatic ceritficate deployment via CloudVision this name must be the same on all WAN routers.
wan_stun_dtls_profile_name: <str; default="STUN-DTLS">
WAN hierarchy¶
Note
This section is only relevant for CV Pathfinder and not for AutoVPN
| Variable | Type | Required | Default | Value Restrictions | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cv_pathfinder_regions | List, items: Dictionary | Define the CV Pathfinder hierarchy. | |||
| - name | String | Required, Unique | |||
| description | String | ||||
| id | Integer | Required | Min: 1 Max: 255 |
The region ID must be unique for the whole WAN deployment. | |
| sites | List, items: Dictionary | All sites are placed in a default zone “ |
|||
| - name | String | Required, Unique | The site name. | ||
| description | String | ||||
| id | Integer | Required | Min: 1 Max: 10000 |
The site ID must be unique within a zone. Given that all the sites are placed in a zone named after the region, the site ID must be unique within a region. |
|
| location | String | Location as a string is resolved on Cloudvision. | |||
| resolved_location | Dictionary | PREVIEW: These keys are in preview mode. The resolved location elements. Needed for internet-exit Zscaler integration until we can autofill it from the lookup plugin. |
|||
| city | String | Required | |||
| country | String | Required | |||
| site_contact | String | ||||
| site_after_hours_contact | String |
# Define the CV Pathfinder hierarchy.
cv_pathfinder_regions:
- name: <str; required; unique>
description: <str>
# The region ID must be unique for the whole WAN deployment.
id: <int; 1-255; required>
# All sites are placed in a default zone "<region_name>-ZONE" with ID 1.
sites:
# The site name.
- name: <str; required; unique>
description: <str>
# The site ID must be unique within a zone.
# Given that all the sites are placed in a zone named after the region, the site ID must be unique within a region.
id: <int; 1-10000; required>
# Location as a string is resolved on Cloudvision.
location: <str>
# PREVIEW: These keys are in preview mode.
#
# The resolved location elements.
# Needed for internet-exit Zscaler integration until we can autofill it from the lookup plugin.
resolved_location:
city: <str; required>
country: <str; required>
site_contact: <str>
site_after_hours_contact: <str>
WAN path-groups and carriers¶
| Variable | Type | Required | Default | Value Restrictions | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| wan_carriers | List, items: Dictionary | List of carriers used for the WAN configuration and their mapping to path-groups. | |||
| - name | String | Required, Unique | Carrier name. | ||
| description | String | Additional information about the carrier for documentation purposes. | |||
| path_group | String | Required | The path-group to which this carrier belongs. | ||
| trusted | Boolean | False |
Set this to true to mark this carrier as “trusted”.WAN interfaces require an inbound access-list to be set unless the carrier is “trusted”. |
||
| wan_path_groups | List, items: Dictionary | List of path-groups used for the WAN configuration. | |||
| - name | String | Required, Unique | Path-group name. | ||
| id | Integer | Required | Path-group id. Required until an auto ID algorithm is implemented. |
||
| description | String | Additional information about the path-group for documentation purposes. | |||
| ipsec | Dictionary | Configuration of IPSec at the path-group level. | |||
| dynamic_peers | Boolean | True |
Enable IPSec for dynamic peers. | ||
| static_peers | Boolean | True |
Enable IPSec for static peers. | ||
| import_path_groups | List, items: Dictionary | List of path-groups to import in this path-group. | |||
| - remote | String | Remote path-group to import. | |||
| local | String | Optional, if not set, the path-group name is used as local. |
|||
| default_preference | String | preferred |
Preference value used when a preference is not given for a path-group in the wan_virtual_topologies.policies input or whenthe path-group is used in an auto generated policy except if excluded_from_default_policy is set to true.<br><br>Valid values are 1-65535 | "preferred" | "alternate".<br><br>preferredis converted to priority 1.<br>alternate` is converted to priority 2. |
||
| excluded_from_default_policy | Boolean | False |
When set to true, the path-group is excluded from AVD auto generated policies. |
||
| dps_keepalive | Dictionary | Period between the transmission of consecutive keepalive messages, and failure threshold. | |||
| interval | String | Interval in milliseconds. Valid values are 50-60000 | |||
| failure_threshold | Integer | 5 |
Min: 2 Max: 100 |
Failure threshold in number of lost keep-alive messages. |
# List of carriers used for the WAN configuration and their mapping to path-groups.
wan_carriers:
# Carrier name.
- name: <str; required; unique>
# Additional information about the carrier for documentation purposes.
description: <str>
# The path-group to which this carrier belongs.
path_group: <str; required>
# Set this to `true` to mark this carrier as "trusted".
# WAN interfaces require an inbound access-list to be set unless the carrier is "trusted".
trusted: <bool; default=False>
# List of path-groups used for the WAN configuration.
wan_path_groups:
# Path-group name.
- name: <str; required; unique>
# Path-group id.
# Required until an auto ID algorithm is implemented.
id: <int; required>
# Additional information about the path-group for documentation purposes.
description: <str>
# Configuration of IPSec at the path-group level.
ipsec:
# Enable IPSec for dynamic peers.
dynamic_peers: <bool; default=True>
# Enable IPSec for static peers.
static_peers: <bool; default=True>
# List of path-groups to import in this path-group.
import_path_groups:
# Remote path-group to import.
- remote: <str>
# Optional, if not set, the path-group `name` is used as local.
local: <str>
# Preference value used when a preference is not given for a path-group in the `wan_virtual_topologies.policies` input or when
# the path-group is used in an auto generated policy except if `excluded_from_default_policy` is set to `true.
#
# Valid values are 1-65535 | "preferred" | "alternate".
#
# `preferred` is converted to priority 1.
# `alternate` is converted to priority 2.
default_preference: <str; default="preferred">
# When set to `true`, the path-group is excluded from AVD auto generated policies.
excluded_from_default_policy: <bool; default=False>
# Period between the transmission of consecutive keepalive messages, and failure threshold.
dps_keepalive:
# Interval in milliseconds. Valid values are 50-60000 | "auto".
#
# When auto, the interval and failure_threshold are automatically determined based on
# path state.
interval: <str>
# Failure threshold in number of lost keep-alive messages.
failure_threshold: <int; 2-100; default=5>
WAN route-servers¶
| Variable | Type | Required | Default | Value Restrictions | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| wan_route_servers | List, items: Dictionary | List of the AutoVPN RRs when using wan_mode=autovpn, or the Pathfinderswhen using wan_mode=cv-pathfinder, to which the device should connect to.This is also used to establish iBGP sessions between WAN route servers. When the route server is part of the same inventory as the WAN routers, only the name is required. |
|||
| - hostname | String | Required, Unique | Route-Reflector hostname. | ||
| vtep_ip | String | Route-Reflector VTEP IP Address. This is usually the IP address under interface Dps1. |
|||
| path_groups | List, items: Dictionary | Path-groups through which the Route Reflector/Pathfinder is reached. | |||
| - name | String | Required, Unique | Path-group name. | ||
| interfaces | List, items: Dictionary | Required | Min Length: 1 | ||
| - name | String | Required, Unique | Interface name. | ||
| ip_address removed | String | The public IPv4 address (without mask) of the Route Reflector for this path-group.This key was removed. Support was removed in AVD version 4.7.0. Use public_ip instead. | |||
| public_ip | String | The public IPv4 address (without mask) of the Route Reflector for this path-group. |
# List of the AutoVPN RRs when using `wan_mode`=`autovpn`, or the Pathfinders
# when using `wan_mode`=`cv-pathfinder`, to which the device should connect to.
# This is also used to establish iBGP sessions between WAN route servers.
#
# When the route server is part of the same inventory as the WAN routers,
# only the name is required.
wan_route_servers:
# Route-Reflector hostname.
- hostname: <str; required; unique>
# Route-Reflector VTEP IP Address. This is usually the IP address under `interface Dps1`.
vtep_ip: <str>
# Path-groups through which the Route Reflector/Pathfinder is reached.
path_groups:
# Path-group name.
- name: <str; required; unique>
interfaces: # >=1 items; required
# Interface name.
- name: <str; required; unique>
# The public IPv4 address (without mask) of the Route Reflector for this path-group.
public_ip: <str>
WAN Virtual topologies¶
WAN virtual topologies leverage Deep Packet Inspection Engine to match traffic.
| Variable | Type | Required | Default | Value Restrictions | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| wan_virtual_topologies | Dictionary | Configure Virtual Topologies for CV Pathfinder and AutoVPN. Auto create a control plane profile/policy/application and enforce it being first in the default VRF. |
|||
| vrfs | List, items: Dictionary | Map a VRF that exists in network_services to an AVT policy. | |||
| - name | String | Required, Unique | VRF name. | ||
| policy | String | DEFAULT-POLICY |
Name of the policy to apply to this VRF. AVD will auto generate a default policy DEFAULT-POLICY and apply it to the VRF(s) where the policy key is not set.It is possible to overwrite the default policy for all VRFs using it by redefining it in the wan_virtual_topologies.policies list using thedefault name DEFAULT-POLICY. |
||
| wan_vni | Integer | Required | Min: 1 Max: 255 |
Required for VRFs carried over AutoVPN or CV Pathfinder WAN. A VRF can have different VNIs between the Datacenters and the WAN. Note that if no VRF default is configured for WAN, AVD will automatically inject the VRF default with wan_vni set to 1.In addition either vrf_id or vrf_vni must be set to enforce consistent route-targets across domains. |
|
| control_plane_virtual_topology | Dictionary | Always injected into the default VRF policy as the first entry. By default, if no path-groups are specified, all locally available path-groups are used in the generated load-balance policy. ID is hardcoded to 254 for the AVT profile in CV Pathfinder mode. |
|||
| name | String | Optional name, if not set CONTROL-PLANE-PROFILE is used. |
|||
| application_profile | String | APP-PROFILE-CONTROL-PLANE |
The application profile to use for control plane traffic. The application profile should be defined under application_classification.application_profiles.If not defined AVD will auto generate an application profile using the provided name or the default value. If not overwritten elsewhere, the application profile is generated matching one application matching the control plane traffic either sourced from or destined to the WAN route servers. |
||
| traffic_class | Integer | Min: 0 Max: 7 |
Set traffic-class for matched traffic. | ||
| dscp | Integer | Min: 0 Max: 63 |
Set DSCP for matched traffic. | ||
| lowest_hop_count | Boolean | False |
Prefer paths with lowest hop-count. Only applicable for wan_mode: "cv-pathfinder". |
||
| constraints | Dictionary | ||||
| jitter | Integer | Min: 0 Max: 10000 |
Jitter requirement for this load balance policy in milliseconds. | ||
| latency | Integer | Min: 0 Max: 10000 |
One way delay requirement for this load balance policy in milliseconds. | ||
| loss_rate | String | Pattern: ^\d+(.\d{1,2})?$ | Loss Rate requirement in percentage for this load balance policy. Value between 0.00 and 100.00. |
||
| path_groups | List, items: Dictionary | Min Length: 1 | |||
| - names | List, items: String | Required | Min Length: 1 | List of path-group names. | |
| - <str> | String | ||||
| preference | String | Valid values are 1-65535 | |||
| internet_exit | Dictionary | ||||
| policy | String | PREVIEW: This key is in preview mode. Internet-exit policy name associated with this virtual_topology. The policy must be defined under cv_pathfinder_internet_exit_policies. |
|||
| policies | List, items: Dictionary | List of virtual toplogies policies. For AutoVPN, each item in the list creates: * one policy with: * one match entry per application_virtual_topologies itemthey are indexed using 10 * <list_index> where list_index starts at 1.* one default-match* one load-balance policy per application_virtual_topologies and one for the default_virtual_topology.* if the policy is associated with the default VRF, a special control-plane rule is injected in the policy with index 1 referring to a control-plane load-balance policy as defined undercontrol_plane_virtual_topology or if not set, the default one.For CV Pathfinder, each item in the list creates: * one policy with: * one match entry per application_virtual_topologies item ordered as in the data.* one last match entry for the default application-profile using default_virtual_topology information.* one profile per application_virtual_topologies item.* one profile for the default_virtual_topology.* one load-balance policy per application_virtual_topologies.* one load_balance policy for the default_virtual_topology.* if the policy is associated with the default VRF, a special control-plane profile is configured and injected first in the policy assigned to the default VRF. This profile points to acontrol-plane load-balance policy as defined under control_plane_virtual_topology or if not set, the default one. |
|||
| - name | String | Required, Unique | Name of the AVT policy. | ||
| application_virtual_topologies | List, items: Dictionary | List of application specific virtual topologies. | |||
| - application_profile | String | Required, Unique | The application profile to use for this virtual topology. It must be a defined application_classification.application_profile. |
||
| name | String | Optional name, if not set <policy_name>-<application_profile> is used. |
|||
| id | Integer | Min: 2 Max: 253 |
ID of the AVT in each VRFs. ID must be unique across all virtual topologies in a policy. ID 1 is reserved for the default_virtual_toplogy. ID 254 is reserved for the control_plane_virtual_topology. id is required when wan_mode is ‘cv-pathfinder’. |
||
| traffic_class | Integer | Min: 0 Max: 7 |
Set traffic-class for matched traffic. | ||
| dscp | Integer | Min: 0 Max: 63 |
Set DSCP for matched traffic. | ||
| lowest_hop_count | Boolean | False |
Prefer paths with lowest hop-count. Only applicable for wan_mode: "cv-pathfinder". |
||
| constraints | Dictionary | ||||
| jitter | Integer | Min: 0 Max: 10000 |
Jitter requirement for this load balance policy in milliseconds. | ||
| latency | Integer | Min: 0 Max: 10000 |
One way delay requirement for this load balance policy in milliseconds. | ||
| loss_rate | String | Pattern: ^\d+(.\d{1,2})?$ | Loss Rate requirement in percentage for this load balance policy. Value between 0.00 and 100.00. |
||
| path_groups | List, items: Dictionary | Min Length: 1 | |||
| - names | List, items: String | Required | Min Length: 1 | List of path-group names. | |
| - <str> | String | ||||
| preference | String | Valid values are 1-65535 | |||
| internet_exit | Dictionary | ||||
| policy | String | PREVIEW: This key is in preview mode. Internet-exit policy name associated with this virtual_topology. The policy must be defined under cv_pathfinder_internet_exit_policies. |
|||
| default_virtual_topology | Dictionary | Required | Default match for the policy. If no default match should be configured, set drop_unmatched to true.Otherwise, in CV Pathfinder mode, a default AVT profile will be configured with ID 1. |
||
| name | String | Optional name, if not set <policy_name>-DEFAULT is used. |
|||
| drop_unmatched | Boolean | False |
When set, no catch-all match is configured for the policy and unmatched traffic is dropped. |
||
| traffic_class | Integer | Min: 0 Max: 7 |
Set traffic-class for matched traffic. | ||
| dscp | Integer | Min: 0 Max: 63 |
Set DSCP for matched traffic. | ||
| lowest_hop_count | Boolean | False |
Prefer paths with lowest hop-count. Only applicable for wan_mode: "cv-pathfinder". |
||
| constraints | Dictionary | ||||
| jitter | Integer | Min: 0 Max: 10000 |
Jitter requirement for this load balance policy in milliseconds. | ||
| latency | Integer | Min: 0 Max: 10000 |
One way delay requirement for this load balance policy in milliseconds. | ||
| loss_rate | String | Pattern: ^\d+(.\d{1,2})?$ | Loss Rate requirement in percentage for this load balance policy. Value between 0.00 and 100.00. |
||
| path_groups | List, items: Dictionary | Min Length: 1 | |||
| - names | List, items: String | Required | Min Length: 1 | List of path-group names. | |
| - <str> | String | ||||
| preference | String | Valid values are 1-65535 | |||
| internet_exit | Dictionary | ||||
| policy | String | PREVIEW: This key is in preview mode. Internet-exit policy name associated with this virtual_topology. The policy must be defined under cv_pathfinder_internet_exit_policies. |
# Configure Virtual Topologies for CV Pathfinder and AutoVPN.
# Auto create a control plane profile/policy/application and enforce it being first in the default VRF.
wan_virtual_topologies:
# Map a VRF that exists in network_services to an AVT policy.
vrfs:
# VRF name.
- name: <str; required; unique>
# Name of the policy to apply to this VRF.
# AVD will auto generate a default policy DEFAULT-POLICY and apply it to the VRF(s)
# where the `policy` key is not set.
# It is possible to overwrite the default policy for all VRFs using it
# by redefining it in the `wan_virtual_topologies.policies` list using the
# default name `DEFAULT-POLICY`.
policy: <str; default="DEFAULT-POLICY">
# Required for VRFs carried over AutoVPN or CV Pathfinder WAN.
#
# A VRF can have different VNIs between the Datacenters and the WAN.
# Note that if no VRF default is configured for WAN, AVD will automatically inject the VRF default with
# `wan_vni` set to `1`.
# In addition either `vrf_id` or `vrf_vni` must be set to enforce consistent route-targets across domains.
wan_vni: <int; 1-255; required>
# Always injected into the default VRF policy as the first entry.
#
# By default, if no path-groups are specified, all locally available path-groups
# are used in the generated load-balance policy.
# ID is hardcoded to 254 for the AVT profile in CV Pathfinder mode.
control_plane_virtual_topology:
# Optional name, if not set `CONTROL-PLANE-PROFILE` is used.
name: <str>
# The application profile to use for control plane traffic.
#
# The application profile should be defined under `application_classification.application_profiles`.
# If not defined AVD will auto generate an application profile using the provided name or the default value.
#
# If not overwritten elsewhere, the application profile is generated matching one application matching the control plane traffic either sourced from or destined to the WAN route servers.
application_profile: <str; default="APP-PROFILE-CONTROL-PLANE">
# Set traffic-class for matched traffic.
traffic_class: <int; 0-7>
# Set DSCP for matched traffic.
dscp: <int; 0-63>
# Prefer paths with lowest hop-count.
# Only applicable for `wan_mode: "cv-pathfinder"`.
lowest_hop_count: <bool; default=False>
constraints:
# Jitter requirement for this load balance policy in milliseconds.
jitter: <int; 0-10000>
# One way delay requirement for this load balance policy in milliseconds.
latency: <int; 0-10000>
# Loss Rate requirement in percentage for this load balance policy.
# Value between 0.00 and 100.00.
loss_rate: <str>
path_groups: # >=1 items
# List of path-group names.
- names: # >=1 items; required
- <str>
# Valid values are 1-65535 | "preferred" | "alternate".
#
# "preferred" is converted to priority 1.
# "alternate" is converted to priority 2.
#
# If not set, each path-group in `names` will be attributed its `default_preference`.
preference: <str>
internet_exit:
# PREVIEW: This key is in preview mode.
#
# Internet-exit policy name associated with this virtual_topology.
# The policy must be defined under `cv_pathfinder_internet_exit_policies`.
policy: <str>
# List of virtual toplogies policies.
#
# For AutoVPN, each item in the list creates:
# * one policy with:
# * one `match` entry per `application_virtual_topologies` item
# they are indexed using `10 * <list_index>` where `list_index` starts at `1`.
# * one `default-match`
# * one load-balance policy per `application_virtual_topologies` and one for the `default_virtual_topology`.
# * if the policy is associated with the default VRF, a special control-plane rule is injected
# in the policy with index `1` referring to a control-plane load-balance policy as defined under
# `control_plane_virtual_topology` or if not set, the default one.
#
# For CV Pathfinder, each item in the list creates:
# * one policy with:
# * one `match` entry per `application_virtual_topologies` item ordered as in the data.
# * one last match entry for the `default` application-profile using `default_virtual_topology` information.
# * one profile per `application_virtual_topologies` item.
# * one profile for the `default_virtual_topology`.
# * one load-balance policy per `application_virtual_topologies`.
# * one load_balance policy for the `default_virtual_topology`.
# * if the policy is associated with the default VRF, a special control-plane profile is configured
# and injected first in the policy assigned to the `default` VRF. This profile points to a
# control-plane load-balance policy as defined under `control_plane_virtual_topology` or if not set, the default one.
policies:
# Name of the AVT policy.
- name: <str; required; unique>
# List of application specific virtual topologies.
application_virtual_topologies:
# The application profile to use for this virtual topology. It must be a defined `application_classification.application_profile`.
- application_profile: <str; required; unique>
# Optional name, if not set `<policy_name>-<application_profile>` is used.
name: <str>
# ID of the AVT in each VRFs. ID must be unique across all virtual topologies in a policy.
# ID 1 is reserved for the default_virtual_toplogy.
# ID 254 is reserved for the control_plane_virtual_topology.
#
# `id` is required when `wan_mode` is 'cv-pathfinder'.
id: <int; 2-253>
# Set traffic-class for matched traffic.
traffic_class: <int; 0-7>
# Set DSCP for matched traffic.
dscp: <int; 0-63>
# Prefer paths with lowest hop-count.
# Only applicable for `wan_mode: "cv-pathfinder"`.
lowest_hop_count: <bool; default=False>
constraints:
# Jitter requirement for this load balance policy in milliseconds.
jitter: <int; 0-10000>
# One way delay requirement for this load balance policy in milliseconds.
latency: <int; 0-10000>
# Loss Rate requirement in percentage for this load balance policy.
# Value between 0.00 and 100.00.
loss_rate: <str>
path_groups: # >=1 items
# List of path-group names.
- names: # >=1 items; required
- <str>
# Valid values are 1-65535 | "preferred" | "alternate".
#
# "preferred" is converted to priority 1.
# "alternate" is converted to priority 2.
#
# If not set, each path-group in `names` will be attributed its `default_preference`.
preference: <str>
internet_exit:
# PREVIEW: This key is in preview mode.
#
# Internet-exit policy name associated with this virtual_topology.
# The policy must be defined under `cv_pathfinder_internet_exit_policies`.
policy: <str>
# Default match for the policy.
# If no default match should be configured, set `drop_unmatched` to `true`.
# Otherwise, in CV Pathfinder mode, a default AVT profile will be configured with ID 1.
default_virtual_topology: # required
# Optional name, if not set `<policy_name>-DEFAULT` is used.
name: <str>
# When set, no `catch-all` match is configured for the policy and unmatched traffic is dropped.
drop_unmatched: <bool; default=False>
# Set traffic-class for matched traffic.
traffic_class: <int; 0-7>
# Set DSCP for matched traffic.
dscp: <int; 0-63>
# Prefer paths with lowest hop-count.
# Only applicable for `wan_mode: "cv-pathfinder"`.
lowest_hop_count: <bool; default=False>
constraints:
# Jitter requirement for this load balance policy in milliseconds.
jitter: <int; 0-10000>
# One way delay requirement for this load balance policy in milliseconds.
latency: <int; 0-10000>
# Loss Rate requirement in percentage for this load balance policy.
# Value between 0.00 and 100.00.
loss_rate: <str>
path_groups: # >=1 items
# List of path-group names.
- names: # >=1 items; required
- <str>
# Valid values are 1-65535 | "preferred" | "alternate".
#
# "preferred" is converted to priority 1.
# "alternate" is converted to priority 2.
#
# If not set, each path-group in `names` will be attributed its `default_preference`.
preference: <str>
internet_exit:
# PREVIEW: This key is in preview mode.
#
# Internet-exit policy name associated with this virtual_topology.
# The policy must be defined under `cv_pathfinder_internet_exit_policies`.
policy: <str>
Application Classification¶
| Variable | Type | Required | Default | Value Restrictions | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| application_classification | Dictionary | Application traffic recognition configuration. | |||
| categories | List, items: Dictionary | List of categories. | |||
| - name | String | Required, Unique | Category name. | ||
| applications | List, items: Dictionary | List of applications. | |||
| - name | String | Application name. | |||
| service | String | Valid Values: - audio-video- chat- default- file-transfer- networking-protocols- peer-to-peer- software-update |
Service Name. Specific service to target for this application. If no service is specified, all supported services of the application are matched. Not all valid values are valid for all applications, check on EOS CLI. |
||
| field_sets | Dictionary | ||||
| l4_ports | List, items: Dictionary | L4 port field-set. | |||
| - name | String | Required, Unique | L4 port field-set name. | ||
| port_values | List, items: String | ||||
| - <str> | String | Port values or range of port values. Port values are between 0 and 65535. |
|||
| ipv4_prefixes | List, items: Dictionary | IPv4 prefix field set. | |||
| - name | String | Required, Unique | IPv4 prefix field-set name. | ||
| prefix_values | List, items: String | ||||
| - <str> | String | IP prefix (ex 1.2.3.0/24). | |||
| applications | Dictionary | ||||
| ipv4_applications | List, items: Dictionary | List of user defined IPv4 applications. The name should be unique over all defined applications (ipv4 and l4). | |||
| - name | String | Required, Unique | Application name. | ||
| src_prefix_set_name | String | Source prefix set name. | |||
| dest_prefix_set_name | String | Destination prefix set name. | |||
| protocols | List, items: String | List of protocols to consider for this application. To use port field-sets (source, destination or both), the list must contain only one or two protocols, either tcp or udp.When using both protocols, one line is rendered for each in the configuration, hence the field-sets must have the same value for tcp_src_port_set_name andudp_src_port_set_name and for tcp_dest_port_set_name and udp_dest_port_set_nameif set in order to generate valid configuration in EOS. |
|||
| - <str> | String | Valid Values: - ahp- esp- icmp- igmp- ospf- pim- rsvp- tcp- udp- vrrp |
|||
| protocol_ranges | List, items: String | Accept protocol value(s) or range(s). Protocol values can be between 1 and 255. |
|||
| - <str> | String | ||||
| udp_src_port_set_name | String | Name of field set for UDP source ports. When the protocols list contain both tcp and udp, this key valuemust be the same as tcp_src_port_set_name. |
|||
| tcp_src_port_set_name | String | Name of field set for TCP source ports. When the protocols list contain both tcp and udp, this key valuemust be the same as udp_src_port_set_name. |
|||
| udp_dest_port_set_name | String | Name of field set for UDP destination ports. When the protocols list contain both tcp and udp, this key valuemust be the same as tcp_dest_port_set_name. |
|||
| tcp_dest_port_set_name | String | Name of field set for TCP destination ports. When the protocols list contain both tcp and udp, this key valuemust be the same as udp_dest_port_set_name. |
|||
| l4_applications | List, items: Dictionary | List of user defined L4 applications. The name should be unique over all defined applications (ipv4 and l4). | |||
| - name | String | Required, Unique | Application name. | ||
| protocols | List, items: String | List of protocols to consider for this application. To use port field-sets (source, destination or both), the list must contain only one or two protocols, either tcp or udp.When using both protocols, one line is rendered for each in the configuration, hence the field-sets must have the same value for tcp_src_port_set_name andudp_src_port_set_name and for tcp_dest_port_set_name and udp_dest_port_set_nameif set in order to generate valid configuration in EOS. |
|||
| - <str> | String | Valid Values: - ahp- esp- icmp- igmp- ospf- pim- rsvp- tcp- udp- vrrp |
|||
| protocol_ranges | List, items: String | Accept protocol value(s) or range(s). Protocol values can be between 1 and 255. |
|||
| - <str> | String | ||||
| udp_src_port_set_name | String | Name of field set for UDP source ports. When the protocols list contain both tcp and udp, this key valuemust be the same as tcp_src_port_set_name. |
|||
| tcp_src_port_set_name | String | Name of field set for TCP source ports. When the protocols list contain both tcp and udp, this key valuemust be the same as udp_src_port_set_name. |
|||
| udp_dest_port_set_name | String | Name of field set for UDP destination ports. When the protocols list contain both tcp and udp, this key valuemust be the same as tcp_dest_port_set_name. |
|||
| tcp_dest_port_set_name | String | Name of field set for TCP destination ports. When the protocols list contain both tcp and udp, this key valuemust be the same as udp_dest_port_set_name. |
|||
| application_profiles | List, items: Dictionary | Group of applications. | |||
| - name | String | Application Profile name. | |||
| applications | List, items: Dictionary | List of applications part of the application profile. | |||
| - name | String | Application Name. | |||
| service | String | Valid Values: - audio-video- chat- default- file-transfer- networking-protocols- peer-to-peer- software-update |
Service Name. Specific service to target for this application. If no service is specified, all supported services of the application are matched. Not all valid values are valid for all applications, check on EOS CLI. |
||
| application_transports | List, items: String | List of transport protocols. | |||
| - <str> | String | Valid Values: - http- https- udp- tcp- ip- ip6- ssl- rtp- sctp- quic |
Transport name. | ||
| categories | List, items: Dictionary | Categories under this application profile. | |||
| - name | String | Name of a category. | |||
| service | String | Valid Values: - audio-video- chat- default- file-transfer- networking-protocols- peer-to-peer- software-update |
Service Name. Specific service to target for this application. If no service is specified, all supported services of the application are matched. Not all valid values are valid for all applications, check on EOS CLI. |
# Application traffic recognition configuration.
application_classification:
# List of categories.
categories:
# Category name.
- name: <str; required; unique>
# List of applications.
applications:
# Application name.
- name: <str>
# Service Name.
# Specific service to target for this application.
# If no service is specified, all supported services of the application are matched.
# Not all valid values are valid for all applications, check on EOS CLI.
service: <str; "audio-video" | "chat" | "default" | "file-transfer" | "networking-protocols" | "peer-to-peer" | "software-update">
field_sets:
# L4 port field-set.
l4_ports:
# L4 port field-set name.
- name: <str; required; unique>
port_values:
# Port values or range of port values.
# Port values are between 0 and 65535.
- <str>
# IPv4 prefix field set.
ipv4_prefixes:
# IPv4 prefix field-set name.
- name: <str; required; unique>
prefix_values:
# IP prefix (ex 1.2.3.0/24).
- <str>
applications:
# List of user defined IPv4 applications. The name should be unique over all defined applications (ipv4 and l4).
ipv4_applications:
# Application name.
- name: <str; required; unique>
# Source prefix set name.
src_prefix_set_name: <str>
# Destination prefix set name.
dest_prefix_set_name: <str>
# List of protocols to consider for this application.
# To use port field-sets (source, destination or both), the list
# must contain only one or two protocols, either `tcp` or `udp`.
# When using both protocols, one line is rendered for each in the configuration,
# hence the field-sets must have the same value for `tcp_src_port_set_name` and
# `udp_src_port_set_name` and for `tcp_dest_port_set_name` and `udp_dest_port_set_name`
# if set in order to generate valid configuration in EOS.
protocols:
- <str; "ahp" | "esp" | "icmp" | "igmp" | "ospf" | "pim" | "rsvp" | "tcp" | "udp" | "vrrp">
# Accept protocol value(s) or range(s).
# Protocol values can be between 1 and 255.
protocol_ranges:
- <str>
# Name of field set for UDP source ports.
# When the `protocols` list contain both `tcp` and `udp`, this key value
# must be the same as `tcp_src_port_set_name`.
udp_src_port_set_name: <str>
# Name of field set for TCP source ports.
# When the `protocols` list contain both `tcp` and `udp`, this key value
# must be the same as `udp_src_port_set_name`.
tcp_src_port_set_name: <str>
# Name of field set for UDP destination ports.
# When the `protocols` list contain both `tcp` and `udp`, this key value
# must be the same as `tcp_dest_port_set_name`.
udp_dest_port_set_name: <str>
# Name of field set for TCP destination ports.
# When the `protocols` list contain both `tcp` and `udp`, this key value
# must be the same as `udp_dest_port_set_name`.
tcp_dest_port_set_name: <str>
# List of user defined L4 applications. The name should be unique over all defined applications (ipv4 and l4).
l4_applications:
# Application name.
- name: <str; required; unique>
# List of protocols to consider for this application.
# To use port field-sets (source, destination or both), the list
# must contain only one or two protocols, either `tcp` or `udp`.
# When using both protocols, one line is rendered for each in the configuration,
# hence the field-sets must have the same value for `tcp_src_port_set_name` and
# `udp_src_port_set_name` and for `tcp_dest_port_set_name` and `udp_dest_port_set_name`
# if set in order to generate valid configuration in EOS.
protocols:
- <str; "ahp" | "esp" | "icmp" | "igmp" | "ospf" | "pim" | "rsvp" | "tcp" | "udp" | "vrrp">
# Accept protocol value(s) or range(s).
# Protocol values can be between 1 and 255.
protocol_ranges:
- <str>
# Name of field set for UDP source ports.
# When the `protocols` list contain both `tcp` and `udp`, this key value
# must be the same as `tcp_src_port_set_name`.
udp_src_port_set_name: <str>
# Name of field set for TCP source ports.
# When the `protocols` list contain both `tcp` and `udp`, this key value
# must be the same as `udp_src_port_set_name`.
tcp_src_port_set_name: <str>
# Name of field set for UDP destination ports.
# When the `protocols` list contain both `tcp` and `udp`, this key value
# must be the same as `tcp_dest_port_set_name`.
udp_dest_port_set_name: <str>
# Name of field set for TCP destination ports.
# When the `protocols` list contain both `tcp` and `udp`, this key value
# must be the same as `udp_dest_port_set_name`.
tcp_dest_port_set_name: <str>
# Group of applications.
application_profiles:
# Application Profile name.
- name: <str>
# List of applications part of the application profile.
applications:
# Application Name.
- name: <str>
# Service Name.
# Specific service to target for this application.
# If no service is specified, all supported services of the application are matched.
# Not all valid values are valid for all applications, check on EOS CLI.
service: <str; "audio-video" | "chat" | "default" | "file-transfer" | "networking-protocols" | "peer-to-peer" | "software-update">
# List of transport protocols.
application_transports:
# Transport name.
- <str; "http" | "https" | "udp" | "tcp" | "ip" | "ip6" | "ssl" | "rtp" | "sctp" | "quic">
# Categories under this application profile.
categories:
# Name of a category.
- name: <str>
# Service Name.
# Specific service to target for this application.
# If no service is specified, all supported services of the application are matched.
# Not all valid values are valid for all applications, check on EOS CLI.
service: <str; "audio-video" | "chat" | "default" | "file-transfer" | "networking-protocols" | "peer-to-peer" | "software-update">
Internet Exit policies¶
Note
This section is only relevant for CV Pathfinder and not for AutoVPN
| Variable | Type | Required | Default | Value Restrictions | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cv_pathfinder_internet_exit_policies | List, items: Dictionary | PREVIEW: These keys are in preview mode. List of internet-exit policies used for the WAN configuration. |
|||
| - name | String | Required, Unique | Internet-exit policy name. | ||
| type | String | Required | Valid Values: - zscaler |
Internet-exit policy type. Only Zscaler supported. |
|
| fallback_to_system_default | Boolean | True |
Add system default exit-group at the end of the policy. | ||
| zscaler | Dictionary | Zscaler information. Only used if type is ‘zscaler’. |
|||
| ipsec_key_salt | String | Required | “Salt” used for auto generation of encryption keys for IPsec tunnels to Zscaler. The keys will be generated as a hash of salt_<hostname>_<policy_name>.Since this salt can be used to deduct the encryption key, it is recommeneded to use vault. |
||
| cloud_name | String | Required | Zscaler cloud name like ‘zscaler1’ or ‘zscalerbeta’. | ||
| domain_name | String | Required | Domain name as configured in Zscaler for the tenant. Used as UFQDN suffix for authentication. | ||
| encrypt_traffic | Boolean | True |
When true the traffic going over the tunnels will be encrypted with AES-256-GCM. Otherwise the traffic will be using NULL encryption.Note that encryption requires a subscription on the Zscaler account. |
||
| download_bandwidth | Integer | Maximum allowed download bandwidth in Mbps for each device using this policy. | |||
| upload_bandwidth | Integer | Maximum allowed upload bandwidth in Mbps for each device using this policy. | |||
| firewall | Dictionary | ||||
| enabled | Boolean | False |
Enforce firewall controls. | ||
| ips | Boolean | False |
Enable IPS Controls for the firewall. | ||
| acceptable_use_policy | Boolean | False |
Display an Acceptable Use Policy (AUP) and require users to accept it. |
# PREVIEW: These keys are in preview mode.
#
# List of internet-exit policies used for the WAN configuration.
cv_pathfinder_internet_exit_policies:
# Internet-exit policy name.
- name: <str; required; unique>
# Internet-exit policy type.
# Only Zscaler supported.
type: <str; "zscaler"; required>
# Add system default exit-group at the end of the policy.
fallback_to_system_default: <bool; default=True>
# Zscaler information. Only used if `type` is 'zscaler'.
zscaler:
# "Salt" used for auto generation of encryption keys for IPsec tunnels to Zscaler.
# The keys will be generated as a hash of `salt_<hostname>_<policy_name>`.
# Since this salt can be used to deduct the encryption key, it is recommeneded to use vault.
ipsec_key_salt: <str; required>
# Zscaler cloud name like 'zscaler1' or 'zscalerbeta'.
cloud_name: <str; required>
# Domain name as configured in Zscaler for the tenant. Used as UFQDN suffix for authentication.
domain_name: <str; required>
# When `true` the traffic going over the tunnels will be encrypted with AES-256-GCM. Otherwise the traffic will be using NULL encryption.
# Note that encryption requires a subscription on the Zscaler account.
encrypt_traffic: <bool; default=True>
# Maximum allowed download bandwidth in Mbps for each device using this policy.
download_bandwidth: <int>
# Maximum allowed upload bandwidth in Mbps for each device using this policy.
upload_bandwidth: <int>
firewall:
# Enforce firewall controls.
enabled: <bool; default=False>
# Enable IPS Controls for the firewall.
ips: <bool; default=False>
# Display an Acceptable Use Policy (AUP) and require users to accept it.
acceptable_use_policy: <bool; default=False>
Zscaler Internet Exit¶
Note
This data model is intended to be autofilled using a lookup plugin. See the top level key description for more information.
| Variable | Type | Required | Default | Value Restrictions | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| zscaler_endpoints | Dictionary | PREVIEW: These keys are in preview mode. Special data model used for WAN internet-exit integration with Zscaler. The model is supposed to be autofilled per-device using the arista.avd.cv_zscaler_endpoints Ansible lookup plugin.Example: yaml<br>zscaler_endpoints: "{{ lookup('arista.avd.cv_zscaler_endpoints', cv_server="<optional servername>", cv_token="<optional token>") }}"<br>The cv_server and cv_token options can be set as inventory variables instead of given as arguments. (Then they will also be used for cv_deploy) |
|||
| primary | Dictionary | Required | |||
| ip_address | String | Required | |||
| datacenter | String | Required | |||
| city | String | Required | |||
| country | String | Required | |||
| latitude | String | Required | |||
| longitude | String | Required | |||
| secondary | Dictionary | ||||
| ip_address | String | Required | |||
| datacenter | String | Required | |||
| city | String | Required | |||
| country | String | Required | |||
| latitude | String | Required | |||
| longitude | String | Required | |||
| tertiary | Dictionary | ||||
| ip_address | String | Required | |||
| datacenter | String | Required | |||
| city | String | Required | |||
| country | String | Required | |||
| latitude | String | Required | |||
| longitude | String | Required |
# PREVIEW: These keys are in preview mode.
#
# Special data model used for WAN internet-exit integration with Zscaler.
# The model is supposed to be autofilled per-device using the `arista.avd.cv_zscaler_endpoints` Ansible lookup plugin.
# Example:
# ```yaml
# zscaler_endpoints: "{{ lookup('arista.avd.cv_zscaler_endpoints', cv_server="<optional servername>", cv_token="<optional token>") }}"
# ```
# The cv_server and cv_token options can be set as inventory variables instead of given as arguments. (Then they will also be used for cv_deploy)
zscaler_endpoints:
primary: # required
ip_address: <str; required>
datacenter: <str; required>
city: <str; required>
country: <str; required>
latitude: <str; required>
longitude: <str; required>
secondary:
ip_address: <str; required>
datacenter: <str; required>
city: <str; required>
country: <str; required>
latitude: <str; required>
longitude: <str; required>
tertiary:
ip_address: <str; required>
datacenter: <str; required>
city: <str; required>
country: <str; required>
latitude: <str; required>
longitude: <str; required>
Management settings¶
| Variable | Type | Required | Default | Value Restrictions | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| event_handlers | List, items: Dictionary | Gives the ability to monitor and react to Syslog messages. Event Handlers provide a powerful and flexible tool that can be used to apply self-healing actions, customize the system behavior, and implement workarounds to problems discovered in the field. |
|||
| - name | String | Required, Unique | Event Handler Name. | ||
| action_type | String | Valid Values: - bash- increment- log |
|||
| action | String | Command to execute. |
|||
| delay | Integer | Event-handler delay in seconds. |
|||
| trigger | String | Valid Values: - on-boot- on-logging- on-startup-config- on-maintenance |
Configure event trigger condition. |
||
| trigger_on_maintenance | Dictionary | Settings required for trigger ‘on-maintenance’. | |||
| operation | String | Required | Valid Values: - enter- exit |
||
| bgp_peer | String | Ipv4/Ipv6 address or peer group name. Trigger condition occurs on maintenance operation of specified BGP peer. |
|||
| action | String | Required | Valid Values: - after- before- all- begin- end |
Action for maintenance operation. | |
| stage | String | Valid Values: - bgp- linkdown- mlag- ratemon |
Action is triggered after/before specified stage. | ||
| vrf | String | VRF name. VRF can be defined for “bgp_peer” only. | |||
| interface | String | Trigger condition occurs on maintenance operation of specified interface. | |||
| unit | String | Name of unit. Trigger condition occurs on maintenance operation of specified unit | |||
| regex | String | Regular expression to use for searching log messages. Required for on-logging trigger. |
|||
| asynchronous | Boolean | False |
Set the action to be non-blocking. |
||
| ipv6_mgmt_destination_networks | List, items: String | List of IPv6 prefixes to configure as static routes towards the OOB IPv6 Management interface gateway. Replaces the default route. |
|||
| - <str> | String | IPv6_network/Mask. | |||
| ipv6_mgmt_gateway | String | Format: ipv6 | OOB Management interface gateway in IPv6 format. Used as next-hop for default gateway or static routes defined under ‘ipv6_mgmt_destination_networks’. |
||
| local_users | List, items: Dictionary | ||||
| - name | String | Required, Unique | Username. | ||
| disabled | Boolean | If true, the user will be removed and all other settings are ignored. Useful for removing the default “admin” user. |
|||
| privilege | Integer | Min: 0 Max: 15 |
Initial privilege level with local EXEC authorization. |
||
| role | String | EOS RBAC Role to be assigned to the user such as “network-admin” or “network-operator”. |
|||
| sha512_password | String | SHA512 Hash of Password. Must be the hash of the password. By default EOS salts the password with the username, so the simplest is to generate the hash on an EOS device using the same username. |
|||
| no_password | Boolean | If set a password will not be configured for this user. “sha512_password” MUST not be defined for this user. |
|||
| ssh_key | String | ||||
| secondary_ssh_key | String | ||||
| shell | String | Valid Values: - /bin/bash- /bin/sh- /sbin/nologin |
Specify shell for the user. |
||
| management_eapi | Dictionary | Default is HTTPS management eAPI enabled. The VRF is set to < mgmt_interface_vrf >. |
|||
| enable_http | Boolean | False |
|||
| enable_https | Boolean | True |
|||
| default_services | Boolean | ||||
| name_servers | List, items: String | List of DNS servers. The VRF is set to < mgmt_interface_vrf >. | |||
| - <str> | String | IPv4 address. | |||
| ntp_settings | Dictionary | NTP settings | |||
| server_vrf | String | EOS only supports NTP servers in one VRF, so this VRF is used for all NTP servers and one local-interface. - use_mgmt_interface_vrf will configure the NTP server(s) under the VRF set with mgmt_interface_vrf and set the mgmt_interface as NTP local-interface.An error will be raised if mgmt_ip or ipv6_mgmt_ip are not configured for the device.- use_inband_mgmt_vrf will configure the NTP server(s) under the VRF set with inband_mgmt_vrf and set the inband_mgmt_interface as NTP local-interface.An error will be raised if inband management is not configured for the device. - Any other string will be used directly as the VRF name but local interface must be set with custom_structured_configuration_ntp if needed.If not set, the VRF is automatically picked up from the global setting default_mgmt_method. |
|||
| servers | List, items: Dictionary | The first server is always set as “preferred”. | |||
| - name | String | IP or hostname e.g., 2.2.2.55, ie.pool.ntp.org. | |||
| burst | Boolean | ||||
| iburst | Boolean | ||||
| key | Integer | Min: 1 Max: 65535 |
|||
| maxpoll | Integer | Min: 3 Max: 17 |
Value of maxpoll between 3 - 17 (Logarithmic). | ||
| minpoll | Integer | Min: 3 Max: 17 |
Value of minpoll between 3 - 17 (Logarithmic). | ||
| version | Integer | Min: 1 Max: 4 |
|||
| authenticate | Boolean | ||||
| authenticate_servers_only | Boolean | ||||
| authentication_keys | List, items: Dictionary | ||||
| - id | Integer | Required, Unique | Min: 1 Max: 65534 |
Key identifier. | |
| hash_algorithm | String | Valid Values: - md5- sha1 |
|||
| key | String | Obfuscated key. | |||
| key_type | String | Valid Values: - 0- 7- 8a |
|||
| trusted_keys | String | List of trusted-keys as string ex. 10-12,15. | |||
| timezone | String | Clock timezone like “CET” or “US/Pacific”. |
# Gives the ability to monitor and react to Syslog messages.
# Event Handlers provide a powerful and flexible tool that can be used to apply self-healing actions,
# customize the system behavior, and implement workarounds to problems discovered in the field.
event_handlers:
# Event Handler Name.
- name: <str; required; unique>
action_type: <str; "bash" | "increment" | "log">
# Command to execute.
action: <str>
# Event-handler delay in seconds.
delay: <int>
# Configure event trigger condition.
trigger: <str; "on-boot" | "on-logging" | "on-startup-config" | "on-maintenance">
# Settings required for trigger 'on-maintenance'.
trigger_on_maintenance:
operation: <str; "enter" | "exit"; required>
# Ipv4/Ipv6 address or peer group name.
# Trigger condition occurs on maintenance operation of specified BGP peer.
bgp_peer: <str>
# Action for maintenance operation.
action: <str; "after" | "before" | "all" | "begin" | "end"; required>
# Action is triggered after/before specified stage.
stage: <str; "bgp" | "linkdown" | "mlag" | "ratemon">
# VRF name. VRF can be defined for "bgp_peer" only.
vrf: <str>
# Trigger condition occurs on maintenance operation of specified interface.
interface: <str>
# Name of unit. Trigger condition occurs on maintenance operation of specified unit
unit: <str>
# Regular expression to use for searching log messages. Required for on-logging trigger.
regex: <str>
# Set the action to be non-blocking.
asynchronous: <bool; default=False>
# List of IPv6 prefixes to configure as static routes towards the OOB IPv6 Management interface gateway.
# Replaces the default route.
ipv6_mgmt_destination_networks:
# IPv6_network/Mask.
- <str>
# OOB Management interface gateway in IPv6 format.
# Used as next-hop for default gateway or static routes defined under 'ipv6_mgmt_destination_networks'.
ipv6_mgmt_gateway: <str>
local_users:
# Username.
- name: <str; required; unique>
# If true, the user will be removed and all other settings are ignored.
# Useful for removing the default "admin" user.
disabled: <bool>
# Initial privilege level with local EXEC authorization.
privilege: <int; 0-15>
# EOS RBAC Role to be assigned to the user such as "network-admin" or "network-operator".
role: <str>
# SHA512 Hash of Password.
# Must be the hash of the password. By default EOS salts the password with the username, so the simplest is to generate the hash on an EOS device using the same username.
sha512_password: <str>
# If set a password will not be configured for this user. "sha512_password" MUST not be defined for this user.
no_password: <bool>
ssh_key: <str>
secondary_ssh_key: <str>
# Specify shell for the user.
shell: <str; "/bin/bash" | "/bin/sh" | "/sbin/nologin">
# Default is HTTPS management eAPI enabled.
# The VRF is set to < mgmt_interface_vrf >.
management_eapi:
enable_http: <bool; default=False>
enable_https: <bool; default=True>
default_services: <bool>
# List of DNS servers. The VRF is set to < mgmt_interface_vrf >.
name_servers:
# IPv4 address.
- <str>
# NTP settings
ntp_settings:
# EOS only supports NTP servers in one VRF, so this VRF is used for all NTP servers and one local-interface.
# - `use_mgmt_interface_vrf` will configure the NTP server(s) under the VRF set with `mgmt_interface_vrf` and set the `mgmt_interface` as NTP local-interface.
# An error will be raised if `mgmt_ip` or `ipv6_mgmt_ip` are not configured for the device.
# - `use_inband_mgmt_vrf` will configure the NTP server(s) under the VRF set with `inband_mgmt_vrf` and set the `inband_mgmt_interface` as NTP local-interface.
# An error will be raised if inband management is not configured for the device.
# - Any other string will be used directly as the VRF name but local interface must be set with `custom_structured_configuration_ntp` if needed.
# If not set, the VRF is automatically picked up from the global setting `default_mgmt_method`.
server_vrf: <str>
# The first server is always set as "preferred".
servers:
# IP or hostname e.g., 2.2.2.55, ie.pool.ntp.org.
- name: <str>
burst: <bool>
iburst: <bool>
key: <int; 1-65535>
# Value of maxpoll between 3 - 17 (Logarithmic).
maxpoll: <int; 3-17>
# Value of minpoll between 3 - 17 (Logarithmic).
minpoll: <int; 3-17>
version: <int; 1-4>
authenticate: <bool>
authenticate_servers_only: <bool>
authentication_keys:
# Key identifier.
- id: <int; 1-65534; required; unique>
hash_algorithm: <str; "md5" | "sha1">
# Obfuscated key.
key: <str>
key_type: <str; "0" | "7" | "8a">
# List of trusted-keys as string ex. 10-12,15.
trusted_keys: <str>
# Clock timezone like "CET" or "US/Pacific".
timezone: <str>
Source-interfaces settings¶
| Variable | Type | Required | Default | Value Restrictions | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| source_interfaces | Dictionary | Configure source-interfaces based on the management interfaces set for other eos_designs data models.By default, no source-interfaces will be configured. They can still be configured manually using eos_cli_config_gen and custom structured configuration.EOS supports a single source-interface per VRF, so an error will be raised in case of conflicts. Errors will also be raised if an interface is not found for a device. |
|||
| domain_lookup | Dictionary | IP Domain Lookup source-interfaces. | |||
| mgmt_interface | Boolean | Configure an IP Domain Lookup source-interface with the interface set by mgmt_interface for the VRF set by mgmt_interface_vrf.mgmt_interface is typically the out-of-band Management interface, and can be set under the node settings, platform settings or as a group/host var. |
|||
| inband_mgmt_interface | Boolean | Configure an IP Domain Lookup source-interface with the interface set by inband_mgmt_interface for the VRF set by inband_mgmt_vrf.inband_mgmt_interface is typically a loopback or SVI interface, and can be set under the node settings. |
|||
| http_client | Dictionary | IP HTTP Client source-interfaces. | |||
| mgmt_interface | Boolean | Configure an IP HTTP Client source-interface with the interface set by mgmt_interface for the VRF set by mgmt_interface_vrf.mgmt_interface is typically the out-of-band Management interface, and can be set under the node settings, platform settings or as a group/host var. |
|||
| inband_mgmt_interface | Boolean | Configure an IP HTTP Client source-interface with the interface set by inband_mgmt_interface for the VRF set by inband_mgmt_vrf.inband_mgmt_interface is typically a loopback or SVI interface, and can be set under the node settings. |
|||
| radius | Dictionary | IP Radius source-interfaces. | |||
| mgmt_interface | Boolean | Configure an IP Radius source-interface with the interface set by mgmt_interface for the VRF set by mgmt_interface_vrf.mgmt_interface is typically the out-of-band Management interface, and can be set under the node settings, platform settings or as a group/host var. |
|||
| inband_mgmt_interface | Boolean | Configure an IP Radius source-interface with the interface set by inband_mgmt_interface for the VRF set by inband_mgmt_vrf.inband_mgmt_interface is typically a loopback or SVI interface, and can be set under the node settings. |
|||
| snmp | Dictionary | SNMP local-interfaces. | |||
| mgmt_interface | Boolean | Configure a SNMP local-interface with the interface set by mgmt_interface for the VRF set by mgmt_interface_vrf.mgmt_interface is typically the out-of-band Management interface, and can be set under the node settings, platform settings or as a group/host var. |
|||
| inband_mgmt_interface | Boolean | Configure a SNMP local-interface with the interface set by inband_mgmt_interface for the VRF set by inband_mgmt_vrf.inband_mgmt_interface is typically a loopback or SVI interface, and can be set under the node settings. |
|||
| ssh_client | Dictionary | IP SSH Client source-interfaces. | |||
| mgmt_interface | Boolean | Configure an IP SSH Client source-interface with the interface set by mgmt_interface for the VRF set by mgmt_interface_vrf.mgmt_interface is typically the out-of-band Management interface, and can be set under the node settings, platform settings or as a group/host var. |
|||
| inband_mgmt_interface | Boolean | Configure an IP SSH Client source-interface with the interface set by inband_mgmt_interface for the VRF set by inband_mgmt_vrf.inband_mgmt_interface is typically a loopback or SVI interface, and can be set under the node settings. |
|||
| tacacs | Dictionary | IP Tacacs source-interfaces. | |||
| mgmt_interface | Boolean | Configure an IP Tacacs source-interface with the interface set by mgmt_interface for the VRF set by mgmt_interface_vrf.mgmt_interface is typically the out-of-band Management interface, and can be set under the node settings, platform settings or as a group/host var. |
|||
| inband_mgmt_interface | Boolean | Configure an IP Tacacs source-interface with the interface set by inband_mgmt_interface for the VRF set by inband_mgmt_vrf.inband_mgmt_interface is typically a loopback or SVI interface, and can be set under the node settings. |
# Configure source-interfaces based on the management interfaces set for other `eos_designs` data models.
# By default, no source-interfaces will be configured. They can still be configured manually using `eos_cli_config_gen` and custom structured configuration.
# EOS supports a single source-interface per VRF, so an error will be raised in case of conflicts.
# Errors will also be raised if an interface is not found for a device.
source_interfaces:
# IP Domain Lookup source-interfaces.
domain_lookup:
# Configure an IP Domain Lookup source-interface with the interface set by `mgmt_interface` for the VRF set by `mgmt_interface_vrf`.
# `mgmt_interface` is typically the out-of-band Management interface, and can be set under the node settings, platform settings or as a group/host var.
mgmt_interface: <bool>
# Configure an IP Domain Lookup source-interface with the interface set by `inband_mgmt_interface` for the VRF set by `inband_mgmt_vrf`.
# `inband_mgmt_interface` is typically a loopback or SVI interface, and can be set under the node settings.
inband_mgmt_interface: <bool>
# IP HTTP Client source-interfaces.
http_client:
# Configure an IP HTTP Client source-interface with the interface set by `mgmt_interface` for the VRF set by `mgmt_interface_vrf`.
# `mgmt_interface` is typically the out-of-band Management interface, and can be set under the node settings, platform settings or as a group/host var.
mgmt_interface: <bool>
# Configure an IP HTTP Client source-interface with the interface set by `inband_mgmt_interface` for the VRF set by `inband_mgmt_vrf`.
# `inband_mgmt_interface` is typically a loopback or SVI interface, and can be set under the node settings.
inband_mgmt_interface: <bool>
# IP Radius source-interfaces.
radius:
# Configure an IP Radius source-interface with the interface set by `mgmt_interface` for the VRF set by `mgmt_interface_vrf`.
# `mgmt_interface` is typically the out-of-band Management interface, and can be set under the node settings, platform settings or as a group/host var.
mgmt_interface: <bool>
# Configure an IP Radius source-interface with the interface set by `inband_mgmt_interface` for the VRF set by `inband_mgmt_vrf`.
# `inband_mgmt_interface` is typically a loopback or SVI interface, and can be set under the node settings.
inband_mgmt_interface: <bool>
# SNMP local-interfaces.
snmp:
# Configure a SNMP local-interface with the interface set by `mgmt_interface` for the VRF set by `mgmt_interface_vrf`.
# `mgmt_interface` is typically the out-of-band Management interface, and can be set under the node settings, platform settings or as a group/host var.
mgmt_interface: <bool>
# Configure a SNMP local-interface with the interface set by `inband_mgmt_interface` for the VRF set by `inband_mgmt_vrf`.
# `inband_mgmt_interface` is typically a loopback or SVI interface, and can be set under the node settings.
inband_mgmt_interface: <bool>
# IP SSH Client source-interfaces.
ssh_client:
# Configure an IP SSH Client source-interface with the interface set by `mgmt_interface` for the VRF set by `mgmt_interface_vrf`.
# `mgmt_interface` is typically the out-of-band Management interface, and can be set under the node settings, platform settings or as a group/host var.
mgmt_interface: <bool>
# Configure an IP SSH Client source-interface with the interface set by `inband_mgmt_interface` for the VRF set by `inband_mgmt_vrf`.
# `inband_mgmt_interface` is typically a loopback or SVI interface, and can be set under the node settings.
inband_mgmt_interface: <bool>
# IP Tacacs source-interfaces.
tacacs:
# Configure an IP Tacacs source-interface with the interface set by `mgmt_interface` for the VRF set by `mgmt_interface_vrf`.
# `mgmt_interface` is typically the out-of-band Management interface, and can be set under the node settings, platform settings or as a group/host var.
mgmt_interface: <bool>
# Configure an IP Tacacs source-interface with the interface set by `inband_mgmt_interface` for the VRF set by `inband_mgmt_vrf`.
# `inband_mgmt_interface` is typically a loopback or SVI interface, and can be set under the node settings.
inband_mgmt_interface: <bool>
sFlow settings¶
| Variable | Type | Required | Default | Value Restrictions | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| fabric_sflow | Dictionary | Default enabling of sFlow for various interface types across the fabric. sFlow can also be enabled/disabled under each of the specific data models. For general sFlow settings see sflow_settings. |
|||
| uplinks | Boolean | Enable sFlow on all fabric uplinks. | |||
| downlinks | Boolean | Enable sFlow on all fabric downlinks. | |||
| endpoints | Boolean | Enable sFlow on all endpoints ports. | |||
| l3_edge | Boolean | Enable sFlow on all p2p_links defined under l3_edge. | |||
| core_interfaces | Boolean | Enable sFlow on all p2p_links defined under core_interfaces. | |||
| mlag_interfaces | Boolean | Enable sFlow on all MLAG peer interfaces. | |||
| sflow_settings | Dictionary | sFlow settings. The sFlow process will only be configured if any interface is enabled for sFlow. For default enabling of sFlow for various interface types across the fabric see fabric_sflow. |
|||
| destinations | List, items: Dictionary | ||||
| - destination | String | Required | sFlow destination name or IP address. | ||
| port | Integer | Min: 1 Max: 65535 |
UDP Port number. The default port number for sFlow is 6343. | ||
| vrf | String | If not set, the VRF is automatically picked up from the global setting default_mgmt_method.The value of vrf will be interpreted according to these rules:- use_mgmt_interface_vrf will configure the sFlow destination under the VRF set with mgmt_interface_vrf and set the mgmt_interface as sFlow source-interface.An error will be raised if mgmt_ip or ipv6_mgmt_ip are not configured for the device.- use_inband_mgmt_vrf will configure the sFlow destination under the VRF set with inband_mgmt_vrf and set the inband_mgmt_interface as sFlow source-interface.An error will be raised if inband management is not configured for the device. - Any other string will be used directly as the VRF name. Remember to set the sflow_settings.vrfs[].source_interface if needed. |
|||
| vrfs | List, items: Dictionary | ||||
| - name | String | Required, Unique | VRF name. | ||
| source_interface | String | Source interface to use for sFlow destinations in this VRF. If set for the VRFs defined by mgmt_interface_vrf or inband_mgmt_vrf, this setting will take precedence. |
# Default enabling of sFlow for various interface types across the fabric.
# sFlow can also be enabled/disabled under each of the specific data models.
# For general sFlow settings see `sflow_settings`.
fabric_sflow:
# Enable sFlow on all fabric uplinks.
uplinks: <bool>
# Enable sFlow on all fabric downlinks.
downlinks: <bool>
# Enable sFlow on all endpoints ports.
endpoints: <bool>
# Enable sFlow on all p2p_links defined under l3_edge.
l3_edge: <bool>
# Enable sFlow on all p2p_links defined under core_interfaces.
core_interfaces: <bool>
# Enable sFlow on all MLAG peer interfaces.
mlag_interfaces: <bool>
# sFlow settings.
# The sFlow process will only be configured if any interface is enabled for sFlow.
# For default enabling of sFlow for various interface types across the fabric see `fabric_sflow`.
sflow_settings:
destinations:
# sFlow destination name or IP address.
- destination: <str; required>
# UDP Port number. The default port number for sFlow is 6343.
port: <int; 1-65535>
# If not set, the VRF is automatically picked up from the global setting `default_mgmt_method`.
# The value of `vrf` will be interpreted according to these rules:
# - `use_mgmt_interface_vrf` will configure the sFlow destination under the VRF set with `mgmt_interface_vrf` and set the `mgmt_interface` as sFlow source-interface.
# An error will be raised if `mgmt_ip` or `ipv6_mgmt_ip` are not configured for the device.
# - `use_inband_mgmt_vrf` will configure the sFlow destination under the VRF set with `inband_mgmt_vrf` and set the `inband_mgmt_interface` as sFlow source-interface.
# An error will be raised if inband management is not configured for the device.
# - Any other string will be used directly as the VRF name. Remember to set the `sflow_settings.vrfs[].source_interface` if needed.
vrf: <str>
vrfs:
# VRF name.
- name: <str; required; unique>
# Source interface to use for sFlow destinations in this VRF.
# If set for the VRFs defined by `mgmt_interface_vrf` or `inband_mgmt_vrf`, this setting will take precedence.
source_interface: <str>
Flow Tracking Settings¶
| Variable | Type | Required | Default | Value Restrictions | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| fabric_flow_tracking | Dictionary | Default enabling of flow-tracking(IPFIX) for various interface types across the fabric. Flow Tracking can also be enabled/disabled under each of the specific data models. For general flow-tracking settings see flow_tracking_settings. |
|||
| uplinks | Dictionary | Enable flow-tracking on all fabric uplinks. | |||
| enabled | Boolean | ||||
| name | String | Flow tracker name as defined in flow_tracking_settings. | |||
| downlinks | Dictionary | Enable flow-tracking on all fabric downlinks. | |||
| enabled | Boolean | ||||
| name | String | Flow tracker name as defined in flow_tracking_settings. | |||
| endpoints | Dictionary | Enable flow-tracking on all endpoints ports. | |||
| enabled | Boolean | ||||
| name | String | Flow tracker name as defined in flow_tracking_settings. | |||
| l3_edge | Dictionary | Enable flow-tracking on all p2p_links defined under l3_edge. | |||
| enabled | Boolean | ||||
| name | String | Flow tracker name as defined in flow_tracking_settings. | |||
| core_interfaces | Dictionary | Enable flow-tracking on all p2p_links defined under core_interfaces. | |||
| enabled | Boolean | ||||
| name | String | Flow tracker name as defined in flow_tracking_settings. | |||
| mlag_interfaces | Dictionary | Enable flow-tracking on all MLAG peer interfaces. | |||
| enabled | Boolean | ||||
| name | String | Flow tracker name as defined in flow_tracking_settings. | |||
| l3_interfaces | Dictionary | Enable flow-tracking on all node.l3_interfaces. | |||
| enabled | Boolean | ||||
| name | String | Flow tracker name as defined in flow_tracking_settings. | |||
| dps_interfaces | Dictionary | Enable flow-tracking on all dps_interfaces. | |||
| enabled | Boolean | ||||
| name | String | Flow tracker name as defined in flow_tracking_settings. | |||
| flow_tracking_settings | Dictionary | PREVIEW: This key is currently not supported Define the flow tracking parameters for this topology. |
|||
| sampled | Dictionary | The options relevant only for flow tracker type sampled. | |||
| encapsulation | Dictionary | ||||
| ipv4_ipv6 | Boolean | ||||
| mpls | Boolean | ||||
| sample | Integer | 10000 |
Min: 1 Max: 4294967295 |
||
| hardware_offload | Dictionary | ||||
| ipv4 | Boolean | Configure hardware offload for IPv4 traffic. | |||
| ipv6 | Boolean | Configure hardware offload for IPv6 traffic. | |||
| threshold_minimum | Integer | Min: 1 Max: 4294967295 |
Minimum number of samples. | ||
| hardware | Dictionary | The options relevant only for flow tracker type hardware. | |||
| record | Dictionary | ||||
| format_ipfix_standard_timestamps_counters | Boolean | Enable software export of IPFIX data records. | |||
| trackers | List, items: Dictionary | See (+) on YAML tab | |||
| - name | String | Required, Unique | Tracker Name | ||
| sampled | Dictionary | The options relevant only for flow tracker type sampled. | |||
| table_size | Integer | Min: 1 Max: 614400 |
Maximum number of entries in flow table. |
||
| record_export | Dictionary | ||||
| mpls | Boolean | Export MPLS forwarding information. | |||
| record_export | Dictionary | ||||
| on_inactive_timeout | Integer | Min: 3000 Max: 900000 |
Flow record inactive export timeout in milliseconds | ||
| on_interval | Integer | Min: 1000 Max: 36000000 |
Flow record export interval in milliseconds | ||
| exporters | List, items: Dictionary | ||||
| - name | String | Required, Unique | Exporter Name | ||
| collector | Dictionary | ||||
| host | String | Collector IPv4 address or IPv6 address or fully qualified domain name | |||
| port | Integer | Min: 1 Max: 65535 |
Collector Port Number | ||
| format | Dictionary | ||||
| ipfix_version | Integer | ||||
| local_interface | String | Local Source Interface | |||
| template_interval | Integer | Min: 5000 Max: 3600000 |
Template interval in milliseconds |
# Default enabling of flow-tracking(IPFIX) for various interface types across the fabric.
# Flow Tracking can also be enabled/disabled under each of the specific data models.
# For general flow-tracking settings see `flow_tracking_settings`.
fabric_flow_tracking:
# Enable flow-tracking on all fabric uplinks.
uplinks:
enabled: <bool>
# Flow tracker name as defined in flow_tracking_settings.
name: <str>
# Enable flow-tracking on all fabric downlinks.
downlinks:
enabled: <bool>
# Flow tracker name as defined in flow_tracking_settings.
name: <str>
# Enable flow-tracking on all endpoints ports.
endpoints:
enabled: <bool>
# Flow tracker name as defined in flow_tracking_settings.
name: <str>
# Enable flow-tracking on all p2p_links defined under l3_edge.
l3_edge:
enabled: <bool>
# Flow tracker name as defined in flow_tracking_settings.
name: <str>
# Enable flow-tracking on all p2p_links defined under core_interfaces.
core_interfaces:
enabled: <bool>
# Flow tracker name as defined in flow_tracking_settings.
name: <str>
# Enable flow-tracking on all MLAG peer interfaces.
mlag_interfaces:
enabled: <bool>
# Flow tracker name as defined in flow_tracking_settings.
name: <str>
# Enable flow-tracking on all node.l3_interfaces.
l3_interfaces:
enabled: <bool>
# Flow tracker name as defined in flow_tracking_settings.
name: <str>
# Enable flow-tracking on all dps_interfaces.
dps_interfaces:
enabled: <bool>
# Flow tracker name as defined in flow_tracking_settings.
name: <str>
# PREVIEW: This key is currently not supported
#
# Define the flow tracking parameters for this topology.
flow_tracking_settings:
# The options relevant only for flow tracker type sampled.
sampled:
encapsulation:
ipv4_ipv6: <bool>
mpls: <bool>
sample: <int; 1-4294967295; default=10000>
hardware_offload:
# Configure hardware offload for IPv4 traffic.
ipv4: <bool>
# Configure hardware offload for IPv6 traffic.
ipv6: <bool>
# Minimum number of samples.
threshold_minimum: <int; 1-4294967295>
# The options relevant only for flow tracker type hardware.
hardware:
record:
# Enable software export of IPFIX data records.
format_ipfix_standard_timestamps_counters: <bool>
trackers: # (1)!
# Tracker Name
- name: <str; required; unique>
# The options relevant only for flow tracker type sampled.
sampled:
# Maximum number of entries in flow table.
table_size: <int; 1-614400>
record_export:
# Export MPLS forwarding information.
mpls: <bool>
record_export:
# Flow record inactive export timeout in milliseconds
on_inactive_timeout: <int; 3000-900000>
# Flow record export interval in milliseconds
on_interval: <int; 1000-36000000>
exporters:
# Exporter Name
- name: <str; required; unique>
collector:
# Collector IPv4 address or IPv6 address or fully qualified domain name
host: <str>
# Collector Port Number
port: <int; 1-65535>
format:
ipfix_version: <int>
# Local Source Interface
local_interface: <str>
# Template interval in milliseconds
template_interval: <int; 5000-3600000>
-
Default Value
SNMP settings¶
| Variable | Type | Required | Default | Value Restrictions | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| snmp_settings | Dictionary | SNMP settings. For SNMP local-interfaces see “source_interfaces.snmp”. Configuration of remote SNMP engine IDs are currently only possible using structured_config. |
|||
| contact | String | SNMP contact. | |||
| location | Boolean | False |
Set SNMP location. Formatted as “ |
||
| vrfs | List, items: Dictionary | Enable/disable SNMP for one or more VRFs. Can be used in combination with “enable_mgmt_interface_vrf” and “enable_inband_mgmt_vrf”. |
|||
| - name | String | Required, Unique | VRF name. | ||
| enable | Boolean | ||||
| enable_mgmt_interface_vrf | Boolean | Enable/disable SNMP for the VRF set with “mgmt_interface_vrf”. Ignored if ‘mgmt_ip’ or ‘ipv6_mgmt_ip’ are not configured for the device. Can be used in combination with “vrfs” and “enable_inband_mgmt_vrf”. |
|||
| enable_inband_mgmt_vrf | Boolean | Enable/disable SNMP for the VRF set with “inband_mgmt_vrf”. Ignored if inband management is not configured for the device. Can be used in combination with “vrfs” and “enable_mgmt_interface_vrf”. |
|||
| compute_local_engineid | Boolean | False |
Generate a local engineId for SNMP using the ‘compute_local_engineid_source’ method. |
||
| compute_local_engineid_source | String | hostname_and_ip |
Valid Values: - hostname_and_ip- system_mac |
compute_local_engineid_source supports:- hostname_and_ip generate a local engineId for SNMP by hashing via SHA1the string generated via the concatenation of the hostname plus the management IP. {{ inventory_hostname }} + {{ switch.mgmt_ip }}. - system_mac generate the switch default engine id for AVD usage.To use this, system_mac_address MUST be set for the device.The formula is f5717f + system_mac_address + 00. |
|
| compute_v3_user_localized_key | Boolean | False |
Requires compute_local_engineid to be true.If enabled, the SNMPv3 passphrases for auth and priv are transformed using RFC 2574, matching the value they would take in EOS CLI. The algorithm requires a local engineId, which is unknown to AVD, hence the necessity to generate one beforehand. |
||
| users | List, items: Dictionary | Configuration of local SNMP users. Configuration of remote SNMP users are currently only possible using structured_config. |
|||
| - name | String | Username. | |||
| group | String | Group name. | |||
| version | String | Valid Values: - v1- v2c- v3 |
|||
| auth | String | Valid Values: - md5- sha- sha256- sha384- sha512 |
|||
| auth_passphrase | String | Cleartext passphrase so the recommendation is to use vault. Requires ‘auth’ to be set. | |||
| priv | String | Valid Values: - des- aes- aes192- aes256 |
|||
| priv_passphrase | String | Cleartext passphrase so the recommendation is to use vault. Requires ‘priv’ to be set. | |||
| hosts | List, items: Dictionary | ||||
| - host | String | Host IP address or name. | |||
| vrf | String | VRF Name. Can be used in combination with “use_mgmt_interface_vrf” and “use_inband_mgmt_vrf” to configure the SNMP host under multiple VRFs. |
|||
| use_mgmt_interface_vrf | Boolean | Configure the SNMP host under the VRF set with “mgmt_interface_vrf”. Ignored if ‘mgmt_ip’ or ‘ipv6_mgmt_ip’ are not configured for the device, so if the host is only configured with this VRF, the host will not be configured at all. Can be used in combination with “vrf” and “use_inband_mgmt_vrf” to configure the SNMP host under multiple VRFs. | |||
| use_inband_mgmt_vrf | Boolean | Configure the SNMP host under the VRF set with “inband_mgmt_vrf”. Ignored if inband management is not configured for the device, so if the host is only configured with this VRF, the host will not be configured at all. Can be used in combination with “vrf” and “use_mgmt_interface_vrf” to configure the SNMP host under multiple VRFs. | |||
| version | String | Valid Values: - 1- 2c- 3 |
|||
| community | String | Community name. | |||
| users | List, items: Dictionary | ||||
| - username | String | ||||
| authentication_level | String | Valid Values: - auth- noauth- priv |
|||
| communities | List, items: Dictionary | ||||
| - name | String | Required, Unique | Community name. | ||
| access | String | Valid Values: - ro- rw |
|||
| access_list_ipv4 | Dictionary | ||||
| name | String | IPv4 access list name. | |||
| access_list_ipv6 | Dictionary | ||||
| name | String | IPv6 access list name. | |||
| view | String | ||||
| ipv4_acls | List, items: Dictionary | ||||
| - name | String | IPv4 access list name. | |||
| vrf | String | ||||
| ipv6_acls | List, items: Dictionary | ||||
| - name | String | IPv6 access list name. | |||
| vrf | String | ||||
| views | List, items: Dictionary | ||||
| - name | String | SNMP view name. | |||
| mib_family_name | String | ||||
| included | Boolean | ||||
| MIB_family_name deprecated | String | This key is deprecated. Support will be removed in AVD version 5.0.0. Use mib_family_name instead. | |||
| groups | List, items: Dictionary | ||||
| - name | String | Group name. | |||
| version | String | Valid Values: - v1- v2c- v3 |
|||
| authentication | String | Valid Values: - auth- noauth- priv |
|||
| read | String | Read view. | |||
| write | String | Write view. | |||
| notify | String | Notify view. | |||
| traps | Dictionary | ||||
| enable | Boolean | False |
Enable or disable all snmp-traps. |
||
| snmp_traps | List, items: Dictionary | ||||
| - name | String | Enable or disable specific snmp-traps and their sub_traps. Examples: - “bgp” - “bgp established” |
|||
| enabled | Boolean | True |
# SNMP settings.
# For SNMP local-interfaces see "source_interfaces.snmp".
# Configuration of remote SNMP engine IDs are currently only possible using `structured_config`.
snmp_settings:
# SNMP contact.
contact: <str>
# Set SNMP location. Formatted as "<fabric_name> <dc_name> <pod_name> <switch_rack> <inventory_hostname>".
location: <bool; default=False>
# Enable/disable SNMP for one or more VRFs.
# Can be used in combination with "enable_mgmt_interface_vrf" and "enable_inband_mgmt_vrf".
vrfs:
# VRF name.
- name: <str; required; unique>
enable: <bool>
# Enable/disable SNMP for the VRF set with "mgmt_interface_vrf".
# Ignored if 'mgmt_ip' or 'ipv6_mgmt_ip' are not configured for the device.
# Can be used in combination with "vrfs" and "enable_inband_mgmt_vrf".
enable_mgmt_interface_vrf: <bool>
# Enable/disable SNMP for the VRF set with "inband_mgmt_vrf".
# Ignored if inband management is not configured for the device.
# Can be used in combination with "vrfs" and "enable_mgmt_interface_vrf".
enable_inband_mgmt_vrf: <bool>
# Generate a local engineId for SNMP using the 'compute_local_engineid_source' method.
compute_local_engineid: <bool; default=False>
# `compute_local_engineid_source` supports:
# - `hostname_and_ip` generate a local engineId for SNMP by hashing via SHA1
# the string generated via the concatenation of the hostname plus the management IP.
# {{ inventory_hostname }} + {{ switch.mgmt_ip }}.
# - `system_mac` generate the switch default engine id for AVD usage.
# To use this, `system_mac_address` MUST be set for the device.
# The formula is f5717f + system_mac_address + 00.
compute_local_engineid_source: <str; "hostname_and_ip" | "system_mac"; default="hostname_and_ip">
# Requires compute_local_engineid to be `true`.
# If enabled, the SNMPv3 passphrases for auth and priv are transformed using RFC 2574, matching the value they would take in EOS CLI.
# The algorithm requires a local engineId, which is unknown to AVD, hence the necessity to generate one beforehand.
compute_v3_user_localized_key: <bool; default=False>
# Configuration of local SNMP users.
# Configuration of remote SNMP users are currently only possible using `structured_config`.
users:
# Username.
- name: <str>
# Group name.
group: <str>
version: <str; "v1" | "v2c" | "v3">
auth: <str; "md5" | "sha" | "sha256" | "sha384" | "sha512">
# Cleartext passphrase so the recommendation is to use vault. Requires 'auth' to be set.
auth_passphrase: <str>
priv: <str; "des" | "aes" | "aes192" | "aes256">
# Cleartext passphrase so the recommendation is to use vault. Requires 'priv' to be set.
priv_passphrase: <str>
hosts:
# Host IP address or name.
- host: <str>
# VRF Name.
# Can be used in combination with "use_mgmt_interface_vrf" and "use_inband_mgmt_vrf" to configure the SNMP host under multiple VRFs.
vrf: <str>
# Configure the SNMP host under the VRF set with "mgmt_interface_vrf". Ignored if 'mgmt_ip' or 'ipv6_mgmt_ip' are not configured for the device, so if the host is only configured with this VRF, the host will not be configured at all. Can be used in combination with "vrf" and "use_inband_mgmt_vrf" to configure the SNMP host under multiple VRFs.
use_mgmt_interface_vrf: <bool>
# Configure the SNMP host under the VRF set with "inband_mgmt_vrf". Ignored if inband management is not configured for the device, so if the host is only configured with this VRF, the host will not be configured at all. Can be used in combination with "vrf" and "use_mgmt_interface_vrf" to configure the SNMP host under multiple VRFs.
use_inband_mgmt_vrf: <bool>
version: <str; "1" | "2c" | "3">
# Community name.
community: <str>
users:
- username: <str>
authentication_level: <str; "auth" | "noauth" | "priv">
communities:
# Community name.
- name: <str; required; unique>
access: <str; "ro" | "rw">
access_list_ipv4:
# IPv4 access list name.
name: <str>
access_list_ipv6:
# IPv6 access list name.
name: <str>
view: <str>
ipv4_acls:
# IPv4 access list name.
- name: <str>
vrf: <str>
ipv6_acls:
# IPv6 access list name.
- name: <str>
vrf: <str>
views:
# SNMP view name.
- name: <str>
mib_family_name: <str>
included: <bool>
# This key is deprecated.
# Support will be removed in AVD version 5.0.0.
# Use <samp>mib_family_name</samp> instead.
MIB_family_name: <str>
groups:
# Group name.
- name: <str>
version: <str; "v1" | "v2c" | "v3">
authentication: <str; "auth" | "noauth" | "priv">
# Read view.
read: <str>
# Write view.
write: <str>
# Notify view.
notify: <str>
traps:
# Enable or disable all snmp-traps.
enable: <bool; default=False>
snmp_traps:
# Enable or disable specific snmp-traps and their sub_traps.
# Examples:
# - "bgp"
# - "bgp established"
- name: <str>
enabled: <bool; default=True>
System settings¶
| Variable | Type | Required | Default | Value Restrictions | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| <node_type_keys.key> | Dictionary | ||||
| defaults | Dictionary | Define variables for all nodes of this type. | |||
| data_plane_cpu_allocation_max | Integer | Min: 1 Max: 128 |
Set the maximum number of CPU used for the data plane. This setting is useful on virtual Route Reflectors and Pathfinders where more CPU cores should be allocated for control plane. |
||
| node_groups | List, items: Dictionary | Define variables related to all nodes part of this group. | |||
| - group | String | Required, Unique | The Node Group Name is used for MLAG domain unless set with ‘mlag_domain_id’. The Node Group Name is also used for peer description on downstream switches’ uplinks. |
||
| nodes | List, items: Dictionary | Define variables per node. | |||
| - name | String | Required, Unique | The Node Name is used as “hostname”. | ||
| data_plane_cpu_allocation_max | Integer | Min: 1 Max: 128 |
Set the maximum number of CPU used for the data plane. This setting is useful on virtual Route Reflectors and Pathfinders where more CPU cores should be allocated for control plane. |
||
| data_plane_cpu_allocation_max | Integer | Min: 1 Max: 128 |
Set the maximum number of CPU used for the data plane. This setting is useful on virtual Route Reflectors and Pathfinders where more CPU cores should be allocated for control plane. |
||
| nodes | List, items: Dictionary | Define variables per node. | |||
| - name | String | Required, Unique | The Node Name is used as “hostname”. | ||
| data_plane_cpu_allocation_max | Integer | Min: 1 Max: 128 |
Set the maximum number of CPU used for the data plane. This setting is useful on virtual Route Reflectors and Pathfinders where more CPU cores should be allocated for control plane. |
||
| default_igmp_snooping_enabled | Boolean | True |
When set to false, disables IGMP snooping at fabric level and overrides per vlan settings. |
||
| default_interface_mtu | Integer | Min: 68 Max: 65535 |
Default interface MTU configured on EOS under “interface defaults”. Can be overridden per platform under platform settings. |
||
| hardware_counters | Dictionary | ||||
| features | List, items: Dictionary | This data model allows to configure the list of hardware counters feature available on Arista platforms. The name key accepts a list of valid_values which MUST be updated to supportnew feature as they are released in EOS. The available values of the different keys like ‘direction’ or ‘address_type’ are feature and hardware dependent and this model DOES NOT validate that the combinations are valid. It is the responsibility of the user of this data model to make sure that the rendered CLI is accepted by the targeted device. Examples: * Use: yaml<br> hardware_counters:<br> features:<br> - name: ip<br> direction: out<br> layer3: true<br> units_packets: true<br>to render: eos<br> hardware counter feature ip out layer3 units packets<br>* Use: yaml<br> hardware_counters:<br> features:<br> - name: route<br> address_type: ipv4<br> vrf: test<br> prefix: 192.168.0.0/24<br>to render: eos<br> hardware counter feature route ipv4 vrf test 192.168.0.0/24<br> |
|||
| - name | String | Valid Values: - acl- decap-group- directflow- ecn- flow-spec- gre tunnel interface- ip- mpls interface- mpls lfib- mpls tunnel- multicast- nexthop- pbr- pdp- policing interface- qos- qos dual-rate-policer- route- routed-port- subinterface- tapagg- traffic-class- traffic-policy- vlan- vlan-interface- vni decap- vni encap- vtep decap- vtep encap |
|||
| direction | String | Valid Values: - in- out- cpu |
Most features support only ‘in’ and ‘out’. Some like traffic-policy support ‘cpu’. Some features DO NOT have any direction. This validation IS NOT made by the schemas. |
||
| address_type | String | Valid Values: - ipv4- ipv6- mac |
Supported only for the following features: - acl: [ipv4, ipv6, mac] if direction is ‘out’ - multicast: [ipv4, ipv6] - route: [ipv4, ipv6] This validation IS NOT made by the schemas. |
||
| layer3 | Boolean | Supported only for the ‘ip’ feature. |
|||
| vrf | String | Supported only for the ‘route’ feature. This validation IS NOT made by the schemas. |
|||
| prefix | String | Supported only for the ‘route’ feature. Mandatory for the ‘route’ feature. This validation IS NOT made by the schemas. |
|||
| units_packets | Boolean | ||||
| internal_vlan_order | Dictionary | See (+) on YAML tab | Internal vlan allocation order and range. | ||
| allocation | String | Required | Valid Values: - ascending- descending |
||
| range | Dictionary | ||||
| beginning | Integer | Required | Min: 2 Max: 4094 |
First VLAN ID. | |
| ending | Integer | Required | Min: 2 Max: 4094 |
Last VLAN ID. | |
| mac_address_table | Dictionary | MAC address-table aging time. Use to change the EOS default of 300. |
|||
| aging_time | Integer | Min: 0 Max: 1000000 |
Aging time in seconds 10-1000000. Enter 0 to disable aging. |
||
| queue_monitor_length | Dictionary | ||||
| enabled | Boolean | Required | |||
| notifying | Boolean | If True, eos_designs will configure queue-monitor length notifying according to theplatform_settings.[].feature_support.queue_monitor_length_notify setting. |
|||
| default_thresholds | Dictionary | ||||
| high | Integer | Required | Default high threshold for Ethernet Interfaces. |
||
| low | Integer | Default low threshold for Ethernet Interfaces. Low threshold support is platform dependent. |
|||
| log | Integer | Logging interval in seconds. | |||
| cpu | Dictionary | ||||
| thresholds | Dictionary | ||||
| high | Integer | Required | |||
| low | Integer | ||||
| tx_latency | Boolean | Enable tx-latency mode. | |||
| redundancy | Dictionary | Redundancy for chassis platforms with dual supervisors | |||
| protocol | String | Valid Values: - sso- rpr |
|||
| serial_number | String | Serial Number of the device. Used for documentation purpose in the fabric documentation as can also be used by the ‘eos_config_deploy_cvp’ role. “serial_number” can also be set directly under node type settings. If both are set, the value under node type settings takes precedence. |
|||
| system_mac_address | String | Set to the same MAC address as available in “show version” on the device. “system_mac_address” can also be set under node type settings. If both are set, the value under node type settings takes precedence. |
<node_type_keys.key>:
# Define variables for all nodes of this type.
defaults:
# Set the maximum number of CPU used for the data plane.
# This setting is useful on virtual Route Reflectors and Pathfinders where more CPU cores should be allocated for control plane.
data_plane_cpu_allocation_max: <int; 1-128>
# Define variables related to all nodes part of this group.
node_groups:
# The Node Group Name is used for MLAG domain unless set with 'mlag_domain_id'.
# The Node Group Name is also used for peer description on downstream switches' uplinks.
- group: <str; required; unique>
# Define variables per node.
nodes:
# The Node Name is used as "hostname".
- name: <str; required; unique>
# Set the maximum number of CPU used for the data plane.
# This setting is useful on virtual Route Reflectors and Pathfinders where more CPU cores should be allocated for control plane.
data_plane_cpu_allocation_max: <int; 1-128>
# Set the maximum number of CPU used for the data plane.
# This setting is useful on virtual Route Reflectors and Pathfinders where more CPU cores should be allocated for control plane.
data_plane_cpu_allocation_max: <int; 1-128>
# Define variables per node.
nodes:
# The Node Name is used as "hostname".
- name: <str; required; unique>
# Set the maximum number of CPU used for the data plane.
# This setting is useful on virtual Route Reflectors and Pathfinders where more CPU cores should be allocated for control plane.
data_plane_cpu_allocation_max: <int; 1-128>
# When set to false, disables IGMP snooping at fabric level and overrides per vlan settings.
default_igmp_snooping_enabled: <bool; default=True>
# Default interface MTU configured on EOS under "interface defaults".
# Can be overridden per platform under platform settings.
default_interface_mtu: <int; 68-65535>
hardware_counters:
# This data model allows to configure the list of hardware counters feature
# available on Arista platforms.
#
# The `name` key accepts a list of valid_values which MUST be updated to support
# new feature as they are released in EOS.
#
# The available values of the different keys like 'direction' or 'address_type'
# are feature and hardware dependent and this model DOES NOT validate that the
# combinations are valid. It is the responsibility of the user of this data model
# to make sure that the rendered CLI is accepted by the targeted device.
#
# Examples:
#
# * Use:
# ```yaml
# hardware_counters:
# features:
# - name: ip
# direction: out
# layer3: true
# units_packets: true
# ```
#
# to render:
# ```eos
# hardware counter feature ip out layer3 units packets
# ```
# * Use:
# ```yaml
# hardware_counters:
# features:
# - name: route
# address_type: ipv4
# vrf: test
# prefix: 192.168.0.0/24
# ```
#
# to render:
# ```eos
# hardware counter feature route ipv4 vrf test 192.168.0.0/24
# ```
features:
- name: <str; "acl" | "decap-group" | "directflow" | "ecn" | "flow-spec" | "gre tunnel interface" | "ip" | "mpls interface" | "mpls lfib" | "mpls tunnel" | "multicast" | "nexthop" | "pbr" | "pdp" | "policing interface" | "qos" | "qos dual-rate-policer" | "route" | "routed-port" | "subinterface" | "tapagg" | "traffic-class" | "traffic-policy" | "vlan" | "vlan-interface" | "vni decap" | "vni encap" | "vtep decap" | "vtep encap">
# Most features support only 'in' and 'out'. Some like traffic-policy support 'cpu'.
# Some features DO NOT have any direction.
# This validation IS NOT made by the schemas.
direction: <str; "in" | "out" | "cpu">
# Supported only for the following features:
# - acl: [ipv4, ipv6, mac] if direction is 'out'
# - multicast: [ipv4, ipv6]
# - route: [ipv4, ipv6]
# This validation IS NOT made by the schemas.
address_type: <str; "ipv4" | "ipv6" | "mac">
# Supported only for the 'ip' feature.
layer3: <bool>
# Supported only for the 'route' feature.
# This validation IS NOT made by the schemas.
vrf: <str>
# Supported only for the 'route' feature.
# Mandatory for the 'route' feature.
# This validation IS NOT made by the schemas.
prefix: <str>
units_packets: <bool>
# Internal vlan allocation order and range.
internal_vlan_order: # (1)!
allocation: <str; "ascending" | "descending"; required>
range:
# First VLAN ID.
beginning: <int; 2-4094; required>
# Last VLAN ID.
ending: <int; 2-4094; required>
# MAC address-table aging time.
# Use to change the EOS default of 300.
mac_address_table:
# Aging time in seconds 10-1000000.
# Enter 0 to disable aging.
aging_time: <int; 0-1000000>
queue_monitor_length:
enabled: <bool; required>
# If True, `eos_designs` will configure `queue-monitor length notifying` according to the
# `platform_settings.[].feature_support.queue_monitor_length_notify` setting.
notifying: <bool>
default_thresholds:
# Default high threshold for Ethernet Interfaces.
high: <int; required>
# Default low threshold for Ethernet Interfaces.
# Low threshold support is platform dependent.
low: <int>
# Logging interval in seconds.
log: <int>
cpu:
thresholds:
high: <int; required>
low: <int>
# Enable tx-latency mode.
tx_latency: <bool>
# Redundancy for chassis platforms with dual supervisors | Optional.
redundancy:
protocol: <str; "sso" | "rpr">
# Serial Number of the device.
# Used for documentation purpose in the fabric documentation as can also be used by the 'eos_config_deploy_cvp' role.
# "serial_number" can also be set directly under node type settings.
# If both are set, the value under node type settings takes precedence.
serial_number: <str>
# Set to the same MAC address as available in "show version" on the device.
# "system_mac_address" can also be set under node type settings.
# If both are set, the value under node type settings takes precedence.
system_mac_address: <str>
-
Default Value
CloudVision Settings¶
| Variable | Type | Required | Default | Value Restrictions | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cvp_ingestauth_key | String | On-premise CVP ingest auth key. If set, TerminAttr will be configured with key-based authentication for on-premise CVP. If not set, TerminAttr will be configured with certificate based authentication: - On-premise using token onboarding. Default token path is ‘/tmp/token’. - CVaaS using token-secure onboarding. Default token path is ‘/tmp/cv-onboarding-token’. Token must be copied to the device first. |
|||
| cvp_instance_ip deprecated | String | IPv4 address or DNS name for CloudVision. This variable only supports an on-premise single-node cluster or the DNS name of a CloudVision as a Service instance. This key is deprecated. Support will be removed in AVD version 5.0.0. Use cvp_instance_ips instead. |
|||
| cvp_instance_ips | List, items: String | List of IPv4 addresses or DNS names for CloudVision. For on-premise CloudVision enter all the nodes of the cluster. For CloudVision as a Service enter the DNS name of the instance. eos_designs only supports one CloudVision cluster. |
|||
| - <str> | String | IPv4 address or DNS name for CloudVision. | |||
| cvp_token_file | String | cvp_token_file is the path to the token file on the switch. If not set the default locations for on-premise or CVaaS will be used. See cvp_ingestauth_key for details. |
|||
| terminattr_disable_aaa | Boolean | False |
|||
| terminattr_ingestexclude | String | /Sysdb/cell/1/agent,/Sysdb/cell/2/agent |
|||
| terminattr_ingestgrpcurl_port | Integer | 9910 |
Port number used for Terminattr connection to an on-premise CloudVision cluster. The port number is always 443 when using CloudVision as a Service, so this value is ignored. |
||
| terminattr_smashexcludes | String | ale,flexCounter,hardware,kni,pulse,strata |
# On-premise CVP ingest auth key. If set, TerminAttr will be configured with key-based authentication for on-premise CVP.
# If not set, TerminAttr will be configured with certificate based authentication:
# - On-premise using token onboarding. Default token path is '/tmp/token'.
# - CVaaS using token-secure onboarding. Default token path is '/tmp/cv-onboarding-token'.
# Token must be copied to the device first.
cvp_ingestauth_key: <str>
# IPv4 address or DNS name for CloudVision.
# This variable only supports an on-premise single-node cluster or the DNS name of a CloudVision as a Service instance.
# This key is deprecated.
# Support will be removed in AVD version 5.0.0.
# Use <samp>cvp_instance_ips</samp> instead.
cvp_instance_ip: <str>
# List of IPv4 addresses or DNS names for CloudVision.
# For on-premise CloudVision enter all the nodes of the cluster.
# For CloudVision as a Service enter the DNS name of the instance.
# `eos_designs` only supports one CloudVision cluster.
cvp_instance_ips:
# IPv4 address or DNS name for CloudVision.
- <str>
# cvp_token_file is the path to the token file on the switch.
# If not set the default locations for on-premise or CVaaS will be used.
# See cvp_ingestauth_key for details.
cvp_token_file: <str>
terminattr_disable_aaa: <bool; default=False>
terminattr_ingestexclude: <str; default="/Sysdb/cell/1/agent,/Sysdb/cell/2/agent">
# Port number used for Terminattr connection to an on-premise CloudVision cluster.
# The port number is always 443 when using CloudVision as a Service, so this value is ignored.
terminattr_ingestgrpcurl_port: <int; default=9910>
terminattr_smashexcludes: <str; default="ale,flexCounter,hardware,kni,pulse,strata">
Endpoint connectivity¶
AVD supports two different data models for defining connectivity to endpoints:
- “Connected Endpoints” is an endpoint-centric model intended for servers or other use cases where most ports have unique configurations.
- “Network Ports” is a compact and port-centric model intended for configuration of generic port configurations on large ranges of ports.
Both data models share the same underlying implementation and can coexist without conflicts. If a switch port is defined in both “Connected Endpoints” and “Network Ports”, the “Connected Endpoints” configuration will take precedence.
Both data models support variable inheritance from profiles defined under port_profiles. The profiles can be shared between the models. Any setting defined under the port_profiles will be inherited from parent_profile to profile to adapter.
Connected endpoints settings¶
- The connected endpoints variables define connectivity from the perspective of the endpoints that connect to the fabric.
- Each endpoint can have one or more
adaptersdefined, under which the connectedswitches,switch_portsandendpoint_portsmust be set. - If port_channel mode is enabled under one “adapter”, all switch_ports connected to that “adapter” will become part of this port-channel.
- The keys used to define connected endpoints are configurable using
connected_endpoints_keys. The default available keys are:serversfirewallsroutersload_balancersstorage_arrayscpesworkstationsaccess_pointsphonesprinterscamerasgeneric_devices
Example with profiles
port_profiles:
- profile: VM_Servers
mode: trunk
vlans: "110-111,120-121,130-131"
spanning_tree_portfast: edge
- profile: MGMT
mode: access
vlans: "110"
- profile: DB_Clusters
mode: trunk
vlans: "140-141"
servers:
- name: server01
rack: RackB
adapters:
# Single homed interface from E0 toward DC1-LEAF1A_Eth5
- endpoint_ports: [ E0 ]
switch_ports: [ Ethernet5 ]
switches: [ DC1-LEAF1A ]
profile: MGMT
# MLAG dual-homed connection from E1 to DC1-LEAF2A_Eth10
# from E2 to DC1-LEAF2B_Eth10
- endpoint_ports: [ E1, E2 ]
switch_ports: [ Ethernet10, Ethernet10 ]
switches: [ DC1-LEAF2A, DC1-LEAF2B ]
profile: DB_Clusters
port_channel:
description: PortChanne1
mode: active
- name: server03
rack: RackC
adapters:
# MLAG dual-homed connection from E0 to DC1-SVC3A_Eth10
# from E1 to DC1-SVC3B_Eth10
- endpoint_ports: [ E0, E1 ]
switch_ports: [ Ethernet10, Ethernet10 ]
switches: [ DC1-SVC3A, DC1-SVC3B ]
profile: VM_Servers
port_channel:
description: PortChanne1
mode: active
# Firewall
firewalls:
- name: FIREWALL01
rack: RackB
adapters:
- endpoint_ports: [ E0, E1 ]
switch_ports: [ Ethernet20, Ethernet20 ]
switches: [ DC1-LEAF2A, DC1-LEAF2B ]
profile: TENANT_A_B
port_channel:
description: PortChanne1
mode: active
# Routers
routers:
- name: ROUTER01
rack: RackB
adapters:
- endpoint_ports: [ Eth0, Eth1 ]
switch_ports: [ Ethernet21, Ethernet21 ]
switches: [ DC1-LEAF2A, DC1-LEAF2B ]
profile: TENANT_A
Example with single attached endpoint
Single attached interface from E0 toward DC1-LEAF1A interface Eth5
Example with MLAG dual-attached endpoint
MLAG dual-homed connection:
- From
E0toDC1-SVC3AinterfaceEth10 - From
E1toDC1-SVC3BinterfaceEth10
Example with EVPN A/A ESI dual-attached endpoint
To help provide consistency when configuring EVPN A/A ESI values, arista.avd provides an abstraction in the form of a short_esi key.
short_esi is an abbreviated 3 octets value to encode Ethernet Segment ID and LACP ID.
Transformation from abstraction to network values is managed by the following Ansible filter plugins:
The plugins provides the following result:
- EVPN ESI: 000:000:0303:0202:0101
- LACP ID: 0303.0202.0101
- Route Target: 03:03:02:02:01:01
In addition, setting the short_esi key to auto generates the short_esi automatically using a hash of the following data elements:
- Port-Channel Interfaces: first two uplink switch hostnames, the ports on those switches, the corresponding endpoint ports and the channel-group ID.
- Port-Channel Subinterface: first two uplink switch hostname, the ports on those switches, the corresponding endpoint ports, the channel-group ID and the subinterface number.
- Ethernet Interfaces: first two uplink switch hostnames, the ports on those switches, the corresponding endpoint ports and the interface number.
It should be noted that arista.avd does not currently check for hash collisions when using short_esi: auto and while the risk of this happening is non-zero, it is small.
Active/Active multihoming connections:
- From
E0toDC1-SVC3AinterfaceEth10 - From
E1toDC1-SVC4AinterfaceEth10
| Variable | Type | Required | Default | Value Restrictions | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| <connected_endpoints_keys.key> | List, items: Dictionary | This should be applied to group_vars or host_vars where endpoints are connecting.connected_endpoints_keys.key is one of the keys under “connected_endpoints_keys”.The default keys are servers, firewalls, routers, load_balancers, and storage_arrays. |
|||
| - name | String | Required, Unique | Endpoint name will be used in the switchport description. | ||
| rack | String | Rack is used for documentation purposes only. | |||
| adapters | List, items: Dictionary | A list of adapters, group by adapters leveraging the same port-profile. | |||
| - switch_ports | List, items: String | Required | List of switch interfaces. The lists endpoint_ports, switch_ports, and switches must have the same length. |
||
| - <str> | String | Switchport interface. | |||
| switches | List, items: String | Required | List of switches. The lists endpoint_ports, switch_ports, and switches must have the same length. |
||
| - <str> | String | Device. | |||
| endpoint_ports | List, items: String | Endpoint ports is used for description, required unless description or descriptions is set.The lists endpoint_ports, switch_ports, descriptions and switches must have the same length.Each list item is one switchport. |
|||
| - <str> | String | Interface name. | |||
| descriptions | List | Unique description per port. When set, takes priority over description. |
|||
| server_ports removed | List, items: String | This key was removed. Support was removed in AVD version 4.0.0. Use endpoint_ports instead. | |||
| - <str> | String | Used for documentation purposes. | |||
| speed | String | Set adapter speed in the format <interface_speed> or forced <interface_speed> or auto <interface_speed>.If not specified speed will be auto. |
|||
| description | String | By default the description is built leveraging <peer>_<peer_interface>.When set this key will override the default value on the physical ports. |
|||
| profile | String | Port-profile name to inherit configuration. | |||
| enabled | Boolean | True |
Administrative state, setting to false will set the port to ‘shutdown’ in the intended configuration. |
||
| mode | String | Valid Values: - access- dot1q-tunnel- trunk- trunk phone |
Interface mode. | ||
| mtu | Integer | Min: 68 Max: 65535 |
|||
| l2_mtu | Integer | Min: 68 Max: 65535 |
“l2_mtu” should only be defined for platforms supporting the “l2 mtu” CLI. |
||
| l2_mru | Integer | Min: 68 Max: 65535 |
“l2_mru” should only be defined for platforms supporting the “l2 mru” CLI. |
||
| native_vlan | Integer | Min: 1 Max: 4094 |
Native VLAN for a trunk port. If both native_vlan and native_vlan_tag, native_vlan_tag takes precedence. |
||
| native_vlan_tag | Boolean | False |
If both native_vlan and native_vlan_tag, native_vlan_tag takes precedence. |
||
| phone_vlan | Integer | Min: 1 Max: 4094 |
Phone VLAN for a mode trunk phone port.Requires mode: trunk phone to be set. |
||
| phone_trunk_mode | String | Valid Values: - tagged- untagged- tagged phone- untagged phone |
Specify if the phone traffic is tagged or untagged. If both data and phone traffic are untagged, MAC-Based VLAN Assignment (MBVA) is used, if supported by the model of switch. |
||
| trunk_groups | List, items: String | Required with enable_trunk_groups: true.Trunk Groups are used for limiting VLANs on trunk ports to VLANs with the same Trunk Group. |
|||
| - <str> | String | ||||
| vlans | String | Interface VLANs - if not set, the EOS default is that all VLANs are allowed for trunk ports, and VLAN 1 will be used for access ports. | |||
| spanning_tree_portfast | String | Valid Values: - edge- network |
|||
| spanning_tree_bpdufilter | String | Valid Values: - enabled- disabled- True- False- true- false |
|||
| spanning_tree_bpduguard | String | Valid Values: - enabled- disabled- True- False- true- false |
|||
| flowcontrol | Dictionary | ||||
| received | String | Valid Values: - received- send- on |
|||
| qos_profile | String | QOS profile name. | |||
| ptp | Dictionary | The global PTP profile parameters will be applied to all connected endpoints where ptp is manually enabled.ptp role master is set to ensure control over the PTP topology. |
|||
| enabled | Boolean | False |
|||
| endpoint_role | String | follower |
Valid Values: - bmca- default- follower |
||
| profile | String | aes67-r16-2016 |
Valid Values: - aes67- aes67-r16-2016- smpte2059-2 |
||
| sflow | Boolean | Configures sFlow on the interface. Overrides fabric_sflow.endpoints setting. |
|||
| flow_tracking | Dictionary | Configures flow-tracking on the interface. Overrides fabric_flow_tracking.endpoints setting. |
|||
| enabled | Boolean | ||||
| name | String | Flow tracker name as defined in flow_tracking_settings. | |||
| link_tracking | Dictionary | Configure the downstream interfaces of a respective Link Tracking Group. If port_channel is defined in an adapter, then the port-channel interface is configured to be the downstream.Else all the ethernet interfaces will be configured as downstream -> to configure single-active EVPN multihomed networks. |
|||
| enabled | Boolean | ||||
| name | String | Tracking group name. The default group name is taken from fabric variable of the switch, link_tracking.groups[0].name with default value being “LT_GROUP1”.Optional if default link_tracking settings are configured on the node. |
|||
| dot1x | Dictionary | 802.1x | |||
| port_control | String | Valid Values: - auto- force-authorized- force-unauthorized |
|||
| port_control_force_authorized_phone | Boolean | ||||
| reauthentication | Boolean | ||||
| pae | Dictionary | ||||
| mode | String | Valid Values: - authenticator |
|||
| authentication_failure | Dictionary | ||||
| action | String | Valid Values: - allow- drop |
|||
| allow_vlan | Integer | Min: 1 Max: 4094 |
|||
| host_mode | Dictionary | ||||
| mode | String | Valid Values: - multi-host- single-host |
|||
| multi_host_authenticated | Boolean | ||||
| mac_based_authentication | Dictionary | ||||
| enabled | Boolean | ||||
| always | Boolean | ||||
| host_mode_common | Boolean | ||||
| timeout | Dictionary | ||||
| idle_host | Integer | Min: 10 Max: 65535 |
|||
| quiet_period | Integer | Min: 1 Max: 65535 |
|||
| reauth_period | String | Range 60-4294967295 or “server”. | |||
| reauth_timeout_ignore | Boolean | ||||
| tx_period | Integer | Min: 1 Max: 65535 |
|||
| reauthorization_request_limit | Integer | Min: 1 Max: 10 |
|||
| unauthorized | Dictionary | ||||
| access_vlan_membership_egress | Boolean | ||||
| native_vlan_membership_egress | Boolean | ||||
| poe | Dictionary | Power Over Ethernet settings applied on port. Only configured if platform supports PoE. | |||
| disabled | Boolean | False |
Disable PoE on a POE capable port. PoE is enabled on all ports that support it by default in EOS. | ||
| priority | String | Valid Values: - critical- high- medium- low |
Prioritize a port’s power in the event that one of the switch’s power supplies loses power. | ||
| reboot | Dictionary | Set the PoE power behavior for a PoE port when the system is rebooted. | |||
| action | String | Valid Values: - maintain- power-off |
PoE action for interface. | ||
| link_down | Dictionary | Set the PoE power behavior for a PoE port when the port goes down. | |||
| action | String | Valid Values: - maintain- power-off |
PoE action for interface. | ||
| power_off_delay | Integer | Min: 1 Max: 86400 |
Number of seconds to delay shutting the power off after a link down event occurs. Default value is 5 seconds in EOS. | ||
| shutdown | Dictionary | Set the PoE power behavior for a PoE port when the port is admin down. | |||
| action | String | Valid Values: - maintain- power-off |
PoE action for interface. | ||
| limit | Dictionary | Override the hardware-negotiated power limit using either wattage or a power class. Note that if using a power class, AVD will automatically convert the class value to the wattage value corresponding to that power class. | |||
| class | Integer | Min: 0 Max: 8 |
|||
| watts | String | ||||
| fixed | Boolean | Set to ignore hardware classification. | |||
| negotiation_lldp | Boolean | Disable to prevent port from negotiating power with powered devices over LLDP. Enabled by default in EOS. | |||
| legacy_detect | Boolean | Allow a subset of legacy devices to work with the PoE switch. Disabled by default in EOS because it can cause false positive detections. | |||
| storm_control | Dictionary | Storm control settings applied on port toward the endpoint. | |||
| all | Dictionary | ||||
| level | String | Configure maximum storm-control level. | |||
| unit | String | percent |
Valid Values: - percent- pps |
Optional variable and is hardware dependent. | |
| broadcast | Dictionary | ||||
| level | String | Configure maximum storm-control level. | |||
| unit | String | percent |
Valid Values: - percent- pps |
Optional variable and is hardware dependent. | |
| multicast | Dictionary | ||||
| level | String | Configure maximum storm-control level. | |||
| unit | String | percent |
Valid Values: - percent- pps |
Optional variable and is hardware dependent. | |
| unknown_unicast | Dictionary | ||||
| level | String | Configure maximum storm-control level. | |||
| unit | String | percent |
Valid Values: - percent- pps |
Optional variable and is hardware dependent. | |
| monitor_sessions | List, items: Dictionary | Used to define switchports as source or destination for monitoring sessions. | |||
| - name | String | Required | Session name. | ||
| role | String | Valid Values: - source- destination |
|||
| source_settings | Dictionary | ||||
| direction | String | Valid Values: - rx- tx- both |
|||
| access_group | Dictionary | ||||
| type | String | Valid Values: - ip- ipv6- mac |
|||
| name | String | ACL name. | |||
| priority | Integer | ||||
| session_settings | Dictionary | Session settings are defined per session name. Different session_settings for the same session name will be combined/merged. |
|||
| encapsulation_gre_metadata_tx | Boolean | ||||
| header_remove_size | Integer | Number of bytes to remove from header. | |||
| access_group | Dictionary | ||||
| type | String | Valid Values: - ip- ipv6- mac |
|||
| name | String | ACL name. | |||
| rate_limit_per_ingress_chip | String | Ratelimit and unit as string. Examples: “100000 bps” “100 kbps” “10 mbps” |
|||
| rate_limit_per_egress_chip | String | Ratelimit and unit as string. Examples: “100000 bps” “100 kbps” “10 mbps” |
|||
| sample | Integer | ||||
| truncate | Dictionary | ||||
| enabled | Boolean | ||||
| size | Integer | Size in bytes. | |||
| ethernet_segment | Dictionary | Settings for all or single-active EVPN multihoming. | |||
| short_esi | String | Required | In format xxxx:xxxx:xxxx or “auto”. Define a manual short-esi (be careful using this on profiles) or set the value to “auto” to automatically generate the value. Please see the notes under “EVPN A/A ESI dual and single-attached endpoint scenarios” before setting short_esi: auto. |
||
| redundancy | String | Valid Values: - all-active- single-active |
If omitted, Port-Channels use the EOS default of all-active. If omitted, Ethernet interfaces are configured as single-active. |
||
| designated_forwarder_algorithm | String | Valid Values: - auto- modulus- preference |
Configure DF algorithm and preferences. - auto: Use preference-based algorithm and assign preference based on position of device in the ‘switches’ list, e.g., assuming a list of three switches, this would assign a preference of 200 to the first switch, 100 to the 2nd, and 0 to the third. - preference: Set preference for each switch manually using designated_forwarder_preferences key. - modulus: Use the default modulus-based algorithm. If omitted, Port-Channels use the EOS default of modulus. If omitted, Ethernet interfaces default to the ‘auto’ mechanism detailed above. |
||
| designated_forwarder_preferences | List, items: Integer | Manual preference as described above, required only for preference algorithm. | |||
| - <int> | Integer | ||||
| dont_preempt | Boolean | Disable preemption for single-active forwarding when auto/manual DF preference is configured. | |||
| port_channel | Dictionary | Used for port-channel adapter. | |||
| mode | String | Valid Values: - active- passive- on |
Port-Channel Mode. | ||
| channel_id | Integer | Port-Channel ID. If no channel_id is specified, an id is generated from the first switch port in the port channel. |
|||
| description | String | By default the description is built leveraging <peer> name or adapter.description when defined.When this key is defined, it will append its content to the physical port description. |
|||
| enabled | Boolean | True |
Port-Channel administrative state. Setting to false will set port to ‘shutdown’ in intended configuration. |
||
| esi removed | String | Format xxxx:xxxx:xxxx.This key was removed. Support was removed in AVD version 4.0.0. Use short_esi instead. | |||
| short_esi deprecated | String | In format xxxx:xxxx:xxxx or “auto”.This key is deprecated. Support will be removed in AVD version 5.0.0. Use ethernet_segment.short_esi instead. | |||
| lacp_fallback | Dictionary | LACP fallback configuration. | |||
| mode | String | Valid Values: - static- individual |
Either static or individual mode is supported. If the mode is set to “individual” the “individual.profile” setting must be defined. |
||
| individual | Dictionary | Define parameters for port-channel member interfaces. Applies only if LACP fallback is set to “individual”. | |||
| profile | String | Port-profile name to inherit configuration. | |||
| timeout | Integer | Timeout in seconds. EOS default is 90 seconds. | |||
| lacp_timer | Dictionary | LACP timer configuration. Applies only when Port-channel mode is not “on”. | |||
| mode | String | Valid Values: - normal- fast |
LACP mode for interface members. | ||
| multiplier | Integer | Number of LACP BPDUs lost before deeming the peer down. EOS default is 3. | |||
| subinterfaces | List, items: Dictionary | Port-Channel L2 Subinterfaces Subinterfaces are only supported on routed port-channels, which means they cannot be configured on MLAG port-channels. Setting short_esi: auto generates the short_esi automatically using a hash of configuration elements. Please see the notes under “EVPN A/A ESI dual-attached endpoint scenario” before setting short_esi: auto. |
|||
| - number | Integer | Subinterface number. | |||
| short_esi | String | In format xxxx:xxxx:xxxx or “auto”. Required for multihomed port-channels with subinterfaces. |
|||
| vlan_id | Integer | Min: 1 Max: 4094 |
VLAN ID to bridge. Default is subinterface number. |
||
| encapsulation_vlan | Dictionary | Client VLAN ID encapsulation. Default is subinterface number. |
|||
| client_dot1q | Integer | Min: 1 Max: 4094 |
|||
| raw_eos_cli | String | EOS CLI rendered directly on the port-channel interface in the final EOS configuration. | |||
| structured_config | Dictionary | Custom structured config added under port_channel_interfaces.[name= |
|||
| validate_state | Boolean | Set to false to disable interface validation by the eos_validate_state role. |
|||
| raw_eos_cli | String | EOS CLI rendered directly on the ethernet interface in the final EOS configuration. | |||
| structured_config | Dictionary | Custom structured config added under ethernet_interfaces.[name= |
# This should be applied to group_vars or host_vars where endpoints are connecting.
# `connected_endpoints_keys.key` is one of the keys under "connected_endpoints_keys".
# The default keys are `servers`, `firewalls`, `routers`, `load_balancers`, and `storage_arrays`.
<connected_endpoints_keys.key>:
# Endpoint name will be used in the switchport description.
- name: <str; required; unique>
# Rack is used for documentation purposes only.
rack: <str>
# A list of adapters, group by adapters leveraging the same port-profile.
adapters:
# List of switch interfaces.
# The lists `endpoint_ports`, `switch_ports`, and `switches` must have the same length.
- switch_ports: # required
# Switchport interface.
- <str>
# List of switches.
# The lists `endpoint_ports`, `switch_ports`, and `switches` must have the same length.
switches: # required
# Device.
- <str>
# Endpoint ports is used for description, required unless `description` or `descriptions` is set.
# The lists `endpoint_ports`, `switch_ports`, `descriptions` and `switches` must have the same length.
# Each list item is one switchport.
endpoint_ports:
# Interface name.
- <str>
# Unique description per port. When set, takes priority over description.
descriptions: <list>
# Set adapter speed in the format `<interface_speed>` or `forced <interface_speed>` or `auto <interface_speed>`.
# If not specified speed will be auto.
speed: <str>
# By default the description is built leveraging `<peer>_<peer_interface>`.
# When set this key will override the default value on the physical ports.
description: <str>
# Port-profile name to inherit configuration.
profile: <str>
# Administrative state, setting to false will set the port to 'shutdown' in the intended configuration.
enabled: <bool; default=True>
# Interface mode.
mode: <str; "access" | "dot1q-tunnel" | "trunk" | "trunk phone">
mtu: <int; 68-65535>
# "l2_mtu" should only be defined for platforms supporting the "l2 mtu" CLI.
l2_mtu: <int; 68-65535>
# "l2_mru" should only be defined for platforms supporting the "l2 mru" CLI.
l2_mru: <int; 68-65535>
# Native VLAN for a trunk port.
# If both `native_vlan` and `native_vlan_tag`, `native_vlan_tag` takes precedence.
native_vlan: <int; 1-4094>
# If both `native_vlan` and `native_vlan_tag`, `native_vlan_tag` takes precedence.
native_vlan_tag: <bool; default=False>
# Phone VLAN for a mode `trunk phone` port.
# Requires `mode: trunk phone` to be set.
phone_vlan: <int; 1-4094>
# Specify if the phone traffic is tagged or untagged.
# If both data and phone traffic are untagged, MAC-Based VLAN Assignment (MBVA) is used, if supported by the model of switch.
phone_trunk_mode: <str; "tagged" | "untagged" | "tagged phone" | "untagged phone">
# Required with `enable_trunk_groups: true`.
# Trunk Groups are used for limiting VLANs on trunk ports to VLANs with the same Trunk Group.
trunk_groups:
- <str>
# Interface VLANs - if not set, the EOS default is that all VLANs are allowed for trunk ports, and VLAN 1 will be used for access ports.
vlans: <str>
spanning_tree_portfast: <str; "edge" | "network">
spanning_tree_bpdufilter: <str; "enabled" | "disabled" | "True" | "False" | "true" | "false">
spanning_tree_bpduguard: <str; "enabled" | "disabled" | "True" | "False" | "true" | "false">
flowcontrol:
received: <str; "received" | "send" | "on">
# QOS profile name.
qos_profile: <str>
# The global PTP profile parameters will be applied to all connected endpoints where `ptp` is manually enabled.
# `ptp role master` is set to ensure control over the PTP topology.
ptp:
enabled: <bool; default=False>
endpoint_role: <str; "bmca" | "default" | "follower"; default="follower">
profile: <str; "aes67" | "aes67-r16-2016" | "smpte2059-2"; default="aes67-r16-2016">
# Configures sFlow on the interface. Overrides `fabric_sflow.endpoints` setting.
sflow: <bool>
# Configures flow-tracking on the interface. Overrides `fabric_flow_tracking.endpoints` setting.
flow_tracking:
enabled: <bool>
# Flow tracker name as defined in flow_tracking_settings.
name: <str>
# Configure the downstream interfaces of a respective Link Tracking Group.
# If `port_channel` is defined in an adapter, then the port-channel interface is configured to be the downstream.
# Else all the ethernet interfaces will be configured as downstream -> to configure single-active EVPN multihomed networks.
link_tracking:
enabled: <bool>
# Tracking group name.
# The default group name is taken from fabric variable of the switch, `link_tracking.groups[0].name` with default value being "LT_GROUP1".
# Optional if default link_tracking settings are configured on the node.
name: <str>
# 802.1x
dot1x:
port_control: <str; "auto" | "force-authorized" | "force-unauthorized">
port_control_force_authorized_phone: <bool>
reauthentication: <bool>
pae:
mode: <str; "authenticator">
authentication_failure:
action: <str; "allow" | "drop">
allow_vlan: <int; 1-4094>
host_mode:
mode: <str; "multi-host" | "single-host">
multi_host_authenticated: <bool>
mac_based_authentication:
enabled: <bool>
always: <bool>
host_mode_common: <bool>
timeout:
idle_host: <int; 10-65535>
quiet_period: <int; 1-65535>
# Range 60-4294967295 or "server".
reauth_period: <str>
reauth_timeout_ignore: <bool>
tx_period: <int; 1-65535>
reauthorization_request_limit: <int; 1-10>
unauthorized:
access_vlan_membership_egress: <bool>
native_vlan_membership_egress: <bool>
# Power Over Ethernet settings applied on port. Only configured if platform supports PoE.
poe:
# Disable PoE on a POE capable port. PoE is enabled on all ports that support it by default in EOS.
disabled: <bool; default=False>
# Prioritize a port's power in the event that one of the switch's power supplies loses power.
priority: <str; "critical" | "high" | "medium" | "low">
# Set the PoE power behavior for a PoE port when the system is rebooted.
reboot:
# PoE action for interface.
action: <str; "maintain" | "power-off">
# Set the PoE power behavior for a PoE port when the port goes down.
link_down:
# PoE action for interface.
action: <str; "maintain" | "power-off">
# Number of seconds to delay shutting the power off after a link down event occurs. Default value is 5 seconds in EOS.
power_off_delay: <int; 1-86400>
# Set the PoE power behavior for a PoE port when the port is admin down.
shutdown:
# PoE action for interface.
action: <str; "maintain" | "power-off">
# Override the hardware-negotiated power limit using either wattage or a power class. Note that if using a power class, AVD will automatically convert the class value to the wattage value corresponding to that power class.
limit:
class: <int; 0-8>
watts: <str>
# Set to ignore hardware classification.
fixed: <bool>
# Disable to prevent port from negotiating power with powered devices over LLDP. Enabled by default in EOS.
negotiation_lldp: <bool>
# Allow a subset of legacy devices to work with the PoE switch. Disabled by default in EOS because it can cause false positive detections.
legacy_detect: <bool>
# Storm control settings applied on port toward the endpoint.
storm_control:
all:
# Configure maximum storm-control level.
level: <str>
# Optional variable and is hardware dependent.
unit: <str; "percent" | "pps"; default="percent">
broadcast:
# Configure maximum storm-control level.
level: <str>
# Optional variable and is hardware dependent.
unit: <str; "percent" | "pps"; default="percent">
multicast:
# Configure maximum storm-control level.
level: <str>
# Optional variable and is hardware dependent.
unit: <str; "percent" | "pps"; default="percent">
unknown_unicast:
# Configure maximum storm-control level.
level: <str>
# Optional variable and is hardware dependent.
unit: <str; "percent" | "pps"; default="percent">
# Used to define switchports as source or destination for monitoring sessions.
monitor_sessions:
# Session name.
- name: <str; required>
role: <str; "source" | "destination">
source_settings:
direction: <str; "rx" | "tx" | "both">
access_group:
type: <str; "ip" | "ipv6" | "mac">
# ACL name.
name: <str>
priority: <int>
# Session settings are defined per session name.
# Different session_settings for the same session name will be combined/merged.
session_settings:
encapsulation_gre_metadata_tx: <bool>
# Number of bytes to remove from header.
header_remove_size: <int>
access_group:
type: <str; "ip" | "ipv6" | "mac">
# ACL name.
name: <str>
# Ratelimit and unit as string.
# Examples:
# "100000 bps"
# "100 kbps"
# "10 mbps"
rate_limit_per_ingress_chip: <str>
# Ratelimit and unit as string.
# Examples:
# "100000 bps"
# "100 kbps"
# "10 mbps"
rate_limit_per_egress_chip: <str>
sample: <int>
truncate:
enabled: <bool>
# Size in bytes.
size: <int>
# Settings for all or single-active EVPN multihoming.
ethernet_segment:
# In format xxxx:xxxx:xxxx or "auto".
# Define a manual short-esi (be careful using this on profiles) or set the value to "auto" to automatically generate the value.
# Please see the notes under "EVPN A/A ESI dual and single-attached endpoint scenarios" before setting `short_esi: auto`.
short_esi: <str; required>
# If omitted, Port-Channels use the EOS default of all-active.
# If omitted, Ethernet interfaces are configured as single-active.
redundancy: <str; "all-active" | "single-active">
# Configure DF algorithm and preferences.
# - auto: Use preference-based algorithm and assign preference based on position of device in the 'switches' list,
# e.g., assuming a list of three switches, this would assign a preference of 200 to the first switch, 100 to the 2nd, and 0 to the third.
# - preference: Set preference for each switch manually using designated_forwarder_preferences key.
# - modulus: Use the default modulus-based algorithm.
# If omitted, Port-Channels use the EOS default of modulus.
# If omitted, Ethernet interfaces default to the 'auto' mechanism detailed above.
designated_forwarder_algorithm: <str; "auto" | "modulus" | "preference">
# Manual preference as described above, required only for preference algorithm.
designated_forwarder_preferences:
- <int>
# Disable preemption for single-active forwarding when auto/manual DF preference is configured.
dont_preempt: <bool>
# Used for port-channel adapter.
port_channel:
# Port-Channel Mode.
mode: <str; "active" | "passive" | "on">
# Port-Channel ID.
# If no channel_id is specified, an id is generated from the first switch port in the port channel.
channel_id: <int>
# By default the description is built leveraging `<peer>` name or `adapter.description` when defined.
# When this key is defined, it will append its content to the physical port description.
description: <str>
# Port-Channel administrative state.
# Setting to false will set port to 'shutdown' in intended configuration.
enabled: <bool; default=True>
# In format xxxx:xxxx:xxxx or "auto".
# This key is deprecated.
# Support will be removed in AVD version 5.0.0.
# Use <samp>ethernet_segment.short_esi</samp> instead.
short_esi: <str>
# LACP fallback configuration.
lacp_fallback:
# Either static or individual mode is supported.
# If the mode is set to "individual" the "individual.profile" setting must be defined.
mode: <str; "static" | "individual">
# Define parameters for port-channel member interfaces. Applies only if LACP fallback is set to "individual".
individual:
# Port-profile name to inherit configuration.
profile: <str>
# Timeout in seconds. EOS default is 90 seconds.
timeout: <int>
# LACP timer configuration. Applies only when Port-channel mode is not "on".
lacp_timer:
# LACP mode for interface members.
mode: <str; "normal" | "fast">
# Number of LACP BPDUs lost before deeming the peer down. EOS default is 3.
multiplier: <int>
# Port-Channel L2 Subinterfaces
# Subinterfaces are only supported on routed port-channels, which means they cannot be configured on MLAG port-channels.
# Setting short_esi: auto generates the short_esi automatically using a hash of configuration elements.
# Please see the notes under "EVPN A/A ESI dual-attached endpoint scenario" before setting short_esi: auto.
subinterfaces:
# Subinterface number.
- number: <int>
# In format xxxx:xxxx:xxxx or "auto".
# Required for multihomed port-channels with subinterfaces.
short_esi: <str>
# VLAN ID to bridge.
# Default is subinterface number.
vlan_id: <int; 1-4094>
# Client VLAN ID encapsulation.
# Default is subinterface number.
encapsulation_vlan:
client_dot1q: <int; 1-4094>
# EOS CLI rendered directly on the port-channel interface in the final EOS configuration.
raw_eos_cli: <str>
# Custom structured config added under port_channel_interfaces.[name=<interface>] for eos_cli_config_gen.
structured_config: <dict>
# Set to false to disable interface validation by the `eos_validate_state` role.
validate_state: <bool>
# EOS CLI rendered directly on the ethernet interface in the final EOS configuration.
raw_eos_cli: <str>
# Custom structured config added under ethernet_interfaces.[name=<interface>] for eos_cli_config_gen.
structured_config: <dict>
Network ports settings¶
The network_ports data model is intended to be used with port_profiles and parent_profiles to keep the configuration generic and compact,
but all features and keys supported under connected_endpoints.adapters are also supported directly under network_ports.
All ranges defined under switch_ports will be expanded to individual port configuration which leads to a some behavioral differences to connected_endpoints:
- By default each port will be configured in a port-channel with one member when leveraging automatic channel-id generation. To configure multiple ports as member of the same port-channel set the channel-id key (see the example below).
- Inconsistent configurations when used with
short_esi: autoordesignated_forwarder_algorithm: auto, since those rely on information from multiple switches and interfaces.
Example using network ports and profiles
# Port Profiles
# Common settings inherited to network_ports
port_profiles:
- profile: common
mode: access
vlans: "999"
spanning_tree_portfast: edge
spanning_tree_bpdufilter: enabled
- profile: ap_with_port_channel
parent_profile: common
vlans: "101"
port_channel:
mode: active
- profile: pc
parent_profile: common
vlans: "100"
# Network Ports
# All switch_ports ranges are expanded into individual port configurations
# Switches are matched with regex matching the full hostname.
network_ports:
- switches:
- network-ports-tests-1
switch_ports:
- Ethernet1-2
profile: pc
description: PCs
- switches:
- network-ports-tests-2$
switch_ports:
- Ethernet1-2
profile: ap_with_port_channel
description: AP1 with port_channel
- switches:
- network-ports-[est]{5}-.*
switch_ports:
- Ethernet3-4
- Ethernet2/1-48
profile: pc
description: PCs
Example using network ports to configure multiple ports in the same port-channel
When defining port-channels, all ranges defined under switch_ports will be expanded to individual port configurations
in a port-channel with one member. To configure multiple ports as members of the same port-channel, set the channel-id key manually
like in this example:
# Network Ports
# By setting the channel_id key under port-channel, interfaces Ethernet3-4 will
# be configured under the same port-channel.
network_ports:
- switches:
- network-ports-tests-1
switch_ports:
- Ethernet3-4
description: Multiple interfaces in the same port-channel
port_channel:
mode: active
channel_id: 42
This will generate the following config:
interface Port-Channel42
description Multiple interfaces in the same port-channel
no shutdown
switchport
!
!
interface Ethernet3
description Multiple interfaces in the same port-channel
no shutdown
channel-group 42 mode active
!
interface Ethernet4
description Multiple interfaces in the same port-channel
no shutdown
channel-group 42 mode active
!
Tip
To leverage automatic channel-id computation and configure port-channel with multiple members, connected_endpoints should be used.
| Variable | Type | Required | Default | Value Restrictions | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| network_ports | List, items: Dictionary | ||||
| - switches | List, items: String | Regex matching the full hostname of one or more switches. The regular expression must match the full hostname. |
|||
| - <str> | String | ||||
| switch_ports | List, items: String | List of ranges using AVD range_expand syntax. For example: switch_ports: - Ethernet1 - Ethernet2-48 All switch_ports ranges are expanded into individual port configurations. For more details and examples of the range_expand syntax, see the arista.avd.range_expand documentation. |
|||
| - <str> | String | ||||
| description | String | Description to be used on all ports. | |||
| speed | String | Set adapter speed in the format <interface_speed> or forced <interface_speed> or auto <interface_speed>.If not specified speed will be auto. |
|||
| profile | String | Port-profile name to inherit configuration. | |||
| enabled | Boolean | True |
Administrative state, setting to false will set the port to ‘shutdown’ in the intended configuration. |
||
| mode | String | Valid Values: - access- dot1q-tunnel- trunk- trunk phone |
Interface mode. | ||
| mtu | Integer | Min: 68 Max: 65535 |
|||
| l2_mtu | Integer | Min: 68 Max: 65535 |
“l2_mtu” should only be defined for platforms supporting the “l2 mtu” CLI. |
||
| l2_mru | Integer | Min: 68 Max: 65535 |
“l2_mru” should only be defined for platforms supporting the “l2 mru” CLI. |
||
| native_vlan | Integer | Min: 1 Max: 4094 |
Native VLAN for a trunk port. If both native_vlan and native_vlan_tag, native_vlan_tag takes precedence. |
||
| native_vlan_tag | Boolean | False |
If both native_vlan and native_vlan_tag, native_vlan_tag takes precedence. |
||
| phone_vlan | Integer | Min: 1 Max: 4094 |
Phone VLAN for a mode trunk phone port.Requires mode: trunk phone to be set. |
||
| phone_trunk_mode | String | Valid Values: - tagged- untagged- tagged phone- untagged phone |
Specify if the phone traffic is tagged or untagged. If both data and phone traffic are untagged, MAC-Based VLAN Assignment (MBVA) is used, if supported by the model of switch. |
||
| trunk_groups | List, items: String | Required with enable_trunk_groups: true.Trunk Groups are used for limiting VLANs on trunk ports to VLANs with the same Trunk Group. |
|||
| - <str> | String | ||||
| vlans | String | Interface VLANs - if not set, the EOS default is that all VLANs are allowed for trunk ports, and VLAN 1 will be used for access ports. | |||
| spanning_tree_portfast | String | Valid Values: - edge- network |
|||
| spanning_tree_bpdufilter | String | Valid Values: - enabled- disabled- True- False- true- false |
|||
| spanning_tree_bpduguard | String | Valid Values: - enabled- disabled- True- False- true- false |
|||
| flowcontrol | Dictionary | ||||
| received | String | Valid Values: - received- send- on |
|||
| qos_profile | String | QOS profile name. | |||
| ptp | Dictionary | The global PTP profile parameters will be applied to all connected endpoints where ptp is manually enabled.ptp role master is set to ensure control over the PTP topology. |
|||
| enabled | Boolean | False |
|||
| endpoint_role | String | follower |
Valid Values: - bmca- default- follower |
||
| profile | String | aes67-r16-2016 |
Valid Values: - aes67- aes67-r16-2016- smpte2059-2 |
||
| sflow | Boolean | Configures sFlow on the interface. Overrides fabric_sflow.endpoints setting. |
|||
| flow_tracking | Dictionary | Configures flow-tracking on the interface. Overrides fabric_flow_tracking.endpoints setting. |
|||
| enabled | Boolean | ||||
| name | String | Flow tracker name as defined in flow_tracking_settings. | |||
| link_tracking | Dictionary | Configure the downstream interfaces of a respective Link Tracking Group. If port_channel is defined in an adapter, then the port-channel interface is configured to be the downstream.Else all the ethernet interfaces will be configured as downstream -> to configure single-active EVPN multihomed networks. |
|||
| enabled | Boolean | ||||
| name | String | Tracking group name. The default group name is taken from fabric variable of the switch, link_tracking.groups[0].name with default value being “LT_GROUP1”.Optional if default link_tracking settings are configured on the node. |
|||
| dot1x | Dictionary | 802.1x | |||
| port_control | String | Valid Values: - auto- force-authorized- force-unauthorized |
|||
| port_control_force_authorized_phone | Boolean | ||||
| reauthentication | Boolean | ||||
| pae | Dictionary | ||||
| mode | String | Valid Values: - authenticator |
|||
| authentication_failure | Dictionary | ||||
| action | String | Valid Values: - allow- drop |
|||
| allow_vlan | Integer | Min: 1 Max: 4094 |
|||
| host_mode | Dictionary | ||||
| mode | String | Valid Values: - multi-host- single-host |
|||
| multi_host_authenticated | Boolean | ||||
| mac_based_authentication | Dictionary | ||||
| enabled | Boolean | ||||
| always | Boolean | ||||
| host_mode_common | Boolean | ||||
| timeout | Dictionary | ||||
| idle_host | Integer | Min: 10 Max: 65535 |
|||
| quiet_period | Integer | Min: 1 Max: 65535 |
|||
| reauth_period | String | Range 60-4294967295 or “server”. | |||
| reauth_timeout_ignore | Boolean | ||||
| tx_period | Integer | Min: 1 Max: 65535 |
|||
| reauthorization_request_limit | Integer | Min: 1 Max: 10 |
|||
| unauthorized | Dictionary | ||||
| access_vlan_membership_egress | Boolean | ||||
| native_vlan_membership_egress | Boolean | ||||
| poe | Dictionary | Power Over Ethernet settings applied on port. Only configured if platform supports PoE. | |||
| disabled | Boolean | False |
Disable PoE on a POE capable port. PoE is enabled on all ports that support it by default in EOS. | ||
| priority | String | Valid Values: - critical- high- medium- low |
Prioritize a port’s power in the event that one of the switch’s power supplies loses power. | ||
| reboot | Dictionary | Set the PoE power behavior for a PoE port when the system is rebooted. | |||
| action | String | Valid Values: - maintain- power-off |
PoE action for interface. | ||
| link_down | Dictionary | Set the PoE power behavior for a PoE port when the port goes down. | |||
| action | String | Valid Values: - maintain- power-off |
PoE action for interface. | ||
| power_off_delay | Integer | Min: 1 Max: 86400 |
Number of seconds to delay shutting the power off after a link down event occurs. Default value is 5 seconds in EOS. | ||
| shutdown | Dictionary | Set the PoE power behavior for a PoE port when the port is admin down. | |||
| action | String | Valid Values: - maintain- power-off |
PoE action for interface. | ||
| limit | Dictionary | Override the hardware-negotiated power limit using either wattage or a power class. Note that if using a power class, AVD will automatically convert the class value to the wattage value corresponding to that power class. | |||
| class | Integer | Min: 0 Max: 8 |
|||
| watts | String | ||||
| fixed | Boolean | Set to ignore hardware classification. | |||
| negotiation_lldp | Boolean | Disable to prevent port from negotiating power with powered devices over LLDP. Enabled by default in EOS. | |||
| legacy_detect | Boolean | Allow a subset of legacy devices to work with the PoE switch. Disabled by default in EOS because it can cause false positive detections. | |||
| storm_control | Dictionary | Storm control settings applied on port toward the endpoint. | |||
| all | Dictionary | ||||
| level | String | Configure maximum storm-control level. | |||
| unit | String | percent |
Valid Values: - percent- pps |
Optional variable and is hardware dependent. | |
| broadcast | Dictionary | ||||
| level | String | Configure maximum storm-control level. | |||
| unit | String | percent |
Valid Values: - percent- pps |
Optional variable and is hardware dependent. | |
| multicast | Dictionary | ||||
| level | String | Configure maximum storm-control level. | |||
| unit | String | percent |
Valid Values: - percent- pps |
Optional variable and is hardware dependent. | |
| unknown_unicast | Dictionary | ||||
| level | String | Configure maximum storm-control level. | |||
| unit | String | percent |
Valid Values: - percent- pps |
Optional variable and is hardware dependent. | |
| monitor_sessions | List, items: Dictionary | Used to define switchports as source or destination for monitoring sessions. | |||
| - name | String | Required | Session name. | ||
| role | String | Valid Values: - source- destination |
|||
| source_settings | Dictionary | ||||
| direction | String | Valid Values: - rx- tx- both |
|||
| access_group | Dictionary | ||||
| type | String | Valid Values: - ip- ipv6- mac |
|||
| name | String | ACL name. | |||
| priority | Integer | ||||
| session_settings | Dictionary | Session settings are defined per session name. Different session_settings for the same session name will be combined/merged. |
|||
| encapsulation_gre_metadata_tx | Boolean | ||||
| header_remove_size | Integer | Number of bytes to remove from header. | |||
| access_group | Dictionary | ||||
| type | String | Valid Values: - ip- ipv6- mac |
|||
| name | String | ACL name. | |||
| rate_limit_per_ingress_chip | String | Ratelimit and unit as string. Examples: “100000 bps” “100 kbps” “10 mbps” |
|||
| rate_limit_per_egress_chip | String | Ratelimit and unit as string. Examples: “100000 bps” “100 kbps” “10 mbps” |
|||
| sample | Integer | ||||
| truncate | Dictionary | ||||
| enabled | Boolean | ||||
| size | Integer | Size in bytes. | |||
| ethernet_segment | Dictionary | Settings for all or single-active EVPN multihoming. | |||
| short_esi | String | Required | In format xxxx:xxxx:xxxx or “auto”. Define a manual short-esi (be careful using this on profiles) or set the value to “auto” to automatically generate the value. Please see the notes under “EVPN A/A ESI dual and single-attached endpoint scenarios” before setting short_esi: auto. |
||
| redundancy | String | Valid Values: - all-active- single-active |
If omitted, Port-Channels use the EOS default of all-active. If omitted, Ethernet interfaces are configured as single-active. |
||
| designated_forwarder_algorithm | String | Valid Values: - auto- modulus- preference |
Configure DF algorithm and preferences. - auto: Use preference-based algorithm and assign preference based on position of device in the ‘switches’ list, e.g., assuming a list of three switches, this would assign a preference of 200 to the first switch, 100 to the 2nd, and 0 to the third. - preference: Set preference for each switch manually using designated_forwarder_preferences key. - modulus: Use the default modulus-based algorithm. If omitted, Port-Channels use the EOS default of modulus. If omitted, Ethernet interfaces default to the ‘auto’ mechanism detailed above. |
||
| designated_forwarder_preferences | List, items: Integer | Manual preference as described above, required only for preference algorithm. | |||
| - <int> | Integer | ||||
| dont_preempt | Boolean | Disable preemption for single-active forwarding when auto/manual DF preference is configured. | |||
| port_channel | Dictionary | Used for port-channel adapter. | |||
| mode | String | Valid Values: - active- passive- on |
Port-Channel Mode. | ||
| channel_id | Integer | Port-Channel ID. If no channel_id is specified, an id is generated from the first switch port in the port channel. |
|||
| description | String | By default the description is built leveraging <peer> name or adapter.description when defined.When this key is defined, it will append its content to the physical port description. |
|||
| enabled | Boolean | True |
Port-Channel administrative state. Setting to false will set port to ‘shutdown’ in intended configuration. |
||
| esi removed | String | Format xxxx:xxxx:xxxx.This key was removed. Support was removed in AVD version 4.0.0. Use short_esi instead. | |||
| short_esi deprecated | String | In format xxxx:xxxx:xxxx or “auto”.This key is deprecated. Support will be removed in AVD version 5.0.0. Use ethernet_segment.short_esi instead. | |||
| lacp_fallback | Dictionary | LACP fallback configuration. | |||
| mode | String | Valid Values: - static- individual |
Either static or individual mode is supported. If the mode is set to “individual” the “individual.profile” setting must be defined. |
||
| individual | Dictionary | Define parameters for port-channel member interfaces. Applies only if LACP fallback is set to “individual”. | |||
| profile | String | Port-profile name to inherit configuration. | |||
| timeout | Integer | Timeout in seconds. EOS default is 90 seconds. | |||
| lacp_timer | Dictionary | LACP timer configuration. Applies only when Port-channel mode is not “on”. | |||
| mode | String | Valid Values: - normal- fast |
LACP mode for interface members. | ||
| multiplier | Integer | Number of LACP BPDUs lost before deeming the peer down. EOS default is 3. | |||
| subinterfaces | List, items: Dictionary | Port-Channel L2 Subinterfaces Subinterfaces are only supported on routed port-channels, which means they cannot be configured on MLAG port-channels. Setting short_esi: auto generates the short_esi automatically using a hash of configuration elements. Please see the notes under “EVPN A/A ESI dual-attached endpoint scenario” before setting short_esi: auto. |
|||
| - number | Integer | Subinterface number. | |||
| short_esi | String | In format xxxx:xxxx:xxxx or “auto”. Required for multihomed port-channels with subinterfaces. |
|||
| vlan_id | Integer | Min: 1 Max: 4094 |
VLAN ID to bridge. Default is subinterface number. |
||
| encapsulation_vlan | Dictionary | Client VLAN ID encapsulation. Default is subinterface number. |
|||
| client_dot1q | Integer | Min: 1 Max: 4094 |
|||
| raw_eos_cli | String | EOS CLI rendered directly on the port-channel interface in the final EOS configuration. | |||
| structured_config | Dictionary | Custom structured config added under port_channel_interfaces.[name= |
|||
| validate_state | Boolean | Set to false to disable interface validation by the eos_validate_state role. |
|||
| raw_eos_cli | String | EOS CLI rendered directly on the ethernet interface in the final EOS configuration. | |||
| structured_config | Dictionary | Custom structured config added under ethernet_interfaces.[name= |
network_ports:
# Regex matching the full hostname of one or more switches.
# The regular expression must match the full hostname.
- switches:
- <str>
# List of ranges using AVD range_expand syntax.
# For example:
#
# switch_ports:
# - Ethernet1
# - Ethernet2-48
#
# All switch_ports ranges are expanded into individual port configurations.
#
# For more details and examples of the `range_expand` syntax, see the [`arista.avd.range_expand` documentation](../../../docs/plugins/Filter_plugins/range_expand.md).
switch_ports:
- <str>
# Description to be used on all ports.
description: <str>
# Set adapter speed in the format `<interface_speed>` or `forced <interface_speed>` or `auto <interface_speed>`.
# If not specified speed will be auto.
speed: <str>
# Port-profile name to inherit configuration.
profile: <str>
# Administrative state, setting to false will set the port to 'shutdown' in the intended configuration.
enabled: <bool; default=True>
# Interface mode.
mode: <str; "access" | "dot1q-tunnel" | "trunk" | "trunk phone">
mtu: <int; 68-65535>
# "l2_mtu" should only be defined for platforms supporting the "l2 mtu" CLI.
l2_mtu: <int; 68-65535>
# "l2_mru" should only be defined for platforms supporting the "l2 mru" CLI.
l2_mru: <int; 68-65535>
# Native VLAN for a trunk port.
# If both `native_vlan` and `native_vlan_tag`, `native_vlan_tag` takes precedence.
native_vlan: <int; 1-4094>
# If both `native_vlan` and `native_vlan_tag`, `native_vlan_tag` takes precedence.
native_vlan_tag: <bool; default=False>
# Phone VLAN for a mode `trunk phone` port.
# Requires `mode: trunk phone` to be set.
phone_vlan: <int; 1-4094>
# Specify if the phone traffic is tagged or untagged.
# If both data and phone traffic are untagged, MAC-Based VLAN Assignment (MBVA) is used, if supported by the model of switch.
phone_trunk_mode: <str; "tagged" | "untagged" | "tagged phone" | "untagged phone">
# Required with `enable_trunk_groups: true`.
# Trunk Groups are used for limiting VLANs on trunk ports to VLANs with the same Trunk Group.
trunk_groups:
- <str>
# Interface VLANs - if not set, the EOS default is that all VLANs are allowed for trunk ports, and VLAN 1 will be used for access ports.
vlans: <str>
spanning_tree_portfast: <str; "edge" | "network">
spanning_tree_bpdufilter: <str; "enabled" | "disabled" | "True" | "False" | "true" | "false">
spanning_tree_bpduguard: <str; "enabled" | "disabled" | "True" | "False" | "true" | "false">
flowcontrol:
received: <str; "received" | "send" | "on">
# QOS profile name.
qos_profile: <str>
# The global PTP profile parameters will be applied to all connected endpoints where `ptp` is manually enabled.
# `ptp role master` is set to ensure control over the PTP topology.
ptp:
enabled: <bool; default=False>
endpoint_role: <str; "bmca" | "default" | "follower"; default="follower">
profile: <str; "aes67" | "aes67-r16-2016" | "smpte2059-2"; default="aes67-r16-2016">
# Configures sFlow on the interface. Overrides `fabric_sflow.endpoints` setting.
sflow: <bool>
# Configures flow-tracking on the interface. Overrides `fabric_flow_tracking.endpoints` setting.
flow_tracking:
enabled: <bool>
# Flow tracker name as defined in flow_tracking_settings.
name: <str>
# Configure the downstream interfaces of a respective Link Tracking Group.
# If `port_channel` is defined in an adapter, then the port-channel interface is configured to be the downstream.
# Else all the ethernet interfaces will be configured as downstream -> to configure single-active EVPN multihomed networks.
link_tracking:
enabled: <bool>
# Tracking group name.
# The default group name is taken from fabric variable of the switch, `link_tracking.groups[0].name` with default value being "LT_GROUP1".
# Optional if default link_tracking settings are configured on the node.
name: <str>
# 802.1x
dot1x:
port_control: <str; "auto" | "force-authorized" | "force-unauthorized">
port_control_force_authorized_phone: <bool>
reauthentication: <bool>
pae:
mode: <str; "authenticator">
authentication_failure:
action: <str; "allow" | "drop">
allow_vlan: <int; 1-4094>
host_mode:
mode: <str; "multi-host" | "single-host">
multi_host_authenticated: <bool>
mac_based_authentication:
enabled: <bool>
always: <bool>
host_mode_common: <bool>
timeout:
idle_host: <int; 10-65535>
quiet_period: <int; 1-65535>
# Range 60-4294967295 or "server".
reauth_period: <str>
reauth_timeout_ignore: <bool>
tx_period: <int; 1-65535>
reauthorization_request_limit: <int; 1-10>
unauthorized:
access_vlan_membership_egress: <bool>
native_vlan_membership_egress: <bool>
# Power Over Ethernet settings applied on port. Only configured if platform supports PoE.
poe:
# Disable PoE on a POE capable port. PoE is enabled on all ports that support it by default in EOS.
disabled: <bool; default=False>
# Prioritize a port's power in the event that one of the switch's power supplies loses power.
priority: <str; "critical" | "high" | "medium" | "low">
# Set the PoE power behavior for a PoE port when the system is rebooted.
reboot:
# PoE action for interface.
action: <str; "maintain" | "power-off">
# Set the PoE power behavior for a PoE port when the port goes down.
link_down:
# PoE action for interface.
action: <str; "maintain" | "power-off">
# Number of seconds to delay shutting the power off after a link down event occurs. Default value is 5 seconds in EOS.
power_off_delay: <int; 1-86400>
# Set the PoE power behavior for a PoE port when the port is admin down.
shutdown:
# PoE action for interface.
action: <str; "maintain" | "power-off">
# Override the hardware-negotiated power limit using either wattage or a power class. Note that if using a power class, AVD will automatically convert the class value to the wattage value corresponding to that power class.
limit:
class: <int; 0-8>
watts: <str>
# Set to ignore hardware classification.
fixed: <bool>
# Disable to prevent port from negotiating power with powered devices over LLDP. Enabled by default in EOS.
negotiation_lldp: <bool>
# Allow a subset of legacy devices to work with the PoE switch. Disabled by default in EOS because it can cause false positive detections.
legacy_detect: <bool>
# Storm control settings applied on port toward the endpoint.
storm_control:
all:
# Configure maximum storm-control level.
level: <str>
# Optional variable and is hardware dependent.
unit: <str; "percent" | "pps"; default="percent">
broadcast:
# Configure maximum storm-control level.
level: <str>
# Optional variable and is hardware dependent.
unit: <str; "percent" | "pps"; default="percent">
multicast:
# Configure maximum storm-control level.
level: <str>
# Optional variable and is hardware dependent.
unit: <str; "percent" | "pps"; default="percent">
unknown_unicast:
# Configure maximum storm-control level.
level: <str>
# Optional variable and is hardware dependent.
unit: <str; "percent" | "pps"; default="percent">
# Used to define switchports as source or destination for monitoring sessions.
monitor_sessions:
# Session name.
- name: <str; required>
role: <str; "source" | "destination">
source_settings:
direction: <str; "rx" | "tx" | "both">
access_group:
type: <str; "ip" | "ipv6" | "mac">
# ACL name.
name: <str>
priority: <int>
# Session settings are defined per session name.
# Different session_settings for the same session name will be combined/merged.
session_settings:
encapsulation_gre_metadata_tx: <bool>
# Number of bytes to remove from header.
header_remove_size: <int>
access_group:
type: <str; "ip" | "ipv6" | "mac">
# ACL name.
name: <str>
# Ratelimit and unit as string.
# Examples:
# "100000 bps"
# "100 kbps"
# "10 mbps"
rate_limit_per_ingress_chip: <str>
# Ratelimit and unit as string.
# Examples:
# "100000 bps"
# "100 kbps"
# "10 mbps"
rate_limit_per_egress_chip: <str>
sample: <int>
truncate:
enabled: <bool>
# Size in bytes.
size: <int>
# Settings for all or single-active EVPN multihoming.
ethernet_segment:
# In format xxxx:xxxx:xxxx or "auto".
# Define a manual short-esi (be careful using this on profiles) or set the value to "auto" to automatically generate the value.
# Please see the notes under "EVPN A/A ESI dual and single-attached endpoint scenarios" before setting `short_esi: auto`.
short_esi: <str; required>
# If omitted, Port-Channels use the EOS default of all-active.
# If omitted, Ethernet interfaces are configured as single-active.
redundancy: <str; "all-active" | "single-active">
# Configure DF algorithm and preferences.
# - auto: Use preference-based algorithm and assign preference based on position of device in the 'switches' list,
# e.g., assuming a list of three switches, this would assign a preference of 200 to the first switch, 100 to the 2nd, and 0 to the third.
# - preference: Set preference for each switch manually using designated_forwarder_preferences key.
# - modulus: Use the default modulus-based algorithm.
# If omitted, Port-Channels use the EOS default of modulus.
# If omitted, Ethernet interfaces default to the 'auto' mechanism detailed above.
designated_forwarder_algorithm: <str; "auto" | "modulus" | "preference">
# Manual preference as described above, required only for preference algorithm.
designated_forwarder_preferences:
- <int>
# Disable preemption for single-active forwarding when auto/manual DF preference is configured.
dont_preempt: <bool>
# Used for port-channel adapter.
port_channel:
# Port-Channel Mode.
mode: <str; "active" | "passive" | "on">
# Port-Channel ID.
# If no channel_id is specified, an id is generated from the first switch port in the port channel.
channel_id: <int>
# By default the description is built leveraging `<peer>` name or `adapter.description` when defined.
# When this key is defined, it will append its content to the physical port description.
description: <str>
# Port-Channel administrative state.
# Setting to false will set port to 'shutdown' in intended configuration.
enabled: <bool; default=True>
# In format xxxx:xxxx:xxxx or "auto".
# This key is deprecated.
# Support will be removed in AVD version 5.0.0.
# Use <samp>ethernet_segment.short_esi</samp> instead.
short_esi: <str>
# LACP fallback configuration.
lacp_fallback:
# Either static or individual mode is supported.
# If the mode is set to "individual" the "individual.profile" setting must be defined.
mode: <str; "static" | "individual">
# Define parameters for port-channel member interfaces. Applies only if LACP fallback is set to "individual".
individual:
# Port-profile name to inherit configuration.
profile: <str>
# Timeout in seconds. EOS default is 90 seconds.
timeout: <int>
# LACP timer configuration. Applies only when Port-channel mode is not "on".
lacp_timer:
# LACP mode for interface members.
mode: <str; "normal" | "fast">
# Number of LACP BPDUs lost before deeming the peer down. EOS default is 3.
multiplier: <int>
# Port-Channel L2 Subinterfaces
# Subinterfaces are only supported on routed port-channels, which means they cannot be configured on MLAG port-channels.
# Setting short_esi: auto generates the short_esi automatically using a hash of configuration elements.
# Please see the notes under "EVPN A/A ESI dual-attached endpoint scenario" before setting short_esi: auto.
subinterfaces:
# Subinterface number.
- number: <int>
# In format xxxx:xxxx:xxxx or "auto".
# Required for multihomed port-channels with subinterfaces.
short_esi: <str>
# VLAN ID to bridge.
# Default is subinterface number.
vlan_id: <int; 1-4094>
# Client VLAN ID encapsulation.
# Default is subinterface number.
encapsulation_vlan:
client_dot1q: <int; 1-4094>
# EOS CLI rendered directly on the port-channel interface in the final EOS configuration.
raw_eos_cli: <str>
# Custom structured config added under port_channel_interfaces.[name=<interface>] for eos_cli_config_gen.
structured_config: <dict>
# Set to false to disable interface validation by the `eos_validate_state` role.
validate_state: <bool>
# EOS CLI rendered directly on the ethernet interface in the final EOS configuration.
raw_eos_cli: <str>
# Custom structured config added under ethernet_interfaces.[name=<interface>] for eos_cli_config_gen.
structured_config: <dict>
Port profiles settings¶
Optional profiles to share common settings for connected_endpoints and/or network_ports. Keys are the same as used under endpoint adapters. Keys defined under endpoints adapters take precedence.
A port profile can refer to another port profile using parent_profile to inherit settings in up to two levels (adapter->profile->parent_profile).
| Variable | Type | Required | Default | Value Restrictions | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| port_profiles | List, items: Dictionary | Optional profiles to share common settings for connected_endpoints and/or network_ports. Keys are the same used under endpoints adapters. Keys defined under endpoints adapters take precedence. |
|||
| - profile | String | Required, Unique | Port profile name. | ||
| parent_profile | String | Parent profile is optional. Port_profiles can refer to another port_profile to inherit settings in up to two levels (adapter->profile->parent_profile). |
|||
| speed | String | Set adapter speed in the format <interface_speed> or forced <interface_speed> or auto <interface_speed>.If not specified speed will be auto. |
|||
| description | String | By default the description is built leveraging <peer>_<peer_interface>.When set this key will override the default value on the physical ports. |
|||
| enabled | Boolean | True |
Administrative state, setting to false will set the port to ‘shutdown’ in the intended configuration. |
||
| mode | String | Valid Values: - access- dot1q-tunnel- trunk- trunk phone |
Interface mode. | ||
| mtu | Integer | Min: 68 Max: 65535 |
|||
| l2_mtu | Integer | Min: 68 Max: 65535 |
“l2_mtu” should only be defined for platforms supporting the “l2 mtu” CLI. |
||
| l2_mru | Integer | Min: 68 Max: 65535 |
“l2_mru” should only be defined for platforms supporting the “l2 mru” CLI. |
||
| native_vlan | Integer | Min: 1 Max: 4094 |
Native VLAN for a trunk port. If both native_vlan and native_vlan_tag, native_vlan_tag takes precedence. |
||
| native_vlan_tag | Boolean | False |
If both native_vlan and native_vlan_tag, native_vlan_tag takes precedence. |
||
| phone_vlan | Integer | Min: 1 Max: 4094 |
Phone VLAN for a mode trunk phone port.Requires mode: trunk phone to be set. |
||
| phone_trunk_mode | String | Valid Values: - tagged- untagged- tagged phone- untagged phone |
Specify if the phone traffic is tagged or untagged. If both data and phone traffic are untagged, MAC-Based VLAN Assignment (MBVA) is used, if supported by the model of switch. |
||
| trunk_groups | List, items: String | Required with enable_trunk_groups: true.Trunk Groups are used for limiting VLANs on trunk ports to VLANs with the same Trunk Group. |
|||
| - <str> | String | ||||
| vlans | String | Interface VLANs - if not set, the EOS default is that all VLANs are allowed for trunk ports, and VLAN 1 will be used for access ports. | |||
| spanning_tree_portfast | String | Valid Values: - edge- network |
|||
| spanning_tree_bpdufilter | String | Valid Values: - enabled- disabled- True- False- true- false |
|||
| spanning_tree_bpduguard | String | Valid Values: - enabled- disabled- True- False- true- false |
|||
| flowcontrol | Dictionary | ||||
| received | String | Valid Values: - received- send- on |
|||
| qos_profile | String | QOS profile name. | |||
| ptp | Dictionary | The global PTP profile parameters will be applied to all connected endpoints where ptp is manually enabled.ptp role master is set to ensure control over the PTP topology. |
|||
| enabled | Boolean | False |
|||
| endpoint_role | String | follower |
Valid Values: - bmca- default- follower |
||
| profile | String | aes67-r16-2016 |
Valid Values: - aes67- aes67-r16-2016- smpte2059-2 |
||
| sflow | Boolean | Configures sFlow on the interface. Overrides fabric_sflow.endpoints setting. |
|||
| flow_tracking | Dictionary | Configures flow-tracking on the interface. Overrides fabric_flow_tracking.endpoints setting. |
|||
| enabled | Boolean | ||||
| name | String | Flow tracker name as defined in flow_tracking_settings. | |||
| link_tracking | Dictionary | Configure the downstream interfaces of a respective Link Tracking Group. If port_channel is defined in an adapter, then the port-channel interface is configured to be the downstream.Else all the ethernet interfaces will be configured as downstream -> to configure single-active EVPN multihomed networks. |
|||
| enabled | Boolean | ||||
| name | String | Tracking group name. The default group name is taken from fabric variable of the switch, link_tracking.groups[0].name with default value being “LT_GROUP1”.Optional if default link_tracking settings are configured on the node. |
|||
| dot1x | Dictionary | 802.1x | |||
| port_control | String | Valid Values: - auto- force-authorized- force-unauthorized |
|||
| port_control_force_authorized_phone | Boolean | ||||
| reauthentication | Boolean | ||||
| pae | Dictionary | ||||
| mode | String | Valid Values: - authenticator |
|||
| authentication_failure | Dictionary | ||||
| action | String | Valid Values: - allow- drop |
|||
| allow_vlan | Integer | Min: 1 Max: 4094 |
|||
| host_mode | Dictionary | ||||
| mode | String | Valid Values: - multi-host- single-host |
|||
| multi_host_authenticated | Boolean | ||||
| mac_based_authentication | Dictionary | ||||
| enabled | Boolean | ||||
| always | Boolean | ||||
| host_mode_common | Boolean | ||||
| timeout | Dictionary | ||||
| idle_host | Integer | Min: 10 Max: 65535 |
|||
| quiet_period | Integer | Min: 1 Max: 65535 |
|||
| reauth_period | String | Range 60-4294967295 or “server”. | |||
| reauth_timeout_ignore | Boolean | ||||
| tx_period | Integer | Min: 1 Max: 65535 |
|||
| reauthorization_request_limit | Integer | Min: 1 Max: 10 |
|||
| unauthorized | Dictionary | ||||
| access_vlan_membership_egress | Boolean | ||||
| native_vlan_membership_egress | Boolean | ||||
| poe | Dictionary | Power Over Ethernet settings applied on port. Only configured if platform supports PoE. | |||
| disabled | Boolean | False |
Disable PoE on a POE capable port. PoE is enabled on all ports that support it by default in EOS. | ||
| priority | String | Valid Values: - critical- high- medium- low |
Prioritize a port’s power in the event that one of the switch’s power supplies loses power. | ||
| reboot | Dictionary | Set the PoE power behavior for a PoE port when the system is rebooted. | |||
| action | String | Valid Values: - maintain- power-off |
PoE action for interface. | ||
| link_down | Dictionary | Set the PoE power behavior for a PoE port when the port goes down. | |||
| action | String | Valid Values: - maintain- power-off |
PoE action for interface. | ||
| power_off_delay | Integer | Min: 1 Max: 86400 |
Number of seconds to delay shutting the power off after a link down event occurs. Default value is 5 seconds in EOS. | ||
| shutdown | Dictionary | Set the PoE power behavior for a PoE port when the port is admin down. | |||
| action | String | Valid Values: - maintain- power-off |
PoE action for interface. | ||
| limit | Dictionary | Override the hardware-negotiated power limit using either wattage or a power class. Note that if using a power class, AVD will automatically convert the class value to the wattage value corresponding to that power class. | |||
| class | Integer | Min: 0 Max: 8 |
|||
| watts | String | ||||
| fixed | Boolean | Set to ignore hardware classification. | |||
| negotiation_lldp | Boolean | Disable to prevent port from negotiating power with powered devices over LLDP. Enabled by default in EOS. | |||
| legacy_detect | Boolean | Allow a subset of legacy devices to work with the PoE switch. Disabled by default in EOS because it can cause false positive detections. | |||
| storm_control | Dictionary | Storm control settings applied on port toward the endpoint. | |||
| all | Dictionary | ||||
| level | String | Configure maximum storm-control level. | |||
| unit | String | percent |
Valid Values: - percent- pps |
Optional variable and is hardware dependent. | |
| broadcast | Dictionary | ||||
| level | String | Configure maximum storm-control level. | |||
| unit | String | percent |
Valid Values: - percent- pps |
Optional variable and is hardware dependent. | |
| multicast | Dictionary | ||||
| level | String | Configure maximum storm-control level. | |||
| unit | String | percent |
Valid Values: - percent- pps |
Optional variable and is hardware dependent. | |
| unknown_unicast | Dictionary | ||||
| level | String | Configure maximum storm-control level. | |||
| unit | String | percent |
Valid Values: - percent- pps |
Optional variable and is hardware dependent. | |
| monitor_sessions | List, items: Dictionary | Used to define switchports as source or destination for monitoring sessions. | |||
| - name | String | Required | Session name. | ||
| role | String | Valid Values: - source- destination |
|||
| source_settings | Dictionary | ||||
| direction | String | Valid Values: - rx- tx- both |
|||
| access_group | Dictionary | ||||
| type | String | Valid Values: - ip- ipv6- mac |
|||
| name | String | ACL name. | |||
| priority | Integer | ||||
| session_settings | Dictionary | Session settings are defined per session name. Different session_settings for the same session name will be combined/merged. |
|||
| encapsulation_gre_metadata_tx | Boolean | ||||
| header_remove_size | Integer | Number of bytes to remove from header. | |||
| access_group | Dictionary | ||||
| type | String | Valid Values: - ip- ipv6- mac |
|||
| name | String | ACL name. | |||
| rate_limit_per_ingress_chip | String | Ratelimit and unit as string. Examples: “100000 bps” “100 kbps” “10 mbps” |
|||
| rate_limit_per_egress_chip | String | Ratelimit and unit as string. Examples: “100000 bps” “100 kbps” “10 mbps” |
|||
| sample | Integer | ||||
| truncate | Dictionary | ||||
| enabled | Boolean | ||||
| size | Integer | Size in bytes. | |||
| ethernet_segment | Dictionary | Settings for all or single-active EVPN multihoming. | |||
| short_esi | String | Required | In format xxxx:xxxx:xxxx or “auto”. Define a manual short-esi (be careful using this on profiles) or set the value to “auto” to automatically generate the value. Please see the notes under “EVPN A/A ESI dual and single-attached endpoint scenarios” before setting short_esi: auto. |
||
| redundancy | String | Valid Values: - all-active- single-active |
If omitted, Port-Channels use the EOS default of all-active. If omitted, Ethernet interfaces are configured as single-active. |
||
| designated_forwarder_algorithm | String | Valid Values: - auto- modulus- preference |
Configure DF algorithm and preferences. - auto: Use preference-based algorithm and assign preference based on position of device in the ‘switches’ list, e.g., assuming a list of three switches, this would assign a preference of 200 to the first switch, 100 to the 2nd, and 0 to the third. - preference: Set preference for each switch manually using designated_forwarder_preferences key. - modulus: Use the default modulus-based algorithm. If omitted, Port-Channels use the EOS default of modulus. If omitted, Ethernet interfaces default to the ‘auto’ mechanism detailed above. |
||
| designated_forwarder_preferences | List, items: Integer | Manual preference as described above, required only for preference algorithm. | |||
| - <int> | Integer | ||||
| dont_preempt | Boolean | Disable preemption for single-active forwarding when auto/manual DF preference is configured. | |||
| port_channel | Dictionary | Used for port-channel adapter. | |||
| mode | String | Valid Values: - active- passive- on |
Port-Channel Mode. | ||
| channel_id | Integer | Port-Channel ID. If no channel_id is specified, an id is generated from the first switch port in the port channel. |
|||
| description | String | By default the description is built leveraging <peer> name or adapter.description when defined.When this key is defined, it will append its content to the physical port description. |
|||
| enabled | Boolean | True |
Port-Channel administrative state. Setting to false will set port to ‘shutdown’ in intended configuration. |
||
| esi removed | String | Format xxxx:xxxx:xxxx.This key was removed. Support was removed in AVD version 4.0.0. Use short_esi instead. | |||
| short_esi deprecated | String | In format xxxx:xxxx:xxxx or “auto”.This key is deprecated. Support will be removed in AVD version 5.0.0. Use ethernet_segment.short_esi instead. | |||
| lacp_fallback | Dictionary | LACP fallback configuration. | |||
| mode | String | Valid Values: - static- individual |
Either static or individual mode is supported. If the mode is set to “individual” the “individual.profile” setting must be defined. |
||
| individual | Dictionary | Define parameters for port-channel member interfaces. Applies only if LACP fallback is set to “individual”. | |||
| profile | String | Port-profile name to inherit configuration. | |||
| timeout | Integer | Timeout in seconds. EOS default is 90 seconds. | |||
| lacp_timer | Dictionary | LACP timer configuration. Applies only when Port-channel mode is not “on”. | |||
| mode | String | Valid Values: - normal- fast |
LACP mode for interface members. | ||
| multiplier | Integer | Number of LACP BPDUs lost before deeming the peer down. EOS default is 3. | |||
| subinterfaces | List, items: Dictionary | Port-Channel L2 Subinterfaces Subinterfaces are only supported on routed port-channels, which means they cannot be configured on MLAG port-channels. Setting short_esi: auto generates the short_esi automatically using a hash of configuration elements. Please see the notes under “EVPN A/A ESI dual-attached endpoint scenario” before setting short_esi: auto. |
|||
| - number | Integer | Subinterface number. | |||
| short_esi | String | In format xxxx:xxxx:xxxx or “auto”. Required for multihomed port-channels with subinterfaces. |
|||
| vlan_id | Integer | Min: 1 Max: 4094 |
VLAN ID to bridge. Default is subinterface number. |
||
| encapsulation_vlan | Dictionary | Client VLAN ID encapsulation. Default is subinterface number. |
|||
| client_dot1q | Integer | Min: 1 Max: 4094 |
|||
| raw_eos_cli | String | EOS CLI rendered directly on the port-channel interface in the final EOS configuration. | |||
| structured_config | Dictionary | Custom structured config added under port_channel_interfaces.[name= |
|||
| validate_state | Boolean | Set to false to disable interface validation by the eos_validate_state role. |
|||
| raw_eos_cli | String | EOS CLI rendered directly on the ethernet interface in the final EOS configuration. | |||
| structured_config | Dictionary | Custom structured config added under ethernet_interfaces.[name= |
# Optional profiles to share common settings for connected_endpoints and/or network_ports.
# Keys are the same used under endpoints adapters. Keys defined under endpoints adapters take precedence.
port_profiles:
# Port profile name.
- profile: <str; required; unique>
# Parent profile is optional.
# Port_profiles can refer to another port_profile to inherit settings in up to two levels (adapter->profile->parent_profile).
parent_profile: <str>
# Set adapter speed in the format `<interface_speed>` or `forced <interface_speed>` or `auto <interface_speed>`.
# If not specified speed will be auto.
speed: <str>
# By default the description is built leveraging `<peer>_<peer_interface>`.
# When set this key will override the default value on the physical ports.
description: <str>
# Administrative state, setting to false will set the port to 'shutdown' in the intended configuration.
enabled: <bool; default=True>
# Interface mode.
mode: <str; "access" | "dot1q-tunnel" | "trunk" | "trunk phone">
mtu: <int; 68-65535>
# "l2_mtu" should only be defined for platforms supporting the "l2 mtu" CLI.
l2_mtu: <int; 68-65535>
# "l2_mru" should only be defined for platforms supporting the "l2 mru" CLI.
l2_mru: <int; 68-65535>
# Native VLAN for a trunk port.
# If both `native_vlan` and `native_vlan_tag`, `native_vlan_tag` takes precedence.
native_vlan: <int; 1-4094>
# If both `native_vlan` and `native_vlan_tag`, `native_vlan_tag` takes precedence.
native_vlan_tag: <bool; default=False>
# Phone VLAN for a mode `trunk phone` port.
# Requires `mode: trunk phone` to be set.
phone_vlan: <int; 1-4094>
# Specify if the phone traffic is tagged or untagged.
# If both data and phone traffic are untagged, MAC-Based VLAN Assignment (MBVA) is used, if supported by the model of switch.
phone_trunk_mode: <str; "tagged" | "untagged" | "tagged phone" | "untagged phone">
# Required with `enable_trunk_groups: true`.
# Trunk Groups are used for limiting VLANs on trunk ports to VLANs with the same Trunk Group.
trunk_groups:
- <str>
# Interface VLANs - if not set, the EOS default is that all VLANs are allowed for trunk ports, and VLAN 1 will be used for access ports.
vlans: <str>
spanning_tree_portfast: <str; "edge" | "network">
spanning_tree_bpdufilter: <str; "enabled" | "disabled" | "True" | "False" | "true" | "false">
spanning_tree_bpduguard: <str; "enabled" | "disabled" | "True" | "False" | "true" | "false">
flowcontrol:
received: <str; "received" | "send" | "on">
# QOS profile name.
qos_profile: <str>
# The global PTP profile parameters will be applied to all connected endpoints where `ptp` is manually enabled.
# `ptp role master` is set to ensure control over the PTP topology.
ptp:
enabled: <bool; default=False>
endpoint_role: <str; "bmca" | "default" | "follower"; default="follower">
profile: <str; "aes67" | "aes67-r16-2016" | "smpte2059-2"; default="aes67-r16-2016">
# Configures sFlow on the interface. Overrides `fabric_sflow.endpoints` setting.
sflow: <bool>
# Configures flow-tracking on the interface. Overrides `fabric_flow_tracking.endpoints` setting.
flow_tracking:
enabled: <bool>
# Flow tracker name as defined in flow_tracking_settings.
name: <str>
# Configure the downstream interfaces of a respective Link Tracking Group.
# If `port_channel` is defined in an adapter, then the port-channel interface is configured to be the downstream.
# Else all the ethernet interfaces will be configured as downstream -> to configure single-active EVPN multihomed networks.
link_tracking:
enabled: <bool>
# Tracking group name.
# The default group name is taken from fabric variable of the switch, `link_tracking.groups[0].name` with default value being "LT_GROUP1".
# Optional if default link_tracking settings are configured on the node.
name: <str>
# 802.1x
dot1x:
port_control: <str; "auto" | "force-authorized" | "force-unauthorized">
port_control_force_authorized_phone: <bool>
reauthentication: <bool>
pae:
mode: <str; "authenticator">
authentication_failure:
action: <str; "allow" | "drop">
allow_vlan: <int; 1-4094>
host_mode:
mode: <str; "multi-host" | "single-host">
multi_host_authenticated: <bool>
mac_based_authentication:
enabled: <bool>
always: <bool>
host_mode_common: <bool>
timeout:
idle_host: <int; 10-65535>
quiet_period: <int; 1-65535>
# Range 60-4294967295 or "server".
reauth_period: <str>
reauth_timeout_ignore: <bool>
tx_period: <int; 1-65535>
reauthorization_request_limit: <int; 1-10>
unauthorized:
access_vlan_membership_egress: <bool>
native_vlan_membership_egress: <bool>
# Power Over Ethernet settings applied on port. Only configured if platform supports PoE.
poe:
# Disable PoE on a POE capable port. PoE is enabled on all ports that support it by default in EOS.
disabled: <bool; default=False>
# Prioritize a port's power in the event that one of the switch's power supplies loses power.
priority: <str; "critical" | "high" | "medium" | "low">
# Set the PoE power behavior for a PoE port when the system is rebooted.
reboot:
# PoE action for interface.
action: <str; "maintain" | "power-off">
# Set the PoE power behavior for a PoE port when the port goes down.
link_down:
# PoE action for interface.
action: <str; "maintain" | "power-off">
# Number of seconds to delay shutting the power off after a link down event occurs. Default value is 5 seconds in EOS.
power_off_delay: <int; 1-86400>
# Set the PoE power behavior for a PoE port when the port is admin down.
shutdown:
# PoE action for interface.
action: <str; "maintain" | "power-off">
# Override the hardware-negotiated power limit using either wattage or a power class. Note that if using a power class, AVD will automatically convert the class value to the wattage value corresponding to that power class.
limit:
class: <int; 0-8>
watts: <str>
# Set to ignore hardware classification.
fixed: <bool>
# Disable to prevent port from negotiating power with powered devices over LLDP. Enabled by default in EOS.
negotiation_lldp: <bool>
# Allow a subset of legacy devices to work with the PoE switch. Disabled by default in EOS because it can cause false positive detections.
legacy_detect: <bool>
# Storm control settings applied on port toward the endpoint.
storm_control:
all:
# Configure maximum storm-control level.
level: <str>
# Optional variable and is hardware dependent.
unit: <str; "percent" | "pps"; default="percent">
broadcast:
# Configure maximum storm-control level.
level: <str>
# Optional variable and is hardware dependent.
unit: <str; "percent" | "pps"; default="percent">
multicast:
# Configure maximum storm-control level.
level: <str>
# Optional variable and is hardware dependent.
unit: <str; "percent" | "pps"; default="percent">
unknown_unicast:
# Configure maximum storm-control level.
level: <str>
# Optional variable and is hardware dependent.
unit: <str; "percent" | "pps"; default="percent">
# Used to define switchports as source or destination for monitoring sessions.
monitor_sessions:
# Session name.
- name: <str; required>
role: <str; "source" | "destination">
source_settings:
direction: <str; "rx" | "tx" | "both">
access_group:
type: <str; "ip" | "ipv6" | "mac">
# ACL name.
name: <str>
priority: <int>
# Session settings are defined per session name.
# Different session_settings for the same session name will be combined/merged.
session_settings:
encapsulation_gre_metadata_tx: <bool>
# Number of bytes to remove from header.
header_remove_size: <int>
access_group:
type: <str; "ip" | "ipv6" | "mac">
# ACL name.
name: <str>
# Ratelimit and unit as string.
# Examples:
# "100000 bps"
# "100 kbps"
# "10 mbps"
rate_limit_per_ingress_chip: <str>
# Ratelimit and unit as string.
# Examples:
# "100000 bps"
# "100 kbps"
# "10 mbps"
rate_limit_per_egress_chip: <str>
sample: <int>
truncate:
enabled: <bool>
# Size in bytes.
size: <int>
# Settings for all or single-active EVPN multihoming.
ethernet_segment:
# In format xxxx:xxxx:xxxx or "auto".
# Define a manual short-esi (be careful using this on profiles) or set the value to "auto" to automatically generate the value.
# Please see the notes under "EVPN A/A ESI dual and single-attached endpoint scenarios" before setting `short_esi: auto`.
short_esi: <str; required>
# If omitted, Port-Channels use the EOS default of all-active.
# If omitted, Ethernet interfaces are configured as single-active.
redundancy: <str; "all-active" | "single-active">
# Configure DF algorithm and preferences.
# - auto: Use preference-based algorithm and assign preference based on position of device in the 'switches' list,
# e.g., assuming a list of three switches, this would assign a preference of 200 to the first switch, 100 to the 2nd, and 0 to the third.
# - preference: Set preference for each switch manually using designated_forwarder_preferences key.
# - modulus: Use the default modulus-based algorithm.
# If omitted, Port-Channels use the EOS default of modulus.
# If omitted, Ethernet interfaces default to the 'auto' mechanism detailed above.
designated_forwarder_algorithm: <str; "auto" | "modulus" | "preference">
# Manual preference as described above, required only for preference algorithm.
designated_forwarder_preferences:
- <int>
# Disable preemption for single-active forwarding when auto/manual DF preference is configured.
dont_preempt: <bool>
# Used for port-channel adapter.
port_channel:
# Port-Channel Mode.
mode: <str; "active" | "passive" | "on">
# Port-Channel ID.
# If no channel_id is specified, an id is generated from the first switch port in the port channel.
channel_id: <int>
# By default the description is built leveraging `<peer>` name or `adapter.description` when defined.
# When this key is defined, it will append its content to the physical port description.
description: <str>
# Port-Channel administrative state.
# Setting to false will set port to 'shutdown' in intended configuration.
enabled: <bool; default=True>
# In format xxxx:xxxx:xxxx or "auto".
# This key is deprecated.
# Support will be removed in AVD version 5.0.0.
# Use <samp>ethernet_segment.short_esi</samp> instead.
short_esi: <str>
# LACP fallback configuration.
lacp_fallback:
# Either static or individual mode is supported.
# If the mode is set to "individual" the "individual.profile" setting must be defined.
mode: <str; "static" | "individual">
# Define parameters for port-channel member interfaces. Applies only if LACP fallback is set to "individual".
individual:
# Port-profile name to inherit configuration.
profile: <str>
# Timeout in seconds. EOS default is 90 seconds.
timeout: <int>
# LACP timer configuration. Applies only when Port-channel mode is not "on".
lacp_timer:
# LACP mode for interface members.
mode: <str; "normal" | "fast">
# Number of LACP BPDUs lost before deeming the peer down. EOS default is 3.
multiplier: <int>
# Port-Channel L2 Subinterfaces
# Subinterfaces are only supported on routed port-channels, which means they cannot be configured on MLAG port-channels.
# Setting short_esi: auto generates the short_esi automatically using a hash of configuration elements.
# Please see the notes under "EVPN A/A ESI dual-attached endpoint scenario" before setting short_esi: auto.
subinterfaces:
# Subinterface number.
- number: <int>
# In format xxxx:xxxx:xxxx or "auto".
# Required for multihomed port-channels with subinterfaces.
short_esi: <str>
# VLAN ID to bridge.
# Default is subinterface number.
vlan_id: <int; 1-4094>
# Client VLAN ID encapsulation.
# Default is subinterface number.
encapsulation_vlan:
client_dot1q: <int; 1-4094>
# EOS CLI rendered directly on the port-channel interface in the final EOS configuration.
raw_eos_cli: <str>
# Custom structured config added under port_channel_interfaces.[name=<interface>] for eos_cli_config_gen.
structured_config: <dict>
# Set to false to disable interface validation by the `eos_validate_state` role.
validate_state: <bool>
# EOS CLI rendered directly on the ethernet interface in the final EOS configuration.
raw_eos_cli: <str>
# Custom structured config added under ethernet_interfaces.[name=<interface>] for eos_cli_config_gen.
structured_config: <dict>
Connected endpoints keys settings¶
The keys used to define Connected Endpoints are configurable using connected_endpoints_keys.
Endpoints connecting to the fabric can be grouped by using separate keys. The keys can be customized to provide a better better organization or grouping of your data.
connected_endpoints_keys should be defined in the top level group_vars for the fabric.
Note
The default values will be overridden if defining this key, so it is recommended to copy the defaults and modify them.
| Variable | Type | Required | Default | Value Restrictions | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| connected_endpoints_keys | List, items: Dictionary | See (+) on YAML tab | Endpoints connecting to the fabric can be grouped by using separate keys. The keys can be customized to provide a better better organization or grouping of your data. connected_endpoints_keys should be defined in the top level group_vars for the fabric.The default values will be overridden if defining this key, so it is recommended to copy the defaults and modify them. |
||
| - key | String | Required, Unique | |||
| type | String | Type used for documentation. | |||
| description | String | Description used for documentation. |
# Endpoints connecting to the fabric can be grouped by using separate keys.
# The keys can be customized to provide a better better organization or grouping of your data.
# `connected_endpoints_keys` should be defined in the top level group_vars for the fabric.
# The default values will be overridden if defining this key, so it is recommended to copy the defaults and modify them.
connected_endpoints_keys: # (1)!
- key: <str; required; unique>
# Type used for documentation.
type: <str>
# Description used for documentation.
description: <str>
-
Default Value
connected_endpoints_keys: - description: Server. key: servers type: server - description: Firewall. key: firewalls type: firewall - description: Router. key: routers type: router - description: Load Balancer. key: load_balancers type: load_balancer - description: Storage Array. key: storage_arrays type: storage_array - description: CPE. key: cpes type: cpe - description: Workstation. key: workstations type: workstation - description: Access Point. key: access_points type: access_point - description: Phone. key: phones type: phone - description: Printer. key: printers type: printer - description: Camera. key: cameras type: camera - description: Generic Device. key: generic_devices type: generic_device
Network Services¶
The network services variables provide an abstracted model to define network services across the fabric. The network services are grouped by tenants. The definition of a tenant may vary between organizations. E.g. tenants can be organizations or departments.
The filtering models defined under Node type network services configuration allows for granular deployment of network services to the fabric leveraging the tenant name and tags applied to the service definition.
- This allows for the reuse of SVI/VLAN IDs across the fabric.
- An error will be returned at runtime in case of duplicate or conflicting SVI/VLAN IDs or VNIs targeted towards the same device.
Network services settings¶
The supported network services for each tenant cover:
- VRFs
- SVIs
- L3 Interfaces
- Loopbacks
- BGP routing
- OSPF routing
- L2 VLANs
- Point-to-point services (Pseudowires, only for MPLS designs)
- Multicast
Typically services within each tenant share common VNI ranges and MAC VRF assignment pattern.
The keys used to define network services are configurable using network_services_keys.
The default available keys is tenants.
| Variable | Type | Required | Default | Value Restrictions | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| <network_services_keys.name> | List, items: Dictionary | ||||
| - name | String | Required, Unique | Specify a tenant name. Tenant provide a construct to group L3 VRFs and L2 VLANs. Networks services can be filtered by tenant name. |
||
| mac_vrf_vni_base | Integer | Min: 0 Max: 16770000 |
Base number for MAC VRF VXLAN Network Identifier (required with VXLAN). VXLAN VNI is derived from the base number with simple addition. i.e. mac_vrf_vni_base = 10000, svi 100 = VNI 10100, svi 300 = VNI 10300. |
||
| mac_vrf_id_base | Integer | Min: 0 Max: 16770000 |
If not set, “mac_vrf_vni_base” will be used. Base number for MAC VRF RD/RT ID (Required unless mac_vrf_vni_base is set) ID is derived from the base number with simple addition. i.e. mac_vrf_id_base = 10000, svi 100 = RD/RT 10100, svi 300 = RD/RT 10300. |
||
| vlan_aware_bundle_number_base | Integer | 0 |
Base number for VLAN aware bundle RD/RT. The “Assigned Number” part of RD/RT is derived from vrf_vni + vlan_aware_bundle_number_base. |
||
| evpn_l2_multi_domain | Boolean | True |
Explicitly extend all VLANs/VLAN-Aware Bundles inside the tenant to remote EVPN domains. |
<network_services_keys.name>:
# Specify a tenant name.
# Tenant provide a construct to group L3 VRFs and L2 VLANs.
# Networks services can be filtered by tenant name.
- name: <str; required; unique>
# Base number for MAC VRF VXLAN Network Identifier (required with VXLAN).
# VXLAN VNI is derived from the base number with simple addition.
# i.e. mac_vrf_vni_base = 10000, svi 100 = VNI 10100, svi 300 = VNI 10300.
mac_vrf_vni_base: <int; 0-16770000>
# If not set, "mac_vrf_vni_base" will be used.
# Base number for MAC VRF RD/RT ID (Required unless mac_vrf_vni_base is set)
# ID is derived from the base number with simple addition.
# i.e. mac_vrf_id_base = 10000, svi 100 = RD/RT 10100, svi 300 = RD/RT 10300.
mac_vrf_id_base: <int; 0-16770000>
# Base number for VLAN aware bundle RD/RT.
# The "Assigned Number" part of RD/RT is derived from vrf_vni + vlan_aware_bundle_number_base.
vlan_aware_bundle_number_base: <int; default=0>
# Explicitly extend all VLANs/VLAN-Aware Bundles inside the tenant to remote EVPN domains.
evpn_l2_multi_domain: <bool; default=True>
| Variable | Type | Required | Default | Value Restrictions | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| new_network_services_bgp_vrf_config | Boolean | Set this key to true in the node type to generate full BGP configurationfor network services even when evpn is not in the address families( evpn is the default address family for l3ls-evpn but not for l2ls).This is false by default except if uplink_type is set to p2p-vrfs, then the default value is true.This may introduce breaking changes to your configuration. |
# Set this key to `true` in the node type to generate full BGP configuration
# for network services even when `evpn` is not in the address families
# (`evpn` is the default address family for `l3ls-evpn` but not for `l2ls`).
#
# This is `false` by default except if `uplink_type` is set to `p2p-vrfs`, then the default value is `true`.
#
# This may introduce breaking changes to your configuration.
new_network_services_bgp_vrf_config: <bool>
Network services VRFs configuration¶
| Variable | Type | Required | Default | Value Restrictions | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| <network_services_keys.name> | List, items: Dictionary | ||||
| - name | String | Required, Unique | Specify a tenant name. Tenant provide a construct to group L3 VRFs and L2 VLANs. Networks services can be filtered by tenant name. |
||
| enable_mlag_ibgp_peering_vrfs | Boolean | MLAG iBGP peering per VRF. By default an iBGP peering is configured per VRF between MLAG peers on separate VLANs. Setting enable_mlag_ibgp_peering_vrfs false under a tenant will change this default to prevent configuration of these peerings and VLANs for all VRFs in the tenant.This setting can be overridden per VRF. |
|||
| redistribute_mlag_ibgp_peering_vrfs | Boolean | True |
Redistribute the connected subnet for the MLAG iBGP peering per VRF into overlay BGP. By default the iBGP peering subnet is redistributed into the overlay routing protocol per VRF. Setting redistribute_mlag_ibgp_peering_vrfs: false under a tenant will change this default to prevent redistribution of these subnets for all VRFs in the tenant.This setting can be overridden per VRF. |
||
| vrfs | List, items: Dictionary | VRFs will only be configured on a node if any of the underlying objects like svis or l3_interfaces apply to the node.It is recommended to only define a VRF in one Tenant. If the same VRF name is used across multiple tenants and those tenants are accepted by filter.tenants on the node, any object set under the duplicate VRFs must either be unique or be an exact match.VRF “default” is partially supported under network-services. Currently the supported options for “default” vrf are route-target, route-distinguisher settings, structured_config, raw_eos_cli in bgp and SVIs are the only supported interface type. Vlan-aware-bundles are supported as well inside default vrf. OSPF is not supported currently. |
|||
| - name | String | Required, Unique | |||
| address_families | List, items: String | ||||
| - <str> | String | Valid Values: - evpn- vpn-ipv4- vpn-ipv6 |
|||
| description | String | VRF description. | |||
| vrf_vni | Integer | Min: 1 Max: 16777215 |
Required if “vrf_id” is not set. The VRF VNI range is not limited, but if vrf_id is not set, “vrf_vni” is used for calculating MLAG iBGP peering vlan id. “vrf_vni” may also be used for VRF RD/RT ID. See “overlay_rd_type” and “overlay_rt_type” for details. See “mlag_ibgp_peering_vrfs.base_vlan” for details. If vrf_vni > 10000 make sure to adjust “mac_vrf_vni_base” accordingly to avoid overlap. |
||
| vrf_id | Integer | Required if “vrf_vni” is not set. “vrf_id” is used as default value for “vrf_vni” and “ospf.process_id” unless those are set. “vrf_id” may also be used for VRF RD/RT ID. See “overlay_rd_type” and “overlay_rt_type” for details. “vrf_id” is preferred over “vrf_vni” for MLAG iBGP peering vlan, see “mlag_ibgp_peering_vrfs.base_vlan” for details. |
|||
| rd_override | String | By default, the VRF RD will be derived from the pattern defined in overlay_rd_type.The rd_override allows us to override this value and statically define it. rd_override supports two formats: - A single number will be used in the RD assigned number subfield (second part of the RD). - A full RD string with colon separator which will override the full RD. |
|||
| rt_override | String | By default, the VRF RT will be derived from the pattern defined in overlay_rt_type.The rt_override allows us to override this value and statically define it. rt_override supports two formats: - A single number will be used in the RT assigned number subfield (second part of the RT). - A full RT string with colon separator which will override the full RT. |
|||
| mlag_ibgp_peering_ipv4_pool | String | IPv4_address/Mask The subnet used for iBGP peering in the VRF. Each MLAG pair will be assigned a subnet based on the ID of the primary MLAG switch. If not set, “mlag_peer_l3_ipv4_pool” or “mlag_peer_ipv4_pool” will be used. |
|||
| ip_helpers | List, items: Dictionary | IP helper for DHCP relay. | |||
| - ip_helper | String | Required, Unique | IPv4 DHCP server IP. | ||
| source_interface | String | Interface name. | |||
| source_vrf | String | VRF to originate DHCP relay packets to DHCP server. If not set, uses current VRF. | |||
| enable_mlag_ibgp_peering_vrfs | Boolean | MLAG iBGP peering per VRF. By default an iBGP peering is configured per VRF between MLAG peers on separate VLANs. Setting enable_mlag_ibgp_peering_vrfs: false under a VRF will change this default and/or override the tenant-wide setting. |
|||
| redistribute_mlag_ibgp_peering_vrfs | Boolean | True |
Redistribute the connected subnet for the MLAG iBGP peering per VRF into overlay BGP. By default the iBGP peering subnet is redistributed into the overlay routing protocol per VRF. Setting redistribute_mlag_ibgp_peering_vrfs: false under a VRF will change this default and/or override the tenant-wide setting. |
||
| mlag_ibgp_peering_vlan | Integer | Min: 1 Max: 4096 |
Manually define the VLAN used on the MLAG pair for the iBGP session. By default this parameter is calculated using the following formula: <mlag_ibgp_peering_vrfs.base_vlan> + <vrf_id> - 1. |
||
| vtep_diagnostic | Dictionary | Enable VTEP Network diagnostics. This will create a loopback with virtual source-nat enable to perform diagnostics from the switch. |
|||
| loopback | Integer | Min: 2 Max: 2100 |
Loopback interface number, required when vtep_diagnotics defined. |
||
| loopback_description | String | Provide a custom description for loopback interface. | |||
| loopback_ip_range | String | IPv4_address/Mask. Loopback ip range, a unique ip is derived from this ranged and assignedto each l3 leaf based on it’s unique id. Loopback is not created unless loopback_ip_range or loopback_ip_pools are set. |
|||
| loopback_ip_pools | List, items: Dictionary | For inventories with multiple PODs a loopback range can be set per POD to avoid overlaps. This only takes effect when loopback_ip_range is not defined, ptional (loopback is not created unless loopback_ip_range or loopback_ip_pools are set). |
|||
| - pod | String | POD name. | |||
| ipv4_pool | String | IPv4_address/Mask. | |||
| static_routes | List, items: Dictionary | List of static routes for v4 and/or v6. This will create static routes inside the tenant VRF. If nodes are not specified, all l3leafs that carry the VRF will also be applied the static routes. If a node has a static route in the VRF, redistribute static will be automatically enabled in that VRF. This automatic behavior can be overridden non-selectively with the redistribute_static knob for the VRF. |
|||
| - destination_address_prefix | String | IPv4_address. | |||
| gateway | String | IPv4_address. | |||
| track_bfd | Boolean | Track next-hop using BFD. | |||
| distance | Integer | Min: 1 Max: 255 |
|||
| tag | Integer | Min: 0 Max: 4294967295 |
|||
| name | String | description. | |||
| metric | Integer | Min: 0 Max: 4294967295 |
|||
| interface | String | ||||
| nodes | List, items: String | ||||
| - <str> | String | ||||
| ipv6_static_routes | List, items: Dictionary | ||||
| - destination_address_prefix | String | IPv6_address. | |||
| gateway | String | ||||
| track_bfd | Boolean | Track next-hop using BFD. | |||
| distance | Integer | Min: 1 Max: 255 |
|||
| tag | Integer | Min: 0 Max: 4294967295 |
|||
| name | String | description. | |||
| metric | Integer | Min: 0 Max: 4294967295 |
|||
| interface | String | ||||
| nodes | List, items: String | ||||
| - <str> | String | ||||
| redistribute_static | Boolean | Non-selectively enabling or disabling redistribute static inside the VRF. | |||
| bgp | Dictionary | ||||
| raw_eos_cli | String | EOS CLI rendered directly on the Router BGP, VRF definition in the final EOS configuration. |
|||
| structured_config | Dictionary | Custom structured config added under router_bgp.vrfs.[name= |
|||
| additional_route_targets | List, items: Dictionary | Configuration of extra route-targets for this VRF. Useful for route-leaking or gateway between address families. | |||
| - type | String | Valid Values: - import- export |
|||
| address_family | String | ||||
| route_target | String | ||||
| nodes | List, items: String | Nodes is required to restrict configuration of BGP neighbors to certain nodes in the network. | |||
| - <str> | String | ||||
| raw_eos_cli | String | EOS CLI rendered directly on the root level of the final EOS configuration. | |||
| structured_config | Dictionary | Custom structured config for eos_cli_config_gen. |
<network_services_keys.name>:
# Specify a tenant name.
# Tenant provide a construct to group L3 VRFs and L2 VLANs.
# Networks services can be filtered by tenant name.
- name: <str; required; unique>
# MLAG iBGP peering per VRF.
# By default an iBGP peering is configured per VRF between MLAG peers on separate VLANs.
# Setting `enable_mlag_ibgp_peering_vrfs` false under a tenant will change this default to prevent configuration of these peerings and VLANs for all VRFs in the tenant.
# This setting can be overridden per VRF.
enable_mlag_ibgp_peering_vrfs: <bool>
# Redistribute the connected subnet for the MLAG iBGP peering per VRF into overlay BGP.
# By default the iBGP peering subnet is redistributed into the overlay routing protocol per VRF.
# Setting `redistribute_mlag_ibgp_peering_vrfs: false` under a tenant will change this default to prevent redistribution of these subnets for all VRFs in the tenant.
# This setting can be overridden per VRF.
redistribute_mlag_ibgp_peering_vrfs: <bool; default=True>
# VRFs will only be configured on a node if any of the underlying objects like `svis` or `l3_interfaces` apply to the node.
#
# It is recommended to only define a VRF in one Tenant. If the same VRF name is used across multiple tenants and those tenants
# are accepted by `filter.tenants` on the node, any object set under the duplicate VRFs must either be unique or be an exact match.
#
# VRF "default" is partially supported under network-services. Currently the supported options for "default" vrf are route-target,
# route-distinguisher settings, structured_config, raw_eos_cli in bgp and SVIs are the only supported interface type.
# Vlan-aware-bundles are supported as well inside default vrf. OSPF is not supported currently.
vrfs:
- name: <str; required; unique>
address_families:
- <str; "evpn" | "vpn-ipv4" | "vpn-ipv6">
# VRF description.
description: <str>
# Required if "vrf_id" is not set.
# The VRF VNI range is not limited, but if vrf_id is not set, "vrf_vni" is used for calculating MLAG iBGP peering vlan id.
# "vrf_vni" may also be used for VRF RD/RT ID. See "overlay_rd_type" and "overlay_rt_type" for details.
# See "mlag_ibgp_peering_vrfs.base_vlan" for details.
# If vrf_vni > 10000 make sure to adjust "mac_vrf_vni_base" accordingly to avoid overlap.
vrf_vni: <int; 1-16777215>
# Required if "vrf_vni" is not set.
# "vrf_id" is used as default value for "vrf_vni" and "ospf.process_id" unless those are set.
# "vrf_id" may also be used for VRF RD/RT ID. See "overlay_rd_type" and "overlay_rt_type" for details.
# "vrf_id" is preferred over "vrf_vni" for MLAG iBGP peering vlan, see "mlag_ibgp_peering_vrfs.base_vlan" for details.
vrf_id: <int>
# By default, the VRF RD will be derived from the pattern defined in `overlay_rd_type`.
# The rd_override allows us to override this value and statically define it.
#
# rd_override supports two formats:
# - A single number will be used in the RD assigned number subfield (second part of the RD).
# - A full RD string with colon separator which will override the full RD.
rd_override: <str>
# By default, the VRF RT will be derived from the pattern defined in `overlay_rt_type`.
# The rt_override allows us to override this value and statically define it.
#
# rt_override supports two formats:
# - A single number will be used in the RT assigned number subfield (second part of the RT).
# - A full RT string with colon separator which will override the full RT.
rt_override: <str>
# IPv4_address/Mask
# The subnet used for iBGP peering in the VRF.
# Each MLAG pair will be assigned a subnet based on the ID of the primary MLAG switch.
# If not set, "mlag_peer_l3_ipv4_pool" or "mlag_peer_ipv4_pool" will be used.
mlag_ibgp_peering_ipv4_pool: <str>
# IP helper for DHCP relay.
ip_helpers:
# IPv4 DHCP server IP.
- ip_helper: <str; required; unique>
# Interface name.
source_interface: <str>
# VRF to originate DHCP relay packets to DHCP server. If not set, uses current VRF.
source_vrf: <str>
# MLAG iBGP peering per VRF.
# By default an iBGP peering is configured per VRF between MLAG peers on separate VLANs.
# Setting `enable_mlag_ibgp_peering_vrfs: false` under a VRF will change this default and/or override the tenant-wide setting.
enable_mlag_ibgp_peering_vrfs: <bool>
# Redistribute the connected subnet for the MLAG iBGP peering per VRF into overlay BGP.
# By default the iBGP peering subnet is redistributed into the overlay routing protocol per VRF.
# Setting `redistribute_mlag_ibgp_peering_vrfs: false` under a VRF will change this default and/or override the tenant-wide setting.
redistribute_mlag_ibgp_peering_vrfs: <bool; default=True>
# Manually define the VLAN used on the MLAG pair for the iBGP session.
# By default this parameter is calculated using the following formula: `<mlag_ibgp_peering_vrfs.base_vlan>` + `<vrf_id>` - 1.
mlag_ibgp_peering_vlan: <int; 1-4096>
# Enable VTEP Network diagnostics.
# This will create a loopback with virtual source-nat enable to perform diagnostics from the switch.
vtep_diagnostic:
# Loopback interface number, required when vtep_diagnotics defined.
loopback: <int; 2-2100>
# Provide a custom description for loopback interface.
loopback_description: <str>
# IPv4_address/Mask.
# Loopback ip range, a unique ip is derived from this ranged and assignedto each l3 leaf based on it's unique id.
# Loopback is not created unless loopback_ip_range or loopback_ip_pools are set.
loopback_ip_range: <str>
# For inventories with multiple PODs a loopback range can be set per POD to avoid overlaps.
# This only takes effect when loopback_ip_range is not defined, ptional (loopback is not created unless loopback_ip_range or loopback_ip_pools are set).
loopback_ip_pools:
# POD name.
- pod: <str>
# IPv4_address/Mask.
ipv4_pool: <str>
# List of static routes for v4 and/or v6.
# This will create static routes inside the tenant VRF.
# If nodes are not specified, all l3leafs that carry the VRF will also be applied the static routes.
# If a node has a static route in the VRF, redistribute static will be automatically enabled in that VRF.
# This automatic behavior can be overridden non-selectively with the redistribute_static knob for the VRF.
static_routes:
# IPv4_address.
- destination_address_prefix: <str>
# IPv4_address.
gateway: <str>
# Track next-hop using BFD.
track_bfd: <bool>
distance: <int; 1-255>
tag: <int; 0-4294967295>
# description.
name: <str>
metric: <int; 0-4294967295>
interface: <str>
nodes:
- <str>
ipv6_static_routes:
# IPv6_address.
- destination_address_prefix: <str>
gateway: <str>
# Track next-hop using BFD.
track_bfd: <bool>
distance: <int; 1-255>
tag: <int; 0-4294967295>
# description.
name: <str>
metric: <int; 0-4294967295>
interface: <str>
nodes:
- <str>
# Non-selectively enabling or disabling redistribute static inside the VRF.
redistribute_static: <bool>
bgp:
# EOS CLI rendered directly on the Router BGP, VRF definition in the final EOS configuration.
raw_eos_cli: <str>
# Custom structured config added under router_bgp.vrfs.[name=<vrf>] for eos_cli_config_gen.
structured_config: <dict>
# Configuration of extra route-targets for this VRF. Useful for route-leaking or gateway between address families.
additional_route_targets:
- type: <str; "import" | "export">
address_family: <str>
route_target: <str>
# Nodes is required to restrict configuration of BGP neighbors to certain nodes in the network.
nodes:
- <str>
# EOS CLI rendered directly on the root level of the final EOS configuration.
raw_eos_cli: <str>
# Custom structured config for eos_cli_config_gen.
structured_config: <dict>
Network services VRF SVIs configuration¶
| Variable | Type | Required | Default | Value Restrictions | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| <network_services_keys.name> | List, items: Dictionary | ||||
| - name | String | Required, Unique | Specify a tenant name. Tenant provide a construct to group L3 VRFs and L2 VLANs. Networks services can be filtered by tenant name. |
||
| vrfs | List, items: Dictionary | VRFs will only be configured on a node if any of the underlying objects like svis or l3_interfaces apply to the node.It is recommended to only define a VRF in one Tenant. If the same VRF name is used across multiple tenants and those tenants are accepted by filter.tenants on the node, any object set under the duplicate VRFs must either be unique or be an exact match.VRF “default” is partially supported under network-services. Currently the supported options for “default” vrf are route-target, route-distinguisher settings, structured_config, raw_eos_cli in bgp and SVIs are the only supported interface type. Vlan-aware-bundles are supported as well inside default vrf. OSPF is not supported currently. |
|||
| - name | String | Required, Unique | |||
| svis | List, items: Dictionary | List of SVIs. This will create both the L3 SVI and L2 VLAN based on filters applied to the node. |
|||
| - id | Integer | Required | Min: 1 Max: 4096 |
SVI interface id and VLAN id. | |
| name | String | Required | VLAN name. | ||
| profile | String | SVI profile name to apply. SVI can refer to one svi_profile which again can refer to another svi_profile to inherit settings in up to two levels (svi -> svi_profile -> svi_parent_profile). |
|||
| tags | List, items: String | ['all'] |
Tags leveraged for networks services filtering. Tags are matched against “filter.tags” defined under node type settings. Tags are also matched against the “node_group” name under node type settings. |
||
| - <str> | String | Tag value. | |||
| evpn_vlan_bundle | String | Name of a bundle defined under ‘evpn_vlan_bundles’ to inherit configuration. The common option “evpn_vlan_aware_bundles” is disregarded for this option. |
|||
| nodes | List, items: Dictionary | Define node specific configuration, such as unique IP addresses. Any keys set here will be merged onto the SVI config, except structured_config keys which will replace the structured_config set on SVI level. |
|||
| - node | String | Required, Unique | l3_leaf inventory hostname. | ||
| tags | List, items: String | ['all'] |
Tags leveraged for networks services filtering. Tags are matched against “filter.tags” defined under node type settings. Tags are also matched against the “node_group” name under node type settings. |
||
| - <str> | String | Tag value. | |||
| name | String | VLAN name. | |||
| enabled | Boolean | Enable or disable interface. | |||
| description | String | SVI description. By default set to VLAN name. |
|||
| ip_address | String | IPv4_address/Mask. Usually set under “nodes” to have unique IPv4 addresses per node. | |||
| ipv6_address | String | IPv6_address/Mask. Usually set under “nodes” to have unique IPv6 addresses per node. | |||
| ipv6_enable | Boolean | Explicitly enable/disable link-local IPv6 addressing. | |||
| ip_address_virtual | String | IPv4_address/Mask. IPv4 VXLAN Anycast IP address. Conserves IP addresses in VXLAN deployments as it doesn’t require unique IP addresses on each node. |
|||
| ipv6_address_virtual deprecated | String | IPv6_address/Mask. ipv6 address virtuals to configure VXLAN Anycast IP address (Optional). If both “ipv6_address_virtual” and “ipv6_address_virtuals” are set, all addresses will be configured. This key is deprecated. Support will be removed in AVD version 5.0.0. Use ipv6_address_virtuals instead. |
|||
| ipv6_address_virtuals | List, items: String | IPv6 VXLAN Anycast IP addresses. Conserves IPv6 addresses in VXLAN deployments as it doesn’t require unique IPv6 addresses on each node. |
|||
| - <str> | String | IPv6_address/Mask. | |||
| ip_address_virtual_secondaries | List, items: String | Secondary IPv4 VXLAN Anycast IP addresses. | |||
| - <str> | String | IPv4_address/Mask. | |||
| ip_virtual_router_addresses | List, items: String | IPv4 VARP addresses. Requires an IP address to be configured on the SVI. If ip_address_virtual is also set, ip_virtual_router_addresses will take precedence if there is an ip_address configured for the node. |
|||
| - <str> | String | IPv4_address/Mask or IPv4_address. IPv4_address/Mask will also configure a static route to the SVI per best practice. |
|||
| ipv6_virtual_router_addresses | List, items: String | IPv6 VARP addresses. Requires an IPv6 address to be configured on the SVI. If ipv6_address_virtuals is also set, ipv6_virtual_router_addresses will take precedence if there is an ipv6_address configured for the node. |
|||
| - <str> | String | IPv6_address. | |||
| ip_helpers | List, items: Dictionary | IP helper for DHCP relay. | |||
| - ip_helper | String | Required, Unique | IPv4 DHCP server IP. | ||
| source_interface | String | Interface name to originate DHCP relay packets to DHCP server. | |||
| source_vrf | String | VRF to originate DHCP relay packets to DHCP server. If not set, EOS uses the VRF on the SVI. | |||
| vni_override | Integer | Min: 1 Max: 16777215 |
By default the VNI will be derived from “mac_vrf_vni_base”. The vni_override allows us to override this value and statically define it (optional). |
||
| rt_override | String | By default the MAC VRF RT will be derived from mac_vrf_id_base + vlan_id. The rt_override allows us to override this value and statically define it. rt_override will default to vni_override if set. rt_override supports two formats: - A single number which will be used in the RT fields instead of mac_vrf_id/mac_vrf_vni (see ‘overlay_rt_type’ for details). - A full RT string with colon separator which will override the full RT. |
|||
| rd_override | String | By default the MAC VRF RD will be derived from mac_vrf_id_base + vlan_id. The rt_override allows us to override this value and statically define it. rd_override will default to rt_override or vni_override if set. rd_override supports two formats: - A single number which will be used in the RD assigned number field instead of mac_vrf_id/mac_vrf_vni (see ‘overlay_rd_type’ for details). - A full RD string with colon separator which will override the full RD. |
|||
| trunk_groups | List, items: String | ||||
| - <str> | String | Trunk groups are used for limiting vlans to trunk ports assigned to the same trunk group. Requires “enable_trunk_groups: true”. |
|||
| vxlan | Boolean | True |
Extend this SVI over VXLAN. | ||
| spanning_tree_priority | Integer | Setting spanning-tree priority per VLAN is only supported with spanning_tree_mode: rapid-pvst under node type settings.The default priority for rapid-PVST is set under the node type settings with spanning_tree_priority (default=32768). |
|||
| mtu | Integer | Interface MTU. | |||
| bgp | Dictionary | ||||
| structured_config | Dictionary | Structured configuration and EOS CLI commands rendered on router_bgp.vlans.[id= This configuration will not be applied to vlan aware bundles. |
|||
| raw_eos_cli | String | EOS CLI rendered directly on the Router BGP, VLAN definition in the final EOS configuration. |
|||
| raw_eos_cli | String | EOS CLI rendered directly on the VLAN interface in the final EOS configuration. |
|||
| structured_config | Dictionary | Custom structured config added under vlan_interfaces.[name= |
|||
| enabled | Boolean | Enable or disable interface. | |||
| description | String | SVI description. By default set to VLAN name. |
|||
| ip_address | String | IPv4_address/Mask. Usually set under “nodes” to have unique IPv4 addresses per node. | |||
| ipv6_address | String | IPv6_address/Mask. Usually set under “nodes” to have unique IPv6 addresses per node. | |||
| ipv6_enable | Boolean | Explicitly enable/disable link-local IPv6 addressing. | |||
| ip_address_virtual | String | IPv4_address/Mask. IPv4 VXLAN Anycast IP address. Conserves IP addresses in VXLAN deployments as it doesn’t require unique IP addresses on each node. |
|||
| ipv6_address_virtual deprecated | String | IPv6_address/Mask. ipv6 address virtuals to configure VXLAN Anycast IP address (Optional). If both “ipv6_address_virtual” and “ipv6_address_virtuals” are set, all addresses will be configured. This key is deprecated. Support will be removed in AVD version 5.0.0. Use ipv6_address_virtuals instead. |
|||
| ipv6_address_virtuals | List, items: String | IPv6 VXLAN Anycast IP addresses. Conserves IPv6 addresses in VXLAN deployments as it doesn’t require unique IPv6 addresses on each node. |
|||
| - <str> | String | IPv6_address/Mask. | |||
| ip_address_virtual_secondaries | List, items: String | Secondary IPv4 VXLAN Anycast IP addresses. | |||
| - <str> | String | IPv4_address/Mask. | |||
| ip_virtual_router_addresses | List, items: String | IPv4 VARP addresses. Requires an IP address to be configured on the SVI. If ip_address_virtual is also set, ip_virtual_router_addresses will take precedence if there is an ip_address configured for the node. |
|||
| - <str> | String | IPv4_address/Mask or IPv4_address. IPv4_address/Mask will also configure a static route to the SVI per best practice. |
|||
| ipv6_virtual_router_addresses | List, items: String | IPv6 VARP addresses. Requires an IPv6 address to be configured on the SVI. If ipv6_address_virtuals is also set, ipv6_virtual_router_addresses will take precedence if there is an ipv6_address configured for the node. |
|||
| - <str> | String | IPv6_address. | |||
| ip_helpers | List, items: Dictionary | IP helper for DHCP relay. | |||
| - ip_helper | String | Required, Unique | IPv4 DHCP server IP. | ||
| source_interface | String | Interface name to originate DHCP relay packets to DHCP server. | |||
| source_vrf | String | VRF to originate DHCP relay packets to DHCP server. If not set, EOS uses the VRF on the SVI. | |||
| vni_override | Integer | Min: 1 Max: 16777215 |
By default the VNI will be derived from “mac_vrf_vni_base”. The vni_override allows us to override this value and statically define it (optional). |
||
| rt_override | String | By default the MAC VRF RT will be derived from mac_vrf_id_base + vlan_id. The rt_override allows us to override this value and statically define it. rt_override will default to vni_override if set. rt_override supports two formats: - A single number which will be used in the RT fields instead of mac_vrf_id/mac_vrf_vni (see ‘overlay_rt_type’ for details). - A full RT string with colon separator which will override the full RT. |
|||
| rd_override | String | By default the MAC VRF RD will be derived from mac_vrf_id_base + vlan_id. The rt_override allows us to override this value and statically define it. rd_override will default to rt_override or vni_override if set. rd_override supports two formats: - A single number which will be used in the RD assigned number field instead of mac_vrf_id/mac_vrf_vni (see ‘overlay_rd_type’ for details). - A full RD string with colon separator which will override the full RD. |
|||
| trunk_groups | List, items: String | ||||
| - <str> | String | Trunk groups are used for limiting vlans to trunk ports assigned to the same trunk group. Requires “enable_trunk_groups: true”. |
|||
| vxlan | Boolean | True |
Extend this SVI over VXLAN. | ||
| spanning_tree_priority | Integer | Setting spanning-tree priority per VLAN is only supported with spanning_tree_mode: rapid-pvst under node type settings.The default priority for rapid-PVST is set under the node type settings with spanning_tree_priority (default=32768). |
|||
| mtu | Integer | Interface MTU. | |||
| bgp | Dictionary | ||||
| structured_config | Dictionary | Structured configuration and EOS CLI commands rendered on router_bgp.vlans.[id= This configuration will not be applied to vlan aware bundles. |
|||
| raw_eos_cli | String | EOS CLI rendered directly on the Router BGP, VLAN definition in the final EOS configuration. |
|||
| raw_eos_cli | String | EOS CLI rendered directly on the VLAN interface in the final EOS configuration. |
|||
| structured_config | Dictionary | Custom structured config added under vlan_interfaces.[name= |
<network_services_keys.name>:
# Specify a tenant name.
# Tenant provide a construct to group L3 VRFs and L2 VLANs.
# Networks services can be filtered by tenant name.
- name: <str; required; unique>
# VRFs will only be configured on a node if any of the underlying objects like `svis` or `l3_interfaces` apply to the node.
#
# It is recommended to only define a VRF in one Tenant. If the same VRF name is used across multiple tenants and those tenants
# are accepted by `filter.tenants` on the node, any object set under the duplicate VRFs must either be unique or be an exact match.
#
# VRF "default" is partially supported under network-services. Currently the supported options for "default" vrf are route-target,
# route-distinguisher settings, structured_config, raw_eos_cli in bgp and SVIs are the only supported interface type.
# Vlan-aware-bundles are supported as well inside default vrf. OSPF is not supported currently.
vrfs:
- name: <str; required; unique>
# List of SVIs.
# This will create both the L3 SVI and L2 VLAN based on filters applied to the node.
svis:
# SVI interface id and VLAN id.
- id: <int; 1-4096; required; unique>
# VLAN name.
name: <str; required>
# SVI profile name to apply.
# SVI can refer to one svi_profile which again can refer to another svi_profile to inherit settings in up to two levels (svi -> svi_profile -> svi_parent_profile).
profile: <str>
# Tags leveraged for networks services filtering.
# Tags are matched against "filter.tags" defined under node type settings.
# Tags are also matched against the "node_group" name under node type settings.
tags: # default=['all']
# Tag value.
- <str>
# Name of a bundle defined under 'evpn_vlan_bundles' to inherit configuration.
# The common option "evpn_vlan_aware_bundles" is disregarded for this option.
evpn_vlan_bundle: <str>
# Define node specific configuration, such as unique IP addresses.
# Any keys set here will be merged onto the SVI config, except `structured_config` keys which will replace the `structured_config` set on SVI level.
nodes:
# l3_leaf inventory hostname.
- node: <str; required; unique>
# Tags leveraged for networks services filtering.
# Tags are matched against "filter.tags" defined under node type settings.
# Tags are also matched against the "node_group" name under node type settings.
tags: # default=['all']
# Tag value.
- <str>
# VLAN name.
name: <str>
# Enable or disable interface.
enabled: <bool>
# SVI description. By default set to VLAN name.
description: <str>
# IPv4_address/Mask. Usually set under "nodes" to have unique IPv4 addresses per node.
ip_address: <str>
# IPv6_address/Mask. Usually set under "nodes" to have unique IPv6 addresses per node.
ipv6_address: <str>
# Explicitly enable/disable link-local IPv6 addressing.
ipv6_enable: <bool>
# IPv4_address/Mask.
# IPv4 VXLAN Anycast IP address.
# Conserves IP addresses in VXLAN deployments as it doesn't require unique IP addresses on each node.
ip_address_virtual: <str>
# IPv6_address/Mask.
# ipv6 address virtuals to configure VXLAN Anycast IP address (Optional).
# If both "ipv6_address_virtual" and "ipv6_address_virtuals" are set, all addresses will be configured.
# This key is deprecated.
# Support will be removed in AVD version 5.0.0.
# Use <samp>ipv6_address_virtuals</samp> instead.
ipv6_address_virtual: <str>
# IPv6 VXLAN Anycast IP addresses.
# Conserves IPv6 addresses in VXLAN deployments as it doesn't require unique IPv6 addresses on each node.
ipv6_address_virtuals:
# IPv6_address/Mask.
- <str>
# Secondary IPv4 VXLAN Anycast IP addresses.
ip_address_virtual_secondaries:
# IPv4_address/Mask.
- <str>
# IPv4 VARP addresses.
# Requires an IP address to be configured on the SVI.
# If ip_address_virtual is also set, ip_virtual_router_addresses will take precedence
# _if_ there is an ip_address configured for the node.
ip_virtual_router_addresses:
# IPv4_address/Mask or IPv4_address.
# IPv4_address/Mask will also configure a static route to the SVI per best practice.
- <str>
# IPv6 VARP addresses.
# Requires an IPv6 address to be configured on the SVI.
# If ipv6_address_virtuals is also set, ipv6_virtual_router_addresses will take precedence
# _if_ there is an ipv6_address configured for the node.
ipv6_virtual_router_addresses:
# IPv6_address.
- <str>
# IP helper for DHCP relay.
ip_helpers:
# IPv4 DHCP server IP.
- ip_helper: <str; required; unique>
# Interface name to originate DHCP relay packets to DHCP server.
source_interface: <str>
# VRF to originate DHCP relay packets to DHCP server. If not set, EOS uses the VRF on the SVI.
source_vrf: <str>
# By default the VNI will be derived from "mac_vrf_vni_base".
# The vni_override allows us to override this value and statically define it (optional).
vni_override: <int; 1-16777215>
# By default the MAC VRF RT will be derived from mac_vrf_id_base + vlan_id.
# The rt_override allows us to override this value and statically define it.
# rt_override will default to vni_override if set.
#
# rt_override supports two formats:
# - A single number which will be used in the RT fields instead of mac_vrf_id/mac_vrf_vni (see 'overlay_rt_type' for details).
# - A full RT string with colon separator which will override the full RT.
rt_override: <str>
# By default the MAC VRF RD will be derived from mac_vrf_id_base + vlan_id.
# The rt_override allows us to override this value and statically define it.
# rd_override will default to rt_override or vni_override if set.
#
# rd_override supports two formats:
# - A single number which will be used in the RD assigned number field instead of mac_vrf_id/mac_vrf_vni (see 'overlay_rd_type' for details).
# - A full RD string with colon separator which will override the full RD.
rd_override: <str>
trunk_groups:
# Trunk groups are used for limiting vlans to trunk ports assigned to the same trunk group.
# Requires "enable_trunk_groups: true".
- <str>
# Extend this SVI over VXLAN.
vxlan: <bool; default=True>
# Setting spanning-tree priority per VLAN is only supported with `spanning_tree_mode: rapid-pvst` under node type settings.
# The default priority for rapid-PVST is set under the node type settings with `spanning_tree_priority` (default=32768).
spanning_tree_priority: <int>
# Interface MTU.
mtu: <int>
bgp:
# Structured configuration and EOS CLI commands rendered on router_bgp.vlans.[id=<vlan>].
# This configuration will not be applied to vlan aware bundles.
structured_config: <dict>
# EOS CLI rendered directly on the Router BGP, VLAN definition in the final EOS configuration.
raw_eos_cli: <str>
# EOS CLI rendered directly on the VLAN interface in the final EOS configuration.
raw_eos_cli: <str>
# Custom structured config added under vlan_interfaces.[name=<interface>] for eos_cli_config_gen.
structured_config: <dict>
# Enable or disable interface.
enabled: <bool>
# SVI description. By default set to VLAN name.
description: <str>
# IPv4_address/Mask. Usually set under "nodes" to have unique IPv4 addresses per node.
ip_address: <str>
# IPv6_address/Mask. Usually set under "nodes" to have unique IPv6 addresses per node.
ipv6_address: <str>
# Explicitly enable/disable link-local IPv6 addressing.
ipv6_enable: <bool>
# IPv4_address/Mask.
# IPv4 VXLAN Anycast IP address.
# Conserves IP addresses in VXLAN deployments as it doesn't require unique IP addresses on each node.
ip_address_virtual: <str>
# IPv6_address/Mask.
# ipv6 address virtuals to configure VXLAN Anycast IP address (Optional).
# If both "ipv6_address_virtual" and "ipv6_address_virtuals" are set, all addresses will be configured.
# This key is deprecated.
# Support will be removed in AVD version 5.0.0.
# Use <samp>ipv6_address_virtuals</samp> instead.
ipv6_address_virtual: <str>
# IPv6 VXLAN Anycast IP addresses.
# Conserves IPv6 addresses in VXLAN deployments as it doesn't require unique IPv6 addresses on each node.
ipv6_address_virtuals:
# IPv6_address/Mask.
- <str>
# Secondary IPv4 VXLAN Anycast IP addresses.
ip_address_virtual_secondaries:
# IPv4_address/Mask.
- <str>
# IPv4 VARP addresses.
# Requires an IP address to be configured on the SVI.
# If ip_address_virtual is also set, ip_virtual_router_addresses will take precedence
# _if_ there is an ip_address configured for the node.
ip_virtual_router_addresses:
# IPv4_address/Mask or IPv4_address.
# IPv4_address/Mask will also configure a static route to the SVI per best practice.
- <str>
# IPv6 VARP addresses.
# Requires an IPv6 address to be configured on the SVI.
# If ipv6_address_virtuals is also set, ipv6_virtual_router_addresses will take precedence
# _if_ there is an ipv6_address configured for the node.
ipv6_virtual_router_addresses:
# IPv6_address.
- <str>
# IP helper for DHCP relay.
ip_helpers:
# IPv4 DHCP server IP.
- ip_helper: <str; required; unique>
# Interface name to originate DHCP relay packets to DHCP server.
source_interface: <str>
# VRF to originate DHCP relay packets to DHCP server. If not set, EOS uses the VRF on the SVI.
source_vrf: <str>
# By default the VNI will be derived from "mac_vrf_vni_base".
# The vni_override allows us to override this value and statically define it (optional).
vni_override: <int; 1-16777215>
# By default the MAC VRF RT will be derived from mac_vrf_id_base + vlan_id.
# The rt_override allows us to override this value and statically define it.
# rt_override will default to vni_override if set.
#
# rt_override supports two formats:
# - A single number which will be used in the RT fields instead of mac_vrf_id/mac_vrf_vni (see 'overlay_rt_type' for details).
# - A full RT string with colon separator which will override the full RT.
rt_override: <str>
# By default the MAC VRF RD will be derived from mac_vrf_id_base + vlan_id.
# The rt_override allows us to override this value and statically define it.
# rd_override will default to rt_override or vni_override if set.
#
# rd_override supports two formats:
# - A single number which will be used in the RD assigned number field instead of mac_vrf_id/mac_vrf_vni (see 'overlay_rd_type' for details).
# - A full RD string with colon separator which will override the full RD.
rd_override: <str>
trunk_groups:
# Trunk groups are used for limiting vlans to trunk ports assigned to the same trunk group.
# Requires "enable_trunk_groups: true".
- <str>
# Extend this SVI over VXLAN.
vxlan: <bool; default=True>
# Setting spanning-tree priority per VLAN is only supported with `spanning_tree_mode: rapid-pvst` under node type settings.
# The default priority for rapid-PVST is set under the node type settings with `spanning_tree_priority` (default=32768).
spanning_tree_priority: <int>
# Interface MTU.
mtu: <int>
bgp:
# Structured configuration and EOS CLI commands rendered on router_bgp.vlans.[id=<vlan>].
# This configuration will not be applied to vlan aware bundles.
structured_config: <dict>
# EOS CLI rendered directly on the Router BGP, VLAN definition in the final EOS configuration.
raw_eos_cli: <str>
# EOS CLI rendered directly on the VLAN interface in the final EOS configuration.
raw_eos_cli: <str>
# Custom structured config added under vlan_interfaces.[name=<interface>] for eos_cli_config_gen.
structured_config: <dict>
Network services VRF L3 Interfaces configuration¶
| Variable | Type | Required | Default | Value Restrictions | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| <network_services_keys.name> | List, items: Dictionary | ||||
| - name | String | Required, Unique | Specify a tenant name. Tenant provide a construct to group L3 VRFs and L2 VLANs. Networks services can be filtered by tenant name. |
||
| vrfs | List, items: Dictionary | VRFs will only be configured on a node if any of the underlying objects like svis or l3_interfaces apply to the node.It is recommended to only define a VRF in one Tenant. If the same VRF name is used across multiple tenants and those tenants are accepted by filter.tenants on the node, any object set under the duplicate VRFs must either be unique or be an exact match.VRF “default” is partially supported under network-services. Currently the supported options for “default” vrf are route-target, route-distinguisher settings, structured_config, raw_eos_cli in bgp and SVIs are the only supported interface type. Vlan-aware-bundles are supported as well inside default vrf. OSPF is not supported currently. |
|||
| - name | String | Required, Unique | |||
| l3_interfaces | List, items: Dictionary | List of L3 interfaces. This will create IP routed interface inside VRF. Length of interfaces, nodes and ip_addresses must match. |
|||
| - interfaces | List, items: String | ||||
| - <str> | String | Interface name. | |||
| encapsulation_dot1q_vlan | List, items: Integer | For sub-interfaces the dot1q vlan is derived from the interface name by default, but can also be specified. | |||
| - <int> | Integer | Min: 1 Max: 4094 |
|||
| ip_addresses | List, items: String | ||||
| - <str> | String | IPv4_address/Mask. | |||
| nodes | List, items: String | ||||
| - <str> | String | Node. | |||
| description | String | ||||
| descriptions | List, items: String | “descriptions” has precedence over “description”. |
|||
| - <str> | String | ||||
| enabled | Boolean | ||||
| mtu | Integer | ||||
| ospf | Dictionary | OSPF interface configuration. | |||
| enabled | Boolean | ||||
| point_to_point | Boolean | False |
|||
| area | String | 0 |
OSPF area ID. | ||
| cost | Integer | OSPF link cost. | |||
| authentication | String | Valid Values: - simple- message-digest |
|||
| simple_auth_key | String | Password used with simple authentication. | |||
| message_digest_keys | List, items: Dictionary | ||||
| - id | Integer | ||||
| hash_algorithm | String | sha512 |
Valid Values: - md5- sha1- sha256- sha384- sha512 |
||
| key | String | Key password. | |||
| pim | Dictionary | Enable PIM sparse-mode on the interface; requires “evpn_l3_multicast” to be enabled on the VRF/Tenant. Enabling this implicitly makes the device a PIM External Gateway (PEG) in EVPN designs only. At least one RP address must be configured for EVPN PEG to be configured. |
|||
| enabled | Boolean | ||||
| flow_tracking | Dictionary | Configures flow-tracking on the interface. Overrides fabric_flow_tracking.l3_interfaces setting. |
|||
| enabled | Boolean | ||||
| name | String | Flow tracker name as defined in flow_tracking_settings. | |||
| structured_config | Dictionary | Custom structured config added under ethernet_interfaces.[name= |
|||
| raw_eos_cli | String | EOS CLI rendered directly on the Ethernet interface in the final EOS configuration. |
<network_services_keys.name>:
# Specify a tenant name.
# Tenant provide a construct to group L3 VRFs and L2 VLANs.
# Networks services can be filtered by tenant name.
- name: <str; required; unique>
# VRFs will only be configured on a node if any of the underlying objects like `svis` or `l3_interfaces` apply to the node.
#
# It is recommended to only define a VRF in one Tenant. If the same VRF name is used across multiple tenants and those tenants
# are accepted by `filter.tenants` on the node, any object set under the duplicate VRFs must either be unique or be an exact match.
#
# VRF "default" is partially supported under network-services. Currently the supported options for "default" vrf are route-target,
# route-distinguisher settings, structured_config, raw_eos_cli in bgp and SVIs are the only supported interface type.
# Vlan-aware-bundles are supported as well inside default vrf. OSPF is not supported currently.
vrfs:
- name: <str; required; unique>
# List of L3 interfaces.
# This will create IP routed interface inside VRF. Length of interfaces, nodes and ip_addresses must match.
l3_interfaces:
- interfaces:
# Interface name.
- <str>
# For sub-interfaces the dot1q vlan is derived from the interface name by default, but can also be specified.
encapsulation_dot1q_vlan:
- <int; 1-4094>
ip_addresses:
# IPv4_address/Mask.
- <str>
nodes:
# Node.
- <str>
description: <str>
# "descriptions" has precedence over "description".
descriptions:
- <str>
enabled: <bool>
mtu: <int>
# OSPF interface configuration.
ospf:
enabled: <bool>
point_to_point: <bool; default=False>
# OSPF area ID.
area: <str; default="0">
# OSPF link cost.
cost: <int>
authentication: <str; "simple" | "message-digest">
# Password used with simple authentication.
simple_auth_key: <str>
message_digest_keys:
- id: <int>
hash_algorithm: <str; "md5" | "sha1" | "sha256" | "sha384" | "sha512"; default="sha512">
# Key password.
key: <str>
# Enable PIM sparse-mode on the interface; requires "evpn_l3_multicast" to be enabled on the VRF/Tenant.
# Enabling this implicitly makes the device a PIM External Gateway (PEG) in EVPN designs only.
# At least one RP address must be configured for EVPN PEG to be configured.
pim:
enabled: <bool>
# Configures flow-tracking on the interface. Overrides `fabric_flow_tracking.l3_interfaces` setting.
flow_tracking:
enabled: <bool>
# Flow tracker name as defined in flow_tracking_settings.
name: <str>
# Custom structured config added under ethernet_interfaces.[name=<interface>] for eos_cli_config_gen.
structured_config: <dict>
# EOS CLI rendered directly on the Ethernet interface in the final EOS configuration.
raw_eos_cli: <str>
Network services VRF Loopbacks configuration¶
Loopbacks are usually configured with vtep_diagnostic which supports IP pools etc.
loopbacks is used to provision extra loopback interfaces with manually assigned
IP addresses on individual nodes.
| Variable | Type | Required | Default | Value Restrictions | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| <network_services_keys.name> | List, items: Dictionary | ||||
| - name | String | Required, Unique | Specify a tenant name. Tenant provide a construct to group L3 VRFs and L2 VLANs. Networks services can be filtered by tenant name. |
||
| vrfs | List, items: Dictionary | VRFs will only be configured on a node if any of the underlying objects like svis or l3_interfaces apply to the node.It is recommended to only define a VRF in one Tenant. If the same VRF name is used across multiple tenants and those tenants are accepted by filter.tenants on the node, any object set under the duplicate VRFs must either be unique or be an exact match.VRF “default” is partially supported under network-services. Currently the supported options for “default” vrf are route-target, route-distinguisher settings, structured_config, raw_eos_cli in bgp and SVIs are the only supported interface type. Vlan-aware-bundles are supported as well inside default vrf. OSPF is not supported currently. |
|||
| - name | String | Required, Unique | |||
| loopbacks | List, items: Dictionary | List of Loopback interfaces. This will create Loopback interfaces inside the VRF. |
|||
| - node | String | Required | |||
| loopback | Integer | Required | Min: 0 Max: 8191 |
||
| ip_address | String | Required | |||
| description | String | ||||
| enabled | Boolean | True |
|||
| ospf | Dictionary | OSPF interface configuration. | |||
| enabled | Boolean | False |
|||
| area | String | 0 |
OSPF area ID. | ||
| raw_eos_cli | String | EOS CLI rendered directly on the Loopback interface in the final EOS configuration. |
<network_services_keys.name>:
# Specify a tenant name.
# Tenant provide a construct to group L3 VRFs and L2 VLANs.
# Networks services can be filtered by tenant name.
- name: <str; required; unique>
# VRFs will only be configured on a node if any of the underlying objects like `svis` or `l3_interfaces` apply to the node.
#
# It is recommended to only define a VRF in one Tenant. If the same VRF name is used across multiple tenants and those tenants
# are accepted by `filter.tenants` on the node, any object set under the duplicate VRFs must either be unique or be an exact match.
#
# VRF "default" is partially supported under network-services. Currently the supported options for "default" vrf are route-target,
# route-distinguisher settings, structured_config, raw_eos_cli in bgp and SVIs are the only supported interface type.
# Vlan-aware-bundles are supported as well inside default vrf. OSPF is not supported currently.
vrfs:
- name: <str; required; unique>
# List of Loopback interfaces.
# This will create Loopback interfaces inside the VRF.
loopbacks:
- node: <str; required>
loopback: <int; 0-8191; required>
ip_address: <str; required>
description: <str>
enabled: <bool; default=True>
# OSPF interface configuration.
ospf:
enabled: <bool; default=False>
# OSPF area ID.
area: <str; default="0">
# EOS CLI rendered directly on the Loopback interface in the final EOS configuration.
raw_eos_cli: <str>
Network services VRF BGP configuration¶
| Variable | Type | Required | Default | Value Restrictions | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| <network_services_keys.name> | List, items: Dictionary | ||||
| - name | String | Required, Unique | Specify a tenant name. Tenant provide a construct to group L3 VRFs and L2 VLANs. Networks services can be filtered by tenant name. |
||
| bgp_peer_groups | List, items: Dictionary | List of BGP peer groups definitions. This will configure BGP peer groups to be used inside the tenant VRF for peering with external devices. Since BGP peer groups are configured at higher BGP level, shared between VRFs, peer_group names should not overlap between VRFs. |
|||
| - name | String | Required, Unique | BGP peer group name. | ||
| nodes | List, items: String | Nodes is required to restrict configuration of BGP neighbors to certain nodes in the network. If not set the peer-group is created on devices which have a bgp_peer mapped to the corresponding peer_group. |
|||
| - <str> | String | ||||
| type | String | Key only used for documentation or validation purposes. | |||
| remote_as | String | BGP AS <1-4294967295> or AS number in asdot notation “<1-65535>.<0-65535>”. For asdot notation in YAML inputs, the value must be put in quotes, to prevent it from being interpreted as a float number. |
|||
| local_as | String | BGP AS <1-4294967295> or AS number in asdot notation “<1-65535>.<0-65535>”. For asdot notation in YAML inputs, the value must be put in quotes, to prevent it from being interpreted as a float number. |
|||
| description | String | ||||
| shutdown | Boolean | ||||
| as_path | Dictionary | BGP AS-PATH options. | |||
| remote_as_replace_out | Boolean | Replace AS number with local AS number. | |||
| prepend_own_disabled | Boolean | Disable prepending own AS number to AS path. | |||
| remove_private_as | Dictionary | Remove private AS numbers in outbound AS path. | |||
| enabled | Boolean | ||||
| all | Boolean | ||||
| replace_as | Boolean | ||||
| remove_private_as_ingress | Dictionary | ||||
| enabled | Boolean | ||||
| replace_as | Boolean | ||||
| peer_filter deprecated | String | Peer-filter name. note: bgp_listen_range_prefix and peer_filter should not be mixed withthe new listen_ranges key above to avoid conflicts.This key is deprecated. Support will be removed in AVD version 5.0.0. Use listen_ranges instead. |
|||
| next_hop_unchanged | Boolean | ||||
| update_source | String | IP address or interface name. | |||
| route_reflector_client | Boolean | ||||
| bfd | Boolean | Enable BFD. | |||
| bfd_timers | Dictionary | Override default BFD timers. BFD must be enabled with bfd: true. |
|||
| interval | Integer | Required | Min: 50 Max: 60000 |
Interval in milliseconds. | |
| min_rx | Integer | Required | Min: 50 Max: 60000 |
Rate in milliseconds. | |
| multiplier | Integer | Required | Min: 3 Max: 50 |
||
| ebgp_multihop | Integer | Min: 1 Max: 255 |
Time-to-live in range of hops. | ||
| next_hop_self | Boolean | ||||
| password | String | ||||
| passive | Boolean | ||||
| default_originate | Dictionary | ||||
| enabled | Boolean | ||||
| always | Boolean | ||||
| route_map | String | Route-map name. | |||
| send_community | String | ‘all’ or a combination of ‘standard’, ‘extended’, ‘large’ and ‘link-bandwidth (w/options)’. | |||
| maximum_routes | Integer | Min: 0 Max: 4294967294 |
Maximum number of routes (0 means unlimited). | ||
| maximum_routes_warning_limit | String | Maximum number of routes after which a warning is issued (0 means never warn) or Percentage of maximum number of routes at which to warn (“<1-100> percent”). |
|||
| maximum_routes_warning_only | Boolean | ||||
| link_bandwidth | Dictionary | ||||
| enabled | Boolean | ||||
| default | String | nn.nn(K | |||
| allowas_in | Dictionary | ||||
| enabled | Boolean | ||||
| times | Integer | Min: 1 Max: 10 |
Number of local ASNs allowed in a BGP update. | ||
| weight | Integer | Min: 0 Max: 65535 |
|||
| timers | String | BGP Keepalive and Hold Timer values in seconds as string “<0-3600> <0-3600>”. | |||
| rib_in_pre_policy_retain | Dictionary | ||||
| enabled | Boolean | ||||
| all | Boolean | ||||
| route_map_in | String | Inbound route-map name. | |||
| route_map_out | String | Outbound route-map name. | |||
| bgp_listen_range_prefix deprecated | String | IP prefix range. note: bgp_listen_range_prefix and peer_filter should not be mixed withthe new listen_ranges key above to avoid conflicts.This key is deprecated. Support will be removed in AVD version 5.0.0. Use listen_ranges instead. |
|||
| session_tracker | String | ||||
| ttl_maximum_hops | Integer | Min: 0 Max: 254 |
Maximum number of hops. | ||
| vrfs | List, items: Dictionary | VRFs will only be configured on a node if any of the underlying objects like svis or l3_interfaces apply to the node.It is recommended to only define a VRF in one Tenant. If the same VRF name is used across multiple tenants and those tenants are accepted by filter.tenants on the node, any object set under the duplicate VRFs must either be unique or be an exact match.VRF “default” is partially supported under network-services. Currently the supported options for “default” vrf are route-target, route-distinguisher settings, structured_config, raw_eos_cli in bgp and SVIs are the only supported interface type. Vlan-aware-bundles are supported as well inside default vrf. OSPF is not supported currently. |
|||
| - name | String | Required, Unique | |||
| bgp_peers | List, items: Dictionary | List of BGP peer definitions. This will configure BGP neighbors inside the tenant VRF for peering with external devices. The configured peer will automatically be activated for ipv4 or ipv6 address family based on the ip address. Note, only ipv4 and ipv6 address families are currently supported in eos_designs. For other address families, use custom_structured configuration with eos_cli_config_gen. |
|||
| - ip_address | String | Required, Unique | IPv4_address or IPv6_address. | ||
| peer_group | String | Peer group name. | |||
| remote_as | String | BGP AS <1-4294967295> or AS number in asdot notation “<1-65535>.<0-65535>”. For asdot notation in YAML inputs, the value must be put in quotes, to prevent it from being interpreted as a float number. |
|||
| description | String | ||||
| password | String | Encrypted password. | |||
| send_community | String | ‘all’ or a combination of ‘standard’, ‘extended’, ‘large’ and ‘link-bandwidth (w/options)’. |
|||
| next_hop_self | Boolean | ||||
| timers | String | BGP Keepalive and Hold Timer values in seconds as string <0-3600> <0-3600>. | |||
| maximum_routes | Integer | Min: 0 Max: 4294967294 |
Maximum number of routes (0 means unlimited). | ||
| maximum_routes_warning_only | Boolean | ||||
| default_originate | Dictionary | ||||
| always | Boolean | ||||
| update_source | String | ||||
| ebgp_multihop | Integer | Min: 1 Max: 255 |
Time-to-live in range of hops. | ||
| nodes | List, items: String | Nodes is required to restrict configuration of BGP neighbors to certain nodes in the network. | |||
| - <str> | String | ||||
| set_ipv4_next_hop | String | IPv4_address Next hop settings can be either ipv4 or ipv6 for one neighbor, this will be applied by a uniquely generated route-map per neighbor. Next hop takes precedence over route_map_out. |
|||
| set_ipv6_next_hop | String | IPv6_address Next hop settings can be either ipv4 or ipv6 for one neighbor, this will be applied by a uniquely generated route-map per neighbor. Next hop takes precedence over route_map_out. |
|||
| route_map_out | String | Route-map name. | |||
| route_map_in | String | Route-map name. | |||
| prefix_list_in | String | Inbound prefix list name. The prefix-list will be associated under the IPv4 or IPv6 address family based on the IP address. |
|||
| prefix_list_out | String | Outbound prefix list name. The prefix-list will be associated under the IPv4 or IPv6 address family based on the IP address. |
|||
| local_as | String | Local BGP AS <1-4294967295> or AS number in asdot notation “<1-65535>.<0-65535>”. For asdot notation in YAML inputs, the value must be put in quotes, to prevent it from being interpreted as a float number. |
|||
| weight | Integer | Min: 0 Max: 65535 |
|||
| bfd | Boolean | ||||
| shutdown | Boolean | ||||
| bgp_peer_groups | List, items: Dictionary | List of BGP peer groups definitions. This will configure BGP peer groups to be used inside the tenant VRF for peering with external devices. Since BGP peer groups are configured at higher BGP level, shared between VRFs, peer_group names should not overlap between VRFs. |
|||
| - name | String | BGP peer group name. | |||
| nodes | List, items: String | Nodes is required to restrict configuration of BGP neighbors to certain nodes in the network. If not set the peer-group is created on devices which have a bgp_peer mapped to the corresponding peer_group. |
|||
| - <str> | String | ||||
| type | String | Key only used for documentation or validation purposes. | |||
| remote_as | String | BGP AS <1-4294967295> or AS number in asdot notation “<1-65535>.<0-65535>”. For asdot notation in YAML inputs, the value must be put in quotes, to prevent it from being interpreted as a float number. |
|||
| local_as | String | BGP AS <1-4294967295> or AS number in asdot notation “<1-65535>.<0-65535>”. For asdot notation in YAML inputs, the value must be put in quotes, to prevent it from being interpreted as a float number. |
|||
| description | String | ||||
| shutdown | Boolean | ||||
| as_path | Dictionary | BGP AS-PATH options. | |||
| remote_as_replace_out | Boolean | Replace AS number with local AS number. | |||
| prepend_own_disabled | Boolean | Disable prepending own AS number to AS path. | |||
| remove_private_as | Dictionary | Remove private AS numbers in outbound AS path. | |||
| enabled | Boolean | ||||
| all | Boolean | ||||
| replace_as | Boolean | ||||
| remove_private_as_ingress | Dictionary | ||||
| enabled | Boolean | ||||
| replace_as | Boolean | ||||
| peer_filter deprecated | String | Peer-filter name. note: bgp_listen_range_prefix and peer_filter should not be mixed withthe new listen_ranges key above to avoid conflicts.This key is deprecated. Support will be removed in AVD version 5.0.0. Use listen_ranges instead. |
|||
| next_hop_unchanged | Boolean | ||||
| update_source | String | IP address or interface name. | |||
| route_reflector_client | Boolean | ||||
| bfd | Boolean | Enable BFD. | |||
| bfd_timers | Dictionary | Override default BFD timers. BFD must be enabled with bfd: true. |
|||
| interval | Integer | Required | Min: 50 Max: 60000 |
Interval in milliseconds. | |
| min_rx | Integer | Required | Min: 50 Max: 60000 |
Rate in milliseconds. | |
| multiplier | Integer | Required | Min: 3 Max: 50 |
||
| ebgp_multihop | Integer | Min: 1 Max: 255 |
Time-to-live in range of hops. | ||
| next_hop_self | Boolean | ||||
| password | String | ||||
| passive | Boolean | ||||
| default_originate | Dictionary | ||||
| enabled | Boolean | ||||
| always | Boolean | ||||
| route_map | String | Route-map name. | |||
| send_community | String | ‘all’ or a combination of ‘standard’, ‘extended’, ‘large’ and ‘link-bandwidth (w/options)’. | |||
| maximum_routes | Integer | Min: 0 Max: 4294967294 |
Maximum number of routes (0 means unlimited). | ||
| maximum_routes_warning_limit | String | Maximum number of routes after which a warning is issued (0 means never warn) or Percentage of maximum number of routes at which to warn (“<1-100> percent”). |
|||
| maximum_routes_warning_only | Boolean | ||||
| link_bandwidth | Dictionary | ||||
| enabled | Boolean | ||||
| default | String | nn.nn(K | |||
| allowas_in | Dictionary | ||||
| enabled | Boolean | ||||
| times | Integer | Min: 1 Max: 10 |
Number of local ASNs allowed in a BGP update. | ||
| weight | Integer | Min: 0 Max: 65535 |
|||
| timers | String | BGP Keepalive and Hold Timer values in seconds as string “<0-3600> <0-3600>”. | |||
| rib_in_pre_policy_retain | Dictionary | ||||
| enabled | Boolean | ||||
| all | Boolean | ||||
| route_map_in | String | Inbound route-map name. | |||
| route_map_out | String | Outbound route-map name. | |||
| bgp_listen_range_prefix deprecated | String | IP prefix range. note: bgp_listen_range_prefix and peer_filter should not be mixed withthe new listen_ranges key above to avoid conflicts.This key is deprecated. Support will be removed in AVD version 5.0.0. Use listen_ranges instead. |
|||
| session_tracker | String | ||||
| ttl_maximum_hops | Integer | Min: 0 Max: 254 |
Maximum number of hops. |
<network_services_keys.name>:
# Specify a tenant name.
# Tenant provide a construct to group L3 VRFs and L2 VLANs.
# Networks services can be filtered by tenant name.
- name: <str; required; unique>
# List of BGP peer groups definitions.
# This will configure BGP peer groups to be used inside the tenant VRF for peering with external devices.
# Since BGP peer groups are configured at higher BGP level, shared between VRFs,
# peer_group names should not overlap between VRFs.
bgp_peer_groups:
# BGP peer group name.
- name: <str; required; unique>
# Nodes is required to restrict configuration of BGP neighbors to certain nodes in the network.
# If not set the peer-group is created on devices which have a bgp_peer mapped to the corresponding peer_group.
nodes:
- <str>
# Key only used for documentation or validation purposes.
type: <str>
# BGP AS <1-4294967295> or AS number in asdot notation "<1-65535>.<0-65535>".
# For asdot notation in YAML inputs, the value must be put in quotes, to prevent it from being interpreted as a float number.
remote_as: <str>
# BGP AS <1-4294967295> or AS number in asdot notation "<1-65535>.<0-65535>".
# For asdot notation in YAML inputs, the value must be put in quotes, to prevent it from being interpreted as a float number.
local_as: <str>
description: <str>
shutdown: <bool>
# BGP AS-PATH options.
as_path:
# Replace AS number with local AS number.
remote_as_replace_out: <bool>
# Disable prepending own AS number to AS path.
prepend_own_disabled: <bool>
# Remove private AS numbers in outbound AS path.
remove_private_as:
enabled: <bool>
all: <bool>
replace_as: <bool>
remove_private_as_ingress:
enabled: <bool>
replace_as: <bool>
# Peer-filter name.
# note: `bgp_listen_range_prefix` and `peer_filter` should not be mixed with
# the new `listen_ranges` key above to avoid conflicts.
# This key is deprecated.
# Support will be removed in AVD version 5.0.0.
# Use <samp>listen_ranges</samp> instead.
peer_filter: <str>
next_hop_unchanged: <bool>
# IP address or interface name.
update_source: <str>
route_reflector_client: <bool>
# Enable BFD.
bfd: <bool>
# Override default BFD timers. BFD must be enabled with `bfd: true`.
bfd_timers:
# Interval in milliseconds.
interval: <int; 50-60000; required>
# Rate in milliseconds.
min_rx: <int; 50-60000; required>
multiplier: <int; 3-50; required>
# Time-to-live in range of hops.
ebgp_multihop: <int; 1-255>
next_hop_self: <bool>
password: <str>
passive: <bool>
default_originate:
enabled: <bool>
always: <bool>
# Route-map name.
route_map: <str>
# 'all' or a combination of 'standard', 'extended', 'large' and 'link-bandwidth (w/options)'.
send_community: <str>
# Maximum number of routes (0 means unlimited).
maximum_routes: <int; 0-4294967294>
# Maximum number of routes after which a warning is issued (0 means never warn) or
# Percentage of maximum number of routes at which to warn ("<1-100> percent").
maximum_routes_warning_limit: <str>
maximum_routes_warning_only: <bool>
link_bandwidth:
enabled: <bool>
# nn.nn(K|M|G) link speed in bits/second.
default: <str>
allowas_in:
enabled: <bool>
# Number of local ASNs allowed in a BGP update.
times: <int; 1-10>
weight: <int; 0-65535>
# BGP Keepalive and Hold Timer values in seconds as string "<0-3600> <0-3600>".
timers: <str>
rib_in_pre_policy_retain:
enabled: <bool>
all: <bool>
# Inbound route-map name.
route_map_in: <str>
# Outbound route-map name.
route_map_out: <str>
# IP prefix range.
# note: `bgp_listen_range_prefix` and `peer_filter` should not be mixed with
# the new `listen_ranges` key above to avoid conflicts.
# This key is deprecated.
# Support will be removed in AVD version 5.0.0.
# Use <samp>listen_ranges</samp> instead.
bgp_listen_range_prefix: <str>
session_tracker: <str>
# Maximum number of hops.
ttl_maximum_hops: <int; 0-254>
# VRFs will only be configured on a node if any of the underlying objects like `svis` or `l3_interfaces` apply to the node.
#
# It is recommended to only define a VRF in one Tenant. If the same VRF name is used across multiple tenants and those tenants
# are accepted by `filter.tenants` on the node, any object set under the duplicate VRFs must either be unique or be an exact match.
#
# VRF "default" is partially supported under network-services. Currently the supported options for "default" vrf are route-target,
# route-distinguisher settings, structured_config, raw_eos_cli in bgp and SVIs are the only supported interface type.
# Vlan-aware-bundles are supported as well inside default vrf. OSPF is not supported currently.
vrfs:
- name: <str; required; unique>
# List of BGP peer definitions.
# This will configure BGP neighbors inside the tenant VRF for peering with external devices.
# The configured peer will automatically be activated for ipv4 or ipv6 address family based on the ip address.
# Note, only ipv4 and ipv6 address families are currently supported in eos_designs.
# For other address families, use custom_structured configuration with eos_cli_config_gen.
bgp_peers:
# IPv4_address or IPv6_address.
- ip_address: <str; required; unique>
# Peer group name.
peer_group: <str>
# BGP AS <1-4294967295> or AS number in asdot notation "<1-65535>.<0-65535>".
# For asdot notation in YAML inputs, the value must be put in quotes, to prevent it from being interpreted as a float number.
remote_as: <str>
description: <str>
# Encrypted password.
password: <str>
# 'all' or a combination of 'standard', 'extended', 'large' and 'link-bandwidth (w/options)'.
send_community: <str>
next_hop_self: <bool>
# BGP Keepalive and Hold Timer values in seconds as string <0-3600> <0-3600>.
timers: <str>
# Maximum number of routes (0 means unlimited).
maximum_routes: <int; 0-4294967294>
maximum_routes_warning_only: <bool>
default_originate:
always: <bool>
update_source: <str>
# Time-to-live in range of hops.
ebgp_multihop: <int; 1-255>
# Nodes is required to restrict configuration of BGP neighbors to certain nodes in the network.
nodes:
- <str>
# IPv4_address
# Next hop settings can be either ipv4 or ipv6 for one neighbor, this will be applied by a uniquely generated route-map per neighbor.
# Next hop takes precedence over route_map_out.
set_ipv4_next_hop: <str>
# IPv6_address
# Next hop settings can be either ipv4 or ipv6 for one neighbor, this will be applied by a uniquely generated route-map per neighbor.
# Next hop takes precedence over route_map_out.
set_ipv6_next_hop: <str>
# Route-map name.
route_map_out: <str>
# Route-map name.
route_map_in: <str>
# Inbound prefix list name.
# The prefix-list will be associated under the IPv4 or IPv6 address family based on the IP address.
prefix_list_in: <str>
# Outbound prefix list name.
# The prefix-list will be associated under the IPv4 or IPv6 address family based on the IP address.
prefix_list_out: <str>
# Local BGP AS <1-4294967295> or AS number in asdot notation "<1-65535>.<0-65535>".
# For asdot notation in YAML inputs, the value must be put in quotes, to prevent it from being interpreted as a float number.
local_as: <str>
weight: <int; 0-65535>
bfd: <bool>
shutdown: <bool>
# List of BGP peer groups definitions.
# This will configure BGP peer groups to be used inside the tenant VRF for peering with external devices.
# Since BGP peer groups are configured at higher BGP level, shared between VRFs,
# peer_group names should not overlap between VRFs.
bgp_peer_groups:
# BGP peer group name.
- name: <str>
# Nodes is required to restrict configuration of BGP neighbors to certain nodes in the network.
# If not set the peer-group is created on devices which have a bgp_peer mapped to the corresponding peer_group.
nodes:
- <str>
# Key only used for documentation or validation purposes.
type: <str>
# BGP AS <1-4294967295> or AS number in asdot notation "<1-65535>.<0-65535>".
# For asdot notation in YAML inputs, the value must be put in quotes, to prevent it from being interpreted as a float number.
remote_as: <str>
# BGP AS <1-4294967295> or AS number in asdot notation "<1-65535>.<0-65535>".
# For asdot notation in YAML inputs, the value must be put in quotes, to prevent it from being interpreted as a float number.
local_as: <str>
description: <str>
shutdown: <bool>
# BGP AS-PATH options.
as_path:
# Replace AS number with local AS number.
remote_as_replace_out: <bool>
# Disable prepending own AS number to AS path.
prepend_own_disabled: <bool>
# Remove private AS numbers in outbound AS path.
remove_private_as:
enabled: <bool>
all: <bool>
replace_as: <bool>
remove_private_as_ingress:
enabled: <bool>
replace_as: <bool>
# Peer-filter name.
# note: `bgp_listen_range_prefix` and `peer_filter` should not be mixed with
# the new `listen_ranges` key above to avoid conflicts.
# This key is deprecated.
# Support will be removed in AVD version 5.0.0.
# Use <samp>listen_ranges</samp> instead.
peer_filter: <str>
next_hop_unchanged: <bool>
# IP address or interface name.
update_source: <str>
route_reflector_client: <bool>
# Enable BFD.
bfd: <bool>
# Override default BFD timers. BFD must be enabled with `bfd: true`.
bfd_timers:
# Interval in milliseconds.
interval: <int; 50-60000; required>
# Rate in milliseconds.
min_rx: <int; 50-60000; required>
multiplier: <int; 3-50; required>
# Time-to-live in range of hops.
ebgp_multihop: <int; 1-255>
next_hop_self: <bool>
password: <str>
passive: <bool>
default_originate:
enabled: <bool>
always: <bool>
# Route-map name.
route_map: <str>
# 'all' or a combination of 'standard', 'extended', 'large' and 'link-bandwidth (w/options)'.
send_community: <str>
# Maximum number of routes (0 means unlimited).
maximum_routes: <int; 0-4294967294>
# Maximum number of routes after which a warning is issued (0 means never warn) or
# Percentage of maximum number of routes at which to warn ("<1-100> percent").
maximum_routes_warning_limit: <str>
maximum_routes_warning_only: <bool>
link_bandwidth:
enabled: <bool>
# nn.nn(K|M|G) link speed in bits/second.
default: <str>
allowas_in:
enabled: <bool>
# Number of local ASNs allowed in a BGP update.
times: <int; 1-10>
weight: <int; 0-65535>
# BGP Keepalive and Hold Timer values in seconds as string "<0-3600> <0-3600>".
timers: <str>
rib_in_pre_policy_retain:
enabled: <bool>
all: <bool>
# Inbound route-map name.
route_map_in: <str>
# Outbound route-map name.
route_map_out: <str>
# IP prefix range.
# note: `bgp_listen_range_prefix` and `peer_filter` should not be mixed with
# the new `listen_ranges` key above to avoid conflicts.
# This key is deprecated.
# Support will be removed in AVD version 5.0.0.
# Use <samp>listen_ranges</samp> instead.
bgp_listen_range_prefix: <str>
session_tracker: <str>
# Maximum number of hops.
ttl_maximum_hops: <int; 0-254>
Network services VRF OSPF configuration¶
| Variable | Type | Required | Default | Value Restrictions | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| <network_services_keys.name> | List, items: Dictionary | ||||
| - name | String | Required, Unique | Specify a tenant name. Tenant provide a construct to group L3 VRFs and L2 VLANs. Networks services can be filtered by tenant name. |
||
| vrfs | List, items: Dictionary | VRFs will only be configured on a node if any of the underlying objects like svis or l3_interfaces apply to the node.It is recommended to only define a VRF in one Tenant. If the same VRF name is used across multiple tenants and those tenants are accepted by filter.tenants on the node, any object set under the duplicate VRFs must either be unique or be an exact match.VRF “default” is partially supported under network-services. Currently the supported options for “default” vrf are route-target, route-distinguisher settings, structured_config, raw_eos_cli in bgp and SVIs are the only supported interface type. Vlan-aware-bundles are supported as well inside default vrf. OSPF is not supported currently. |
|||
| - name | String | Required, Unique | |||
| ospf | Dictionary | Router OSPF configuration. This will create an OSPF routing instance in the tenant VRF. If there is no nodes definition, the OSPF instance will be created on all leafs where the VRF is deployed. This will also cause automatic OSPF redistribution into BGP unless explicitly turned off with “redistribute_ospf: false”. |
|||
| enabled | Boolean | ||||
| process_id | Integer | If not set, “vrf_id” will be used. | |||
| router_id | String | If not set, switch router_id will be used. | |||
| max_lsa | Integer | ||||
| bfd | Boolean | False |
|||
| redistribute_bgp | Dictionary | ||||
| enabled | Boolean | True |
|||
| route_map | String | Route-map name. | |||
| redistribute_connected | Dictionary | ||||
| enabled | Boolean | False |
|||
| route_map | String | Route-map name. | |||
| nodes | List, items: String | ||||
| - <str> | String | Hostname. | |||
| redistribute_ospf | Boolean | True |
Non-selectively enabling or disabling redistribute ospf inside the VRF. | ||
| svis | List, items: Dictionary | List of SVIs. This will create both the L3 SVI and L2 VLAN based on filters applied to the node. |
|||
| - id | Integer | Required | Min: 1 Max: 4096 |
SVI interface id and VLAN id. | |
| nodes | List, items: Dictionary | Define node specific configuration, such as unique IP addresses. Any keys set here will be merged onto the SVI config, except structured_config keys which will replace the structured_config set on SVI level. |
|||
| - node | String | Required, Unique | l3_leaf inventory hostname. | ||
| ospf | Dictionary | OSPF interface configuration. | |||
| enabled | Boolean | ||||
| point_to_point | Boolean | True |
|||
| area | String | 0 |
OSPF area ID. | ||
| cost | Integer | OSPF link cost. | |||
| authentication | String | Valid Values: - simple- message-digest |
|||
| simple_auth_key | String | Password used with simple authentication. | |||
| message_digest_keys | List, items: Dictionary | ||||
| - id | Integer | ||||
| hash_algorithm | String | sha512 |
Valid Values: - md5- sha1- sha256- sha384- sha512 |
||
| key | String | Type 7 encrypted key. | |||
| ospf | Dictionary | OSPF interface configuration. | |||
| enabled | Boolean | ||||
| point_to_point | Boolean | True |
|||
| area | String | 0 |
OSPF area ID. | ||
| cost | Integer | OSPF link cost. | |||
| authentication | String | Valid Values: - simple- message-digest |
|||
| simple_auth_key | String | Password used with simple authentication. | |||
| message_digest_keys | List, items: Dictionary | ||||
| - id | Integer | ||||
| hash_algorithm | String | sha512 |
Valid Values: - md5- sha1- sha256- sha384- sha512 |
||
| key | String | Type 7 encrypted key. | |||
| svi_profiles | List, items: Dictionary | Profiles to share common settings for SVIs under <network_services_key>.[].vrfs.svis.Keys are the same used under SVIs. Keys defined under SVIs take precedence. Note: structured configuration is not merged recursively and will be taken directly from the most specific level in the following order: 1. svi.nodes[inventory_hostname].structured_config 2. svi_profile.nodes[inventory_hostname].structured_config 3. svi_parent_profile.nodes[inventory_hostname].structured_config 4. svi.structured_config 5. svi_profile.structured_config 6. svi_parent_profile.structured_config |
|||
| - profile | String | Required, Unique | Profile name. | ||
| nodes | List, items: Dictionary | Define node specific configuration, such as unique IP addresses. Any keys set here will be merged onto the SVI config, except structured_config keys which will replace the structured_config set on SVI level. |
|||
| - node | String | Required, Unique | l3_leaf inventory hostname. | ||
| ospf | Dictionary | OSPF interface configuration. | |||
| enabled | Boolean | ||||
| point_to_point | Boolean | True |
|||
| area | String | 0 |
OSPF area ID. | ||
| cost | Integer | OSPF link cost. | |||
| authentication | String | Valid Values: - simple- message-digest |
|||
| simple_auth_key | String | Password used with simple authentication. | |||
| message_digest_keys | List, items: Dictionary | ||||
| - id | Integer | ||||
| hash_algorithm | String | sha512 |
Valid Values: - md5- sha1- sha256- sha384- sha512 |
||
| key | String | Type 7 encrypted key. | |||
| ospf | Dictionary | OSPF interface configuration. | |||
| enabled | Boolean | ||||
| point_to_point | Boolean | True |
|||
| area | String | 0 |
OSPF area ID. | ||
| cost | Integer | OSPF link cost. | |||
| authentication | String | Valid Values: - simple- message-digest |
|||
| simple_auth_key | String | Password used with simple authentication. | |||
| message_digest_keys | List, items: Dictionary | ||||
| - id | Integer | ||||
| hash_algorithm | String | sha512 |
Valid Values: - md5- sha1- sha256- sha384- sha512 |
||
| key | String | Type 7 encrypted key. |
<network_services_keys.name>:
# Specify a tenant name.
# Tenant provide a construct to group L3 VRFs and L2 VLANs.
# Networks services can be filtered by tenant name.
- name: <str; required; unique>
# VRFs will only be configured on a node if any of the underlying objects like `svis` or `l3_interfaces` apply to the node.
#
# It is recommended to only define a VRF in one Tenant. If the same VRF name is used across multiple tenants and those tenants
# are accepted by `filter.tenants` on the node, any object set under the duplicate VRFs must either be unique or be an exact match.
#
# VRF "default" is partially supported under network-services. Currently the supported options for "default" vrf are route-target,
# route-distinguisher settings, structured_config, raw_eos_cli in bgp and SVIs are the only supported interface type.
# Vlan-aware-bundles are supported as well inside default vrf. OSPF is not supported currently.
vrfs:
- name: <str; required; unique>
# Router OSPF configuration.
# This will create an OSPF routing instance in the tenant VRF. If there is no nodes definition, the OSPF instance will be
# created on all leafs where the VRF is deployed. This will also cause automatic OSPF redistribution into BGP unless
# explicitly turned off with "redistribute_ospf: false".
ospf:
enabled: <bool>
# If not set, "vrf_id" will be used.
process_id: <int>
# If not set, switch router_id will be used.
router_id: <str>
max_lsa: <int>
bfd: <bool; default=False>
redistribute_bgp:
enabled: <bool; default=True>
# Route-map name.
route_map: <str>
redistribute_connected:
enabled: <bool; default=False>
# Route-map name.
route_map: <str>
nodes:
# Hostname.
- <str>
# Non-selectively enabling or disabling redistribute ospf inside the VRF.
redistribute_ospf: <bool; default=True>
# List of SVIs.
# This will create both the L3 SVI and L2 VLAN based on filters applied to the node.
svis:
# SVI interface id and VLAN id.
- id: <int; 1-4096; required; unique>
# Define node specific configuration, such as unique IP addresses.
# Any keys set here will be merged onto the SVI config, except `structured_config` keys which will replace the `structured_config` set on SVI level.
nodes:
# l3_leaf inventory hostname.
- node: <str; required; unique>
# OSPF interface configuration.
ospf:
enabled: <bool>
point_to_point: <bool; default=True>
# OSPF area ID.
area: <str; default="0">
# OSPF link cost.
cost: <int>
authentication: <str; "simple" | "message-digest">
# Password used with simple authentication.
simple_auth_key: <str>
message_digest_keys:
- id: <int>
hash_algorithm: <str; "md5" | "sha1" | "sha256" | "sha384" | "sha512"; default="sha512">
# Type 7 encrypted key.
key: <str>
# OSPF interface configuration.
ospf:
enabled: <bool>
point_to_point: <bool; default=True>
# OSPF area ID.
area: <str; default="0">
# OSPF link cost.
cost: <int>
authentication: <str; "simple" | "message-digest">
# Password used with simple authentication.
simple_auth_key: <str>
message_digest_keys:
- id: <int>
hash_algorithm: <str; "md5" | "sha1" | "sha256" | "sha384" | "sha512"; default="sha512">
# Type 7 encrypted key.
key: <str>
# Profiles to share common settings for SVIs under `<network_services_key>.[].vrfs.svis`.
# Keys are the same used under SVIs. Keys defined under SVIs take precedence.
# Note: structured configuration is not merged recursively and will be taken directly from the most specific level in the following order:
# 1. svi.nodes[inventory_hostname].structured_config
# 2. svi_profile.nodes[inventory_hostname].structured_config
# 3. svi_parent_profile.nodes[inventory_hostname].structured_config
# 4. svi.structured_config
# 5. svi_profile.structured_config
# 6. svi_parent_profile.structured_config
svi_profiles:
# Profile name.
- profile: <str; required; unique>
# Define node specific configuration, such as unique IP addresses.
# Any keys set here will be merged onto the SVI config, except `structured_config` keys which will replace the `structured_config` set on SVI level.
nodes:
# l3_leaf inventory hostname.
- node: <str; required; unique>
# OSPF interface configuration.
ospf:
enabled: <bool>
point_to_point: <bool; default=True>
# OSPF area ID.
area: <str; default="0">
# OSPF link cost.
cost: <int>
authentication: <str; "simple" | "message-digest">
# Password used with simple authentication.
simple_auth_key: <str>
message_digest_keys:
- id: <int>
hash_algorithm: <str; "md5" | "sha1" | "sha256" | "sha384" | "sha512"; default="sha512">
# Type 7 encrypted key.
key: <str>
# OSPF interface configuration.
ospf:
enabled: <bool>
point_to_point: <bool; default=True>
# OSPF area ID.
area: <str; default="0">
# OSPF link cost.
cost: <int>
authentication: <str; "simple" | "message-digest">
# Password used with simple authentication.
simple_auth_key: <str>
message_digest_keys:
- id: <int>
hash_algorithm: <str; "md5" | "sha1" | "sha256" | "sha384" | "sha512"; default="sha512">
# Type 7 encrypted key.
key: <str>
Network services L2 VLANs configuration¶
| Variable | Type | Required | Default | Value Restrictions | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| <network_services_keys.name> | List, items: Dictionary | ||||
| - name | String | Required, Unique | Specify a tenant name. Tenant provide a construct to group L3 VRFs and L2 VLANs. Networks services can be filtered by tenant name. |
||
| l2vlans | List, items: Dictionary | Define L2 network services organized by vlan id. | |||
| - id | Integer | Required | Min: 1 Max: 4094 |
VLAN ID. | |
| vni_override | Integer | Min: 1 Max: 16777215 |
By default the VNI will be derived from mac_vrf_vni_base. The vni_override, allows to override this value and statically define it. |
||
| rt_override | String | By default the MAC VRF RT will be derived from mac_vrf_id_base + vlan_id. The rt_override allows us to override this value and statically define it. rt_override will default to vni_override if set. rt_override supports two formats: - A single number which will be used in the RT fields instead of mac_vrf_id/mac_vrf_vni (see ‘overlay_rt_type’ for details). - A full RT string with colon separator which will override the full RT. |
|||
| rd_override | String | By default the MAC VRF RD will be derived from mac_vrf_id_base + vlan_id. The rt_override allows us to override this value and statically define it. rd_override will default to rt_override or vni_override if set. rd_override supports two formats: - A single number which will be used in the RD assigned number field instead of mac_vrf_id/mac_vrf_vni (see ‘overlay_rd_type’ for details). - A full RD string with colon separator which will override the full RD. |
|||
| name | String | Required | VLAN name. | ||
| tags | List, items: String | Tags leveraged for networks services filtering. Tags are matched against filter.tags defined under node type settings. Tags are also matched against the node_group name under node type settings. |
|||
| - <str> | String | all |
|||
| vxlan | Boolean | True |
Extend this L2VLAN over VXLAN. | ||
| spanning_tree_priority | Integer | Setting spanning-tree priority per VLAN is only supported with spanning_tree_mode: rapid-pvst under node type settings.The default priority for rapid-PVST is set under the node type settings with spanning_tree_priority (default=32768). |
|||
| evpn_vlan_bundle | String | Name of a bundle defined under ‘evpn_vlan_bundles’ to inherit configuration. The common option “evpn_vlan_aware_bundles” is disregarded for this option. |
|||
| trunk_groups | List, items: String | ||||
| - <str> | String | Trunk groups are used for limiting vlans to trunk ports assigned to the same trunk group. Requires enable_trunk_groups: true. |
|||
| bgp | Dictionary | ||||
| structured_config | Dictionary | Custom structured config added under router_bgp.vlans.[id= This configuration will not be applied to vlan aware bundles. |
|||
| raw_eos_cli | String | EOS cli commands rendered on router_bgp.vlans. This configuration will not be applied to vlan aware bundles. |
<network_services_keys.name>:
# Specify a tenant name.
# Tenant provide a construct to group L3 VRFs and L2 VLANs.
# Networks services can be filtered by tenant name.
- name: <str; required; unique>
# Define L2 network services organized by vlan id.
l2vlans:
# VLAN ID.
- id: <int; 1-4094; required; unique>
# By default the VNI will be derived from mac_vrf_vni_base.
# The vni_override, allows to override this value and statically define it.
vni_override: <int; 1-16777215>
# By default the MAC VRF RT will be derived from mac_vrf_id_base + vlan_id.
# The rt_override allows us to override this value and statically define it.
# rt_override will default to vni_override if set.
#
# rt_override supports two formats:
# - A single number which will be used in the RT fields instead of mac_vrf_id/mac_vrf_vni (see 'overlay_rt_type' for details).
# - A full RT string with colon separator which will override the full RT.
rt_override: <str>
# By default the MAC VRF RD will be derived from mac_vrf_id_base + vlan_id.
# The rt_override allows us to override this value and statically define it.
# rd_override will default to rt_override or vni_override if set.
#
# rd_override supports two formats:
# - A single number which will be used in the RD assigned number field instead of mac_vrf_id/mac_vrf_vni (see 'overlay_rd_type' for details).
# - A full RD string with colon separator which will override the full RD.
rd_override: <str>
# VLAN name.
name: <str; required>
# Tags leveraged for networks services filtering.
# Tags are matched against filter.tags defined under node type settings.
# Tags are also matched against the node_group name under node type settings.
tags:
- <str; default="all">
# Extend this L2VLAN over VXLAN.
vxlan: <bool; default=True>
# Setting spanning-tree priority per VLAN is only supported with `spanning_tree_mode: rapid-pvst` under node type settings.
# The default priority for rapid-PVST is set under the node type settings with `spanning_tree_priority` (default=32768).
spanning_tree_priority: <int>
# Name of a bundle defined under 'evpn_vlan_bundles' to inherit configuration.
# The common option "evpn_vlan_aware_bundles" is disregarded for this option.
evpn_vlan_bundle: <str>
trunk_groups:
# Trunk groups are used for limiting vlans to trunk ports assigned to the same trunk group.
# Requires enable_trunk_groups: true.
- <str>
bgp:
# Custom structured config added under router_bgp.vlans.[id=<vlan>] for eos_cli_config_gen.
# This configuration will not be applied to vlan aware bundles.
structured_config: <dict>
# EOS cli commands rendered on router_bgp.vlans.
# This configuration will not be applied to vlan aware bundles.
raw_eos_cli: <str>
Network services point-to-point services configuration¶
| Variable | Type | Required | Default | Value Restrictions | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| <network_services_keys.name> | List, items: Dictionary | ||||
| - name | String | Required, Unique | Specify a tenant name. Tenant provide a construct to group L3 VRFs and L2 VLANs. Networks services can be filtered by tenant name. |
||
| pseudowire_rt_base | Integer | Pseudowire RT base, used to generate route targets for VPWS services. Avoid overlapping route target spaces between different services. |
|||
| point_to_point_services | List, items: Dictionary | Point to point services (pseudowires). Only supported for node types with “network_services.l1: true”. By default this is only set for node type “pe” with “design.type: mpls” |
|||
| - name | String | Required, Unique | Pseudowire name. | ||
| type | String | vpws-pseudowire |
Valid Values: - vpws-pseudowire |
||
| subinterfaces | List, items: Dictionary | Subinterfaces will create subinterfaces and additional pseudowires/patch panel config for each endpoint. | |||
| - number | Integer | Required, Unique | Subinterface number. | ||
| endpoints | List, items: Dictionary | Min Length: 2 Max Length: 2 |
Pseudowire terminating endpoints. Must have exactly two items. | ||
| - id | Integer | Required | Pseudowire ID on this endpoint. | ||
| nodes | List, items: String | Required | Min Length: 1 | Usually one node. With ESI multihoming we support two nodes per pseudowire endpoint. | |
| - <str> | String | ||||
| interfaces | List, items: String | Required | Min Length: 1 | Interfaces patched to the pseudowire on this endpoints. The list of interfaces is mapped to the list of nodes, so they must have the same length. |
|
| - <str> | String | ||||
| port_channel | Dictionary | ||||
| mode | String | Valid Values: - active- on |
|||
| short_esi | String | ||||
| lldp_disable | Boolean | Disable LLDP RX/TX on port mode pseudowire services. |
<network_services_keys.name>:
# Specify a tenant name.
# Tenant provide a construct to group L3 VRFs and L2 VLANs.
# Networks services can be filtered by tenant name.
- name: <str; required; unique>
# Pseudowire RT base, used to generate route targets for VPWS services.
# Avoid overlapping route target spaces between different services.
pseudowire_rt_base: <int>
# Point to point services (pseudowires).
# Only supported for node types with "network_services.l1: true".
# By default this is only set for node type "pe" with "design.type: mpls"
point_to_point_services:
# Pseudowire name.
- name: <str; required; unique>
type: <str; "vpws-pseudowire"; default="vpws-pseudowire">
# Subinterfaces will create subinterfaces and additional pseudowires/patch panel config for each endpoint.
subinterfaces:
# Subinterface number.
- number: <int; required; unique>
# Pseudowire terminating endpoints. Must have exactly two items.
endpoints: # 2-2 items
# Pseudowire ID on this endpoint.
- id: <int; required>
# Usually one node. With ESI multihoming we support two nodes per pseudowire endpoint.
nodes: # >=1 items; required
- <str>
# Interfaces patched to the pseudowire on this endpoints.
# The list of interfaces is mapped to the list of nodes, so they must have the same length.
interfaces: # >=1 items; required
- <str>
port_channel:
mode: <str; "active" | "on">
short_esi: <str>
# Disable LLDP RX/TX on port mode pseudowire services.
lldp_disable: <bool>
Network services multicast configuration¶
| Variable | Type | Required | Default | Value Restrictions | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| <network_services_keys.name> | List, items: Dictionary | ||||
| - name | String | Required, Unique | Specify a tenant name. Tenant provide a construct to group L3 VRFs and L2 VLANs. Networks services can be filtered by tenant name. |
||
| evpn_l2_multicast | Dictionary | Enable EVPN L2 Multicast for all SVIs and l2vlans within Tenant. - Multicast group binding is created only for Multicast traffic. BULL traffic will use ingress-replication. - Configures binding between VXLAN, VLAN, and multicast group IPv4 address using the following formula: < evpn_l2_multicast.underlay_l2_multicast_group_ipv4_pool > + < vlan_id - 1 > + < evpn_l2_multicast.underlay_l2_multicast_group_ipv4_pool_offset >. - The recommendation is to assign a /20 block within the 232.0.0.0/8 Source-Specific Multicast range. - Enables redistribute igmp on the router bgp MAC VRF.- When evpn_l2_multicast.enabled is true for a VLAN or a tenant, “igmp snooping” and “igmp snooping querier” will always be enabled - overriding those individual settings. - Requires evpn_multicast to also be set to true. |
|||
| enabled | Boolean | ||||
| underlay_l2_multicast_group_ipv4_pool | String | IPv4_address/Mask. | |||
| underlay_l2_multicast_group_ipv4_pool_offset | Integer | ||||
| evpn_l3_multicast | Dictionary | Enable L3 Multicast for all SVIs and l3vlans within Tenant. - In the evpn-l3ls design type, this enables L3 EVPN Multicast (aka OISM)’. - Multicast group binding for VRF is created only for Multicast traffic. BULL traffic will use ingress-replication. - Configures binding between VXLAN, VLAN, and multicast group IPv4 address using the following formula: < l3_multicast.evpn_underlay_l3_multicast_group_ipv4_pool > + < vrf_vni - 1 > + < l3_multicast.evpn_underlay_l3_multicast_group_ipv4_pool_offset >. - The recommendation is to assign a /20 block within the 232.0.0.0/8 Source-Specific Multicast range. - If enabled on an SVI using the anycast default gateway feature, a diagnostic loopback (see below) MUST be configured to source IGMP traffic. - Enables evpn multicast on the router bgp VRF.- When enabled on an SVI: - If switch is part of an MLAG pair, enables “pim ipv4 sparse-mode” on the SVI. - If switch is standalone or A-A MH, enables “ip igmp” on the SVI. - If “ip address virtual” is configured, enables “pim ipv4 local-interface” and uses the diagnostic Loopback defined in the VRF - Requires evpn_multicast to also be set to true. |
|||
| enabled | Boolean | ||||
| evpn_underlay_l3_multicast_group_ipv4_pool | String | Required | IPv4_address/Mask. | ||
| evpn_underlay_l3_multicast_group_ipv4_pool_offset | Integer | ||||
| evpn_peg | List, items: Dictionary | For each group of nodes, allow configuration of EVPN PEG options. The first group of settings where the device’s hostname is present in the ‘nodes’ list will be used. |
|||
| - nodes | List, items: String | A description will be applied to all nodes with RP addresses configured if not set. | |||
| - <str> | String | ||||
| transit | Boolean | Enable EVPN PEG transit mode. | |||
| pim_rp_addresses | List, items: Dictionary | For each group of nodes, allow configuration of RP Addresses & associated groups. |
|||
| - rps | List, items: String | Min Length: 1 | List of Rendevouz Points. | ||
| - <str> | String | RP address. | |||
| nodes | List, items: String | Restrict configuration to specific nodes. Configuration Will be applied to all nodes if not set. |
|||
| - <str> | String | ||||
| groups | List, items: String | ||||
| - <str> | String | Group_prefix/mask. | |||
| access_list_name | String | List of groups to associate with the RP address set in ‘rp’. If access_list_name is set, a standard access-list will be configured matching these groups. Otherwise the groups are configured directly on the RP command. |
|||
| igmp_snooping_querier | Dictionary | Enable IGMP snooping querier for each SVI/l2vlan within tenant, by default using IP address of Loopback 0. When enabled, IGMP snooping querier will only be configured on L3 devices, i.e., uplink_type: p2p. |
|||
| enabled | Boolean | Will be enabled automatically if “evpn_l2_multicast” is enabled. | |||
| source_address | String | Format: ipv4 | Default IP address of Loopback0. | ||
| version | Integer | 2 |
Valid Values: - 1- 2- 3 |
||
| vrfs | List, items: Dictionary | VRFs will only be configured on a node if any of the underlying objects like svis or l3_interfaces apply to the node.It is recommended to only define a VRF in one Tenant. If the same VRF name is used across multiple tenants and those tenants are accepted by filter.tenants on the node, any object set under the duplicate VRFs must either be unique or be an exact match.VRF “default” is partially supported under network-services. Currently the supported options for “default” vrf are route-target, route-distinguisher settings, structured_config, raw_eos_cli in bgp and SVIs are the only supported interface type. Vlan-aware-bundles are supported as well inside default vrf. OSPF is not supported currently. |
|||
| - name | String | Required, Unique | |||
| evpn_l3_multicast | Dictionary | Explicitly enable or disable evpn_l3_multicast to override setting of <network_services_key>.[].evpn_l3_multicast.enabled.Allow override of <network_services_key>.[].evpn_l3_multicast node_settings.Requires evpn_multicast to also be set to true. |
|||
| enabled | Boolean | ||||
| evpn_peg | List, items: Dictionary | For each group of nodes, allow configuration of EVPN PEG features. | |||
| - nodes | List, items: String | Restrict configuration to specific nodes. Will apply to all nodes with RP addresses configured if not set. |
|||
| - <str> | String | ||||
| transit | Boolean | False |
Enable EVPN PEG transit mode. | ||
| pim_rp_addresses | List, items: Dictionary | For each group of nodes, allow configuration of RP Addresses & associated groups. |
|||
| - rps | List, items: String | A minimum of one RP must be specified. | |||
| - <str> | String | RP address. | |||
| nodes | List, items: String | Restrict configuration to specific nodes. Configuration Will be applied to all nodes if not set. |
|||
| - <str> | String | ||||
| groups | List, items: String | ||||
| - <str> | String | Group_prefix/mask. | |||
| access_list_name | String | List of groups to associate with the RP addresses set in ‘rps’. If access_list_name is set, a standard access-list will be configured matching these groups. Otherwise the groups are configured directly on the RP command. |
|||
| evpn_l2_multi_domain | Boolean | Explicitly extend all VLANs/VLAN-Aware Bundles inside the VRF to remote EVPN domains. Overrides <network_services_key>.[].evpn_l2_multi_domain. |
|||
| svis | List, items: Dictionary | List of SVIs. This will create both the L3 SVI and L2 VLAN based on filters applied to the node. |
|||
| - id | Integer | Required | Min: 1 Max: 4096 |
SVI interface id and VLAN id. | |
| nodes | List, items: Dictionary | Define node specific configuration, such as unique IP addresses. Any keys set here will be merged onto the SVI config, except structured_config keys which will replace the structured_config set on SVI level. |
|||
| - node | String | Required, Unique | l3_leaf inventory hostname. | ||
| evpn_l2_multicast | Dictionary | Explicitly enable or disable evpn_l2_multicast to override setting of <network_services_key>.[].evpn_l2_multicast.enabled.When evpn_l2_multicast.enabled is set to true for a vlan or a tenant, “igmp snooping” and “igmp snooping querier” will always be enabled, overriding those individual settings. Requires evpn_multicast to also be set to true. |
|||
| enabled | Boolean | ||||
| evpn_l3_multicast | Dictionary | Explicitly enable or disable evpn_l3_multicast to override setting of <network_services_key>.[].evpn_l3_multicast.enabled and <network_services_key>.[].vrfs.[].evpn_l3_multicast.enabled.Requires evpn_multicast to also be set to true. |
|||
| enabled | Boolean | ||||
| igmp_snooping_enabled | Boolean | Enable IGMP Snooping (Enabled by default on EOS). | |||
| igmp_snooping_querier | Dictionary | ||||
| enabled | Boolean | Will be enabled automatically if evpn_l2_multicast is enabled. | |||
| source_address | String | IPv4_address If not set, IP address of “Loopback0” will be used. |
|||
| version | Integer | Valid Values: - 1- 2- 3 |
IGMP Version (By default EOS uses IGMP version 2 for IGMP querier). | ||
| evpn_l2_multicast | Dictionary | Explicitly enable or disable evpn_l2_multicast to override setting of <network_services_key>.[].evpn_l2_multicast.enabled.When evpn_l2_multicast.enabled is set to true for a vlan or a tenant, “igmp snooping” and “igmp snooping querier” will always be enabled, overriding those individual settings. Requires evpn_multicast to also be set to true. |
|||
| enabled | Boolean | ||||
| evpn_l3_multicast | Dictionary | Explicitly enable or disable evpn_l3_multicast to override setting of <network_services_key>.[].evpn_l3_multicast.enabled and <network_services_key>.[].vrfs.[].evpn_l3_multicast.enabled.Requires evpn_multicast to also be set to true. |
|||
| enabled | Boolean | ||||
| igmp_snooping_enabled | Boolean | Enable IGMP Snooping (Enabled by default on EOS). | |||
| igmp_snooping_querier | Dictionary | ||||
| enabled | Boolean | Will be enabled automatically if evpn_l2_multicast is enabled. | |||
| source_address | String | IPv4_address If not set, IP address of “Loopback0” will be used. |
|||
| version | Integer | Valid Values: - 1- 2- 3 |
IGMP Version (By default EOS uses IGMP version 2 for IGMP querier). | ||
| l2vlans | List, items: Dictionary | Define L2 network services organized by vlan id. | |||
| - id | Integer | Required | Min: 1 Max: 4094 |
VLAN ID. | |
| evpn_l2_multicast | Dictionary | Explicitly enable or disable evpn_l2_multicast to override setting of <network_services_key>.[].evpn_l2_multicast.enabled.When evpn_l2_multicast.enabled is set to true for a vlan or a tenant, igmp snooping and igmp snooping querier will always be enabled, overriding those individual settings. Requires evpn_multicast to also be set to true. |
|||
| enabled | Boolean | ||||
| igmp_snooping_enabled | Boolean | True |
Activate or deactivate IGMP snooping. | ||
| igmp_snooping_querier | Dictionary | Enable igmp snooping querier, by default using IP address of Loopback 0. When enabled, igmp snooping querier will only be configured on l3 devices, i.e., uplink_type: p2p. |
|||
| enabled | Boolean | Will be enabled automatically if evpn_l2_multicast is enabled. | |||
| source_address | String | IPv4_address If not set, IP address of “Loopback0” will be used. |
|||
| version | Integer | 2 |
Valid Values: - 1- 2- 3 |
||
| svi_profiles | List, items: Dictionary | Profiles to share common settings for SVIs under <network_services_key>.[].vrfs.svis.Keys are the same used under SVIs. Keys defined under SVIs take precedence. Note: structured configuration is not merged recursively and will be taken directly from the most specific level in the following order: 1. svi.nodes[inventory_hostname].structured_config 2. svi_profile.nodes[inventory_hostname].structured_config 3. svi_parent_profile.nodes[inventory_hostname].structured_config 4. svi.structured_config 5. svi_profile.structured_config 6. svi_parent_profile.structured_config |
|||
| - profile | String | Required, Unique | Profile name. | ||
| nodes | List, items: Dictionary | Define node specific configuration, such as unique IP addresses. Any keys set here will be merged onto the SVI config, except structured_config keys which will replace the structured_config set on SVI level. |
|||
| - node | String | Required, Unique | l3_leaf inventory hostname. | ||
| evpn_l2_multicast | Dictionary | Explicitly enable or disable evpn_l2_multicast to override setting of <network_services_key>.[].evpn_l2_multicast.enabled.When evpn_l2_multicast.enabled is set to true for a vlan or a tenant, “igmp snooping” and “igmp snooping querier” will always be enabled, overriding those individual settings. Requires evpn_multicast to also be set to true. |
|||
| enabled | Boolean | ||||
| evpn_l3_multicast | Dictionary | Explicitly enable or disable evpn_l3_multicast to override setting of <network_services_key>.[].evpn_l3_multicast.enabled and <network_services_key>.[].vrfs.[].evpn_l3_multicast.enabled.Requires evpn_multicast to also be set to true. |
|||
| enabled | Boolean | ||||
| igmp_snooping_enabled | Boolean | Enable IGMP Snooping (Enabled by default on EOS). | |||
| igmp_snooping_querier | Dictionary | ||||
| enabled | Boolean | Will be enabled automatically if evpn_l2_multicast is enabled. | |||
| source_address | String | IPv4_address If not set, IP address of “Loopback0” will be used. |
|||
| version | Integer | Valid Values: - 1- 2- 3 |
IGMP Version (By default EOS uses IGMP version 2 for IGMP querier). | ||
| evpn_l2_multicast | Dictionary | Explicitly enable or disable evpn_l2_multicast to override setting of <network_services_key>.[].evpn_l2_multicast.enabled.When evpn_l2_multicast.enabled is set to true for a vlan or a tenant, “igmp snooping” and “igmp snooping querier” will always be enabled, overriding those individual settings. Requires evpn_multicast to also be set to true. |
|||
| enabled | Boolean | ||||
| evpn_l3_multicast | Dictionary | Explicitly enable or disable evpn_l3_multicast to override setting of <network_services_key>.[].evpn_l3_multicast.enabled and <network_services_key>.[].vrfs.[].evpn_l3_multicast.enabled.Requires evpn_multicast to also be set to true. |
|||
| enabled | Boolean | ||||
| igmp_snooping_enabled | Boolean | Enable IGMP Snooping (Enabled by default on EOS). | |||
| igmp_snooping_querier | Dictionary | ||||
| enabled | Boolean | Will be enabled automatically if evpn_l2_multicast is enabled. | |||
| source_address | String | IPv4_address If not set, IP address of “Loopback0” will be used. |
|||
| version | Integer | Valid Values: - 1- 2- 3 |
IGMP Version (By default EOS uses IGMP version 2 for IGMP querier). |
<network_services_keys.name>:
# Specify a tenant name.
# Tenant provide a construct to group L3 VRFs and L2 VLANs.
# Networks services can be filtered by tenant name.
- name: <str; required; unique>
# Enable EVPN L2 Multicast for all SVIs and l2vlans within Tenant.
# - Multicast group binding is created only for Multicast traffic. BULL traffic will use ingress-replication.
# - Configures binding between VXLAN, VLAN, and multicast group IPv4 address using the following formula:
# < evpn_l2_multicast.underlay_l2_multicast_group_ipv4_pool > + < vlan_id - 1 > + < evpn_l2_multicast.underlay_l2_multicast_group_ipv4_pool_offset >.
# - The recommendation is to assign a /20 block within the 232.0.0.0/8 Source-Specific Multicast range.
# - Enables `redistribute igmp` on the router bgp MAC VRF.
# - When evpn_l2_multicast.enabled is true for a VLAN or a tenant, "igmp snooping" and "igmp snooping querier" will always be enabled - overriding those individual settings.
# - Requires `evpn_multicast` to also be set to `true`.
evpn_l2_multicast:
enabled: <bool>
# IPv4_address/Mask.
underlay_l2_multicast_group_ipv4_pool: <str>
underlay_l2_multicast_group_ipv4_pool_offset: <int>
# Enable L3 Multicast for all SVIs and l3vlans within Tenant.
# - In the evpn-l3ls design type, this enables L3 EVPN Multicast (aka OISM)'.
# - Multicast group binding for VRF is created only for Multicast traffic. BULL traffic will use ingress-replication.
# - Configures binding between VXLAN, VLAN, and multicast group IPv4 address using the following formula:
# < l3_multicast.evpn_underlay_l3_multicast_group_ipv4_pool > + < vrf_vni - 1 > + < l3_multicast.evpn_underlay_l3_multicast_group_ipv4_pool_offset >.
# - The recommendation is to assign a /20 block within the 232.0.0.0/8 Source-Specific Multicast range.
# - If enabled on an SVI using the anycast default gateway feature, a diagnostic loopback (see below) MUST be configured to source IGMP traffic.
# - Enables `evpn multicast` on the router bgp VRF.
# - When enabled on an SVI:
# - If switch is part of an MLAG pair, enables "pim ipv4 sparse-mode" on the SVI.
# - If switch is standalone or A-A MH, enables "ip igmp" on the SVI.
# - If "ip address virtual" is configured, enables "pim ipv4 local-interface" and uses the diagnostic Loopback defined in the VRF
# - Requires `evpn_multicast` to also be set to `true`.
evpn_l3_multicast:
enabled: <bool>
# IPv4_address/Mask.
evpn_underlay_l3_multicast_group_ipv4_pool: <str; required>
evpn_underlay_l3_multicast_group_ipv4_pool_offset: <int>
# For each group of nodes, allow configuration of EVPN PEG options.
# The first group of settings where the device's hostname is present in the 'nodes' list will be used.
evpn_peg:
# A description will be applied to all nodes with RP addresses configured if not set.
- nodes:
- <str>
# Enable EVPN PEG transit mode.
transit: <bool>
# For each group of nodes, allow configuration of RP Addresses & associated groups.
pim_rp_addresses:
# List of Rendevouz Points.
- rps: # >=1 items
# RP address.
- <str>
# Restrict configuration to specific nodes.
# Configuration Will be applied to all nodes if not set.
nodes:
- <str>
groups:
# Group_prefix/mask.
- <str>
# List of groups to associate with the RP address set in 'rp'.
# If access_list_name is set, a standard access-list will be configured matching these groups.
# Otherwise the groups are configured directly on the RP command.
access_list_name: <str>
# Enable IGMP snooping querier for each SVI/l2vlan within tenant, by default using IP address of Loopback 0.
# When enabled, IGMP snooping querier will only be configured on L3 devices, i.e., uplink_type: p2p.
igmp_snooping_querier:
# Will be enabled automatically if "evpn_l2_multicast" is enabled.
enabled: <bool>
# Default IP address of Loopback0.
source_address: <str>
version: <int; 1 | 2 | 3; default=2>
# VRFs will only be configured on a node if any of the underlying objects like `svis` or `l3_interfaces` apply to the node.
#
# It is recommended to only define a VRF in one Tenant. If the same VRF name is used across multiple tenants and those tenants
# are accepted by `filter.tenants` on the node, any object set under the duplicate VRFs must either be unique or be an exact match.
#
# VRF "default" is partially supported under network-services. Currently the supported options for "default" vrf are route-target,
# route-distinguisher settings, structured_config, raw_eos_cli in bgp and SVIs are the only supported interface type.
# Vlan-aware-bundles are supported as well inside default vrf. OSPF is not supported currently.
vrfs:
- name: <str; required; unique>
# Explicitly enable or disable evpn_l3_multicast to override setting of `<network_services_key>.[].evpn_l3_multicast.enabled`.
# Allow override of `<network_services_key>.[].evpn_l3_multicast` node_settings.
# Requires `evpn_multicast` to also be set to `true`.
evpn_l3_multicast:
enabled: <bool>
# For each group of nodes, allow configuration of EVPN PEG features.
evpn_peg:
# Restrict configuration to specific nodes.
# Will apply to all nodes with RP addresses configured if not set.
- nodes:
- <str>
# Enable EVPN PEG transit mode.
transit: <bool; default=False>
# For each group of nodes, allow configuration of RP Addresses & associated groups.
pim_rp_addresses:
# A minimum of one RP must be specified.
- rps:
# RP address.
- <str>
# Restrict configuration to specific nodes.
# Configuration Will be applied to all nodes if not set.
nodes:
- <str>
groups:
# Group_prefix/mask.
- <str>
# List of groups to associate with the RP addresses set in 'rps'.
# If access_list_name is set, a standard access-list will be configured matching these groups.
# Otherwise the groups are configured directly on the RP command.
access_list_name: <str>
# Explicitly extend all VLANs/VLAN-Aware Bundles inside the VRF to remote EVPN domains.
# Overrides `<network_services_key>.[].evpn_l2_multi_domain`.
evpn_l2_multi_domain: <bool>
# List of SVIs.
# This will create both the L3 SVI and L2 VLAN based on filters applied to the node.
svis:
# SVI interface id and VLAN id.
- id: <int; 1-4096; required; unique>
# Define node specific configuration, such as unique IP addresses.
# Any keys set here will be merged onto the SVI config, except `structured_config` keys which will replace the `structured_config` set on SVI level.
nodes:
# l3_leaf inventory hostname.
- node: <str; required; unique>
# Explicitly enable or disable evpn_l2_multicast to override setting of `<network_services_key>.[].evpn_l2_multicast.enabled`.
# When evpn_l2_multicast.enabled is set to true for a vlan or a tenant, "igmp snooping" and "igmp snooping querier" will always be enabled, overriding those individual settings.
# Requires `evpn_multicast` to also be set to `true`.
evpn_l2_multicast:
enabled: <bool>
# Explicitly enable or disable evpn_l3_multicast to override setting of `<network_services_key>.[].evpn_l3_multicast.enabled` and `<network_services_key>.[].vrfs.[].evpn_l3_multicast.enabled`.
# Requires `evpn_multicast` to also be set to `true`.
evpn_l3_multicast:
enabled: <bool>
# Enable IGMP Snooping (Enabled by default on EOS).
igmp_snooping_enabled: <bool>
igmp_snooping_querier:
# Will be enabled automatically if evpn_l2_multicast is enabled.
enabled: <bool>
# IPv4_address
# If not set, IP address of "Loopback0" will be used.
source_address: <str>
# IGMP Version (By default EOS uses IGMP version 2 for IGMP querier).
version: <int; 1 | 2 | 3>
# Explicitly enable or disable evpn_l2_multicast to override setting of `<network_services_key>.[].evpn_l2_multicast.enabled`.
# When evpn_l2_multicast.enabled is set to true for a vlan or a tenant, "igmp snooping" and "igmp snooping querier" will always be enabled, overriding those individual settings.
# Requires `evpn_multicast` to also be set to `true`.
evpn_l2_multicast:
enabled: <bool>
# Explicitly enable or disable evpn_l3_multicast to override setting of `<network_services_key>.[].evpn_l3_multicast.enabled` and `<network_services_key>.[].vrfs.[].evpn_l3_multicast.enabled`.
# Requires `evpn_multicast` to also be set to `true`.
evpn_l3_multicast:
enabled: <bool>
# Enable IGMP Snooping (Enabled by default on EOS).
igmp_snooping_enabled: <bool>
igmp_snooping_querier:
# Will be enabled automatically if evpn_l2_multicast is enabled.
enabled: <bool>
# IPv4_address
# If not set, IP address of "Loopback0" will be used.
source_address: <str>
# IGMP Version (By default EOS uses IGMP version 2 for IGMP querier).
version: <int; 1 | 2 | 3>
# Define L2 network services organized by vlan id.
l2vlans:
# VLAN ID.
- id: <int; 1-4094; required; unique>
# Explicitly enable or disable evpn_l2_multicast to override setting of `<network_services_key>.[].evpn_l2_multicast.enabled`.
# When evpn_l2_multicast.enabled is set to true for a vlan or a tenant, igmp snooping and igmp snooping querier will always be enabled, overriding those individual settings.
# Requires `evpn_multicast` to also be set to `true`.
evpn_l2_multicast:
enabled: <bool>
# Activate or deactivate IGMP snooping.
igmp_snooping_enabled: <bool; default=True>
# Enable igmp snooping querier, by default using IP address of Loopback 0.
# When enabled, igmp snooping querier will only be configured on l3 devices, i.e., uplink_type: p2p.
igmp_snooping_querier:
# Will be enabled automatically if evpn_l2_multicast is enabled.
enabled: <bool>
# IPv4_address
# If not set, IP address of "Loopback0" will be used.
source_address: <str>
version: <int; 1 | 2 | 3; default=2>
# Profiles to share common settings for SVIs under `<network_services_key>.[].vrfs.svis`.
# Keys are the same used under SVIs. Keys defined under SVIs take precedence.
# Note: structured configuration is not merged recursively and will be taken directly from the most specific level in the following order:
# 1. svi.nodes[inventory_hostname].structured_config
# 2. svi_profile.nodes[inventory_hostname].structured_config
# 3. svi_parent_profile.nodes[inventory_hostname].structured_config
# 4. svi.structured_config
# 5. svi_profile.structured_config
# 6. svi_parent_profile.structured_config
svi_profiles:
# Profile name.
- profile: <str; required; unique>
# Define node specific configuration, such as unique IP addresses.
# Any keys set here will be merged onto the SVI config, except `structured_config` keys which will replace the `structured_config` set on SVI level.
nodes:
# l3_leaf inventory hostname.
- node: <str; required; unique>
# Explicitly enable or disable evpn_l2_multicast to override setting of `<network_services_key>.[].evpn_l2_multicast.enabled`.
# When evpn_l2_multicast.enabled is set to true for a vlan or a tenant, "igmp snooping" and "igmp snooping querier" will always be enabled, overriding those individual settings.
# Requires `evpn_multicast` to also be set to `true`.
evpn_l2_multicast:
enabled: <bool>
# Explicitly enable or disable evpn_l3_multicast to override setting of `<network_services_key>.[].evpn_l3_multicast.enabled` and `<network_services_key>.[].vrfs.[].evpn_l3_multicast.enabled`.
# Requires `evpn_multicast` to also be set to `true`.
evpn_l3_multicast:
enabled: <bool>
# Enable IGMP Snooping (Enabled by default on EOS).
igmp_snooping_enabled: <bool>
igmp_snooping_querier:
# Will be enabled automatically if evpn_l2_multicast is enabled.
enabled: <bool>
# IPv4_address
# If not set, IP address of "Loopback0" will be used.
source_address: <str>
# IGMP Version (By default EOS uses IGMP version 2 for IGMP querier).
version: <int; 1 | 2 | 3>
# Explicitly enable or disable evpn_l2_multicast to override setting of `<network_services_key>.[].evpn_l2_multicast.enabled`.
# When evpn_l2_multicast.enabled is set to true for a vlan or a tenant, "igmp snooping" and "igmp snooping querier" will always be enabled, overriding those individual settings.
# Requires `evpn_multicast` to also be set to `true`.
evpn_l2_multicast:
enabled: <bool>
# Explicitly enable or disable evpn_l3_multicast to override setting of `<network_services_key>.[].evpn_l3_multicast.enabled` and `<network_services_key>.[].vrfs.[].evpn_l3_multicast.enabled`.
# Requires `evpn_multicast` to also be set to `true`.
evpn_l3_multicast:
enabled: <bool>
# Enable IGMP Snooping (Enabled by default on EOS).
igmp_snooping_enabled: <bool>
igmp_snooping_querier:
# Will be enabled automatically if evpn_l2_multicast is enabled.
enabled: <bool>
# IPv4_address
# If not set, IP address of "Loopback0" will be used.
source_address: <str>
# IGMP Version (By default EOS uses IGMP version 2 for IGMP querier).
version: <int; 1 | 2 | 3>
SVI profiles settings¶
SVI profiles can be leveraged to share common settings between SVIs.
- Keys are the same as those used under SVI settings, except for the
tagskey. - Keys defined under SVIs take precedence.
-
Structured configuration is not merged recursively and will be taken directly from the most specific level in the following order:
- svi.nodes[inventory_hostname].structured_config
- svi_profile.nodes[inventory_hostname].structured_config
- svi_parent_profile.nodes[inventory_hostname].structured_config
- svi.structured_config
- svi_profile.structured_config
- svi_parent_profile.structured_config
| Variable | Type | Required | Default | Value Restrictions | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| svi_profiles | List, items: Dictionary | Profiles to share common settings for SVIs under <network_services_key>.[].vrfs.svis.Keys are the same used under SVIs. Keys defined under SVIs take precedence. Note: structured configuration is not merged recursively and will be taken directly from the most specific level in the following order: 1. svi.nodes[inventory_hostname].structured_config 2. svi_profile.nodes[inventory_hostname].structured_config 3. svi_parent_profile.nodes[inventory_hostname].structured_config 4. svi.structured_config 5. svi_profile.structured_config 6. svi_parent_profile.structured_config |
|||
| - profile | String | Required, Unique | Profile name. | ||
| parent_profile | String | Parent SVI profile name to apply. svi_profiles can refer to another svi_profile to inherit settings in up to two levels (svi -> svi_profile -> svi_parent_profile). |
|||
| nodes | List, items: Dictionary | Define node specific configuration, such as unique IP addresses. Any keys set here will be merged onto the SVI config, except structured_config keys which will replace the structured_config set on SVI level. |
|||
| - node | String | Required, Unique | l3_leaf inventory hostname. | ||
| name | String | VLAN name. | |||
| enabled | Boolean | Enable or disable interface. | |||
| description | String | SVI description. By default set to VLAN name. |
|||
| ip_address | String | IPv4_address/Mask. Usually set under “nodes” to have unique IPv4 addresses per node. | |||
| ipv6_address | String | IPv6_address/Mask. Usually set under “nodes” to have unique IPv6 addresses per node. | |||
| ipv6_enable | Boolean | Explicitly enable/disable link-local IPv6 addressing. | |||
| ip_address_virtual | String | IPv4_address/Mask. IPv4 VXLAN Anycast IP address. Conserves IP addresses in VXLAN deployments as it doesn’t require unique IP addresses on each node. |
|||
| ipv6_address_virtual deprecated | String | IPv6_address/Mask. ipv6 address virtuals to configure VXLAN Anycast IP address (Optional). If both “ipv6_address_virtual” and “ipv6_address_virtuals” are set, all addresses will be configured. This key is deprecated. Support will be removed in AVD version 5.0.0. Use ipv6_address_virtuals instead. |
|||
| ipv6_address_virtuals | List, items: String | IPv6 VXLAN Anycast IP addresses. Conserves IPv6 addresses in VXLAN deployments as it doesn’t require unique IPv6 addresses on each node. |
|||
| - <str> | String | IPv6_address/Mask. | |||
| ip_address_virtual_secondaries | List, items: String | Secondary IPv4 VXLAN Anycast IP addresses. | |||
| - <str> | String | IPv4_address/Mask. | |||
| ip_virtual_router_addresses | List, items: String | IPv4 VARP addresses. Requires an IP address to be configured on the SVI. If ip_address_virtual is also set, ip_virtual_router_addresses will take precedence if there is an ip_address configured for the node. |
|||
| - <str> | String | IPv4_address/Mask or IPv4_address. IPv4_address/Mask will also configure a static route to the SVI per best practice. |
|||
| ipv6_virtual_router_addresses | List, items: String | IPv6 VARP addresses. Requires an IPv6 address to be configured on the SVI. If ipv6_address_virtuals is also set, ipv6_virtual_router_addresses will take precedence if there is an ipv6_address configured for the node. |
|||
| - <str> | String | IPv6_address. | |||
| ip_helpers | List, items: Dictionary | IP helper for DHCP relay. | |||
| - ip_helper | String | Required, Unique | IPv4 DHCP server IP. | ||
| source_interface | String | Interface name to originate DHCP relay packets to DHCP server. | |||
| source_vrf | String | VRF to originate DHCP relay packets to DHCP server. If not set, EOS uses the VRF on the SVI. | |||
| vni_override | Integer | Min: 1 Max: 16777215 |
By default the VNI will be derived from “mac_vrf_vni_base”. The vni_override allows us to override this value and statically define it (optional). |
||
| rt_override | String | By default the MAC VRF RT will be derived from mac_vrf_id_base + vlan_id. The rt_override allows us to override this value and statically define it. rt_override will default to vni_override if set. rt_override supports two formats: - A single number which will be used in the RT fields instead of mac_vrf_id/mac_vrf_vni (see ‘overlay_rt_type’ for details). - A full RT string with colon separator which will override the full RT. |
|||
| rd_override | String | By default the MAC VRF RD will be derived from mac_vrf_id_base + vlan_id. The rt_override allows us to override this value and statically define it. rd_override will default to rt_override or vni_override if set. rd_override supports two formats: - A single number which will be used in the RD assigned number field instead of mac_vrf_id/mac_vrf_vni (see ‘overlay_rd_type’ for details). - A full RD string with colon separator which will override the full RD. |
|||
| trunk_groups | List, items: String | ||||
| - <str> | String | Trunk groups are used for limiting vlans to trunk ports assigned to the same trunk group. Requires “enable_trunk_groups: true”. |
|||
| vxlan | Boolean | True |
Extend this SVI over VXLAN. | ||
| spanning_tree_priority | Integer | Setting spanning-tree priority per VLAN is only supported with spanning_tree_mode: rapid-pvst under node type settings.The default priority for rapid-PVST is set under the node type settings with spanning_tree_priority (default=32768). |
|||
| mtu | Integer | Interface MTU. | |||
| bgp | Dictionary | ||||
| structured_config | Dictionary | Structured configuration and EOS CLI commands rendered on router_bgp.vlans.[id= This configuration will not be applied to vlan aware bundles. |
|||
| raw_eos_cli | String | EOS CLI rendered directly on the Router BGP, VLAN definition in the final EOS configuration. |
|||
| raw_eos_cli | String | EOS CLI rendered directly on the VLAN interface in the final EOS configuration. |
|||
| structured_config | Dictionary | Custom structured config added under vlan_interfaces.[name= |
|||
| name | String | VLAN name. | |||
| enabled | Boolean | Enable or disable interface. | |||
| description | String | SVI description. By default set to VLAN name. |
|||
| ip_address | String | IPv4_address/Mask. Usually set under “nodes” to have unique IPv4 addresses per node. | |||
| ipv6_address | String | IPv6_address/Mask. Usually set under “nodes” to have unique IPv6 addresses per node. | |||
| ipv6_enable | Boolean | Explicitly enable/disable link-local IPv6 addressing. | |||
| ip_address_virtual | String | IPv4_address/Mask. IPv4 VXLAN Anycast IP address. Conserves IP addresses in VXLAN deployments as it doesn’t require unique IP addresses on each node. |
|||
| ipv6_address_virtual deprecated | String | IPv6_address/Mask. ipv6 address virtuals to configure VXLAN Anycast IP address (Optional). If both “ipv6_address_virtual” and “ipv6_address_virtuals” are set, all addresses will be configured. This key is deprecated. Support will be removed in AVD version 5.0.0. Use ipv6_address_virtuals instead. |
|||
| ipv6_address_virtuals | List, items: String | IPv6 VXLAN Anycast IP addresses. Conserves IPv6 addresses in VXLAN deployments as it doesn’t require unique IPv6 addresses on each node. |
|||
| - <str> | String | IPv6_address/Mask. | |||
| ip_address_virtual_secondaries | List, items: String | Secondary IPv4 VXLAN Anycast IP addresses. | |||
| - <str> | String | IPv4_address/Mask. | |||
| ip_virtual_router_addresses | List, items: String | IPv4 VARP addresses. Requires an IP address to be configured on the SVI. If ip_address_virtual is also set, ip_virtual_router_addresses will take precedence if there is an ip_address configured for the node. |
|||
| - <str> | String | IPv4_address/Mask or IPv4_address. IPv4_address/Mask will also configure a static route to the SVI per best practice. |
|||
| ipv6_virtual_router_addresses | List, items: String | IPv6 VARP addresses. Requires an IPv6 address to be configured on the SVI. If ipv6_address_virtuals is also set, ipv6_virtual_router_addresses will take precedence if there is an ipv6_address configured for the node. |
|||
| - <str> | String | IPv6_address. | |||
| ip_helpers | List, items: Dictionary | IP helper for DHCP relay. | |||
| - ip_helper | String | Required, Unique | IPv4 DHCP server IP. | ||
| source_interface | String | Interface name to originate DHCP relay packets to DHCP server. | |||
| source_vrf | String | VRF to originate DHCP relay packets to DHCP server. If not set, EOS uses the VRF on the SVI. | |||
| vni_override | Integer | Min: 1 Max: 16777215 |
By default the VNI will be derived from “mac_vrf_vni_base”. The vni_override allows us to override this value and statically define it (optional). |
||
| rt_override | String | By default the MAC VRF RT will be derived from mac_vrf_id_base + vlan_id. The rt_override allows us to override this value and statically define it. rt_override will default to vni_override if set. rt_override supports two formats: - A single number which will be used in the RT fields instead of mac_vrf_id/mac_vrf_vni (see ‘overlay_rt_type’ for details). - A full RT string with colon separator which will override the full RT. |
|||
| rd_override | String | By default the MAC VRF RD will be derived from mac_vrf_id_base + vlan_id. The rt_override allows us to override this value and statically define it. rd_override will default to rt_override or vni_override if set. rd_override supports two formats: - A single number which will be used in the RD assigned number field instead of mac_vrf_id/mac_vrf_vni (see ‘overlay_rd_type’ for details). - A full RD string with colon separator which will override the full RD. |
|||
| trunk_groups | List, items: String | ||||
| - <str> | String | Trunk groups are used for limiting vlans to trunk ports assigned to the same trunk group. Requires “enable_trunk_groups: true”. |
|||
| vxlan | Boolean | True |
Extend this SVI over VXLAN. | ||
| spanning_tree_priority | Integer | Setting spanning-tree priority per VLAN is only supported with spanning_tree_mode: rapid-pvst under node type settings.The default priority for rapid-PVST is set under the node type settings with spanning_tree_priority (default=32768). |
|||
| mtu | Integer | Interface MTU. | |||
| bgp | Dictionary | ||||
| structured_config | Dictionary | Structured configuration and EOS CLI commands rendered on router_bgp.vlans.[id= This configuration will not be applied to vlan aware bundles. |
|||
| raw_eos_cli | String | EOS CLI rendered directly on the Router BGP, VLAN definition in the final EOS configuration. |
|||
| raw_eos_cli | String | EOS CLI rendered directly on the VLAN interface in the final EOS configuration. |
|||
| structured_config | Dictionary | Custom structured config added under vlan_interfaces.[name= |
# Profiles to share common settings for SVIs under `<network_services_key>.[].vrfs.svis`.
# Keys are the same used under SVIs. Keys defined under SVIs take precedence.
# Note: structured configuration is not merged recursively and will be taken directly from the most specific level in the following order:
# 1. svi.nodes[inventory_hostname].structured_config
# 2. svi_profile.nodes[inventory_hostname].structured_config
# 3. svi_parent_profile.nodes[inventory_hostname].structured_config
# 4. svi.structured_config
# 5. svi_profile.structured_config
# 6. svi_parent_profile.structured_config
svi_profiles:
# Profile name.
- profile: <str; required; unique>
# Parent SVI profile name to apply.
# svi_profiles can refer to another svi_profile to inherit settings in up to two levels (svi -> svi_profile -> svi_parent_profile).
parent_profile: <str>
# Define node specific configuration, such as unique IP addresses.
# Any keys set here will be merged onto the SVI config, except `structured_config` keys which will replace the `structured_config` set on SVI level.
nodes:
# l3_leaf inventory hostname.
- node: <str; required; unique>
# VLAN name.
name: <str>
# Enable or disable interface.
enabled: <bool>
# SVI description. By default set to VLAN name.
description: <str>
# IPv4_address/Mask. Usually set under "nodes" to have unique IPv4 addresses per node.
ip_address: <str>
# IPv6_address/Mask. Usually set under "nodes" to have unique IPv6 addresses per node.
ipv6_address: <str>
# Explicitly enable/disable link-local IPv6 addressing.
ipv6_enable: <bool>
# IPv4_address/Mask.
# IPv4 VXLAN Anycast IP address.
# Conserves IP addresses in VXLAN deployments as it doesn't require unique IP addresses on each node.
ip_address_virtual: <str>
# IPv6_address/Mask.
# ipv6 address virtuals to configure VXLAN Anycast IP address (Optional).
# If both "ipv6_address_virtual" and "ipv6_address_virtuals" are set, all addresses will be configured.
# This key is deprecated.
# Support will be removed in AVD version 5.0.0.
# Use <samp>ipv6_address_virtuals</samp> instead.
ipv6_address_virtual: <str>
# IPv6 VXLAN Anycast IP addresses.
# Conserves IPv6 addresses in VXLAN deployments as it doesn't require unique IPv6 addresses on each node.
ipv6_address_virtuals:
# IPv6_address/Mask.
- <str>
# Secondary IPv4 VXLAN Anycast IP addresses.
ip_address_virtual_secondaries:
# IPv4_address/Mask.
- <str>
# IPv4 VARP addresses.
# Requires an IP address to be configured on the SVI.
# If ip_address_virtual is also set, ip_virtual_router_addresses will take precedence
# _if_ there is an ip_address configured for the node.
ip_virtual_router_addresses:
# IPv4_address/Mask or IPv4_address.
# IPv4_address/Mask will also configure a static route to the SVI per best practice.
- <str>
# IPv6 VARP addresses.
# Requires an IPv6 address to be configured on the SVI.
# If ipv6_address_virtuals is also set, ipv6_virtual_router_addresses will take precedence
# _if_ there is an ipv6_address configured for the node.
ipv6_virtual_router_addresses:
# IPv6_address.
- <str>
# IP helper for DHCP relay.
ip_helpers:
# IPv4 DHCP server IP.
- ip_helper: <str; required; unique>
# Interface name to originate DHCP relay packets to DHCP server.
source_interface: <str>
# VRF to originate DHCP relay packets to DHCP server. If not set, EOS uses the VRF on the SVI.
source_vrf: <str>
# By default the VNI will be derived from "mac_vrf_vni_base".
# The vni_override allows us to override this value and statically define it (optional).
vni_override: <int; 1-16777215>
# By default the MAC VRF RT will be derived from mac_vrf_id_base + vlan_id.
# The rt_override allows us to override this value and statically define it.
# rt_override will default to vni_override if set.
#
# rt_override supports two formats:
# - A single number which will be used in the RT fields instead of mac_vrf_id/mac_vrf_vni (see 'overlay_rt_type' for details).
# - A full RT string with colon separator which will override the full RT.
rt_override: <str>
# By default the MAC VRF RD will be derived from mac_vrf_id_base + vlan_id.
# The rt_override allows us to override this value and statically define it.
# rd_override will default to rt_override or vni_override if set.
#
# rd_override supports two formats:
# - A single number which will be used in the RD assigned number field instead of mac_vrf_id/mac_vrf_vni (see 'overlay_rd_type' for details).
# - A full RD string with colon separator which will override the full RD.
rd_override: <str>
trunk_groups:
# Trunk groups are used for limiting vlans to trunk ports assigned to the same trunk group.
# Requires "enable_trunk_groups: true".
- <str>
# Extend this SVI over VXLAN.
vxlan: <bool; default=True>
# Setting spanning-tree priority per VLAN is only supported with `spanning_tree_mode: rapid-pvst` under node type settings.
# The default priority for rapid-PVST is set under the node type settings with `spanning_tree_priority` (default=32768).
spanning_tree_priority: <int>
# Interface MTU.
mtu: <int>
bgp:
# Structured configuration and EOS CLI commands rendered on router_bgp.vlans.[id=<vlan>].
# This configuration will not be applied to vlan aware bundles.
structured_config: <dict>
# EOS CLI rendered directly on the Router BGP, VLAN definition in the final EOS configuration.
raw_eos_cli: <str>
# EOS CLI rendered directly on the VLAN interface in the final EOS configuration.
raw_eos_cli: <str>
# Custom structured config added under vlan_interfaces.[name=<interface>] for eos_cli_config_gen.
structured_config: <dict>
# VLAN name.
name: <str>
# Enable or disable interface.
enabled: <bool>
# SVI description. By default set to VLAN name.
description: <str>
# IPv4_address/Mask. Usually set under "nodes" to have unique IPv4 addresses per node.
ip_address: <str>
# IPv6_address/Mask. Usually set under "nodes" to have unique IPv6 addresses per node.
ipv6_address: <str>
# Explicitly enable/disable link-local IPv6 addressing.
ipv6_enable: <bool>
# IPv4_address/Mask.
# IPv4 VXLAN Anycast IP address.
# Conserves IP addresses in VXLAN deployments as it doesn't require unique IP addresses on each node.
ip_address_virtual: <str>
# IPv6_address/Mask.
# ipv6 address virtuals to configure VXLAN Anycast IP address (Optional).
# If both "ipv6_address_virtual" and "ipv6_address_virtuals" are set, all addresses will be configured.
# This key is deprecated.
# Support will be removed in AVD version 5.0.0.
# Use <samp>ipv6_address_virtuals</samp> instead.
ipv6_address_virtual: <str>
# IPv6 VXLAN Anycast IP addresses.
# Conserves IPv6 addresses in VXLAN deployments as it doesn't require unique IPv6 addresses on each node.
ipv6_address_virtuals:
# IPv6_address/Mask.
- <str>
# Secondary IPv4 VXLAN Anycast IP addresses.
ip_address_virtual_secondaries:
# IPv4_address/Mask.
- <str>
# IPv4 VARP addresses.
# Requires an IP address to be configured on the SVI.
# If ip_address_virtual is also set, ip_virtual_router_addresses will take precedence
# _if_ there is an ip_address configured for the node.
ip_virtual_router_addresses:
# IPv4_address/Mask or IPv4_address.
# IPv4_address/Mask will also configure a static route to the SVI per best practice.
- <str>
# IPv6 VARP addresses.
# Requires an IPv6 address to be configured on the SVI.
# If ipv6_address_virtuals is also set, ipv6_virtual_router_addresses will take precedence
# _if_ there is an ipv6_address configured for the node.
ipv6_virtual_router_addresses:
# IPv6_address.
- <str>
# IP helper for DHCP relay.
ip_helpers:
# IPv4 DHCP server IP.
- ip_helper: <str; required; unique>
# Interface name to originate DHCP relay packets to DHCP server.
source_interface: <str>
# VRF to originate DHCP relay packets to DHCP server. If not set, EOS uses the VRF on the SVI.
source_vrf: <str>
# By default the VNI will be derived from "mac_vrf_vni_base".
# The vni_override allows us to override this value and statically define it (optional).
vni_override: <int; 1-16777215>
# By default the MAC VRF RT will be derived from mac_vrf_id_base + vlan_id.
# The rt_override allows us to override this value and statically define it.
# rt_override will default to vni_override if set.
#
# rt_override supports two formats:
# - A single number which will be used in the RT fields instead of mac_vrf_id/mac_vrf_vni (see 'overlay_rt_type' for details).
# - A full RT string with colon separator which will override the full RT.
rt_override: <str>
# By default the MAC VRF RD will be derived from mac_vrf_id_base + vlan_id.
# The rt_override allows us to override this value and statically define it.
# rd_override will default to rt_override or vni_override if set.
#
# rd_override supports two formats:
# - A single number which will be used in the RD assigned number field instead of mac_vrf_id/mac_vrf_vni (see 'overlay_rd_type' for details).
# - A full RD string with colon separator which will override the full RD.
rd_override: <str>
trunk_groups:
# Trunk groups are used for limiting vlans to trunk ports assigned to the same trunk group.
# Requires "enable_trunk_groups: true".
- <str>
# Extend this SVI over VXLAN.
vxlan: <bool; default=True>
# Setting spanning-tree priority per VLAN is only supported with `spanning_tree_mode: rapid-pvst` under node type settings.
# The default priority for rapid-PVST is set under the node type settings with `spanning_tree_priority` (default=32768).
spanning_tree_priority: <int>
# Interface MTU.
mtu: <int>
bgp:
# Structured configuration and EOS CLI commands rendered on router_bgp.vlans.[id=<vlan>].
# This configuration will not be applied to vlan aware bundles.
structured_config: <dict>
# EOS CLI rendered directly on the Router BGP, VLAN definition in the final EOS configuration.
raw_eos_cli: <str>
# EOS CLI rendered directly on the VLAN interface in the final EOS configuration.
raw_eos_cli: <str>
# Custom structured config added under vlan_interfaces.[name=<interface>] for eos_cli_config_gen.
structured_config: <dict>
EVPN VLAN aware bundles settings¶
Optional VLAN aware bundles to share common settings for l2vlans which are supposed to use the same vlan-aware-bundle.
| Variable | Type | Required | Default | Value Restrictions | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| evpn_vlan_bundles | List, items: Dictionary | ||||
| - name | String | Required, Unique | Specify an EVPN vlan-aware-bundle name. EVPN vlan-aware-bundles group L2 VLANs and define common settings. |
||
| id | Integer | Required | “id” may be used for vlan-aware-bundle RD/RT ID so it should not overlap with l2vlan IDs which are not part of this bundle. See “overlay_rd_type” and “overlay_rt_type” for details. |
||
| rt_override | String | By default the MAC VRF bundle RT will be derived from mac_vrf_id_base + bundle_id. The rt_override allows us to override this value and statically define it. rt_override will default to vni_override if set. rt_override supports two formats: - A single number which will be used in the RT fields instead of mac_vrf_id/mac_vrf_vni (see ‘overlay_rt_type’ for details). - A full RT string with colon separator which will override the full RT. |
|||
| rd_override | String | By default the MAC VRF bundle RD will be derived from mac_vrf_id_base + bundle_id. The rt_override allows us to override this value and statically define it. rd_override will default to rt_override or vni_override if set. rd_override supports two formats: - A single number which will be used in the RD assigned number field instead of mac_vrf_id/mac_vrf_vni (see ‘overlay_rd_type’ for details). - A full RD string with colon separator which will override the full RD. |
|||
| evpn_l2_multi_domain | Boolean | Explicitly extend VLAN-Aware Bundle to remote EVPN domains. Overrides <network_services_key>.[].evpn_l2_multi_domain. |
|||
| bgp | Dictionary | ||||
| raw_eos_cli | String | EOS cli commands rendered on router_bgp.vlans-aware-bundle. |
evpn_vlan_bundles:
# Specify an EVPN vlan-aware-bundle name.
# EVPN vlan-aware-bundles group L2 VLANs and define common settings.
- name: <str; required; unique>
# "id" may be used for vlan-aware-bundle RD/RT ID so it should not overlap with l2vlan IDs which are not part of this bundle.
# See "overlay_rd_type" and "overlay_rt_type" for details.
id: <int; required>
# By default the MAC VRF bundle RT will be derived from mac_vrf_id_base + bundle_id.
# The rt_override allows us to override this value and statically define it.
# rt_override will default to vni_override if set.
#
# rt_override supports two formats:
# - A single number which will be used in the RT fields instead of mac_vrf_id/mac_vrf_vni (see 'overlay_rt_type' for details).
# - A full RT string with colon separator which will override the full RT.
rt_override: <str>
# By default the MAC VRF bundle RD will be derived from mac_vrf_id_base + bundle_id.
# The rt_override allows us to override this value and statically define it.
# rd_override will default to rt_override or vni_override if set.
#
# rd_override supports two formats:
# - A single number which will be used in the RD assigned number field instead of mac_vrf_id/mac_vrf_vni (see 'overlay_rd_type' for details).
# - A full RD string with colon separator which will override the full RD.
rd_override: <str>
# Explicitly extend VLAN-Aware Bundle to remote EVPN domains.
# Overrides `<network_services_key>.[].evpn_l2_multi_domain`.
evpn_l2_multi_domain: <bool>
bgp:
# EOS cli commands rendered on router_bgp.vlans-aware-bundle.
raw_eos_cli: <str>
Network services keys settings¶
Network Services can be grouped by using separate keys.
The keys can be customized to provide a better better organization or grouping of your data.
network_services_keys should be defined in the top level group_vars for the fabric.
Note
The default values will be overridden if defining this key, so it is recommended to copy the defaults and modify them.
| Variable | Type | Required | Default | Value Restrictions | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| network_services_keys | List, items: Dictionary | [{'name': 'tenants'}] |
Network Services can be grouped by using separate keys. The keys can be customized to provide a better better organization or grouping of your data. network_services_keys should be defined in the top level group_vars for the fabric.The default values will be overridden if defining this key, so it is recommended to copy the defaults and modify them. |
||
| - name | String | Required, Unique |
# Network Services can be grouped by using separate keys.
# The keys can be customized to provide a better better organization or grouping of your data.
# `network_services_keys` should be defined in the top level group_vars for the fabric.
# The default values will be overridden if defining this key, so it is recommended to copy the defaults and modify them.
network_services_keys: # default=[{'name': 'tenants'}]
- name: <str; required; unique>
Platform settings¶
Set platform specific settings like TCAM profile and reload delay.
If the platform is not defined, it will load parameters from the platform tagged default.
Management interface is modified for specific platforms like modular platforms with dual supervisor support and container EOS.
Note
The reload delay values should be reviewed and tuned to the specific environment.
Note
The default values will be overridden if defining this key, so it is recommended to copy the defaults and modify them.
| Variable | Type | Required | Default | Value Restrictions | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| platform_settings | List, items: Dictionary | See (+) on YAML tab | |||
| - platforms | List, items: String | ||||
| - <str> | String | ||||
| trident_forwarding_table_partition | String | Only applied when evpn_multicast is true. | |||
| reload_delay | Dictionary | ||||
| mlag | Integer | Min: 0 Max: 86400 |
In seconds. | ||
| non_mlag | Integer | Min: 0 Max: 86400 |
In seconds. | ||
| tcam_profile | String | ||||
| lag_hardware_only | Boolean | ||||
| default_interface_mtu | Integer | Min: 68 Max: 65535 |
Default interface MTU configured on EOS under “interface defaults”. Takes precedence over the root key “default_interface_mtu”. |
||
| feature_support | Dictionary | ||||
| queue_monitor_length_notify | Boolean | True |
|||
| interface_storm_control | Boolean | True |
|||
| poe | Boolean | False |
|||
| per_interface_mtu | Boolean | True |
Support for configuration of per interface MTU for p2p links, MLAG SVIs and Network Services. Effectively this means that all settings regarding interface MTU will be ignored if this is false. Platforms without support for per interface MTU can use a single default interface MTU setting. Set this via “default_interface_mtu” |
||
| bgp_update_wait_install | Boolean | True |
Disables FIB updates and route advertisement when the BGP instance is initiated until the BGP convergence state is reached. Can be overridden by setting “bgp_update_wait_install” host/group_vars. |
||
| bgp_update_wait_for_convergence | Boolean | True |
Do not advertise reachability to a prefix until that prefix has been installed in hardware. This will eliminate any temporary black holes due to a BGP speaker advertising reachability to a prefix that may not yet be installed into the forwarding plane. Can be overridden by setting “bgp_update_wait_for_convergence” host/group_vars. |
||
| management_interface | String | Management1 |
|||
| security_entropy_sources | Dictionary | Entropy source improves the randomness of the numbers used to generate MACsec’s cryptographic keys. | |||
| hardware | Boolean | Use a hardware based source. | |||
| haveged | Boolean | Use the HAVEGE algorithm. | |||
| cpu_jitter | Boolean | Use the Jitter RNG algorithm of a CPU based source. | |||
| hardware_exclusive | Boolean | Only use entropy from the hardware source. | |||
| structured_config | Dictionary | Custom structured config for eos_cli_config_gen. | |||
| raw_eos_cli | String | EOS CLI rendered directly on the root level of the final EOS configuration. | |||
| platform_speed_groups | List, items: Dictionary | Set Hardware Speed Groups per Platform. | |||
| - platform | String | Required, Unique | |||
| speeds | List, items: Dictionary | ||||
| - speed | String | Required, Unique | |||
| speed_groups | List, items: String | ||||
| - <str> | String |
platform_settings: # (1)!
- platforms:
- <str>
# Only applied when evpn_multicast is true.
trident_forwarding_table_partition: <str>
reload_delay:
# In seconds.
mlag: <int; 0-86400>
# In seconds.
non_mlag: <int; 0-86400>
tcam_profile: <str>
lag_hardware_only: <bool>
# Default interface MTU configured on EOS under "interface defaults".
# Takes precedence over the root key "default_interface_mtu".
default_interface_mtu: <int; 68-65535>
feature_support:
queue_monitor_length_notify: <bool; default=True>
interface_storm_control: <bool; default=True>
poe: <bool; default=False>
# Support for configuration of per interface MTU for p2p links, MLAG SVIs and Network Services.
# Effectively this means that all settings regarding interface MTU will be ignored if this is false.
# Platforms without support for per interface MTU can use a single default interface MTU setting. Set this via "default_interface_mtu"
per_interface_mtu: <bool; default=True>
# Disables FIB updates and route advertisement when the BGP instance is initiated until the BGP convergence state is reached.
# Can be overridden by setting "bgp_update_wait_install" host/group_vars.
bgp_update_wait_install: <bool; default=True>
# Do not advertise reachability to a prefix until that prefix has been installed in hardware.
# This will eliminate any temporary black holes due to a BGP speaker advertising reachability to a prefix that may not yet be installed into the forwarding plane.
# Can be overridden by setting "bgp_update_wait_for_convergence" host/group_vars.
bgp_update_wait_for_convergence: <bool; default=True>
management_interface: <str; default="Management1">
# Entropy source improves the randomness of the numbers used to generate MACsec's cryptographic keys.
security_entropy_sources:
# Use a hardware based source.
hardware: <bool>
# Use the HAVEGE algorithm.
haveged: <bool>
# Use the Jitter RNG algorithm of a CPU based source.
cpu_jitter: <bool>
# Only use entropy from the hardware source.
hardware_exclusive: <bool>
# Custom structured config for eos_cli_config_gen.
structured_config: <dict>
# EOS CLI rendered directly on the root level of the final EOS configuration.
raw_eos_cli: <str>
# Set Hardware Speed Groups per Platform.
platform_speed_groups:
- platform: <str; required; unique>
speeds:
- speed: <str; required; unique>
speed_groups:
- <str>
-
Default Value
platform_settings: - feature_support: queue_monitor_length_notify: false platforms: - default reload_delay: mlag: 300 non_mlag: 330 - feature_support: queue_monitor_length_notify: false platforms: - 7050X3 reload_delay: mlag: 300 non_mlag: 330 trident_forwarding_table_partition: flexible exact-match 16384 l2-shared 98304 l3-shared 131072 - feature_support: poe: true queue_monitor_length_notify: false platforms: - 720XP reload_delay: mlag: 300 non_mlag: 330 trident_forwarding_table_partition: flexible exact-match 16384 l2-shared 98304 l3-shared 131072 - feature_support: poe: true queue_monitor_length_notify: false management_interface: Management0 platforms: - '750' - '755' - '758' reload_delay: mlag: 300 non_mlag: 330 - feature_support: poe: true queue_monitor_length_notify: false platforms: - 720DP - 722XP - 710P reload_delay: mlag: 300 non_mlag: 330 - lag_hardware_only: true platforms: - 7280R - 7280R2 - 7020R reload_delay: mlag: 900 non_mlag: 1020 tcam_profile: vxlan-routing - platforms: - 7280R3 reload_delay: mlag: 900 non_mlag: 1020 - lag_hardware_only: true management_interface: Management0 platforms: - 7500R - 7500R2 reload_delay: mlag: 900 non_mlag: 1020 tcam_profile: vxlan-routing - management_interface: Management0 platforms: - 7500R3 - 7800R3 reload_delay: mlag: 900 non_mlag: 1020 - feature_support: bgp_update_wait_for_convergence: true bgp_update_wait_install: false interface_storm_control: true queue_monitor_length_notify: false management_interface: Management1/1 platforms: - 7358X4 reload_delay: mlag: 300 non_mlag: 330 - management_interface: Management0 platforms: - 7368X4 reload_delay: mlag: 300 non_mlag: 330 - management_interface: Management0 platforms: - 7300X3 reload_delay: mlag: 1200 non_mlag: 1320 trident_forwarding_table_partition: flexible exact-match 16384 l2-shared 98304 l3-shared 131072 - feature_support: bgp_update_wait_for_convergence: false bgp_update_wait_install: false interface_storm_control: false queue_monitor_length_notify: false platforms: - VEOS - VEOS-LAB - vEOS - vEOS-lab reload_delay: mlag: 300 non_mlag: 330 - feature_support: bgp_update_wait_for_convergence: false bgp_update_wait_install: false interface_storm_control: false queue_monitor_length_notify: false management_interface: Management0 platforms: - CEOS - cEOS - ceos - cEOSLab reload_delay: mlag: 300 non_mlag: 330
PTP settings¶
See the Configuring PTP how-to for details.
| Variable | Type | Required | Default | Value Restrictions | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ptp | Dictionary | ||||
| enabled | Boolean | ||||
| profile | String | aes67-r16-2016 |
Valid Values: - aes67- smpte2059-2- aes67-r16-2016 |
||
| domain | Integer | Min: 0 Max: 255 |
|||
| auto_clock_identity | Boolean | True |
|||
| ptp_profiles | List, items: Dictionary | See (+) on YAML tab | |||
| - profile | String | PTP profile. | |||
| announce | Dictionary | PTP announce interval. | |||
| interval | Integer | Min: -7 Max: 4 |
|||
| timeout | Integer | Min: 2 Max: 255 |
|||
| delay_req | Integer | Min: -7 Max: 8 |
|||
| sync_message | Dictionary | PTP sync message interval. | |||
| interval | Integer | Min: -7 Max: 3 |
|||
| transport | String | Valid Values: - ipv4 |
ptp:
enabled: <bool>
profile: <str; "aes67" | "smpte2059-2" | "aes67-r16-2016"; default="aes67-r16-2016">
domain: <int; 0-255>
auto_clock_identity: <bool; default=True>
ptp_profiles: # (1)!
# PTP profile.
- profile: <str>
# PTP announce interval.
announce:
interval: <int; -7-4>
timeout: <int; 2-255>
delay_req: <int; -7-8>
# PTP sync message interval.
sync_message:
interval: <int; -7-3>
transport: <str; "ipv4">
-
Default Value
ptp_profiles: - announce: interval: 0 timeout: 3 delay_req: -3 profile: aes67-r16-2016 sync_message: interval: -3 transport: ipv4 - announce: interval: -2 timeout: 3 delay_req: -4 profile: smpte2059-2 sync_message: interval: -4 transport: ipv4 - announce: interval: 2 timeout: 3 delay_req: 0 profile: aes67 sync_message: interval: 0 transport: ipv4
Custom Structured Configuration¶
See the Custom Structured Configuration how-to for details.
| Variable | Type | Required | Default | Value Restrictions | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| custom_structured_configuration_list_merge | String | append_rp |
Valid Values: - replace- append- keep- prepend- append_rp- prepend_rp |
The List-merge strategy used when merging custom structured configurations. This applies to all vars prefixed by prefixes in custom_structured_configuration_prefixand all data under the various structured_config options.The available list merge strategies: - replace:- Any list will be replaced with the list defined in custom structured configurations. - append:- Existing list items with the same “Primary key”-value will be updated. - New items will be appended to the existing list (including duplicates). - keep:- Only set list if there is no existing list or existing list is None.- prepend:- Existing list items with the same “Primary key”-value will be updated. - New items will be prepended to the existing list (including duplicates). - append_rp:- Existing list items with the same “Primary key”-value will be updated. - New unique items will be appended to the existing list. - prepend_rp:- Existing list items with the same “Primary key”-value will be updated. - New unique items will be prepended to the existing list. |
|
| custom_structured_configuration_prefix | List, items: String | ['custom_structured_configuration_'] |
Custom EOS Structured Configuration keys can be set on any group or host_var level using the name of the corresponding eos_cli_config_gen key prefixed with content of custom_structured_configuration_prefix.The content of Custom Structured Configuration variables will be merged with the structured config generated by the eos_designs role. The merge is done recursively, so it is possible to update a sub-key of a variable set by eos_designs role already.The merge follow these recursive merge strategies: - New keys will be added for all types. - Existing keys of type “List” with a “Primary key” set in the schema: - Strategy can be changed with custom_structured_configuration_list_merge. Default strategy:- Existing list items with the same “Primary key”-value will be updated. - New unique items will be appended to the existing list - Other keys of type “List” will have new unique items appended the the existing list. - Existing keys of type “Dictionary” will recursively merge - Other existing keys will be replaced. |
||
| - <str> | String |
# The List-merge strategy used when merging custom structured configurations.
#
# This applies to all vars prefixed by prefixes in `custom_structured_configuration_prefix`
# and all data under the various `structured_config` options.
#
# The available list merge strategies:
# - `replace`:
# - Any list will be replaced with the list defined in custom structured configurations.
# - `append`:
# - Existing list items with the same "Primary key"-value will be updated.
# - New items will be appended to the existing list (including duplicates).
# - `keep`:
# - Only set list if there is no existing list or existing list is `None`.
# - `prepend`:
# - Existing list items with the same "Primary key"-value will be updated.
# - New items will be prepended to the existing list (including duplicates).
# - `append_rp`:
# - Existing list items with the same "Primary key"-value will be updated.
# - New unique items will be appended to the existing list.
# - `prepend_rp`:
# - Existing list items with the same "Primary key"-value will be updated.
# - New unique items will be prepended to the existing list.
custom_structured_configuration_list_merge: <str; "replace" | "append" | "keep" | "prepend" | "append_rp" | "prepend_rp"; default="append_rp">
# Custom EOS Structured Configuration keys can be set on any group or host_var level using the name
# of the corresponding `eos_cli_config_gen` key prefixed with content of `custom_structured_configuration_prefix`.
#
# The content of Custom Structured Configuration variables will be merged with the structured config generated by the eos_designs role.
#
# The merge is done recursively, so it is possible to update a sub-key of a variable set by `eos_designs` role already.
#
# The merge follow these recursive merge strategies:
# - New keys will be added for all types.
# - Existing keys of type "List" with a "Primary key" set in the schema:
# - Strategy can be changed with `custom_structured_configuration_list_merge`. Default strategy:
# - Existing list items with the same "Primary key"-value will be updated.
# - New unique items will be appended to the existing list
# - Other keys of type "List" will have new unique items appended the the existing list.
# - Existing keys of type "Dictionary" will recursively merge
# - Other existing keys will be replaced.
custom_structured_configuration_prefix: # default=['custom_structured_configuration_']
- <str>
CloudVision Topology settings¶
Generate AVD topology configurations directly from a given CloudVision topology.
This feature is intended to be used for the integration of AVD and CloudVision Studios.
The topology should be pulled from the CloudVision “Inventory and Topology Studio” inputs. Device IDs must be translated to hostnames.
This feature currently provides the following configurations based on the given CloudVision topology and default_interfaces:
uplink_switchesuplink_interfacesuplink_switch_interfacesmlag_interfacesplatform(if set)mgmt_interface(if interface “ManagementX” is found in the list)
Note
Any derived configuration can be overridden by setting the key manually.
Even keys set under node type defaults will take precedence over these derived configurations.
When using parallel links between the same devices for L3 uplinks it is important to set
max_uplink_switches and max_parallel_uplinks to ensure consistent IP addressing.
cv_topology example
To use this feature set default_interfaces according to the intended design (see default_intefaces for details) and set use_cv_topology to true.
Provide a full topology under cv_topology like this example:
use_cv_topology: true
cv_topology:
- hostname: s2-spine2
platform: vEOS-LAB
interfaces:
- name: Ethernet2
neighbor: s2-leaf1
neighbor_interface: Ethernet3
- name: Ethernet3
neighbor: s2-leaf2
neighbor_interface: Ethernet3
- name: Ethernet4
neighbor: s2-leaf3
neighbor_interface: Ethernet3
- name: Ethernet5
neighbor: s2-leaf4
neighbor_interface: Ethernet3
- name: Ethernet7
neighbor: s2-brdr1
neighbor_interface: Ethernet3
- name: Ethernet8
neighbor: s2-brdr2
neighbor_interface: Ethernet3
- name: Management0
neighbor: 00:1c:73:aa:bb:cc
neighbor_interface: Ethernet21
- hostname: s1-spine1
...cut for readability...
| Variable | Type | Required | Default | Value Restrictions | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cv_topology | List, items: Dictionary | Generate AVD configurations directly from the given CloudVision topology. Activate this feature by setting use_cv_topology to true.Requires default_interfaces to be set for the relevant platforms and node types to detect the proper interface roles automatically.Neighbor hostnames must match the inventory hostnames of the AVD inventory to be taken into consideration. |
|||
| - hostname | String | Required, Unique | |||
| platform | String | Required | |||
| interfaces | List, items: Dictionary | Required | |||
| - name | String | Required, Unique | |||
| neighbor | String | ||||
| neighbor_interface | String | ||||
| use_cv_topology | Boolean | Generate AVD configurations directly from a given CloudVision topology. See cv_topology for details. |
# Generate AVD configurations directly from the given CloudVision topology.
# Activate this feature by setting `use_cv_topology` to `true`.
# Requires `default_interfaces` to be set for the relevant platforms and node types to detect the proper interface roles automatically.
# Neighbor hostnames must match the inventory hostnames of the AVD inventory to be taken into consideration.
cv_topology:
- hostname: <str; required; unique>
platform: <str; required>
interfaces: # required
- name: <str; required; unique>
neighbor: <str>
neighbor_interface: <str>
# Generate AVD configurations directly from a given CloudVision topology.
# See `cv_topology` for details.
use_cv_topology: <bool>